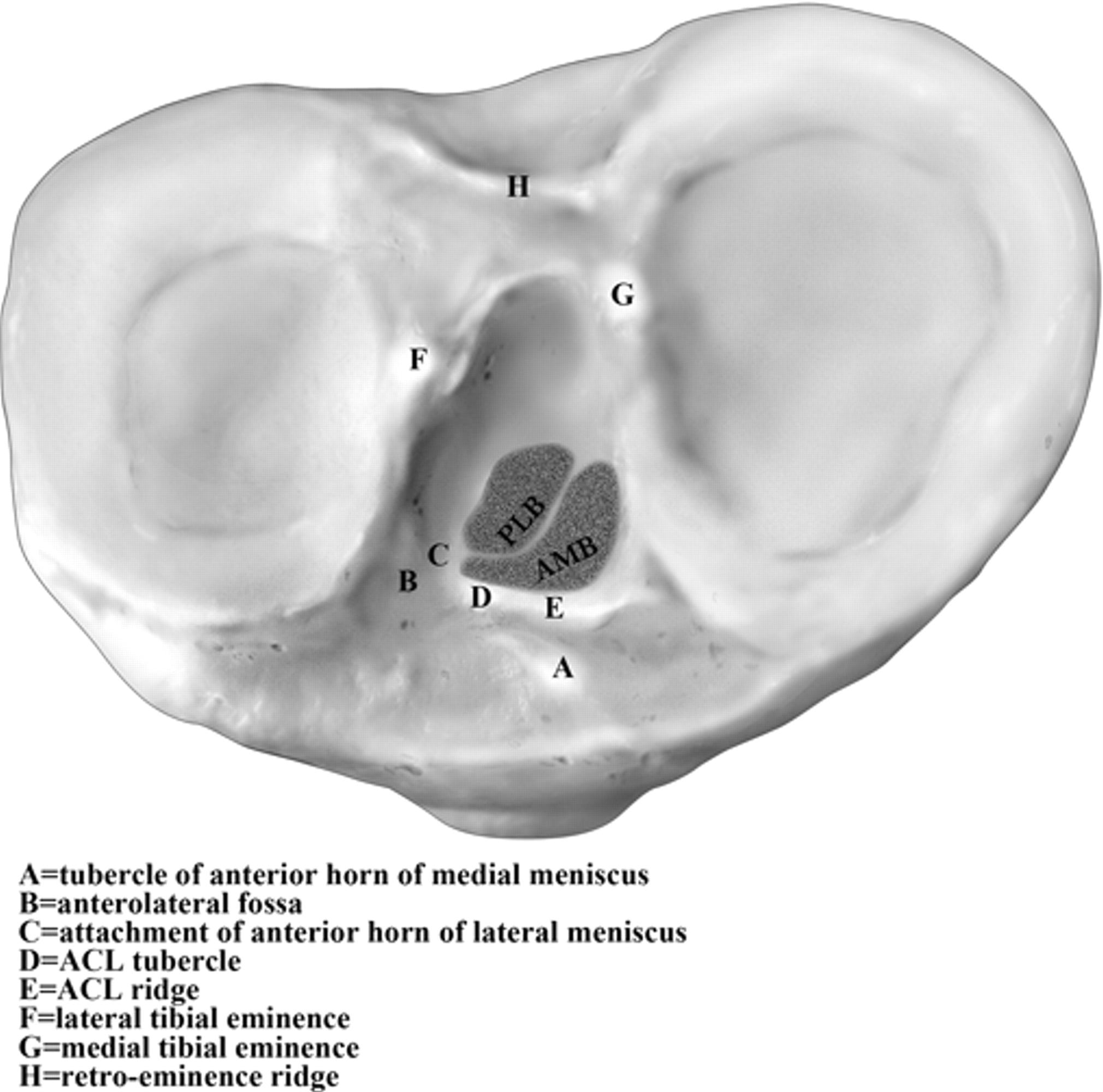
43 meniscus diagram of the knee
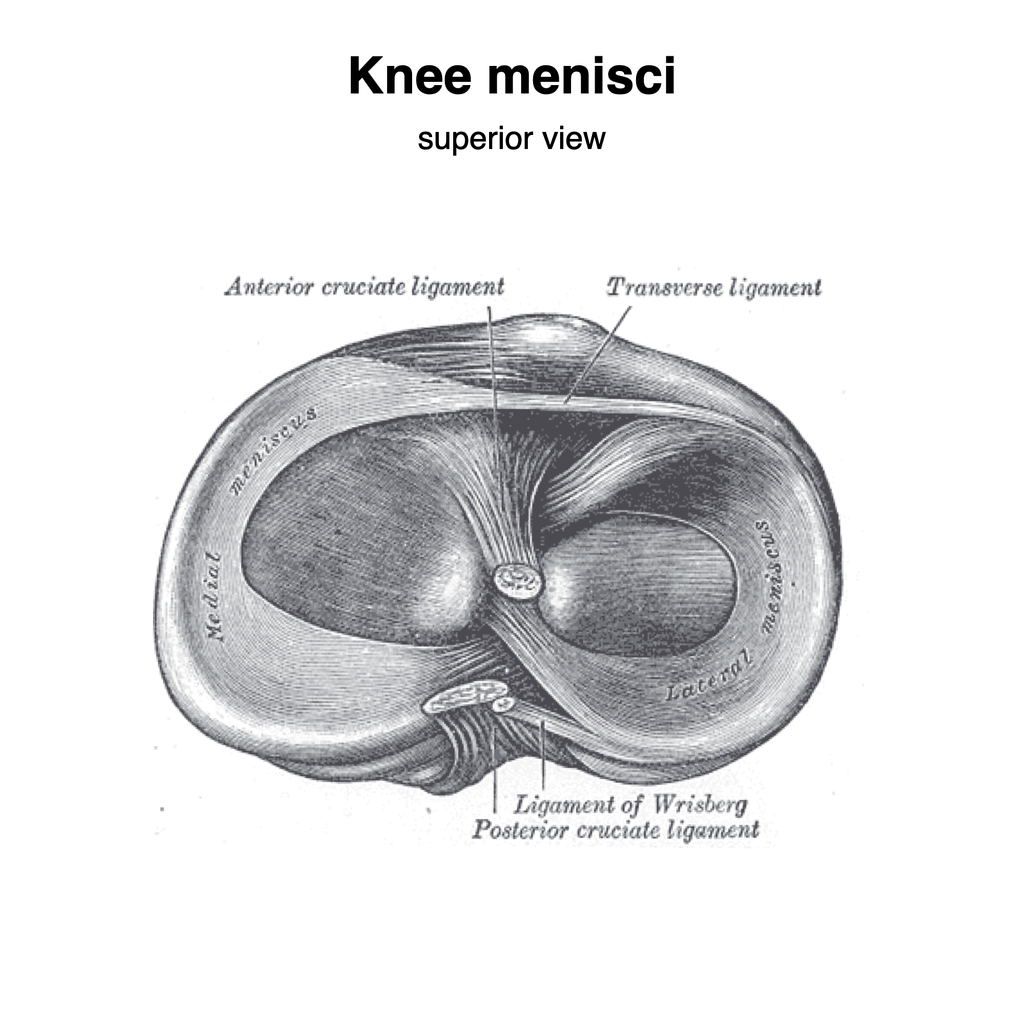
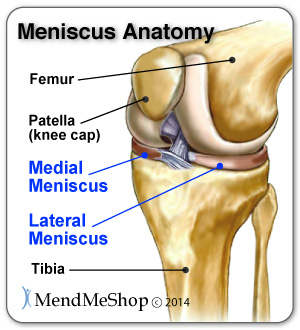
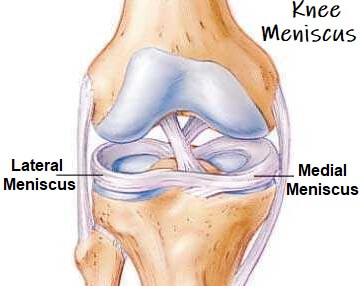
The knee is the joint where the large bones of the upper leg (femur), lower leg (tibia), and kneecap ( patella) meet. Two pieces of "C-shaped" cartilage called the meniscus cushion the ends of the femur and tibia at the knee joint. A tear in this cartilage is called a meniscal tear. Meniscal tears have different names - longitudinal, flap ... The diagram above is a cross section of the knee from the viewpoint looking down at the top of the shin bone (tibia). As you can see, the lateral meniscus on the outside of your knee is C shaped and thicker on the outer rim. The medial meniscus on the inside of your knee is also thicker on the outer rim and has a more oblong shape.
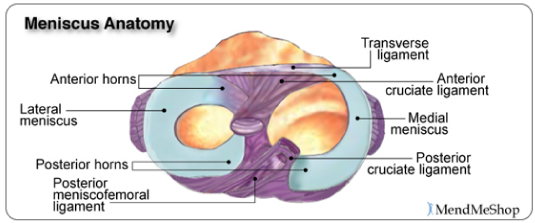
The soft tissue structure in the knee includes 2 menisci, the medial meniscus (located on the inside of the knee) and the lateral meniscus (located on the outside of the knee). Menisci are crescent-shaped pads of fibrocartilage that sit on the end of the tibia bone (tibial condyles) and form a concave surface for the rounded ends of the femur ...

Meniscus diagram of the knee
Dec 31, 2019 · Knee pain could be the result of a problem with any one of these components, or a combination of several. You may be experiencing knee pain and want to know the possible causes. The diagram, below, is a handy guide to the possible reasons for your pain. Pain at the front above the knee Famous Physical Therapists Bob Schrupp and Brad Heineck describe 3 tests you can do to determine if you have torn the cartilage or meniscus in your knee. Sim... A diagram of the knee, showing the medial meniscus. The medial meniscus is a half-circle piece of cartilage in the knee that's located on the inner side. The purpose of the medial meniscus is to reduce the force between the tibia and femur bones during activities such as walking, running or jumping.
