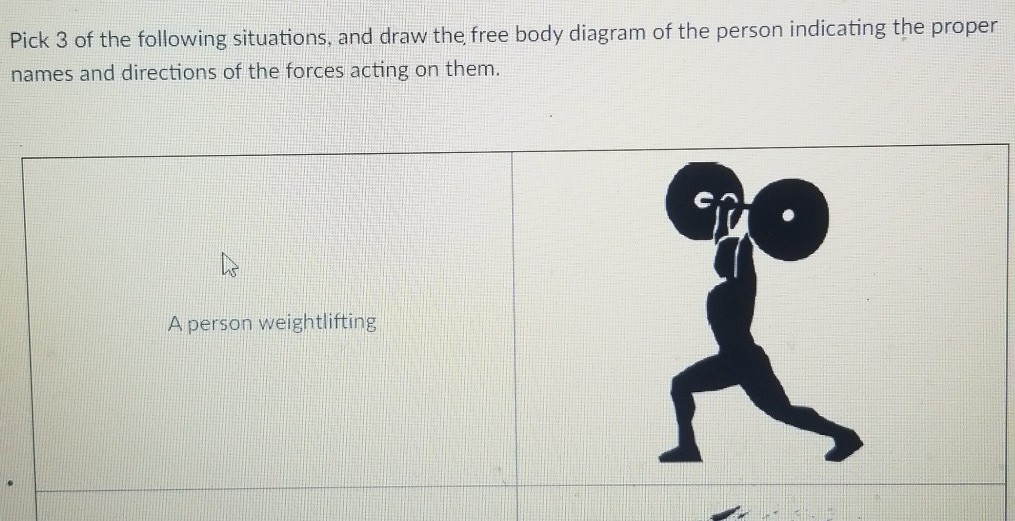
44 draw a free-body diagram for the weight lifter.
Reducing the weight of our footer. Linked. 14. Do I have to apply more force than gravity to lift my leg above the ground? Related. 7. Free body diagram with forces of friction. 0. ... My question is about the ommision of pseudo forces when we draw the free body diagram from an inertial frame of reference. 0. On a rocket, thrust is used in opposition to weight. On many rockets, lift is used to stabilize and control the direction of flight. On an airplane, most of the aerodynamic forces are generated by the wings and the tail surfaces. For a rocket, the aerodynamic forces are generated by the fins, nose cone, and body tube.
T = ma + w where T is the tension in the cable to lift the elevator, m is the mass of the elevator (which we have to solve for), a is the acceleration of the elevator (positive since it's going up), and w is the weight of the elevator (which we have as 5500 N). Solving first for mass: w = mg and. 5500 =- m(10) so. m = 550 kg.

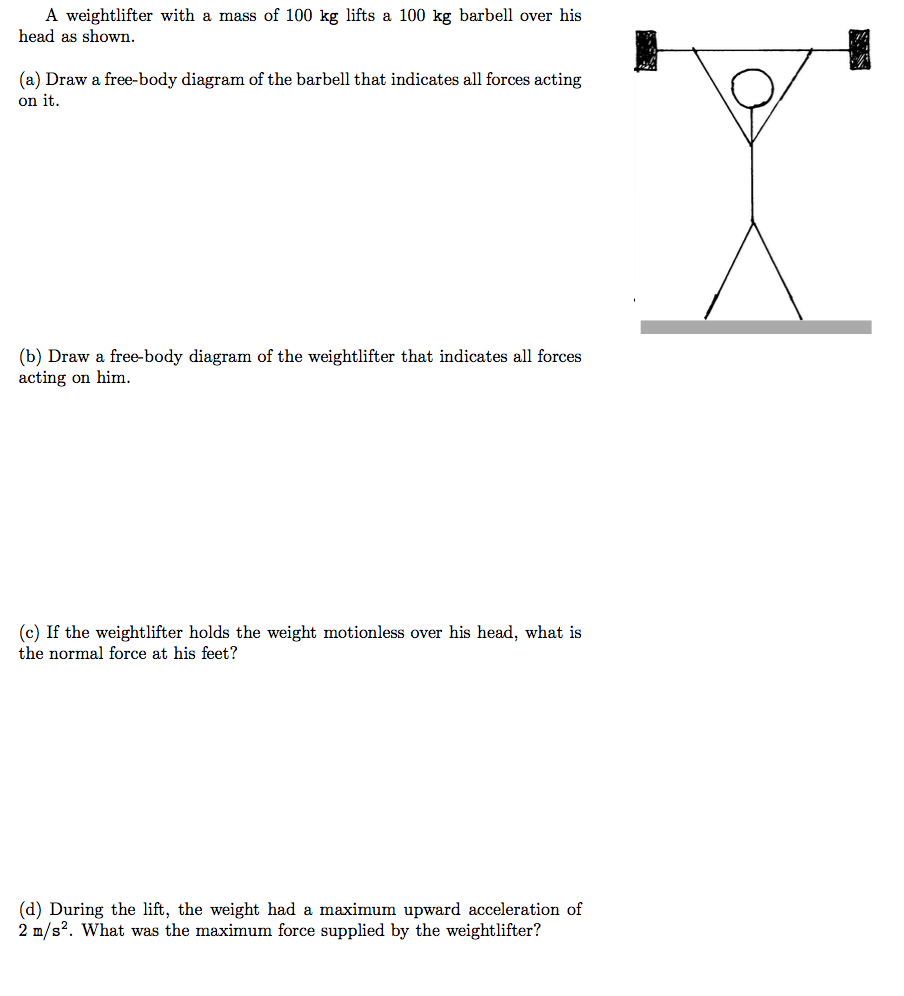
Draw a free-body diagram for the weight lifter.
• Draw a free-body diagram of the indeterminate beams indicating the end moments at the joint. • Draw the shearing force diagrams of the beam by considering the freebody diagram of each span of the beam in the case of a multi-span structure. 11.6 Analysis of Indeterminate Frames. Mar 21, 2017 — The second part is obviously simple fg and the force of the barbell on the weight lifter point down and normal force from the barbell points ... A steel cable with mass is lifting a girder. The girder is speeding up. Part A Draw a free-body diagram for the steel cable. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The length of the...
