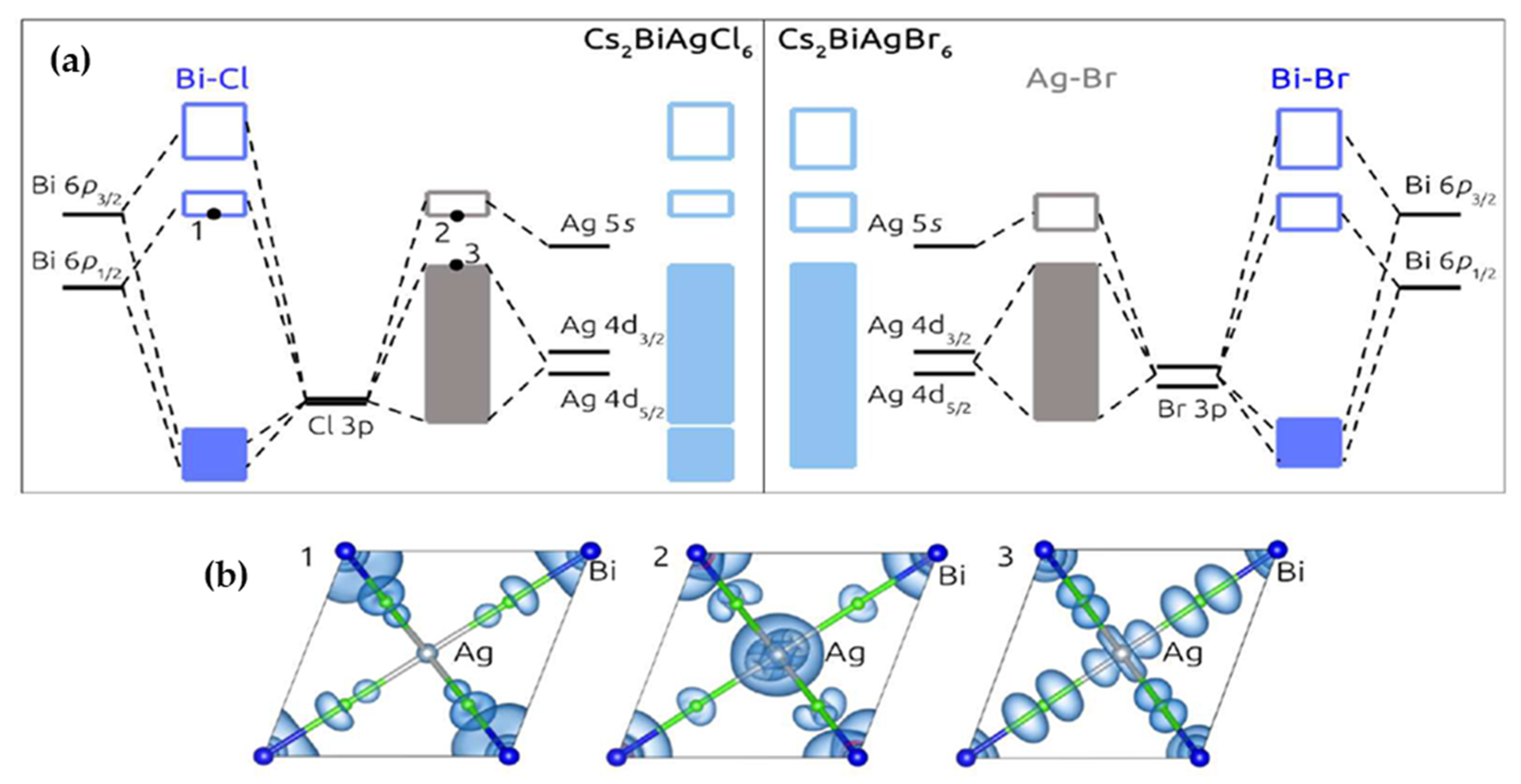
41 cs molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbitals --LCAO-MO Rather than pursuing the exact one-electron diatomic molecule solution further, we will use the variational method to obtain apppp proximate molecular orbitals for this problem. We will choose a trial function using a sum of one electron orbitals centered on nucleus A and one electron orbitals centered on nucleus B ... Download scientific diagram | MO diagram of T d [CsO 4 ] + , as interaction between a Cs + ion and an [O] 4 fragment. The interactions within A 1 symmetry ...
Jan 3, 2021 — A molecular orbital diagram that can be applied to any homonuclear diatomic molecule with two identical alkali metal atoms (Li2 and Cs2, ...
