40 transfer function block diagram
This block diagram can certainly be recreated in Simulink. I suggest you start with 'Transfer Function' blocks and 'Sum' blocks, to match the transfer functions and sums in the diagram. I am not sure what the 'F' blocks in your diagram refer to, but if they are simply gains, then you can use a 'Gain' block to represent each one.
A block diagram can be used simply to represent the composition and interconnection of a system. Also, it can be used, together with transfer functions, to represent the cause-and-effect relationships throughout the system. Transfer Function is defined as the relationship between an input signal and an output signal to a device. Block diagram rules
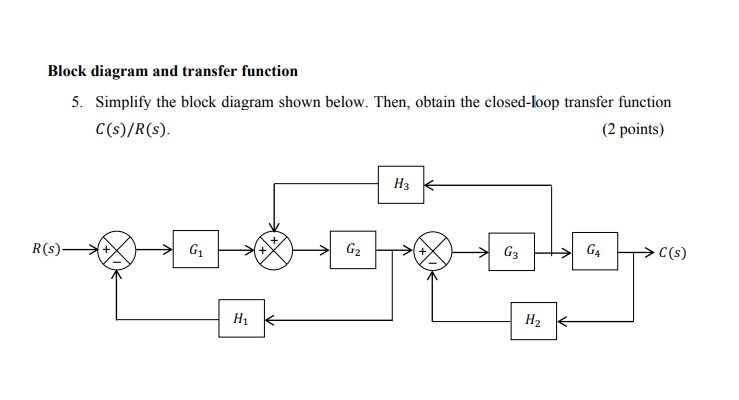
2. Block diagram models The block diagram is a diagrammatic means to represent the cause-and-effect relationship of system variables. It consists of unidirectional, operational blocks that represent the transfer function of the variables of interests. Fig.4: Components of a block diagram for a linear, time-invariant system
