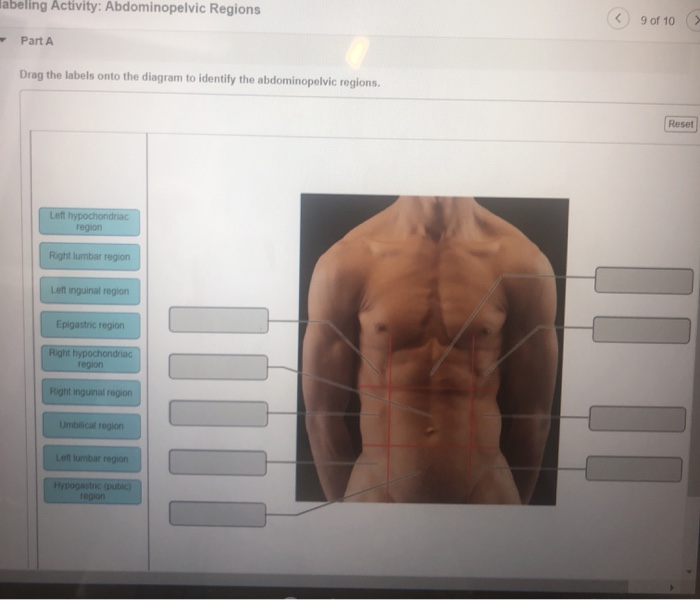
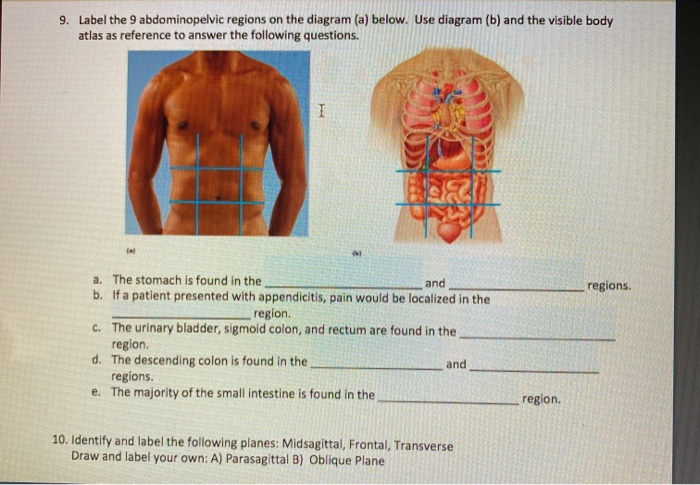
43 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions.
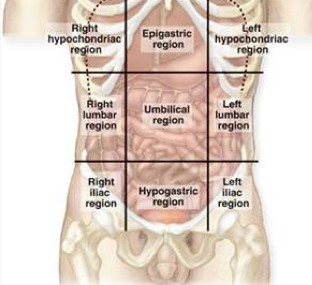
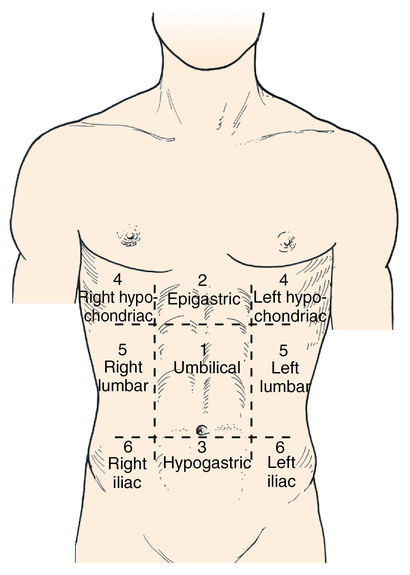
Labelled diagram. Counting. by Kramsel2. Labelled diagram. Label the Layers of the Earth. by Elizabetheck. Labelled diagram. Regions of the United States. by Jessical1. Hypochondriac Regions (Left and Right): the prefix "hypo" means below or under. The word "chondriac" means cartilage, which is referring to the cartilage of the ribs. When we put them together, this is the abdominal region that is under the ribs. Boom. Easy. So you have a right and left hypochondriac region.
Label the abdominopelvic regions. Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions. ANSWER: Correct Art-labeling Activity: Posterior Anatomical Landmarks Learning Goal: To learn the posterior anatomical landmarks. Label the posterior anatomical landmarks. A free graphing calcula to r - graph function, examine ...

Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions.
