41 if you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is
Minkowski Spacetime Diagrams Instructions. These are the instructions for my script-based spacetime diagram generator. Using a script-based system provides for a lot more options than could be easily accommodated with a graphical user interface (GUI). On the other hand, it requires reading instructions (sigh), which no one likes to do. If you are looking at a spacetime diagram that plots the worldline of an inertial observer moving with respect to the given frame with velocity ##v## such that her time coordinate is called ##t'## and the origin of her frame coincides with the origin of the frame of the diagram we're looking at (basically the quintessential beginners' spacetime diagram, but I wanted to explicitly state ...
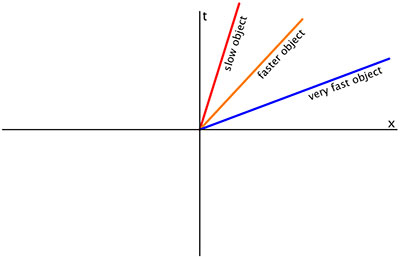
Here the object is observed to be moving at some speed v. Drawing a spacetime diagram draw horizontal and vertical axes. If you draw a spacetime diagram the worldline of an object that is traveling by you at constant speed is slanted if you draw a spacetime diagram the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is.
If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is
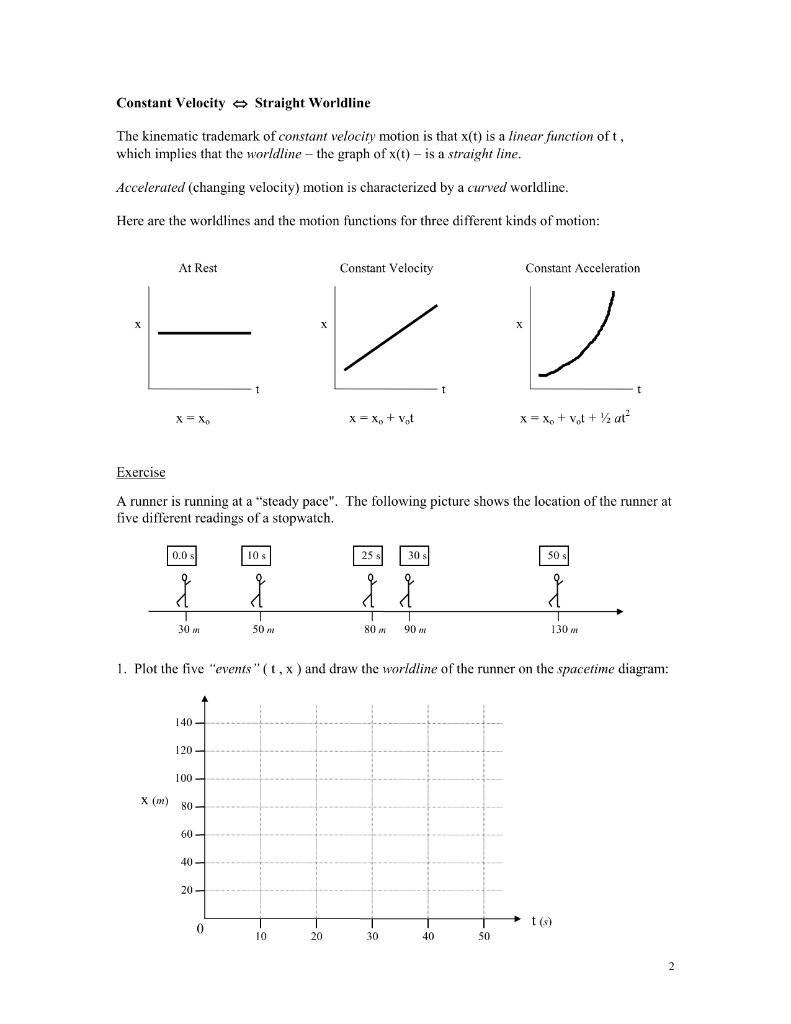
These diagrams are just like ordinary co-ordinate plots of x and y that you might have drawn up until now. However, there is an added axis of time. It is convention to plot this time axis vertically in the diagram. We will look at the case of 2-D space-time, i.e. one time axis, and one space axis, say X-axis. Thus, a space-time diagram looks like: Drawing and Interpreting Space-Time Diagrams. A Space-Time Diagram (STD) is a time versus position graph. For convenience, we plot ct rather than t on the vertical axis so that both axes are in the same units. Distances will often be referred to as lightdays (c-days), lightmonths (c-months), and lightyears (c-years or c-y).Conversely ct can be given in metres, kilometers, lightyears, and so on. I was drawing a spacetime diagram to relate Doppler shift effect but i stuck at a point which i can't understand This is what I'm trying to draw An object with mirror is moving away from me with a velocity of 50% speed of light When each second passes in my clock i send light pulses at that object. I sent 4 light pulses in 4 second.