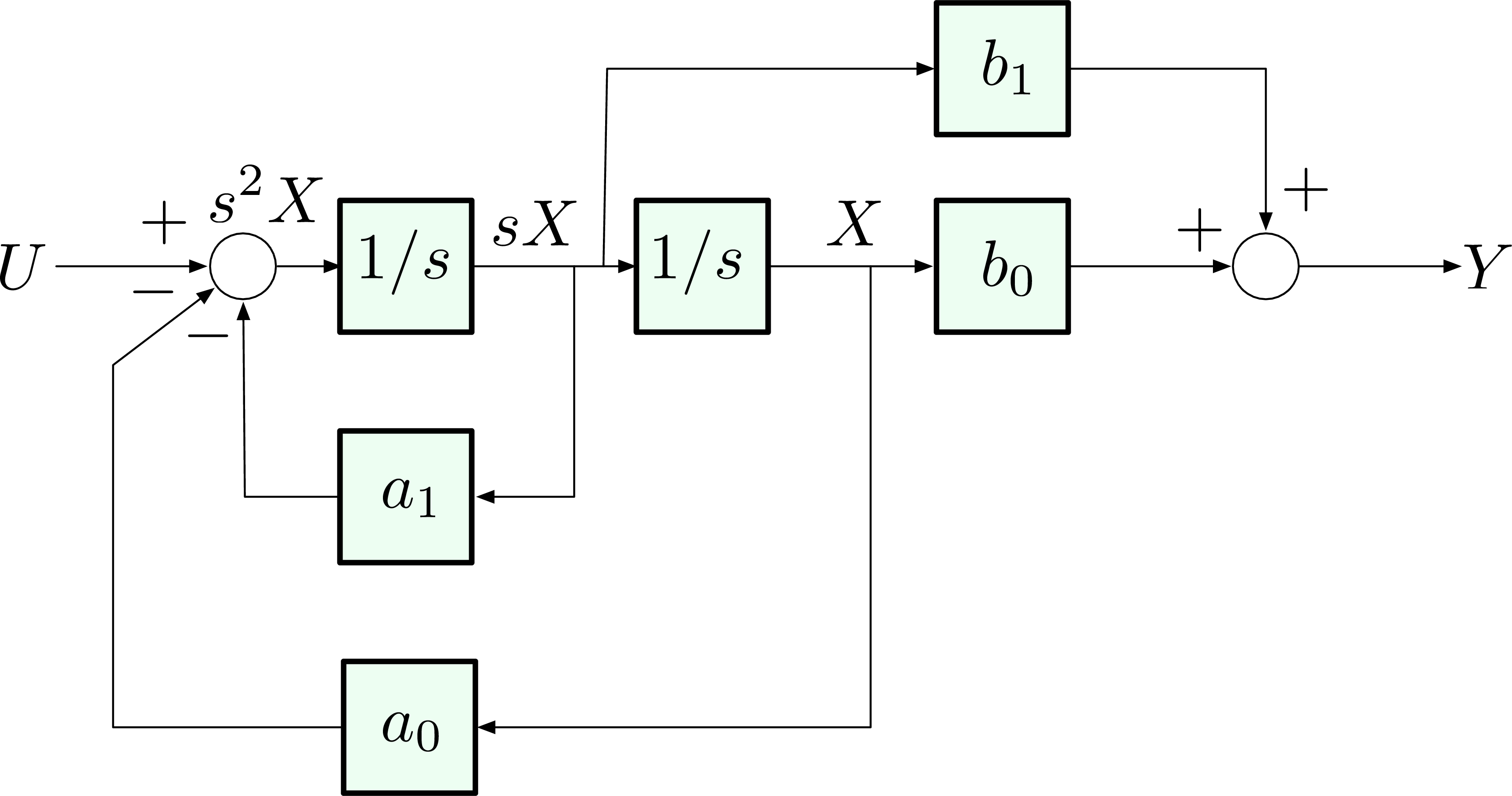
Transfer function block diagram
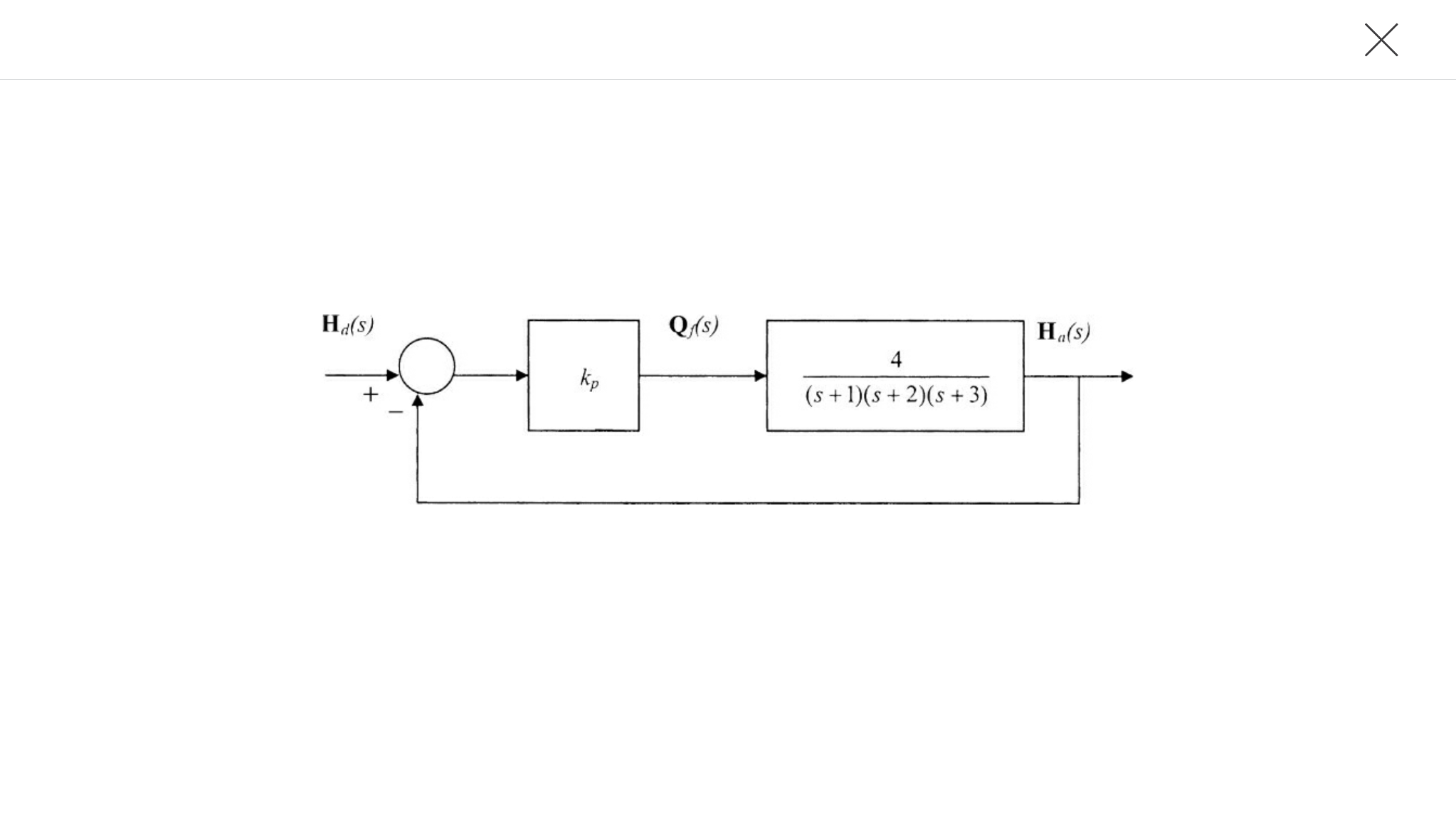
Transfer function with speed changer MOTOR POSITION WITH LOAD BLOCK DIAGRAM 22 x 1/(L a s+R a) K I a (s) m + 1/s - T E b (s) 1/(J T s+B) T(s) (s) K e N 1 /N 2 E Q L (s) a (s) L (s) L J s (R J B L)s (K K R B )s N N K E(s) s T E a m 2 a m m a 3 a m 2 1 T a L = Q Motor position transfer function with speed changer. Note: multiplication by s
The block diagram for n transfer functions G1,.Ga ..... G, in cascade is given in Fig. 7-11. Xl Xÿ Xn Fig. 7-11 The output transform for any block is equal to the input transform multiplied by the transfer function (see Section 6.1). Therefore X2 = XaG1, X3 = X2G2 .....
Step 1 − Find the transfer function of block diagram by considering one input at a time and make the remaining inputs as zero. Step 2 − Repeat step 1 for remaining inputs. Step 3 − Get the overall transfer function by adding all those transfer functions. The block diagram reduction process takes more time for complicated systems.
Transfer function block diagram.
The transfer function of this single block is the sum of the transfer functions of those two blocks. The equivalent block diagram is shown below. Similarly, you can represent parallel connection of ‘n’ blocks with a single block. The transfer function of this single block is the algebraic sum of the transfer functions of all those ‘n’ blocks.
Transfer function block diagram. 1. Find the difference equation and draw the simulation diagram. 4. Find transfer function from root locus and step response diagram? 3. Poles and zeros of a transfer function. 0. Block diagram for a complex impulse response. 0. Inverse Fourier of Two-Pole Transfer Function.
A block diagram is used to represent a control system in diagram form. In other words, the practical representation of a control system is its block diagram. Each element of the control system is represented with a block and the block is the symbolic representation of the transfer function of that element.