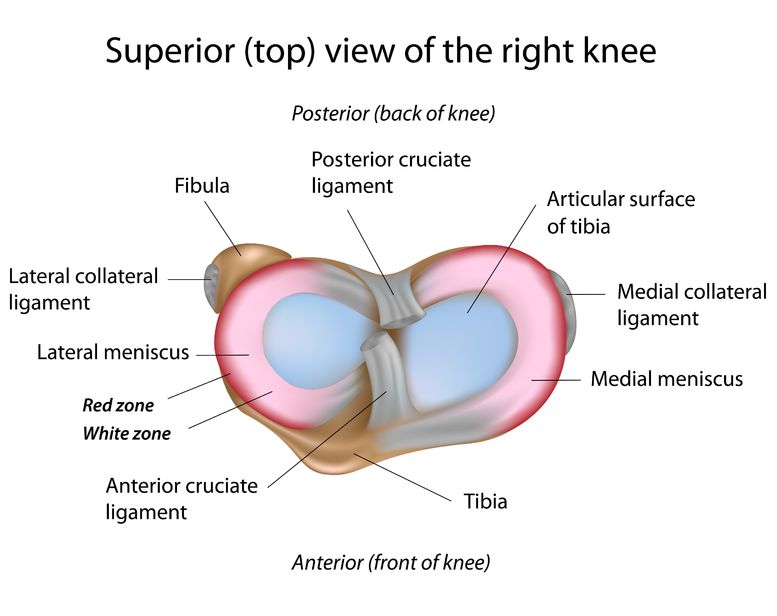
Meniscus diagram of the knee. The knee joint is a hinge type synovial joint, which mainly allows for flexion and extension (and a small degree of medial and lateral rotation). It is formed by articulations between the patella, femur and tibia. In this article, we shall examine the anatomy of the knee joint - its articulating surfaces, ligaments and neurovascular supply. This first knee pain diagnosis chart focuses on pain at the front of the knee. Then next one, further down, looks at pain behind the knee. A. Pain Above the Knee Cap (yellow). Quadriceps Tendinopathy: Damage to the quadriceps tendon causing pain above the kneecap that is worse with activity. LEARN MORE> B. Outer Knee Pain (blue). Iliotibial Band Syndrome: Most common. 2.1 Meniscus Anatomy. The knee joint contains the meniscus structure, comprised of both a medial and a lateral component situated between the corresponding femoral condyle and tibial plateau (Figure 1) [].Each is a glossy-white, complex tissue comprised of cells, specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules, and region-specific innervation and vascularization. Diagram of Knee Joint showing Meniscus. The meniscus is a crescent-shaped structure composed of cartilage that functions to distribute body weight evenly across the three bones that make up the knee joint: the thigh bone, shin bone, and knee cap. The surfaces of these bones are covered with cartilage, which allows the bones to move smoothly against each other without causing damage to the bone.
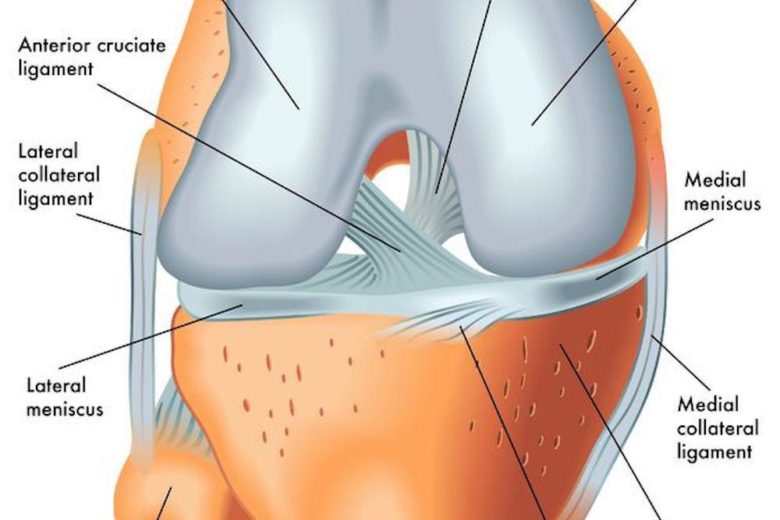
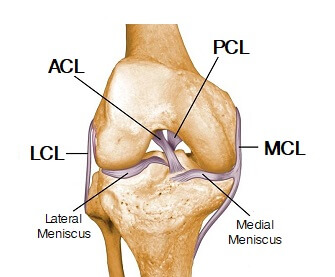
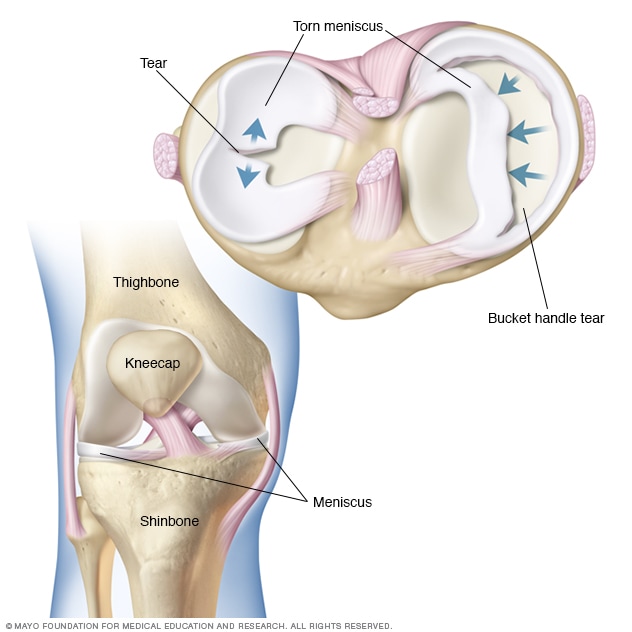
A meniscus tear is a common knee injury. The meniscus is a rubbery, C-shaped disc that cushions your knee. Each knee has two menisci (plural of meniscus) —one at the outer edge of the knee and one at the inner edge. The menisci keep your knee steady by balancing your weight across the knee. A torn meniscus can prevent your knee from working ... The lateral or "outside" collateral ligament (LCL) connects the femur to the smaller bone in the lower leg (fibula). The