Cs molecular orbital diagram
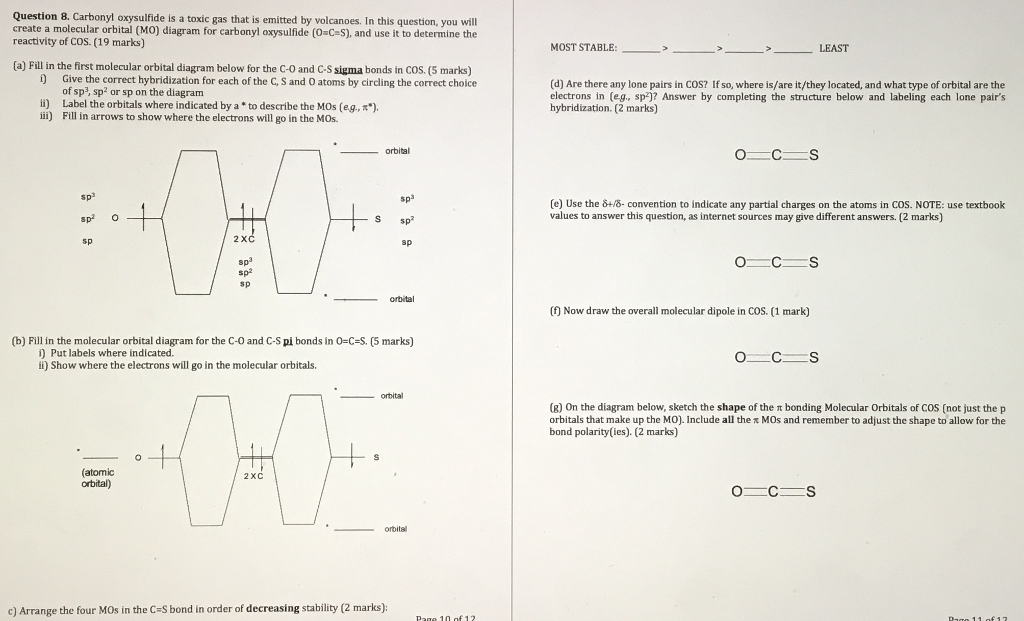
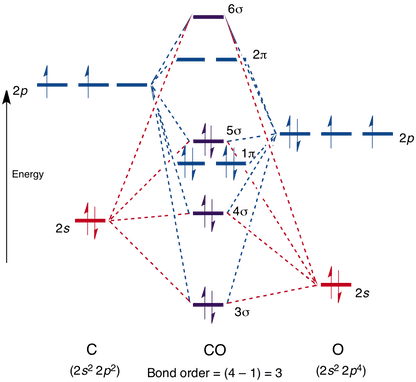
Let us know see how we can draw the Lewis Structure for CS2. 1. Carbon belongs to Group 4 of the periodic table. Therefore, the number of valence electrons in the Carbon atom =4. Sulfur (S) belonging to Group 6 has 6 valence electrons. CS2 has two S atoms, hence, the valence electrons in sulfur here are 6*2=12. Molecular orbital 'resembles' ... χχχB. Orbital patterns: 2 orbitals: 1 bonding, 1 antibonding 3 orbitals 1 bonding, 1 non-bonding, 1 antibonding (details depend on relative energies) Always break MO diagrams down into components based on symmetry. Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure [Cs(18-crown-6) 2] + e ... Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals.