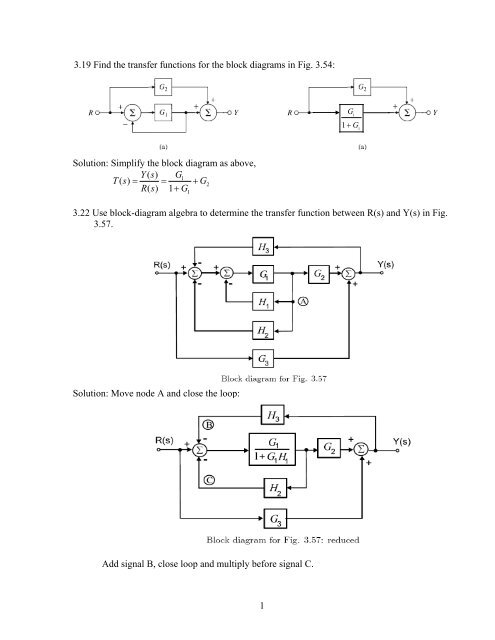
160 BLOCK DIAGRAM ALGEBRA AND TRANSFER FUNCTIONS OF SYSTEMS [CHAP. 7 Let the - 1 block be absorbed into the summing point: Step 4c Step 5: By Equation (7.3), the output C, due to input U is C, = [G2/(1 + G1G2)]U. The total output is C=C,+C,= [ ~ 1 +G2G2] [ A] [ A] IGIR + 7.8 REDUCTION OF COMPLICATED BLOCK