collateral ligaments control the sideways motion of your knee and brace it against unusual movement. There are two meniscal cartilages in the knee that act as shock-absorbers - one on the inner and one on the outer side. Medial meniscectomy in the ACL-intact knee has little effect on anterior-posterior motion, but in the ACL-deficient knee, it results in an increase in anterior-posterior tibial translation of up to 58% at 90 o of flexion. 109 Shoemaker and Markolf demonstrated that the posterior horn of the medial meniscus is the most important structure ... A meniscus tear is a common knee joint injury. How well the knee will heal and whether surgery will be needed depends in large part on the type of tear (See figure in appendix) and how bad the tear is. Work with your doctor to plan a rehabilitation (rehab) program that helps you regain as much strength and flexibility in your knee as possible.
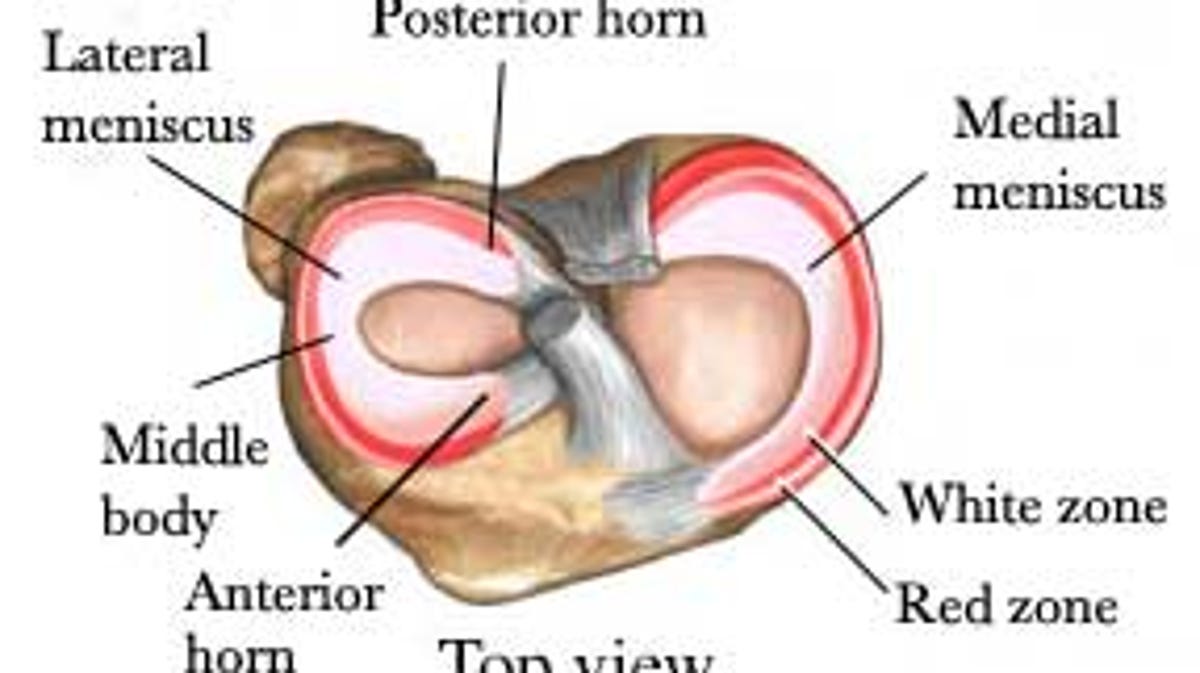
Articular cartilage lines the joint surfaces of the bones in the knee (tibia, femur, and patella, or kneecap). The medial and lateral meniscus are two thicker wedge-shaped pads of cartilage attached to the leg bone (tibia). Each meniscus is curved in a C-shape, with the front part of the cartilage called the anterior horn and the back part called the posterior horn. The seriousness of a meniscus tear depends on which one in injured and the location, type, and shape of the tear. When a meniscus tear occurs, is it usually the medial rather than the lateral meniscus that is damaged. This is because the lateral meniscus, unlike the medial meniscus, has a section that is not attached to the wall of the knee joint. MRI Knee - Coronal and Sagittal PDFS - Meniscus tear. These proton-density fat-suppressed ( PDFS) images are water sensitive (fluid is bright) A high signal line passes obliquely through the medial meniscus posteriorly. This line represents synovial fluid from the knee joint which has leaked into the torn meniscus. Dr. Ebraheim's educational animated video describes the Anatomy of the Meniscus.The meniscus is a cushion structure made of cartilage which fits within the k...