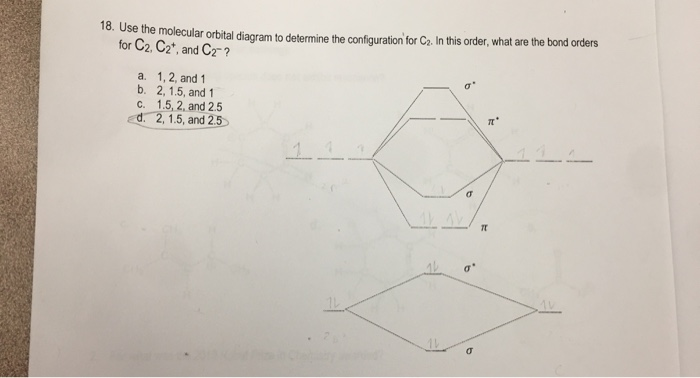
Cs molecular orbital diagram. If we talked about the ground-state Cesium Electron Configuration (Cs), than it is written as the following; 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 4d 10 5s 2 5p 6 6s 1. Now many of the users must be wondering what exactly it is, therefore for them, they have two choices: either they learn the direct electronic configuration or they learn ... FREE Answer to 10. Use the molecular orbital diagram to determine the configuration for Cs. In this order, what are the bond order...1 answer · 0 votes: at ze 7t2P 2PT 20 777 . 11 2² azer c IL 1 2PM 2PM Bond order = Bonding election- Anilibonding aboton (6) 10 = 102 le che son) for crime 60-3-15 one ... the case of CS and PN. Their ground-state electron configuration is given by (core) (50)'(60)~(70)~(2n)~ The basis specified above provides 10 occupied and 41 unoccupied (virtual) molecular orbitals. There is a large energy gap between the valence orbitals (5~, 60, 70 and The Aufbau principle tells you that the lowest-energy orbitals fill first, but the specific order isn't sequential in a way that's easy to memorize. See Resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p orbitals, and the n = 3 level only has s, p and d orbitals.
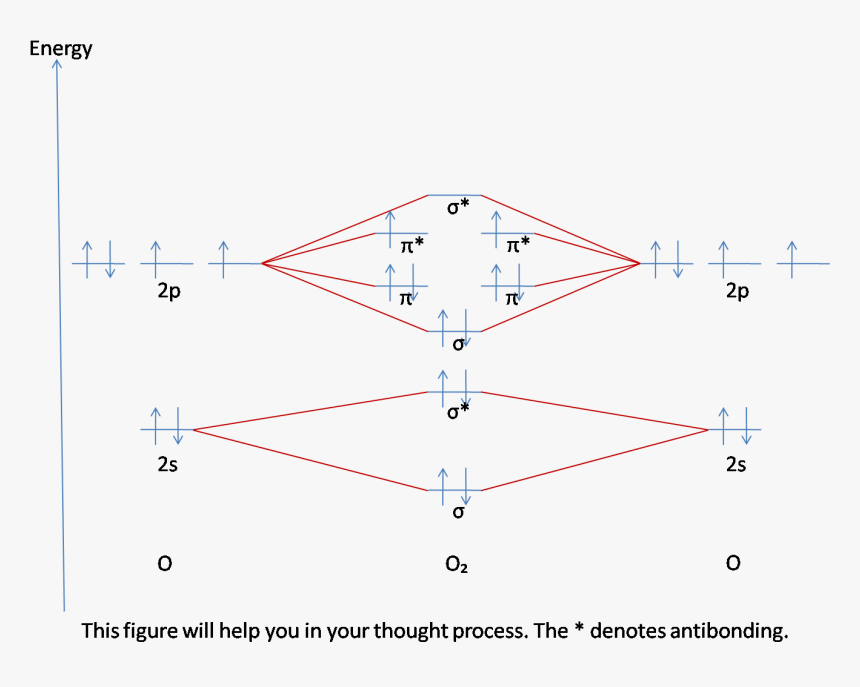
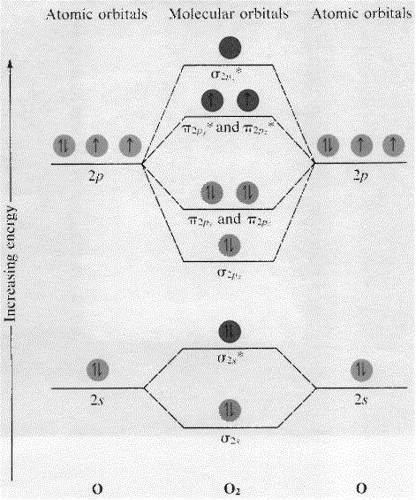
These must make 4 sigma symmetry molecular orbitals with an average energy equal to the average energy of the 4 atomic orbitals. In N 2 and in most other diatomic molecules (NO, NS, CO, CS) there are 4 sigma symmetry molecular orbitals made from a mixing of the 2s and 2p z atomic orbitals on each atom. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Okay let's do the orbital diagram for iron, iron we know is on its ground state of 26 electrons, so we know the first electrons are going to go into the 1s orbital and we said 2 electrons can fall into the 1s orbital. After the 1s orbital is a 2s, 2 electrons are going to go in there as well, then you have the 2p and don't forget the p ... Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. 100% (34 ratings) Transcribed image text: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for N2 and then identify the bond order Bond order 0.5 O 1.5 O 2.5 2s 2s Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Previous question Next question. orbitals are used. So CS is like C≡O except you use 3s,3p orbitals for . the example thus ignores 1s on C and 1s,2s,2p on S Similar point, Cl uses 3s,3p and Br uses 4s,4p. Cl (right) more electronegative, so orbitals lower in energy than Br (left) orbitals are from interaction of sp hybrids, make linear C-C bonds, however the diagram Molecular orbitals and bond lengths found with Spartan can be used to better understand how the actual structure of a molecule or ion relates to its resonance structures. In this experiment, the valence atomic orbitals for hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur atoms will be calculated. Molecular orbitals for H 2, N 2, CS, 4 answersgot a question telling us to produce an M O diagram. A molecular little diagram for F two plus and status box. So first things first.