DIAGRAMS The block diagram of a practical feedback control system is often quite complicated.
H1 align="center">enotes: mechatronics and controls

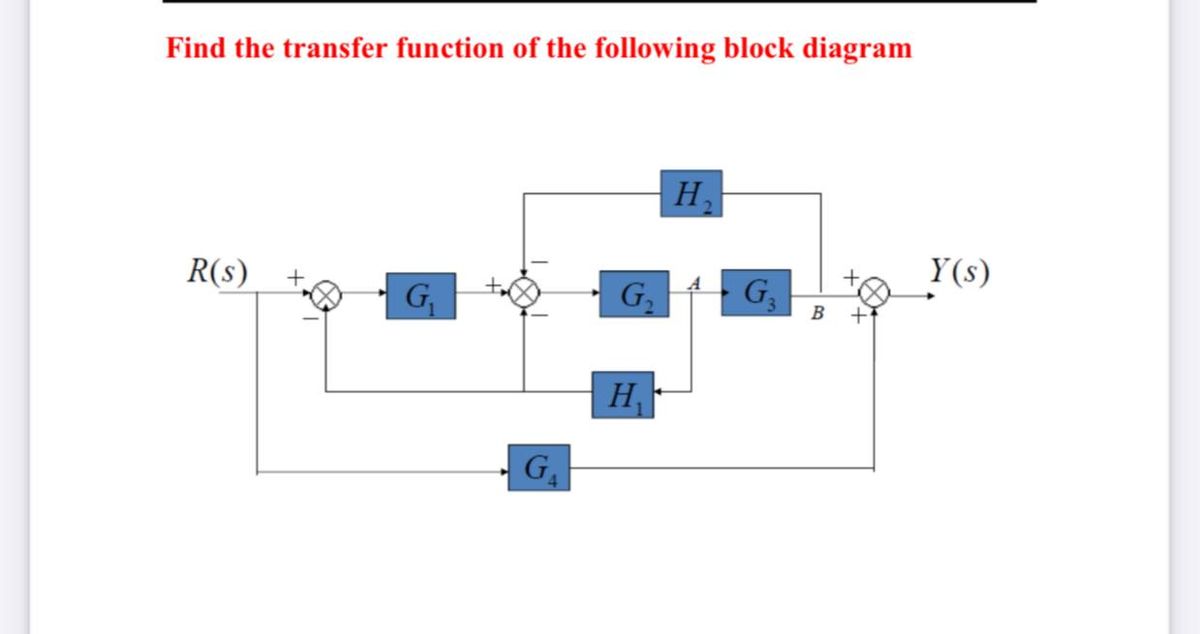

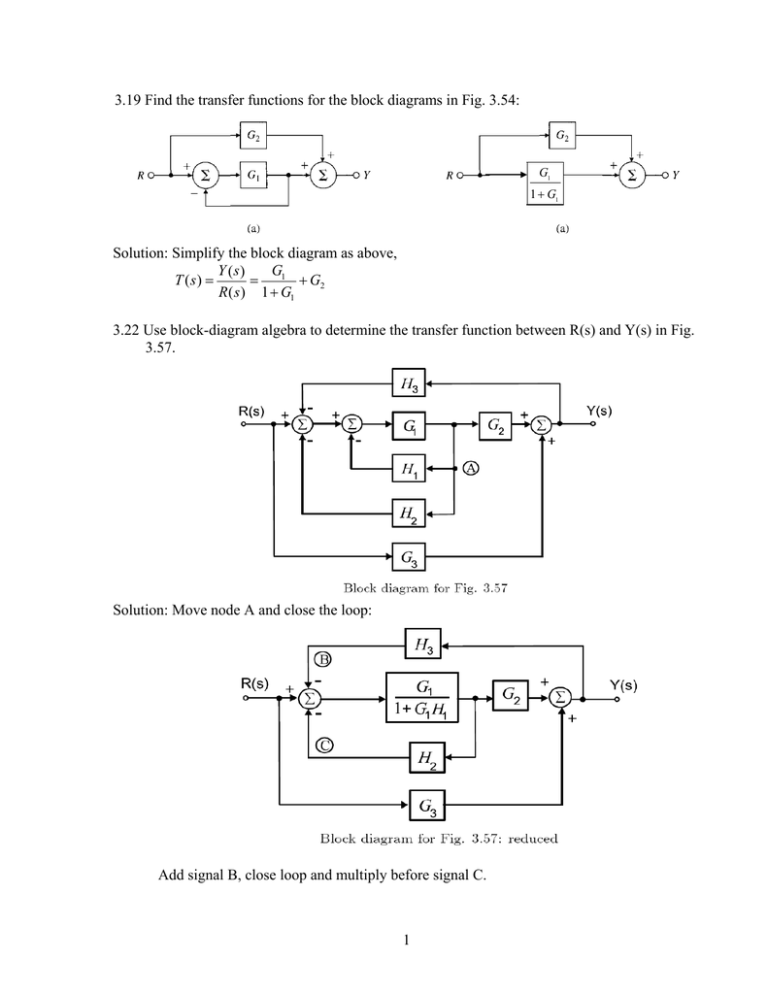





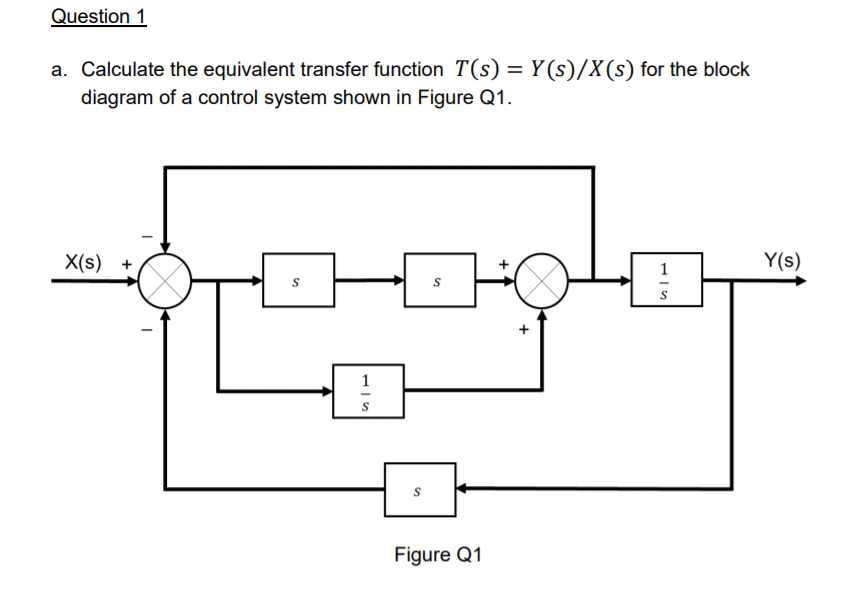















0 Response to "40 transfer function block diagram"
Post a Comment