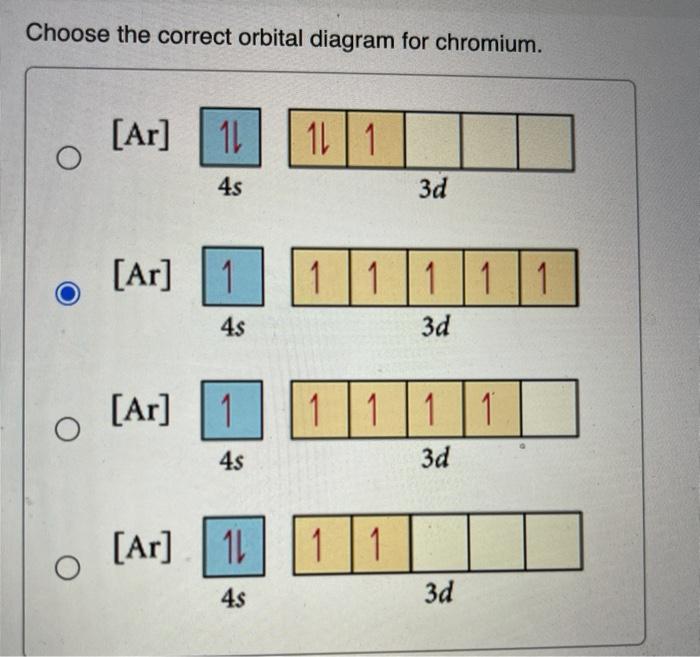
42 orbital diagram for chromium
Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau...
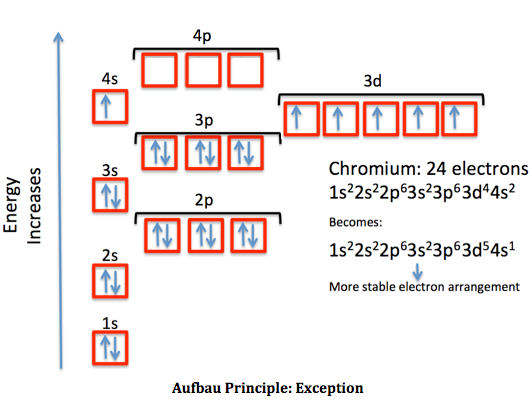
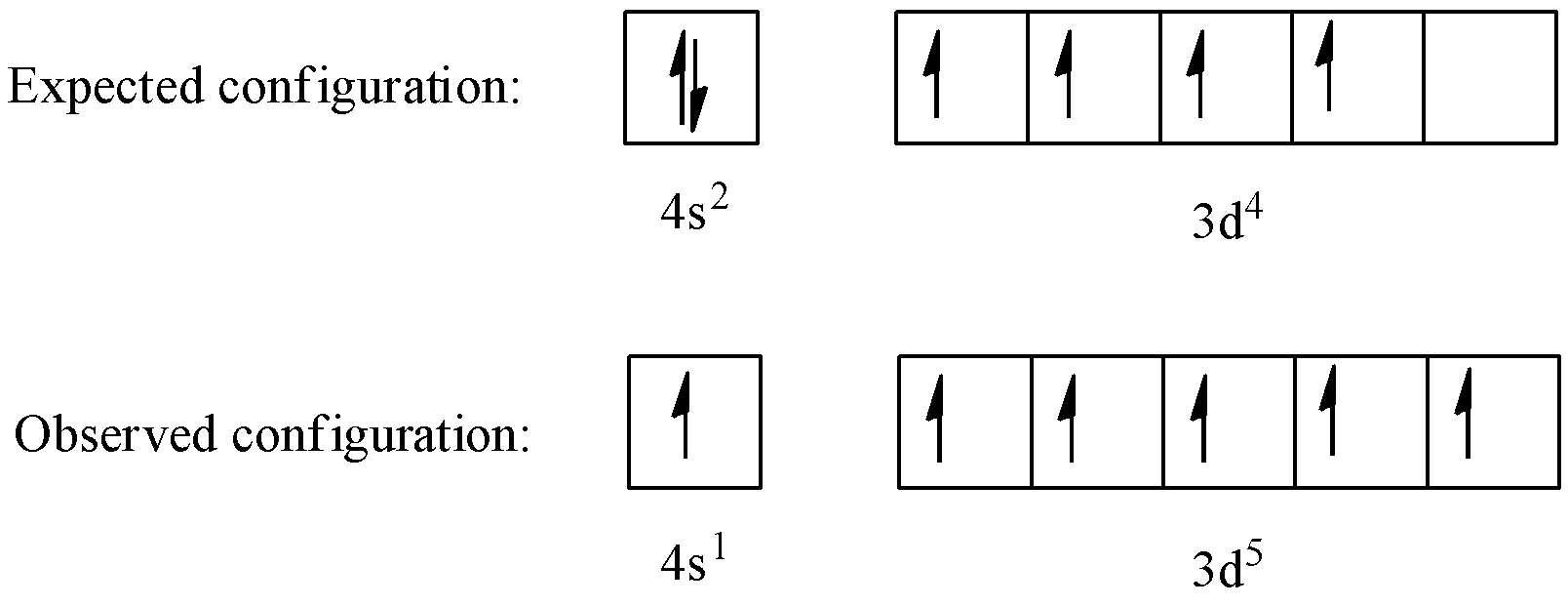
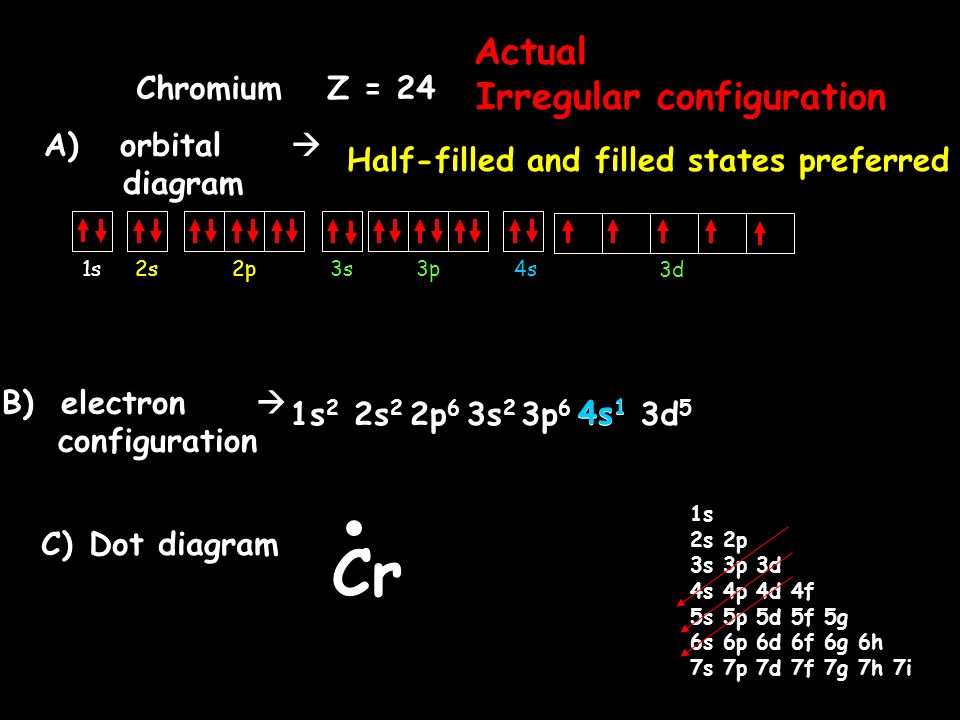
In the case of chromium, this means that one of the 4s electrons will go to the 3d orbital, resulting in two half-filled sub-shells where all electrons within each sub-shell have the same spin. In the case of copper, a similar thing happens. The difference is that the 4s electron moves into an almost-filled 3d shell in order to completely fill it.