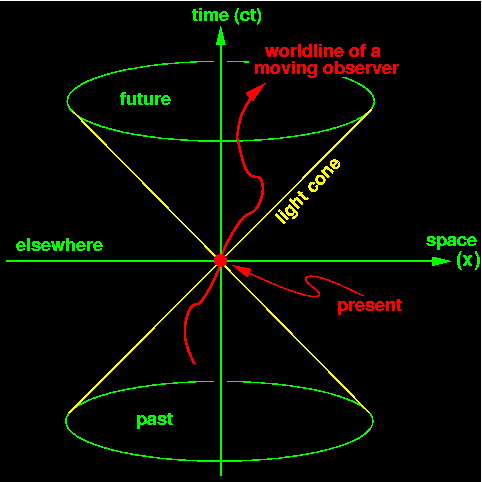
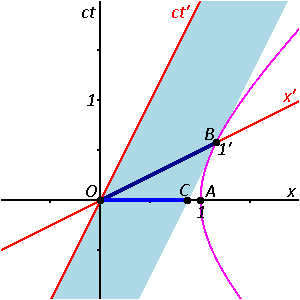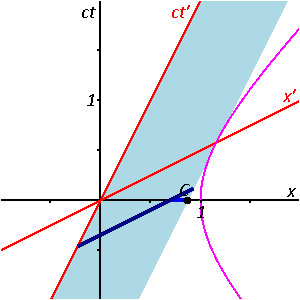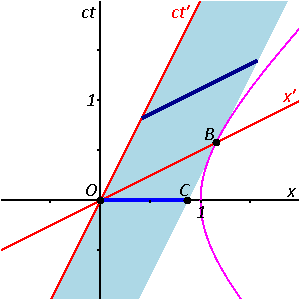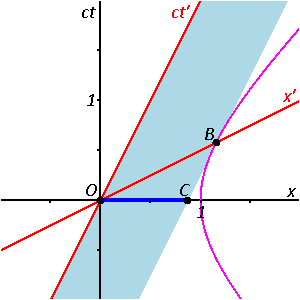
If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is. A spacetime diagram is a graphical illustration of the properties of space and time in the special theory of relativity.Spacetime diagrams allow a qualitative understanding of the corresponding phenomena like time dilation and length contraction without mathematical equations.. The history of an object's location throughout all time traces out a line, referred to as the object's world line, in ... Introduction to special relativity and Minkowski spacetime diagrams. Including multiple observers in the "most obvious" way led to some problems. Let's see how we can start to solve those problems by introducing (what we'll later call) Minkowski spacetime diagrams. This is the currently selected item. time goes on," we imply that we read the space-time diagram from bottom (t=0) to top. Imag-ine Planet A sends a spacecraft to Planet B at a speed of one half the speed of light (0.5c). The worldline of this spacecraft is represented by the blue line. It is sloped, because its po-sition changes with time. The slope on this graph is 2. If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is; Jon secada if i never knew you; Treasures of the vatican; The noblest of man and a woman; Which of the following objects has a size similar to that of lapilli? Home Contact ...
Nov 21, 2018 · If you draw a spacetime diagram the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is curved suppose two lines appear to be parallel but eventually meet. The minkowski diagram also known as a spacetime diagram was developed in 1908 by hermann minkowski and provides an illustration of the properties of space and time in the special theory of relativity. Suppose you claim that you are feeling the effects of a gravitational field. ... she is in free-fall. Image that you are sitting in a closed room when, magically, it is lifted from Earth and sent accelerating through space with an acceleration of 1g. ... If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is stationary in your ... If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is traveling by you at constant speed is. slanted. If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is. curved. Suppose two lines appear to be parallel but eventually meet. What type of geometry are you dealing with? If you draw a spacetime diagram, how will the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you appear? asked Dec 16, 2019 in Physics & Space Science by Pizza_Boy introductory-astronomy
If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is traveling by you at constant speed is . horizontal. curved. slanted. a circle. vertical. slanted. If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is. a circle. vertical. slanted. horizontal. curved. curved. Suppose two lines appear ... time diagram is called a world line of that object, and may be thought of as a chain of many events •Note that a world line in a space-time diagram may not be the same shape as the path of an object through space Rocket ship accelerating in #-direction (path in space is straight)!" # Rocket ship accelerating in #-direction (path in space-time ... If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is traveling by you at a constant speed is? slanted. If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is? curved. Two parallel lines eventually meet. What type of geometry are you dealing with? You're right that space-time diagrams are drawn for a particular Lorentz frame, but one doesn't directly "compare" space-time diagrams. You draw the world-line of the particle of interest, choose whatever point you're interesting in looking at, identify whatever stuff you're interested in in your S-T diagram (simultaneous points, etc.), perform ...
A worldline can be defined as ‘a curve in spacetime joining the positions of a particle throughout its existence.’ Each object has its own worldline within a given reference frame. The worldline thus describes the entire history and future of the object. A worldline is composed of an infinite continuum of events (e.g., the location of the red ball
If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is traveling by you at constant speed is vertical. a circle. curved. slanted. horizontal. slanted. If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is a circle. vertical. slanted. curved. horizontal.