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in L a T e X by means of the package MOdiagram.For information about the more traditional molecular structure diagrams see our documentation about chemistry formulae.
Thus, the hydrogen bonding properties of water enhance the solubility of CO 2 over CS 2 and OCS. The LUMO orbitals for OCS and CS 2 are stable (have negative potential energy, Figure 4) and are ...
The molecular orbital diagram for #C_2# Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular Orbital Theory. 1 Answer Stefan V. Dec 2, 2016 Here's what I got. Explanation: The problem provides you with the MO diagram for the #"C"_2# molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. You need to ...
Answer (1 of 5): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
Property Name Property Value Reference; Molecular Weight: 44.08: Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) XLogP3-AA: 1.2: Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the
6:21For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store! Correlation Diagrams ...Apr 8, 2016 · Uploaded by Knowvio
Steps to form OF2 Lewis Structure Diagram. Step 1: Find the Total number of Valence Electrons. The first and foremost step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons in an OF2 molecule. Oxygen belongs to group 16, the chalcogen family, and has a valency of 6. Fluorine belongs to the family of halogen in group 17 and has a valency of 7.
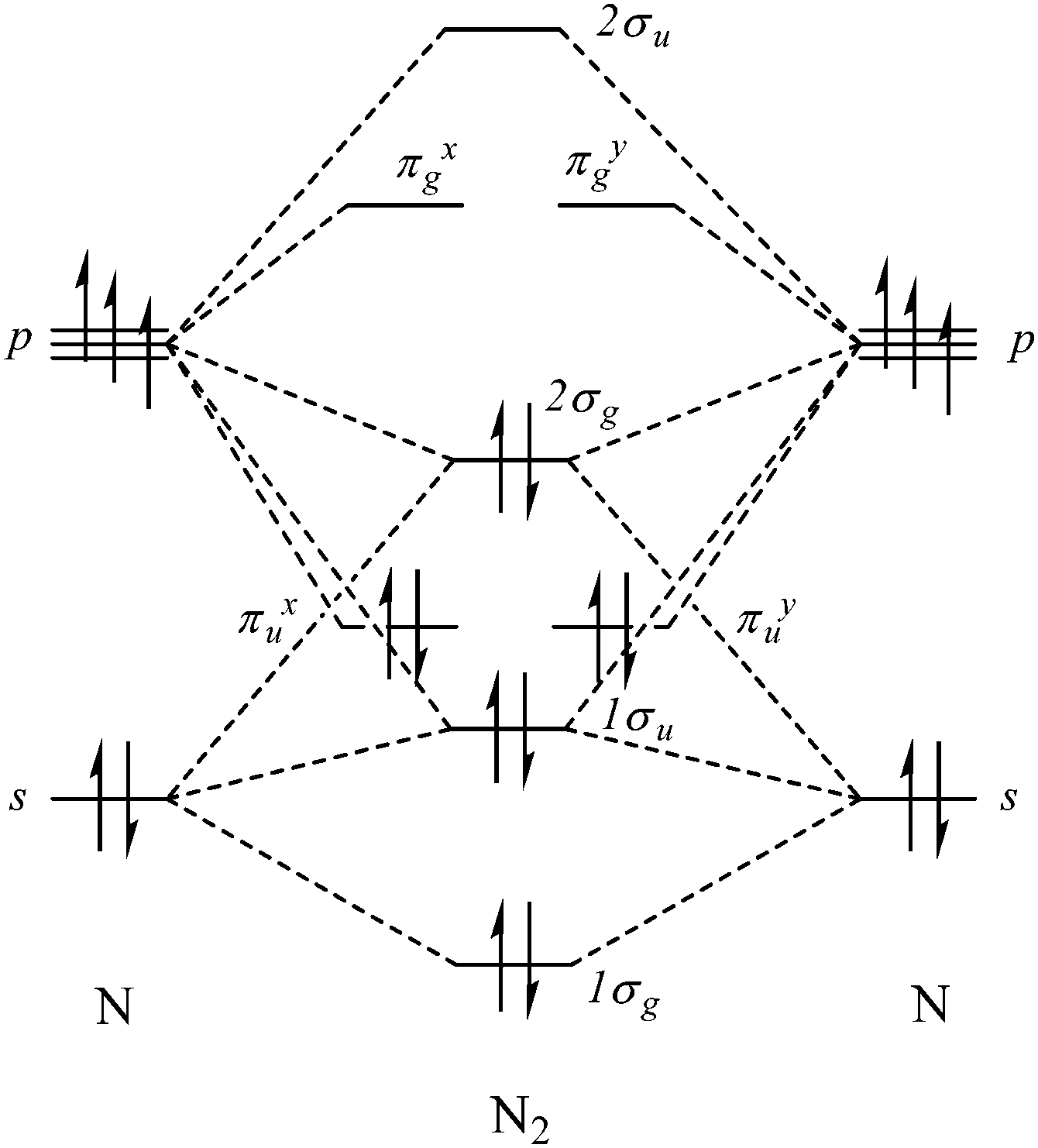
Mechanistic Aspects Of Dinitrogen Cleavage And Hydrogenation To Produce Ammonia In Catalysis And Organometallic Chemistry Relevance Of Metal Hydride Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C3cs60206k
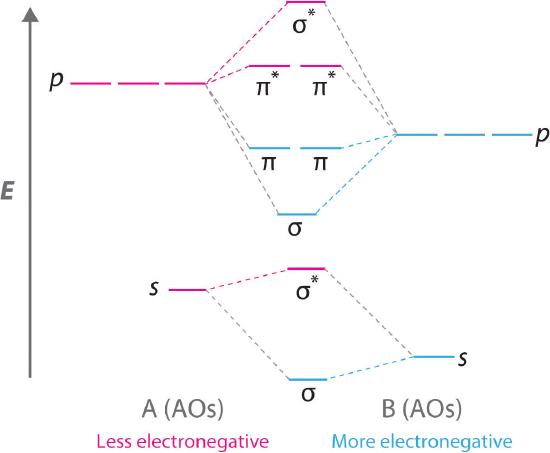
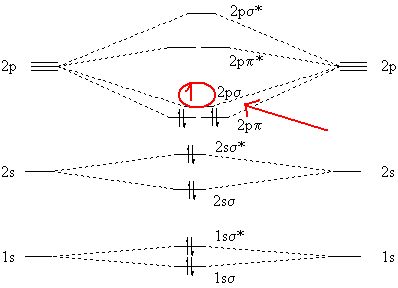
molecular orbital energy level diagram for CS below by: i. Sketching and naming . only : the molecular orbitals (MOs). ii. ... Label all atomic and molecular orbitals on your diagram, and include tie lines to show the linear combinations that form each molecular orbital.
ORBITALS - are specific regions of space where electrons may exist - The SHAPE of an orbital is defined by the SUBSHELL it is in - The ENERGY of an orbital is defined by both the SHELL the orbital is in AND the kind of SUBSHELL it is in ARRANGEMENT OF SHELLS, SUBSHELLS, AND ORBITALS - Shells are numbered.
Draw And Explain The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Carbon Molecule Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
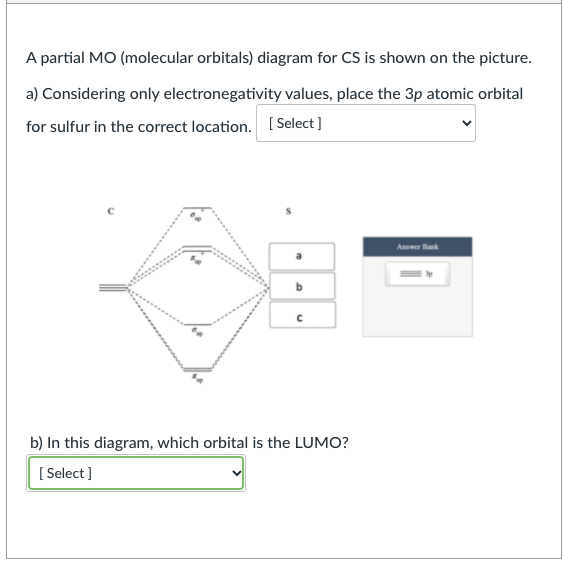
A partial Mo (molecular orbitals) diagram for CS is shown on the picture. a) Considering only electronegativity values, place the 3p atomic orbital for sulfur in the correct location. [Select] Answer Bank b ь b) In this diagram, which orbital is the LUMO? [Select] b) In this diagram, which orbital is the LUMO?