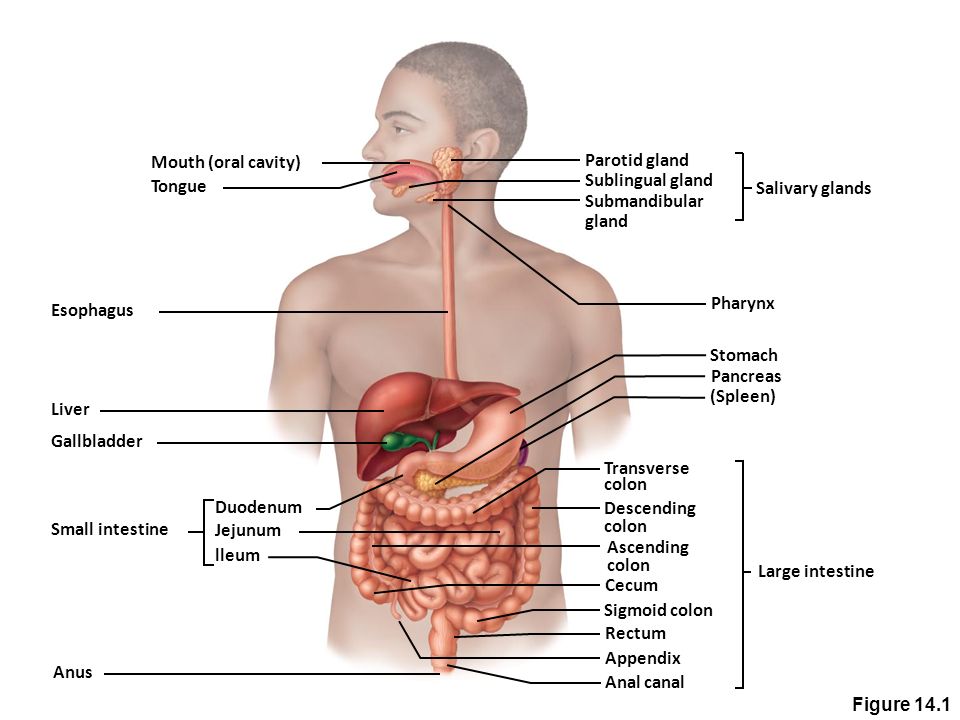
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is a flat triangular bone located at the back of the trunk and resides over the posterior surface of ribs two to seven. The scapula, along with the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum, make up the pectoral (shoulder) girdle which connects the upper limb of the appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton. Plasma Membrane - Components. It is composed of the following constituents: Phospholipids - forms the ultimate fabric of the membrane. Peripheral proteins - present on the outer or inner surface of phospholipid bilayer but are not implanted in the hydrophobic core. Cholesterol - folded between the hydrophobic tails of phospholipid membrane. The regions occupied by stomach are epigastric, umbilical and hypochondriac regions. It lies between the esophagus and the duodenum on the upper-left portion of the abdominal cavity. Stomach is divisible into cardiac portion which in turn is divided into fundus and body whereas the pyloric division of the stomach is further sub-divided into ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions.. Mapping regions of the genome that contain genes involved in specifying a quantitative trait is done using molecular tags such as AFLP or, more commonly SNPs. This is an early step in identifying and sequencing the actual genes underlying trait variation. Abdominopelvic cavity The more inferior cavity of the ventral cavity, separated by the diaphragm, and containing two parts, the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity, not separated by a muscular or membrane wall Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the sectional planes of from BIOL 2301 at Houston Community College. Body Cavities. The cavities, or spaces, of the body contain the internal organs, or viscera.The two main cavities are called the ventral and dorsal cavities. The ventral is the larger cavity and is subdivided into two parts (thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities) by the diaphragm, a dome-shaped respiratory muscle.. Thoracic cavity
Define anatomy and physiology and describe their ... it) to determine its range of motion. ... abdominopelvic cavity and list the organs they contain. anterior (cephalad) - head. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the body planes and sections. (figure 1.22) left boxes: median (midsagittal) plane - front head to toe. median section - rectum, intestines. middle boxes: frontal (coronal) plane - front side to side. frontal section - heart, liver, stomach. b) The ventral cavity: located toward the front of the body, is divided into abdominopelvic cavity and thoracic cavity by the divided into abdominopelvic ... Image: Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions.