The Knee Joint. Jeannot Olivet / Getty Images. The knee is one of the most commonly injured joints in the body. The knee joint is the junction of the thigh and the leg (part of the lower extremity ). The femur (thigh bone) contacts the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint. The patella (kneecap) sits over the front of the knee joint.
Pain in the knee joint: usually on the inside (medial), outside (lateral) or back of the knee. Swelling. Catching or locking of the knee joint. Inability to fully extend or bend the knee joint. Limping. The symptoms of a meniscus tear are similar to other medical conditions or problems. Always see your health care provider for a diagnosis.
The meniscus is a rubbery, flexible piece of cartilage that provides cushioning between the bones in the knee. There are actually two menisci in each knee. Each individual meniscus is formed to fit the area of the joint surrounding it: The medial meniscus, which is located on the inside of the knee, is shaped like a C.
The meniscus is a small C-shaped piece of tissue in the knee, generally referred to as 'the cartilage,' that lies between your thigh bone (the femur) and your shin bone (the tibia). It acts as a shock absorber within the knee when walking, running and bending. Each knee has an inner (medial) and outer (lateral) meniscus which can tear.
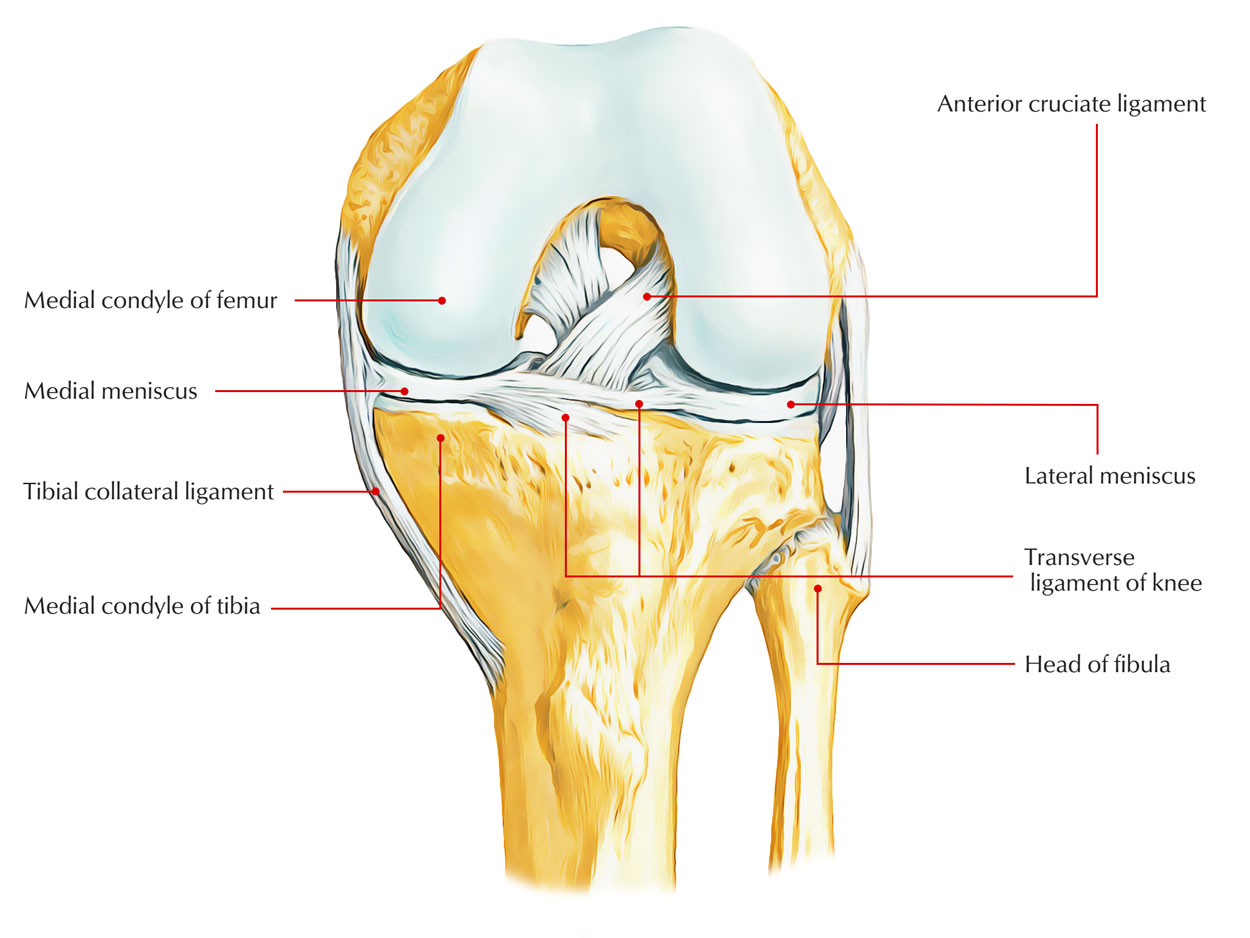
Knee joint (Articulatio genu) The knee joint is a synovial joint that connects three bones; the femur, tibia and patella.It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations; the tibiofemoral joint and patellofemoral joint.The tibiofemoral joint is an articulation between the tibia and the femur, while the patellofemoral joint is an articulation between the patella and the femur.