N2 2 molecular orbital diagram. Bond order is 3 and it is paramagnetic. Molecular orbital diagram n2 2. Answers to molecular orbitals problem set 1. In n 2 and in most other diatomic molecules no ns co cs there are 4 sigma symmetry molecular orbitals made from a mixing of the 2s and 2p z atomic orbitals on each atom.
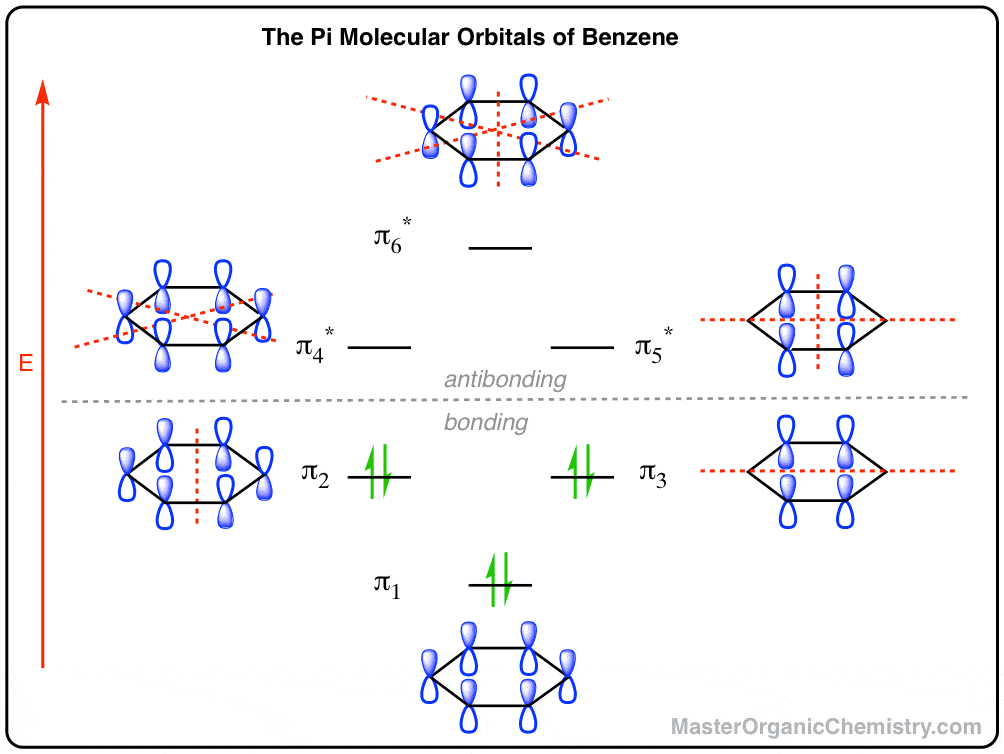
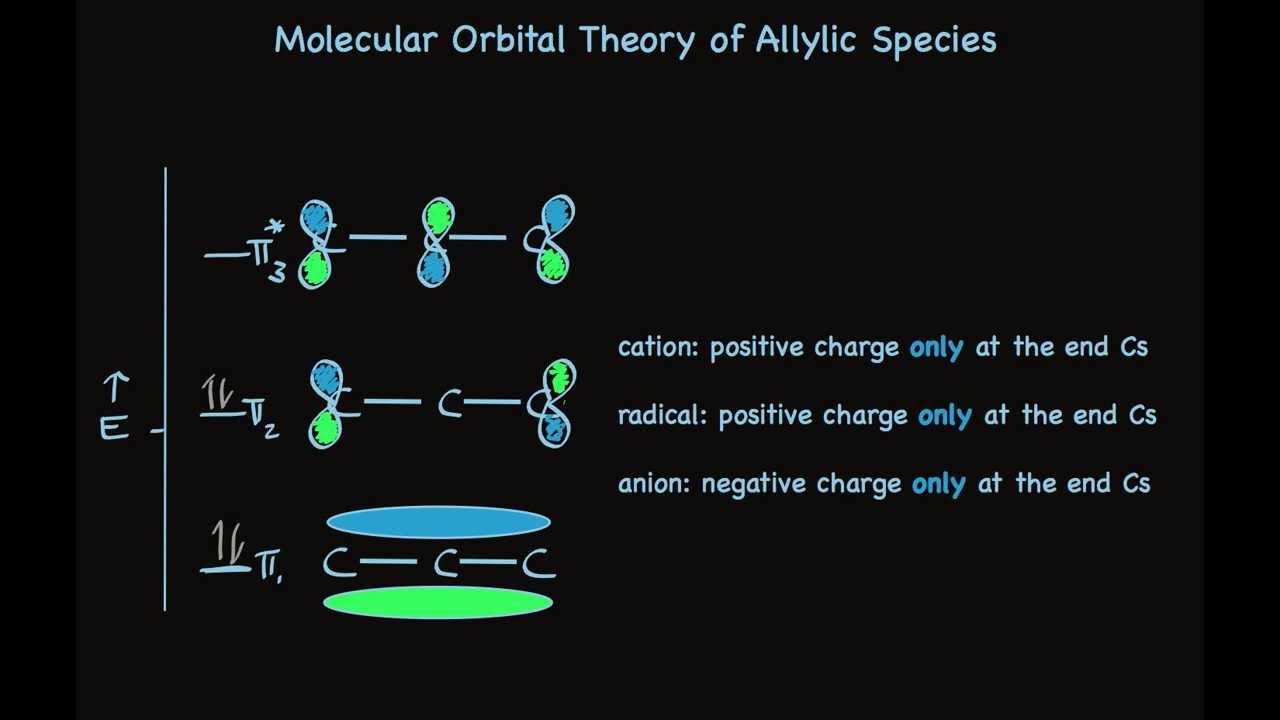
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Theory. The Valence Bond Theory fails to answer certain questions like why