The order of filling the orbitals with electrons in the Cr atom is an exception to the rule. Expected electronic configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 4 But in reality, one electron moves from the 4s orbital to the 3d orbital: Electronic configuration of the Chromium atom in ascending order of orbital energies:

Orbital diagram for chromium
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
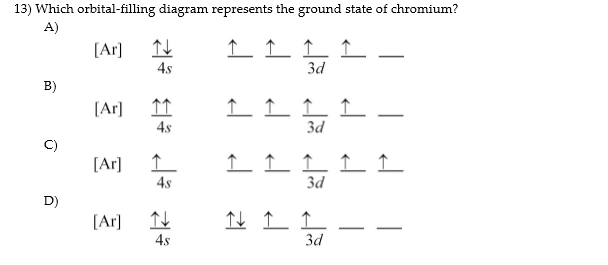
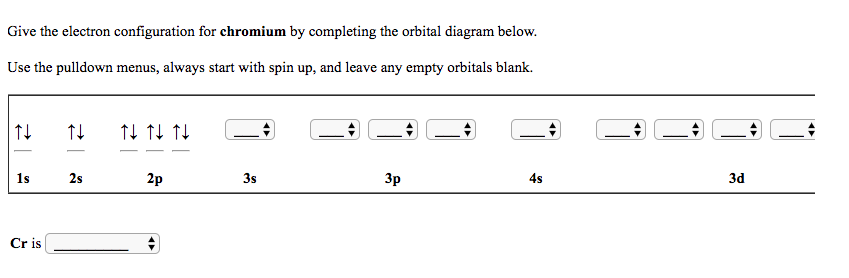
6. Draw the orbital diagram for the chromium atom. Is a chromium atom paramagnetic or diamagmetic? SA. Draw the orbital diagram for the zinc atom.ls a zinc atom paramagnetic or diamagmetie? Question: 6. Draw the orbital diagram for the chromium atom. Is a chromium atom paramagnetic or diamagmetic? SA.
Orbital diagram for chromium.
Re: Why are Copper and Chromium exceptions? When doing the electron configurations for these elements, they are exceptions to the general rule because a completely full or half full d sub-level is more stable than a partially filled d sub-level, so an electron from the 4s orbital is excited and rises to a 3d orbital.
Answer: Go to the following website to find the orbital diagram of any element of any Oxidation state. Orbital Energy Diagram and Atomic Electron Configuration Tool As for an actual diagram (per Wiki) is above. You can also find the electron configuration on both websites. For an overview and ...
Orbital diagram for chromium? 1s22s2 2p63s23p64s13d5. What is an orbital diagram of chromium? 1s22s2 2p63s23p64s13d5 Chromium (along with copper) have irregular electron configurations.
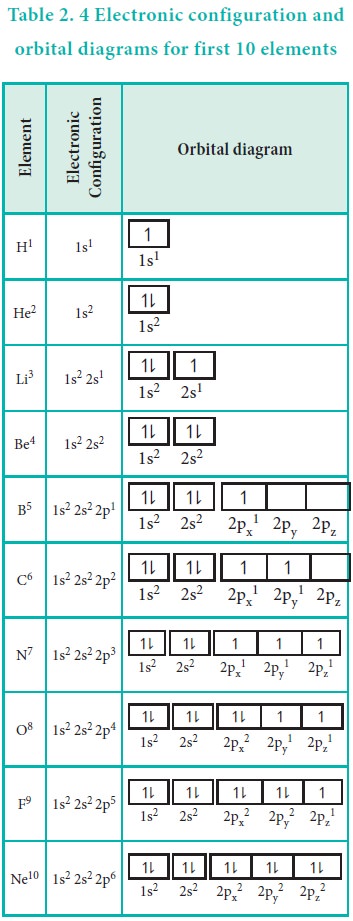
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
Orbital diagram for chromium. Orbital diagram for iron. Orbital diagram for copper. Orbital diagram for zinc. Electron configuration for copper. Electron configuration for fluorine. Electron configuration for sodium. Electron configuration for phosphorous. Electron configuration for scandium.
Hund's rule states that, orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron and that each of the single electrons must have the same spin. TRUE. As per Hund's rule, each 'p' orbital receives one electron before a second electron is added. TRUE. For _____, the 52nd electron must pair ...
Orbital Diagram For Chromium Fill In The Energy Orbital Diagram For The Following Atom Criii Be Sure To Label Orbitals N And L Quantum Numbers And Place Electrons In The Appropriate Energy Level You Will Not Fill All. Orbital Diagram For Chromium Figure 5 From Relation Between Local Composition Chemical.