The following diagram depicts the sky as it would have appeared to Herschel when he first observed Uranus in 1781, as well as the same part of the sky over the next several nights. Label the indicated objects as stars or planets. Part B After the discovery of Uranus, astronomers calculated its orbit and predicted its position in the sky using ... Part A Drag the labels to identify major regions of the adrenal gland. Reset Help Capsule Zona glomerulosa Zona fasciculata Adrenal cortex Diagram of an adrenal gland in section Zona reticularis Adrenal medulla Micrograph showing the major; Question: <Endocrine HW Art-labeling Activity: The Adrenal Gland 11 of 18 > Identify the major regions of ... 2. List several major organs of each system, and identify them in a dissected rat, human cadaver or cadaver image, or dissectible human torso model. 3. Name the correct organ system for each organ studied in the laboratory. Organ Systems Overview Materials Freshly killed or preserved rat (predissected by instructor as a Drag and drop onto image questions require students to drag and drop an image or text onto a background image to a preset location. You will define Drop zones which determine whe the r or not a student is correct. For example, a question might ask a student to drag and drop labels onto a diagram to illustrate a process.
Signal recognition particle SRP binds to the signal peptide as it emerges from the ribosome. part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stages of the life cycle not all labels will be used answer chapter 8 reading quiz question 2.
Editor's note: Replace figure with one that includes all muscles from table for example figure 10.7 from Marieb or 9.8 from Amerman. The orbicularis oris is a circular muscle that moves the lips, and the orbicularis oculi is a circular muscle that closes the eye. The occipitofrontalis muscle elevates the scalp and eyebrows. The muscle has a frontal belly and an occipital belly (near the ...
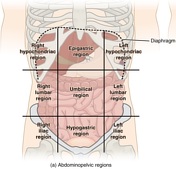
Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the organ systems. ... ANSWER: Correct Art-labeling Activity: Abdominopelvic Regions Learning Goal: To ...
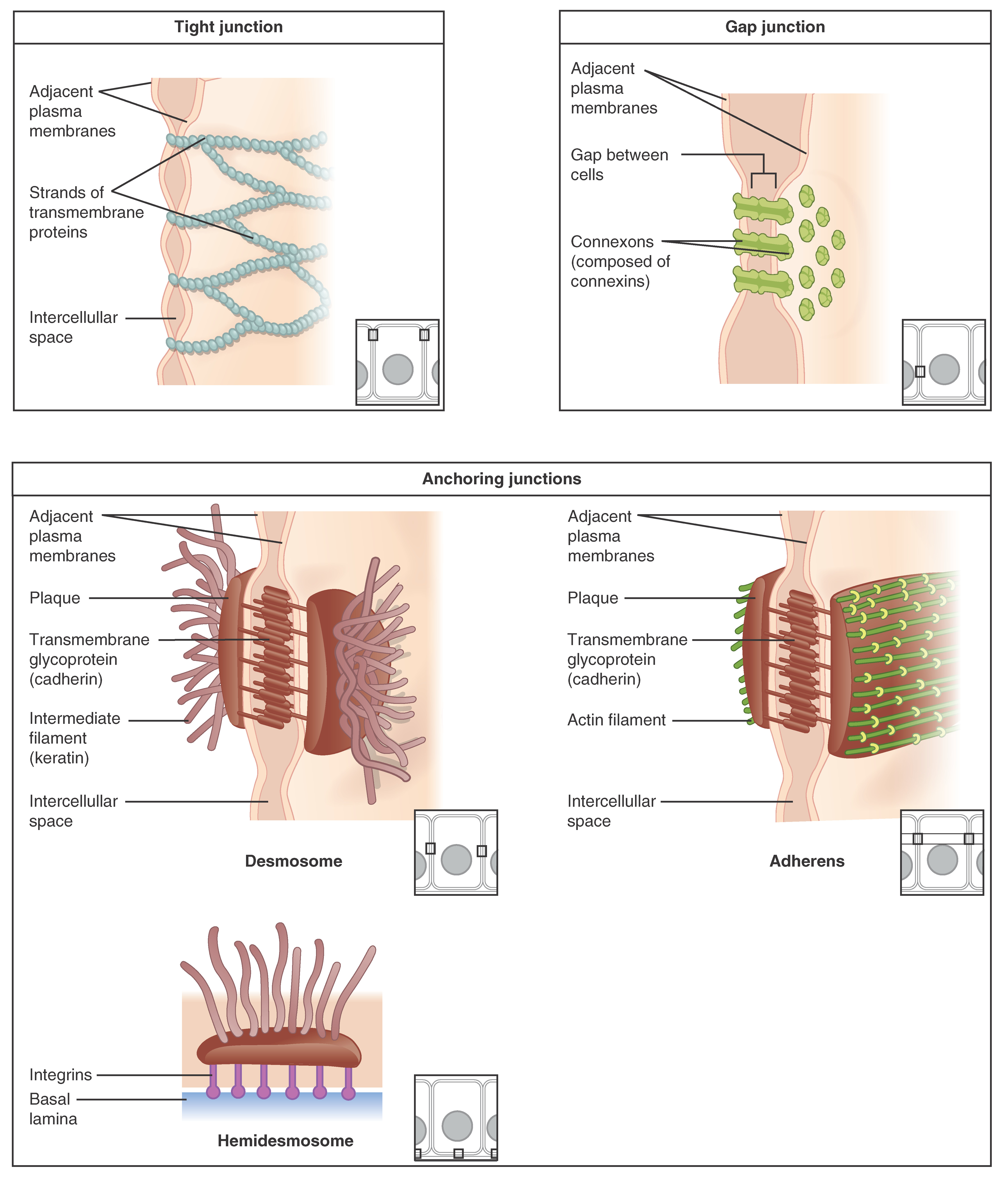
Identify the different epithelia of the body, and describe the chief function(s) and location(s) of each. An epithelium (ep″ ı˘-the ′le-um; "covering") is a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity (Figure 4.1). Epithelial tissue occurs in two different forms:
Demonstrate the anatomical position; Describe the human body using directional and regional terms; Identify three planes most commonly used in the study of ...
The muscles of the abdomen protect vital organs underneath and provide structure for the spine. These muscles help the body bend at the waist. The major muscles of the abdomen include the rectus ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions. The spleen is located in the _____ quadrant. left upper. ... Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the anterior anatomical landmarks on the inferior half of the body.
The nasal vestibule opens into a nasal cavity and extends into nasopharynx through internal nares. The pharynx is made up of three regions, nasopharynx, ...
Drag the labels to identify the structures of a long bone. Part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures associated with ganglia in sympathetic pathways (collateral ganglia) reset help lateralam . Association, improve visualization of structure contours, assist students in the. The diaphysis and the epiphysis (figure .
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the path a secretory protein follows from synthesis to secretion Not all labels will be used? ha.
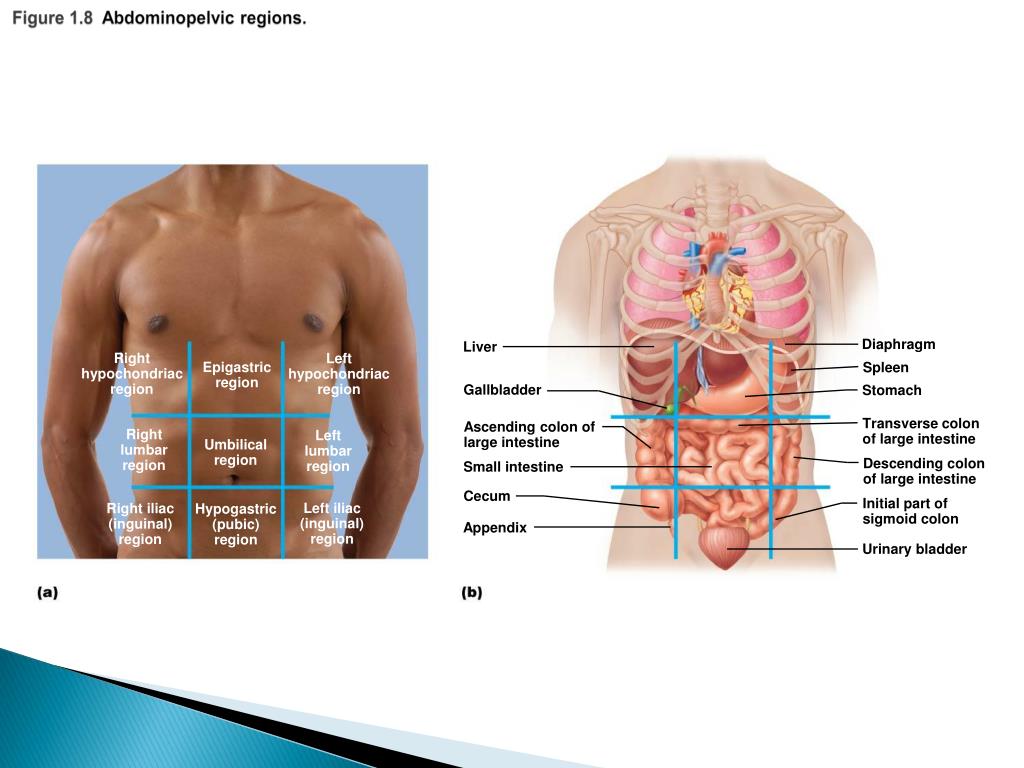
divided into abdominopelvic cavity and thoracic cavity by the diaphragm. The abdominopelvic cavity is subdivided into abdominal cavity (which holds liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, spleen, kidney, small, and large intestines) and the pelvic cavity (which holds the urinary bladder and reproductive organs).