He 2 molecule does not exist and why O 2 is paramagnetic. Therefore in 1932 F. Hood and R.S. Mulliken came up with Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like the ones above.
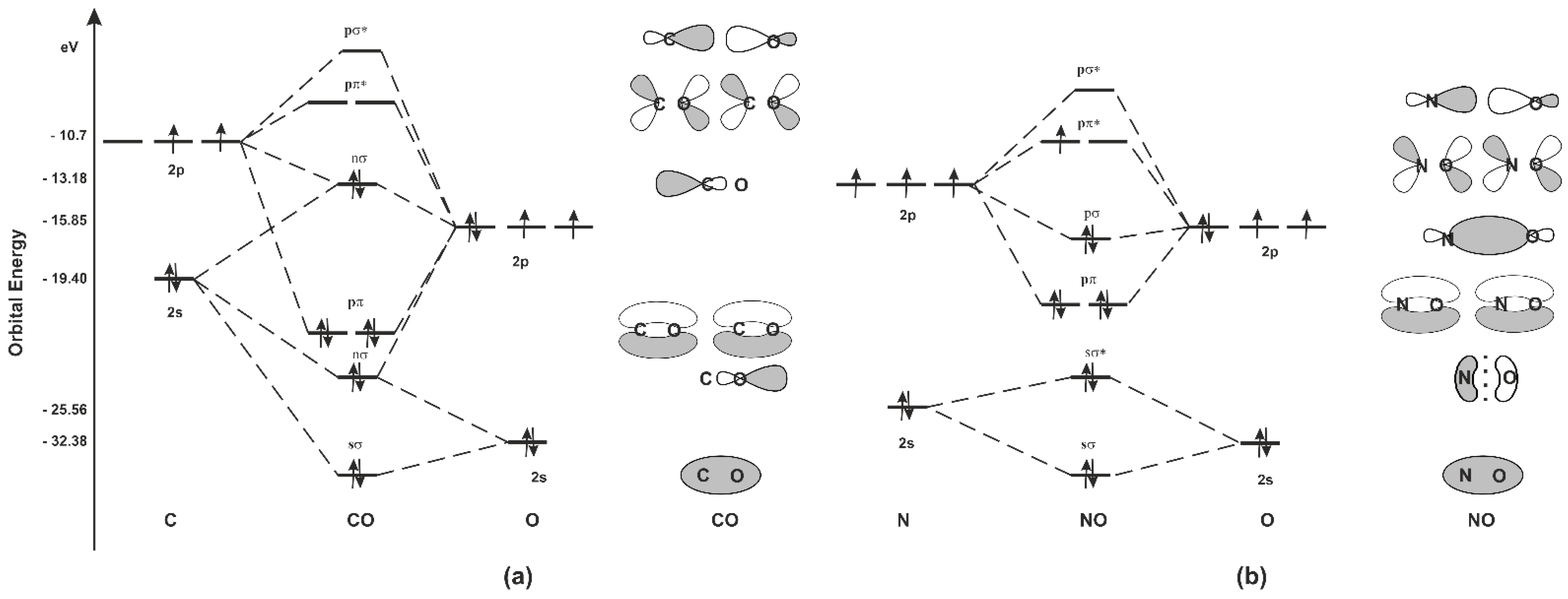
Ijms Free Full Text Carbon Monoxide And Nitric Oxide As Examples Of The Youngest Class Of Transmitters Html
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
Draw a molecular orbital energy diagram for CS (carbon sulfide). Compare the outcome with CO, and predict the coordination chemistry of CS.