Draw a free-body diagram for the weight lifter.. When drawing free-body diagrams, each force is represented by an arrow (a vector). The size of the arrow shows the relative magnitude of the force, while the direction the arrow is pointing tells ... This is a key concept when dealing with free body diagrams and its calculation is relatively simple through the use of basic trigonometric functions. Let's discover how. How to calculate the normal force. Draw a free body diagram of the body coming in contact with the surface of interest and identify all the forces acting on it. Draw a free-body diagram for the weight lifter. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be g graded. Previous ... Calculating Shear Force Diagram - Step 2: Keep moving across the beam, stopping at every load that acts on the beam. When you get to a load, add to the Shear Force Diagram by the amount of the force. In this case we have come to a negative 20kN force, so we will minus 20kN from the existing 10kN. i.e. 10kN - 20kN = -10kN.
[insert a free body diagram showing the applied, frictional, gravitational and normal forces on the still box] First, note that the net force is 0 and find the normal force of the surface on the box. Since the box is not moving, this force must be equal in magnitude to the gravitational force acting in the opposite direction. Oct 19, 2004 — a) [ 5 points ] Draw a free-body diagram for the box when the pole makes ... weightlifter squats to pick it up, lifts the barbell, and then.14 pages Classify the beams shown in Figure 3.1 through Figure 3.5 as stable, determinate, or indeterminate, and state the degree of indeterminacy where necessary.. Fig. 3.1. Beam. Solution. First, draw the free-body diagram of each beam. To determine the classification, apply equation 3.3 or equation 3.4.. Using equation 3.3, r = 7, m = 2, c = 0, j = 3. Applying the equation leads to 3(2) + 7 > 3(3 ... Simple machines are devices with few or no moving parts that make work easier. Students are introduced to the six types of simple machines — the wedge, wheel and axle, lever, inclined plane, screw, and pulley — in the context of the construction of a pyramid, gaining high-level insights into tools that have been used since ancient times and are still in use today. In two hands-on ...