Orbital diagram of Chromium (Cr) 25: Orbital diagram of Manganese (Mn) 26: Orbital diagram of Iron (Fe) 27: Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co) 28: Orbital diagram of Nickel (Ni) 29: Orbital diagram of Copper (Cu) 30: Orbital diagram of Zinc (Zn) 31: Orbital diagram of Gallium (Ga) 32: Orbital diagram of Germanium (Ge) 33: Orbital diagram of Arsenic ...
To write the orbital diagram for the Chromium (Cr) first we need to write the electron configuration for just Cr. To do that we need to find the number of e...
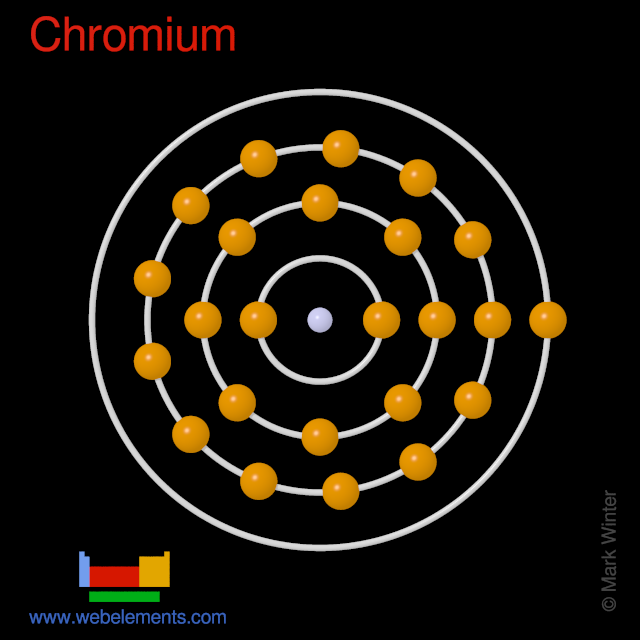
What is the correct orbital diagram for chromium? It should have four shells/rings there should be two electrons on the first shell, 8 electrons on the second shell, 8 shells on the third shell ...
Use a d orbital diagram to predict any changes in color and paramagnetism that might occur when aqueous chromium as Cr(H2O)6 2+ reacts with NaCN.

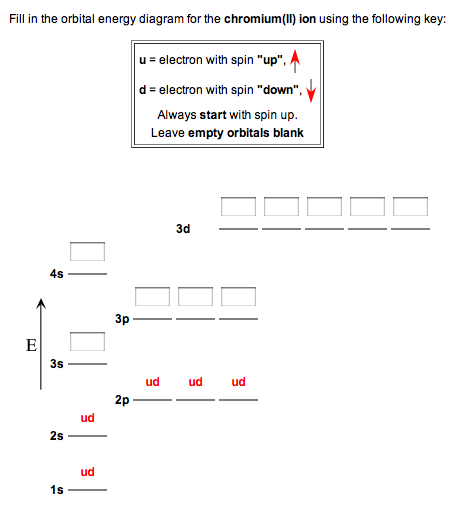
Fill in the energy orbital diagram for the following atom cr(iii). be sure to label orbitals by n and l quantum numbers, and place electrons in the appropriate energy level. you will not fill all




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)






/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)
![Solved] Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the chromium ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/questions/2019/11/5ddb2298a912b_ScreenShot20191124at7.38.39PM.png)









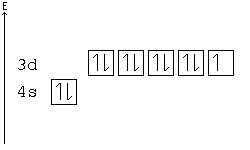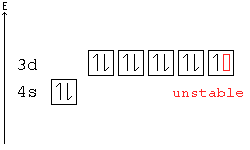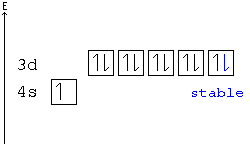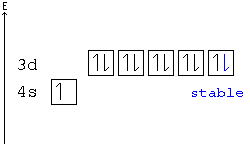
0 Response to "42 orbital diagram for chromium"
Post a Comment