Developing Drug Molecules For Therapy With Carbon Monoxide Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C2cs15317c
[Cs(18-crown-6) 2] + e ... Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals.
Molecular orbital 'resembles' ... χχχB. Orbital patterns: 2 orbitals: 1 bonding, 1 antibonding 3 orbitals 1 bonding, 1 non-bonding, 1 antibonding (details depend on relative energies) Always break MO diagrams down into components based on symmetry. Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure
Let us know see how we can draw the Lewis Structure for CS2. 1. Carbon belongs to Group 4 of the periodic table. Therefore, the number of valence electrons in the Carbon atom =4. Sulfur (S) belonging to Group 6 has 6 valence electrons. CS2 has two S atoms, hence, the valence electrons in sulfur here are 6*2=12.

Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Most Stable A Homeworklib

Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Molecular Orbital Theory Others Angle White Text Png Pngwing











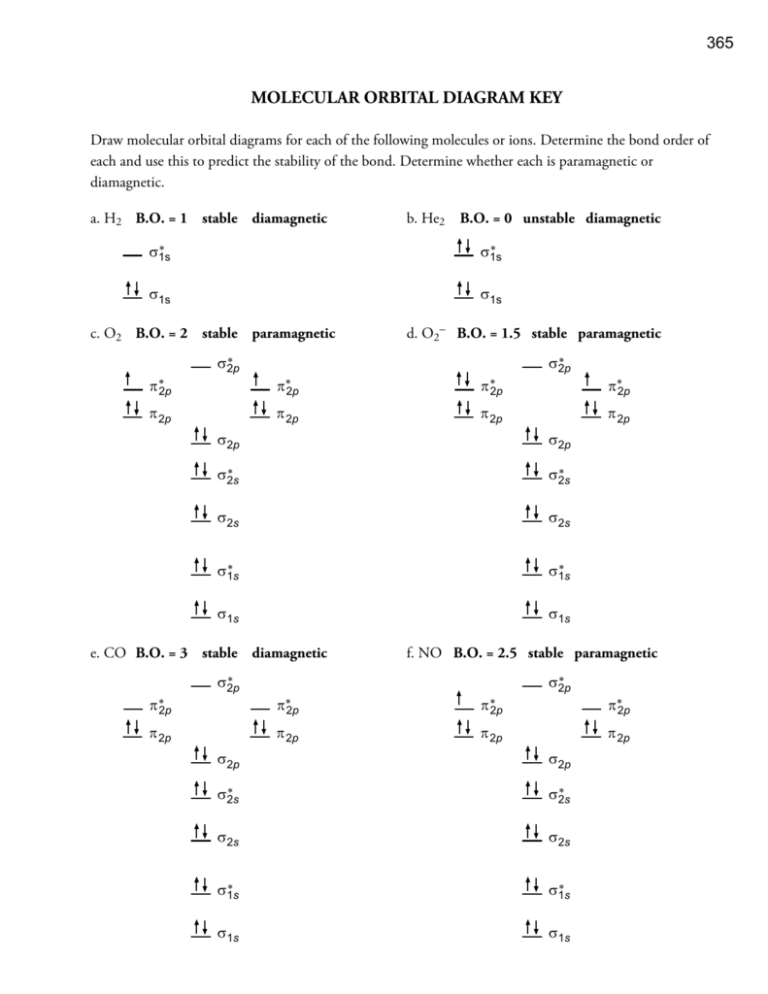

0 Response to "41 cs molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment