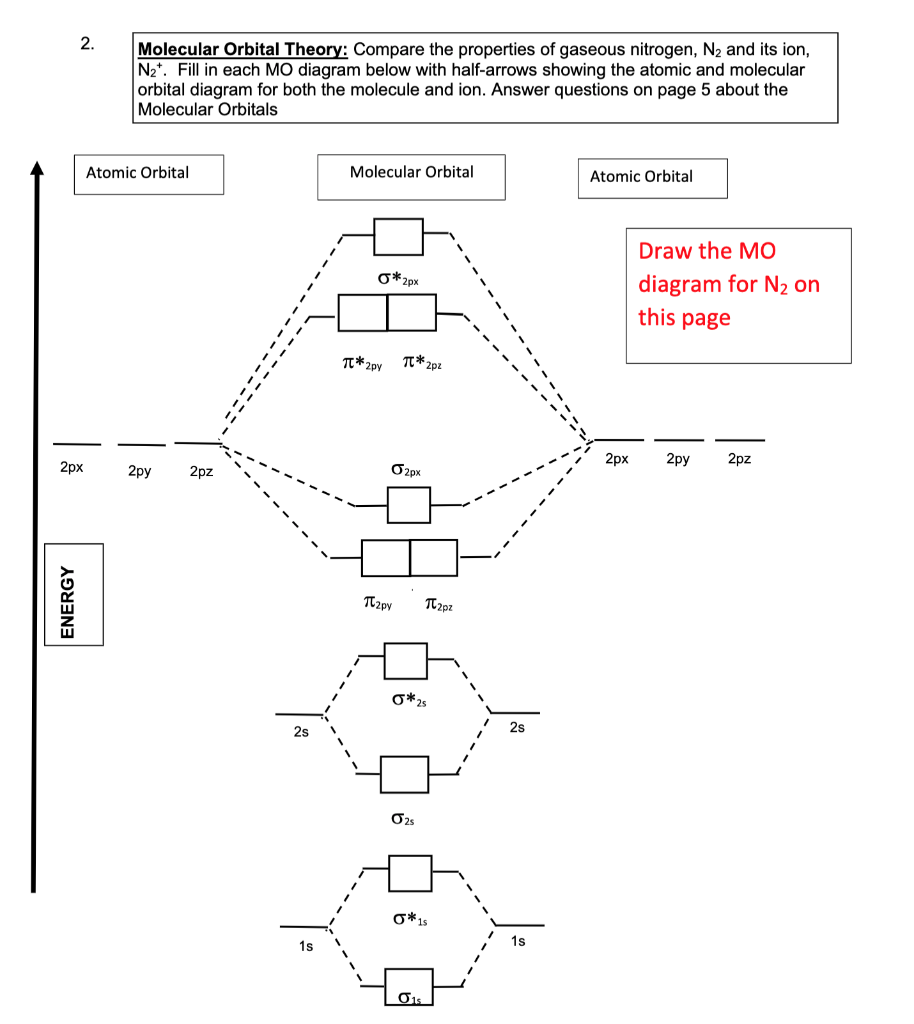
43 mo diagram for n2
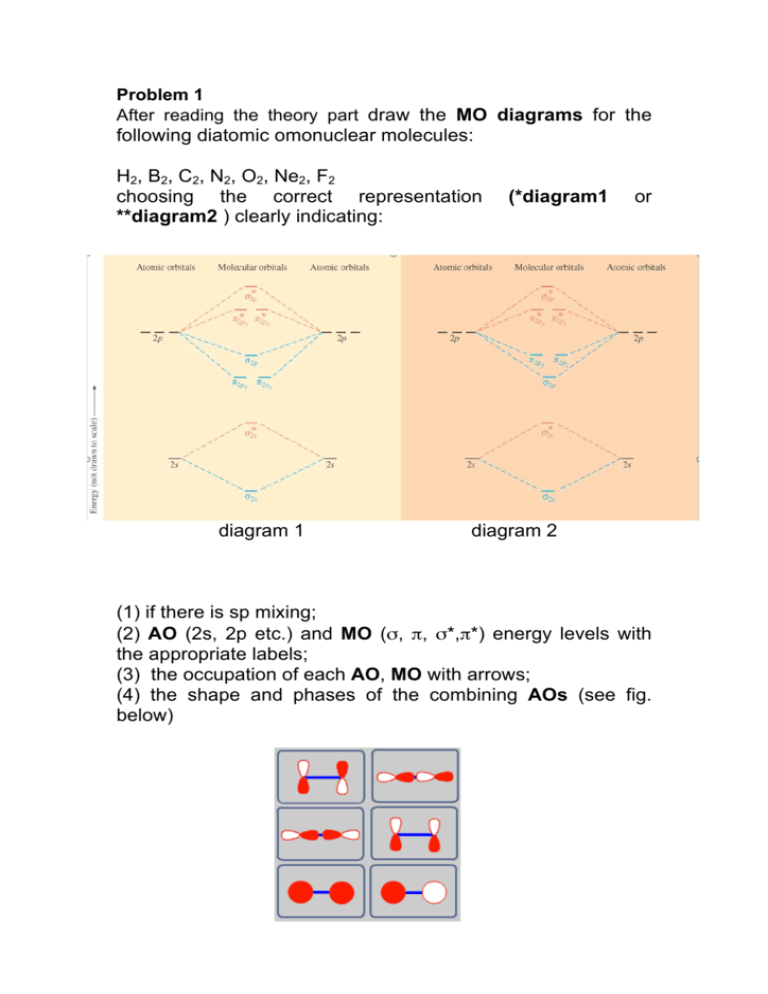
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc). One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen ... Clip makes it super easy to turn any public video into a formative assessment activity in your classroom. 1.
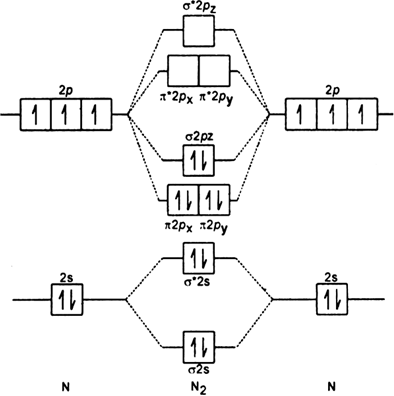
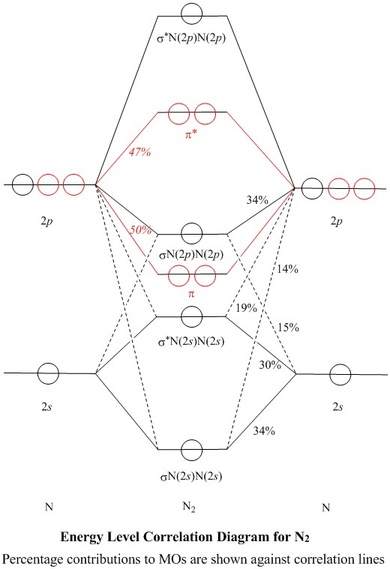
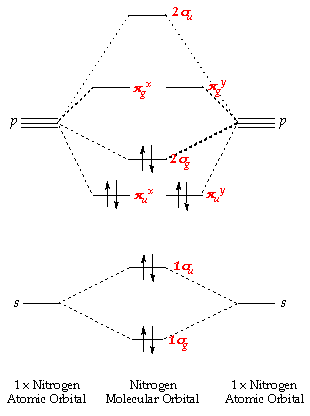
If we build the MO diagram for "N"_2, it looks like this: First though, notice that the p orbitals are supposed to be degenerate. They weren't drawn that way on this diagram, but they should be. Anyways, for the electron configurations, you would use a notation like the above. g means "gerade", or even symmetry upon inversion, and u means "ungerade", or odd symmetry upon inversion.