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the tissues and structures. Reset Help central cand matrix Group 2 lacuna Group 2 Group 2 osteocyte in lacuna Group 2 C chondrocyto Group 2 bono (osseous tissue) Group 1 ... This tissue is rigid but provides flexible support to specific regions. It places in areas where there is constant and direct ...
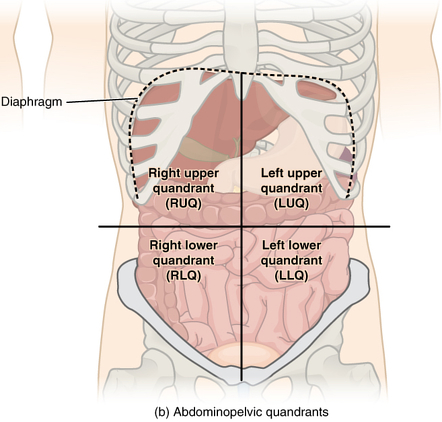
Identify and use anatomical terms to correctly label the following regions on Figure 1: BIO 113 Fall 2011 LAB 1 Page 2 Abdominal: The ... Abdominopelvic Quadrants and Regions . The abdominopelvic cavity is quite large and contains many organs, so it is helpful to ...
The abdominopelvic cavity is the largest cavity in the body. ... Identify each of the muscle tissue sub-types via a picture or diagram.
1 Answer to Provide an accurate directional term to complete the following sentences: a. The spinal cavity is _____ to the cranial cavity. b. The thoracic cavity is _____ to the abdominopelvic cavity. c. The hypogastric region is _____ to the umbilical region. d....
Transcribed image text: labeling Activity: Abdominopelvic Regions C 9 of 10 Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions. Reset Left hypochondriac region Right lumbar region Left inguinal region Epigastric region Right hypochondriac region Rightinguinal region Umbilical region Len lumbar region Hypogastric (pubic)
Label the abdominopelvic regions. Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions. ANSWER: Correct Artlabeling Activity: Terms of Anatomical Direction, Part 1 Learning Goal: To learn the terms of anatomical direction. Label the terms of anatomical direction.
Abdominal Four Quadrants. The abdominopelvic region can be divided into four quadrants. These quadrants are defined by the intersection of the sagittal plane with the umbilical plane (the transverse plane through the navel). Clinicians use these regions to determine the organs and tissues that may be causing pain or discomfort in that region.
Define homeostasis. 8. Why is homeostatic regulation important to an organism? See the blue Answers tab at the back of the book. RESPONSE: Room temperature.
Identifying the Bones of the Skull The bones of the skull (Figures 9.1-9.10, pp. 123-131) are described in Tables 9.1 and 9.2 on p. 128. As you read through this material, identify each bone on an in-tact and/or Beauchene skull (see Figure 9.10). Note: Important bone markings are listed in the tables for
The regions occupied by stomach are epigastric, umbilical and hypochondriac regions. It lies between the esophagus and the duodenum on the upper-left portion of the abdominal cavity. Stomach is divisible into cardiac portion which in turn is divided into fundus and body whereas the pyloric division of the stomach is further sub-divided into ...
Plasma Membrane - Components. It is composed of the following constituents: Phospholipids - forms the ultimate fabric of the membrane. Peripheral proteins - present on the outer or inner surface of phospholipid bilayer but are not implanted in the hydrophobic core. Cholesterol - folded between the hydrophobic tails of phospholipid membrane.
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is a flat triangular bone located at the back of the trunk and resides over the posterior surface of ribs two to seven. The scapula, along with the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum, make up the pectoral (shoulder) girdle which connects the upper limb of the appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton.








:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11181/regions-of-the-upper-limb_english__1_.jpg)





0 Response to "43 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the abdominopelvic regions."
Post a Comment