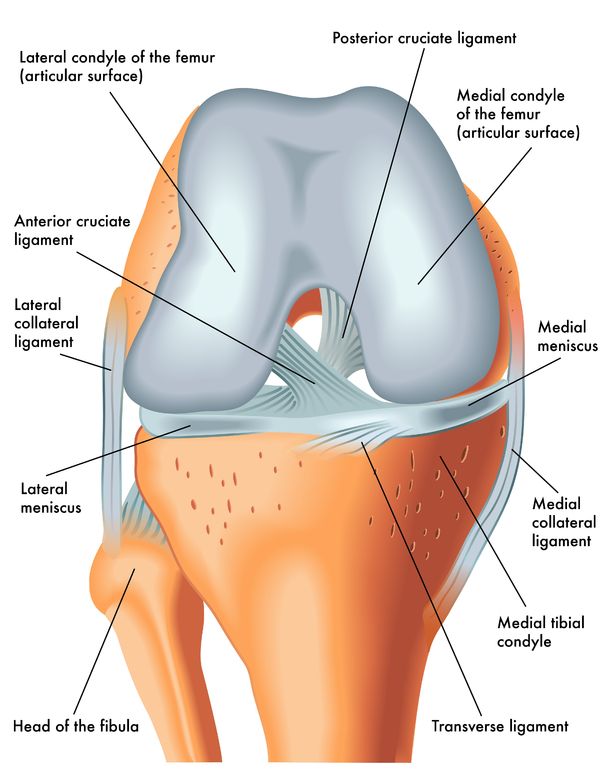
Meniscus anatomy diagram. In this image, you will find Lateral collateral ligament, Lateral meniscus, Fibula, Femur, Posterior cruciate ligaments, Anterior cruciate ligament, Medial meniscus, Medial collateral ligament, Patellar ligament (out), Tibia in it. Our LATEST youtube film is ready to run. Just need a glimpse, leave your valuable advice ...
Jan 20, 2018 · Medial meniscus. The medial meniscus is the central band of cartilage attached to the tibia, or shinbone. The band goes around the knee joint in a crescent-shaped path and is located between the ...
The dog knee injury is very common in the field. If you want to manage a knee injury, you might have a good piece of knowledge on the dog knee anatomy.Here, I will show you everything on the dog knee, including the bone involvement, ligaments, tendons and their arrangement with a labeled diagram.
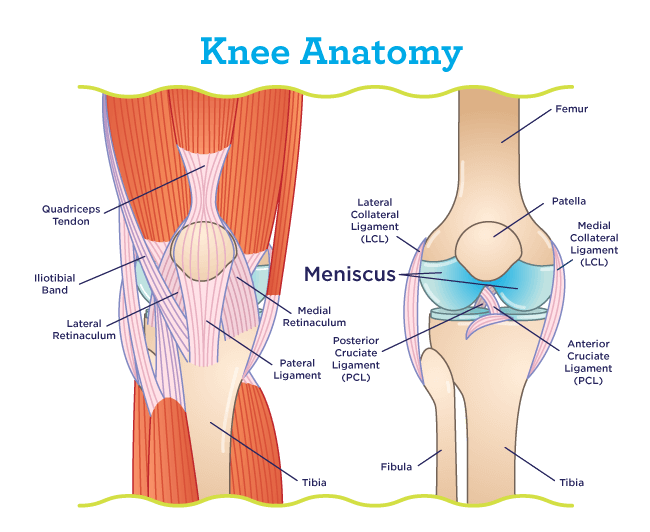
Knee joint anatomy involves looking at each of the different structures in and around the knee. The knee joint is the largest and one of the most complex joints in the human body. There are various muscles that control movement, ligaments that give stability, special cartilage to absorb pressure and various other structures to ensure smooth ...
The given diagram of the knee joint can help you to understand its various parts and the description given below will give you an insight of the functioning of the knee. ⚫ Bone. There are three bones in the knee namely the femur which is the thigh bone, tibia which is the shin bone and patella which is the knee cap.
Any form of arthritis or injury may cause a knee effusion. Meniscal tear: Damage to a meniscus, the cartilage that cushions the knee, often occurs with twisting the knee. Large tears may cause the ...
The knee meniscus is a special layer of cartilage that lines the knee joint. The job of the meniscus is to cushion the knee joint and transfer forces between the tibia and femur, the thigh and shin bones. Most of the joints in our body are lined with a thin layer of articular cartilage, made of collagen and chondroitin. This provides a smooth ...
Diagram of meniscal tear patterns: (A) Vertical or longitudinal (Bucket-handle). (B) Oblique - tears are known as flap or parrot beak tears. (C) Radial meniscus tear (or Transverse) - start on the inside white zone and goes to the middle body. A radial meniscus tear can continue to tear and reach the outside red zone.
Posterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Injury FAQ. The medial meniscus is the cushion that is located on the inside part of the knee. It is generally divided into 3 separate portions, the anterior horn, the mid-body and the posterior horn. The posterior horn is the thickest and most important for overall function of the knee.
A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries. Any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, especially when putting your full weight on it, can lead to a torn meniscus. Each of your knees has two C-shaped pieces of cartilage that act like a cushion between your shinbone and your thighbone (menisci). A torn ...
Anatomy of the Knee. The knee is the largest joint in your body and one of the most easily injured.It is a pivotal hinge joint in the leg that allows for a variety of movements (i.e. flexion, extension, medial rotation, and lateral rotation) and it connects the tibia and the fibula, with the thigh bone (femur).
Lateral meniscus. The lateral meniscus is attached to the shin and is located on the outer side of the knee. This C-shaped, rubbery, cartilage plays a key role in maintaining stability of the knee ...
A diagram of the knee, showing the medial meniscus. The medial meniscus is a half-circle piece of cartilage in the knee that's located on the inner side. The purpose of the medial meniscus is to reduce the force between the tibia and femur bones during activities such as walking, running or jumping.
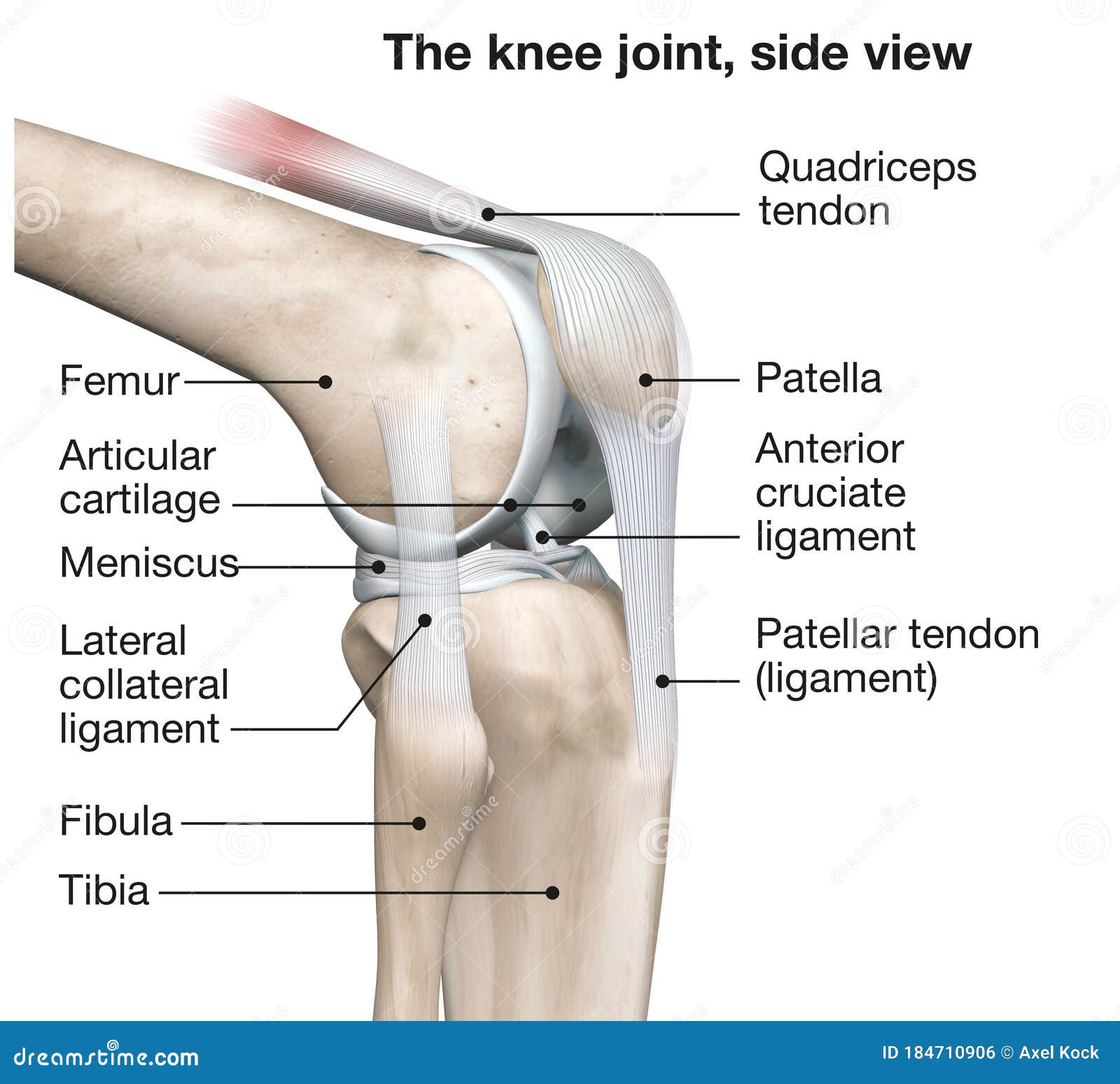
Knee Joint Anatomy Side View Medical 3d Illustration Stock Illustration Illustration Of Anatomy Tendon 184710906
Famous Physical Therapists Bob Schrupp and Brad Heineck describe 3 tests you can do to determine if you have torn the cartilage or meniscus in your knee. Sim...