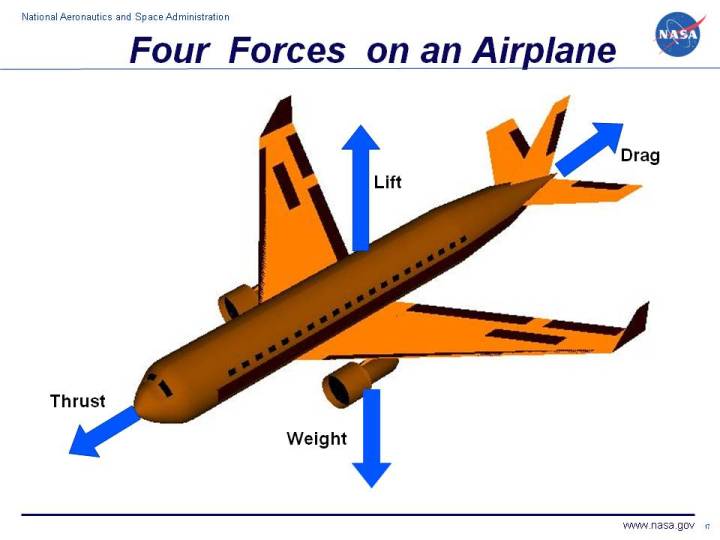
A force may be thought of as a push or pull in a specific direction. A force is a vector quantity so a force has both a magnitude and a direction. When describing forces, we have to specify both the magnitude and the direction.This slide shows the forces that act on an airplane in flight.. Weight Weight is a force that is always directed toward the center of the earth. An airplane with a welght of 3500 N flying through the air. The vertical lift on the plane is 4500 N, the friction with the air is 1500 N, and the force applied by the engines Draw a free body diagram of this situation and find the net force acting on the alrplane. Draw a free body diagram of an 6.4 kg ball falling towards earth. Calculate the weight of the ball. The can of paint is two-fifths of the plank length from the front. Find the percentage of the total weight carried by the painter in front. Assume that the plank is horizontal as they carry it. Solution. We start by identifying the object in equilibrium (the plank), and drawing a free-body diagram for it (we'll call the length of the plank \(L\)).
Answer to Question #168164 in Physics for van. Blocks A, B, and C are placed as in the figure below and connected by ropes of negligible mass. Both A and B weigh 25.0N each, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between each block and the surface is 0.35. Block C descend with constant velocity. a) Draw separate free-body diagrams showing the ...
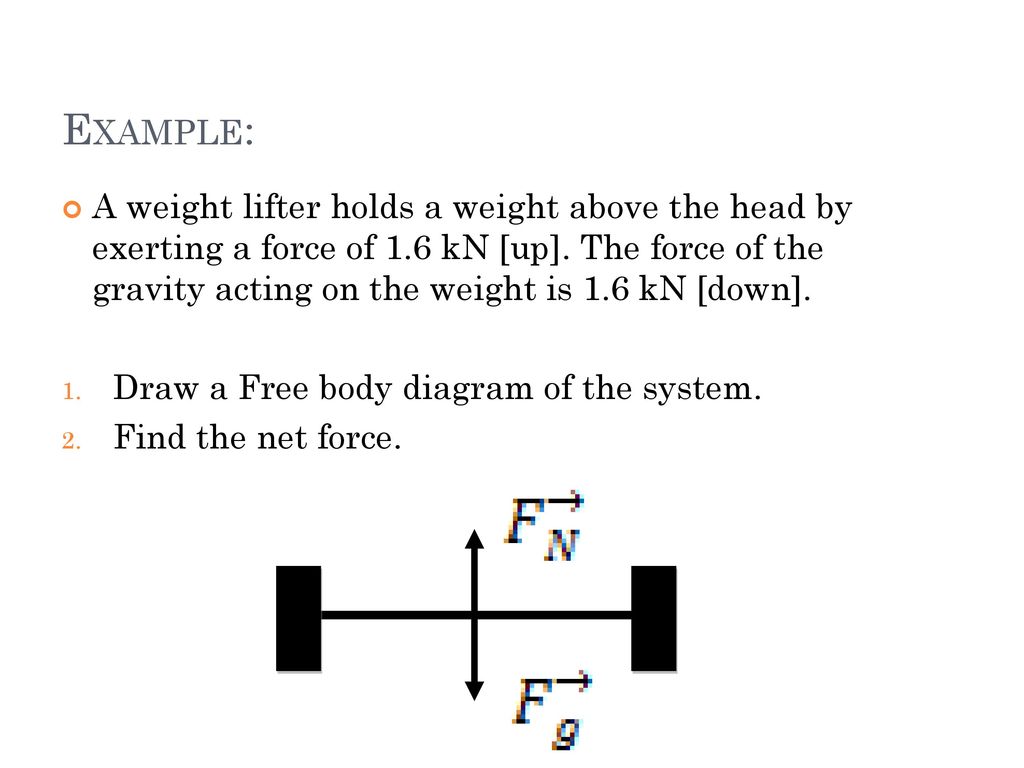
May 19, 2014 — Start a free-body diagram by drawing an outline of the object. mg. The weight vector is drawn ... Weight. Next, draw the forces acting ON.7 pages
This free Workout Chart template focuses on weight lifting exercises, and can be used to structure your overall weight lifting program, including warm up, core body, upper body, lower body, and cool down exercises.This workout chart allows you to list the type of exercise, how many sets and reps, how much weight, and the resting time in between sets.

A Person With A Mass Of 60 Kg Stands In An Elevator Draw A Force Diagram For The Person And Indicate The Magnitude Of Each Of The Forces Acting On The Person
The weight of boom ABC and the combined weight of the truck and driver are as shown. Determine the reaction at each of the two ( a ) front wheels H , ( b ) rear wheels K . First, I drew a free body diagram in order to clearly see all the forces and distances acting on the crane. Since the crane is at equilibrium summation of Fy = 0.