Einstein S Postulates 1 The Laws Of Nature Are The Same For Everyone 2 The Speed Of Light In A Vacuum Is Constant For All Observers Ppt Download
d. Draw a worldline for Angela, who is traveling away from you at a speed of 100,000 km/s. 49. Highly Sloped Worldline. Make a spacetime diagram on which the time axis is marked in seconds and the space axis is marked in light-seconds. Draw a worldline with a slope of 300 (from the horizontal). At what speed would an object have to be traveling ...
The worldline of an object that is not moving at constant velocity, i.e., is accelerating, will not be a straight line, but will curve according to the acceleration. However, since no object may move at a speed greater than c , at all times the worldline of an object makes an angle with the horizontal that is greater than or equal to .
To measure proper-time you need to measure the arc-length of a curve, that is the world-line of the observer. Once you understand that you will no longer need to draw scores of dashed lines. Space-time diagrams will still remain useful of course.
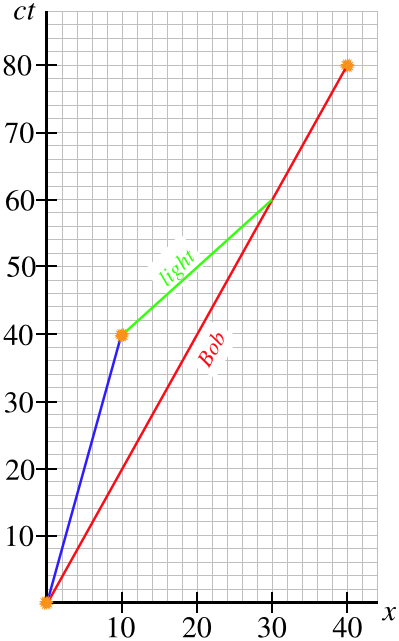
A light flash leaves a master clock at x = 0 at time t = -12 s, is reflected from an object a certain distance in the -x direction from the origin, and then returns to the origin at t = +8 s. From this information, we can infer that the spacetime coordinates of the reflection event are [t, x] =. This graph shows a spacetime diagram for a car.
May 14, 2009. May 14, 2009. #1. granpa. 2,268. 7. here is my poor effort at teaching newbies how to draw spacetime diagrams (somebody has to do it): first draw your x axis. this represents space. (one dimension of it anyway. one dimension is enough for most thought experiments) the y axis represents time. imagine there is a stationary observer ...
Draw the worldline of an object (Object A) that is at rest in whatever frame you're using; it will be a vertical line going straight up the page. Next draw the worldline of an object (Object B) moving at .9c to the right relative to A; this will be a line that slants up and to the right, rising ten units for every nine units sideways.
10) If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is traveling by you at constant speed is . A) vertical. B) horizontal. C) slanted. D) curved. E) a circle. Answer: C. 11) If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is . A) vertical. B) horizontal. C) slanted. D) curved. E) a ...
Assuming you are sitting still as you take this quiz, how would you draw your own worldline on a spacetime diagram? A straight, vertical line. Planes traveling between Seattle and Tokyo often go near Alaska because. the distance is shorter. If your wordline is following the straightest possible path through spacetime, then. you will be weightless.
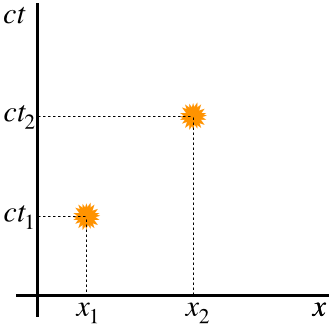
A space-time diagram shows the history of objects moving through space (usually in just one dimension). A speci c point on a space-time diagram is called an \event." To make a space-time diagram, take many snapshots of the objects over time and set them on top of each other. Lines in the diagram are like \contrails" through time.
If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is traveling by you at constant speed is-slanted.-horizontal.-a circle.-curved.-vertical.-slanted. If you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is-horizontal.-slanted.-vertical.-a circle.-curved. curved. Suppose two lines appear to ...
I was drawing a spacetime diagram to relate Doppler shift effect but i stuck at a point which i can't understand This is what I'm trying to draw An object with mirror is moving away from me with a velocity of 50% speed of light When each second passes in my clock i send light pulses at that object. I sent 4 light pulses in 4 second.
Drawing and Interpreting Space-Time Diagrams. A Space-Time Diagram (STD) is a time versus position graph. For convenience, we plot ct rather than t on the vertical axis so that both axes are in the same units. Distances will often be referred to as lightdays (c-days), lightmonths (c-months), and lightyears (c-years or c-y).Conversely ct can be given in metres, kilometers, lightyears, and so on.
These diagrams are just like ordinary co-ordinate plots of x and y that you might have drawn up until now. However, there is an added axis of time. It is convention to plot this time axis vertically in the diagram. We will look at the case of 2-D space-time, i.e. one time axis, and one space axis, say X-axis. Thus, a space-time diagram looks like:

If You Draw A Spacetime Diagram The Worldline Of An Object That Is Accelerating Away From You Is Wiring Site Resource















0 Response to "41 if you draw a spacetime diagram, the worldline of an object that is accelerating away from you is"
Post a Comment