Dec 31, 2019 · Knee pain could be the result of a problem with any one of these components, or a combination of several. You may be experiencing knee pain and want to know the possible causes. The diagram, below, is a handy guide to the possible reasons for your pain. Pain at the front above the knee
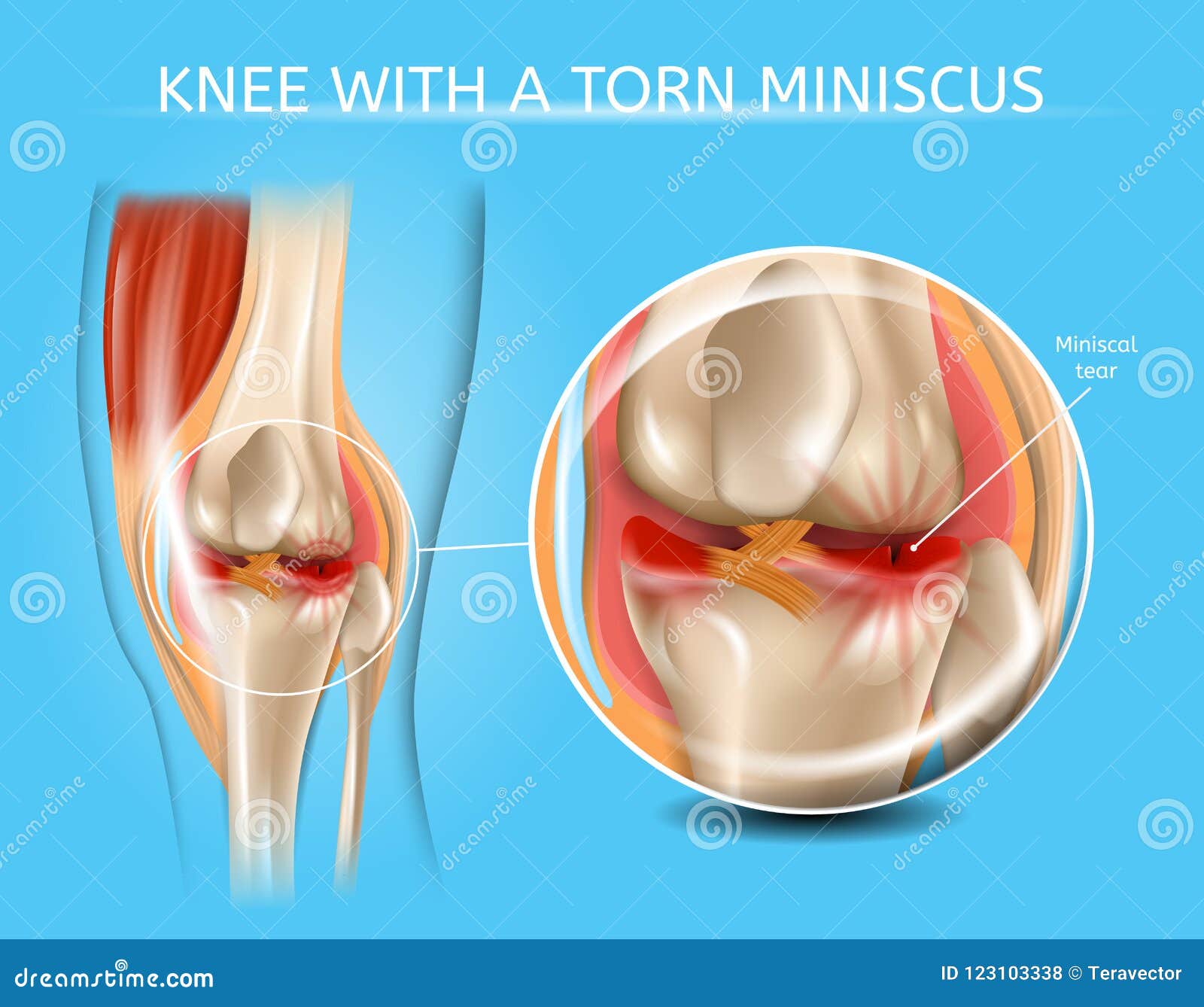
Injured Knee Joint With Torn Meniscus Vector Chart Stock Vector Illustration Of Healthcare Chart 123103338

Knee Anatomy Including Ligaments Cartilage And Meniscus Anatomy Of The Knee Knee Joint Anterior Cruciate Ligament





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WhatisMeniscalCyst_2549646_Final_1-dfb0f73f6d6a4548a7ef0485e7d7d869.jpg)


/188058334-crop-56aae7425f9b58b7d0091480.jpg)






/vector-illustration-of-a-meniscus-tear-and-surgery-871162428-03ac23d73f854954a8082f2ae3ce9219.jpg)








0 Response to "43 meniscus diagram of the knee"
Post a Comment