(a) Draw a free-body diagram for each block, showing the force of gravity on Physics A crate is pulled right with a force of 82.0N to the left wtih a force of 115N upward with a force of 565N and downward with a force of 236N Fine the net external force in the X direction Find the net external force in the y
1 Answer to Determine the smallest horizontal force P required to pull out wedge A. The crate has a weight of 240 lb and the coefficient of static friction at all contacting surfaces is µs = 0.7. Neglect the weight of the wedge B 15
The weight of the books exerts a downward force on the table. ... it is helpful to draw diagrams. Draw each object apart from the other. ... Free-Body Diagrams 4:34
Once you have the reactions, draw your Free Body Diagram and Shear Force Diagram underneath the beam. Finally calculating the moments can be done in the following steps: 2. From left to right, make "cuts" before and after each reaction/load. To calculate the bending moment of a beam, we must work in the same way we did for the Shear Force ...
Oct 25, 2015 · 2 postsA weightlifter stands up at constant speed from a squatting position while holding a heavy barbell across his shoulders. Draw the free body ...
It helps to draw a new free-body diagram showing all of the horizontal and vertical components of each force acting on the system. Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): When the vectors are projected onto vertical and horizontal axes, their components along those axes must add to zero, since the tightrope walker is stationary.

Free Body Q Extra Practice Bpk 201 Practice Questions Free Body Diagrams Modified From Practice Studocu
Please draw the free body diagram and if correct answer will upvote A weight W is Suspended from a rigid bar, which is Suspended by two identical steel wires as shown a The bar is initially Chefore the weight is applied) horizontal, If the angle the bar makes with the horizontal (after the weight is applied) must not exceed 2, for the maximum permissible value of the distance a'.
For T₂, its free-body diagram shows us it is only responsible for the mass of m₂, we can say that T₂ = a * m₂. With that said, T₂ = (2.4 m/s²) * (2 kg) = 4.8 N . On the other hand, T₁ is the tension force that pulls both the weight of m₁ and m₂.
Multiple-Body Problems. For the two-body problem above, we can consider 3 different free-body diagrams. For three bodies in motion together, we can consider up to 6 different free-body diagrams: the 3 objects independently, 2 objects at a go, and all 3 together. Find the force between any two bodies by simplifying a 3-body diagram into 2 bodies.
Mass is a scalar quantity, but weight is a vector quantity. It is the measure of the quantity of matter contained in a body, but weight is the measure of force with which the Earth attracts the body. While Mass of a body is always constant but weight varies from place to place. 19. State the S.I. units of (a) mass and (b) weight.

Solved Of An Object With Mass 1 5 Kg Sitting On A Table While Someone Draw The Free Body Diagram What Is The Normal Force Pushed Down On It With A Force Of 7n
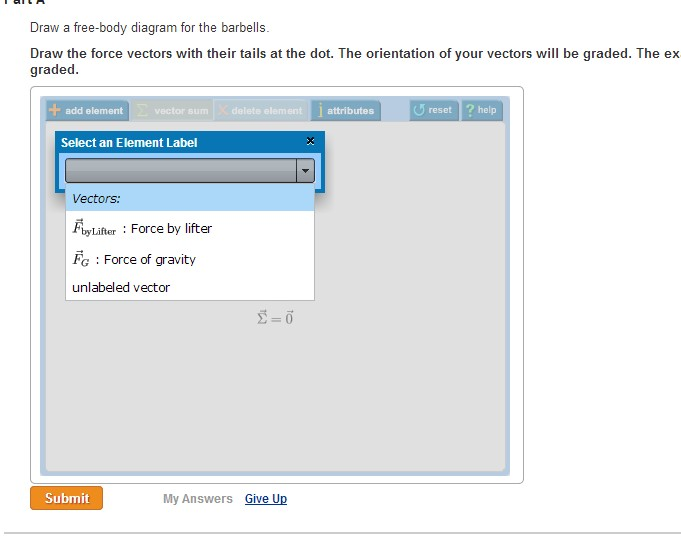
Draw a free-body diagram for the weight lifter. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. Free Body Diagram: A free body diagram is the simple ...1 answer · Top answer: Here figure represent the free body diagram of the weightlifter in squatting position along with the barbell: Free Body diagram Here the Weight...
B) Draw a free-body diagram for the weight lifter. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded.1 answer · 0 votes: Fo G1
The loaded cart has a mass of 28.0 kg, and the force of friction is 60.0 N. (a) Draw a free-body diagram for the system of . Physics. 1. The weight in the following diagram has a mass of 0.750 kg and the cart has a mass of 0.52 kg. There is a friction force of 2.1 N acting on the cart. What is the tension in the string?
ratio 3 (i) Draw a labelled diagram of this system. In your diagram indicate clearly the points of application and the directions of the load and effort. (ii) Why should the lower block of this pulley system be of negligible weight. Answer: (ii) Let the weight of lower block and pulley be w Therefore L + w = 3 T = L = 3 T - w Effort, E = T
A steel cable with mass is lifting a girder. The girder is speeding up. Part A Draw a free-body diagram for the steel cable. Draw the vectors starting at the black dots. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The length of the...
Mar 21, 2017 — The second part is obviously simple fg and the force of the barbell on the weight lifter point down and normal force from the barbell points ...
• Draw a free-body diagram of the indeterminate beams indicating the end moments at the joint. • Draw the shearing force diagrams of the beam by considering the freebody diagram of each span of the beam in the case of a multi-span structure. 11.6 Analysis of Indeterminate Frames.

A Weightlifter Stands Up At Constant Speed From A Squatting Position While Holding A Heavy Barbell Across His Shoulders Draw A Free Body Diagram For The Weight Lifter Draw The Force Vectors With
























0 Response to "44 draw a free-body diagram for the weight lifter."
Post a Comment