For the first part of the problem, we're being asked to complete the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for an excited state of the N2 molecule. The given electron configuration for the excited state N2 is: (σ1s2) (σ*1s2) (σ2s2) (σ*2s2) (π2p4) (σ2p1) (π*2p1) From this, we can fill-up the molecular orbital diagram for the excited state N2:
Mo diagram for n2
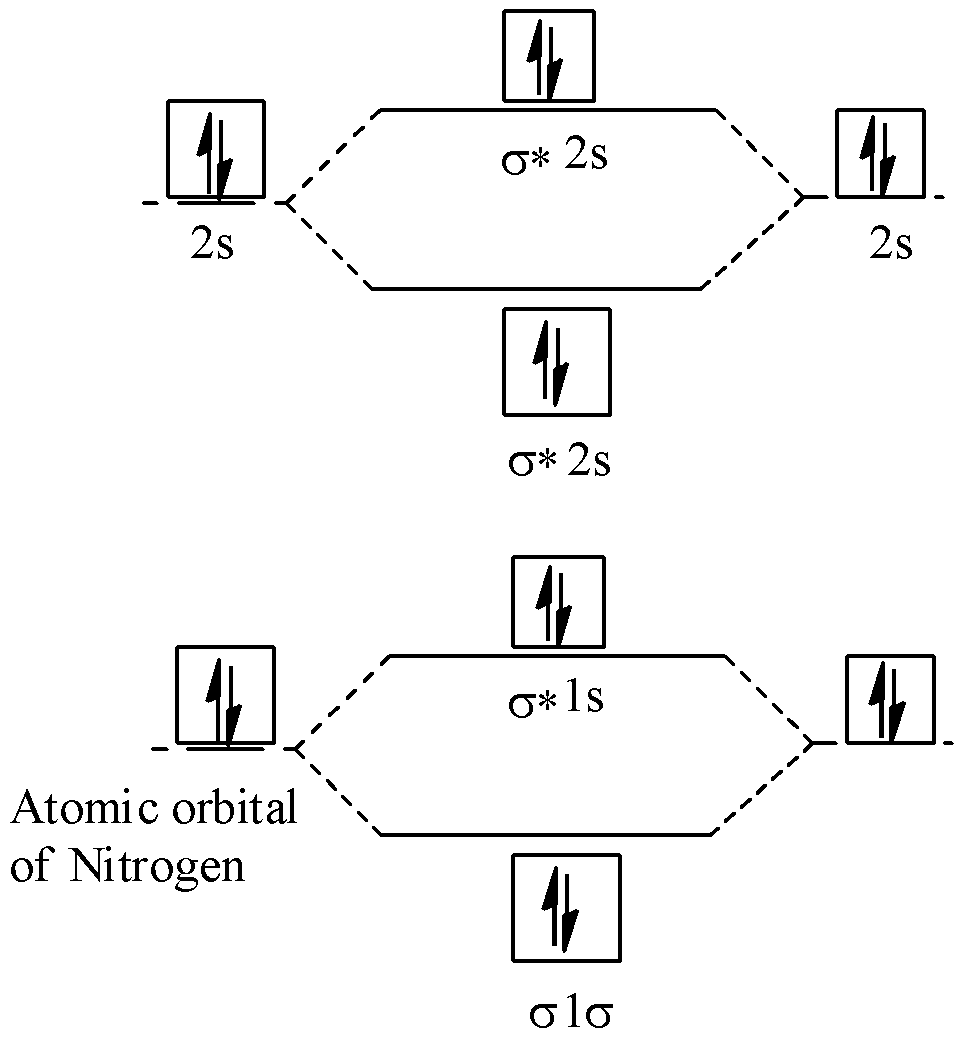
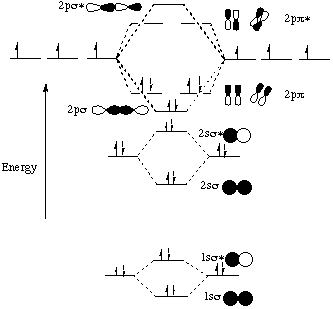
How is the molecular orbital diagram of N2 determined? Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of N2 using its diagram. one atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a N2 molecule will have 14 electrons so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond next 2 in 1s sigma anti bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma anti bond orbital
the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the N2 molecule. Draw Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, indluding any core electrons ら Question : the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the N2 molecule.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Mo diagram for n2.
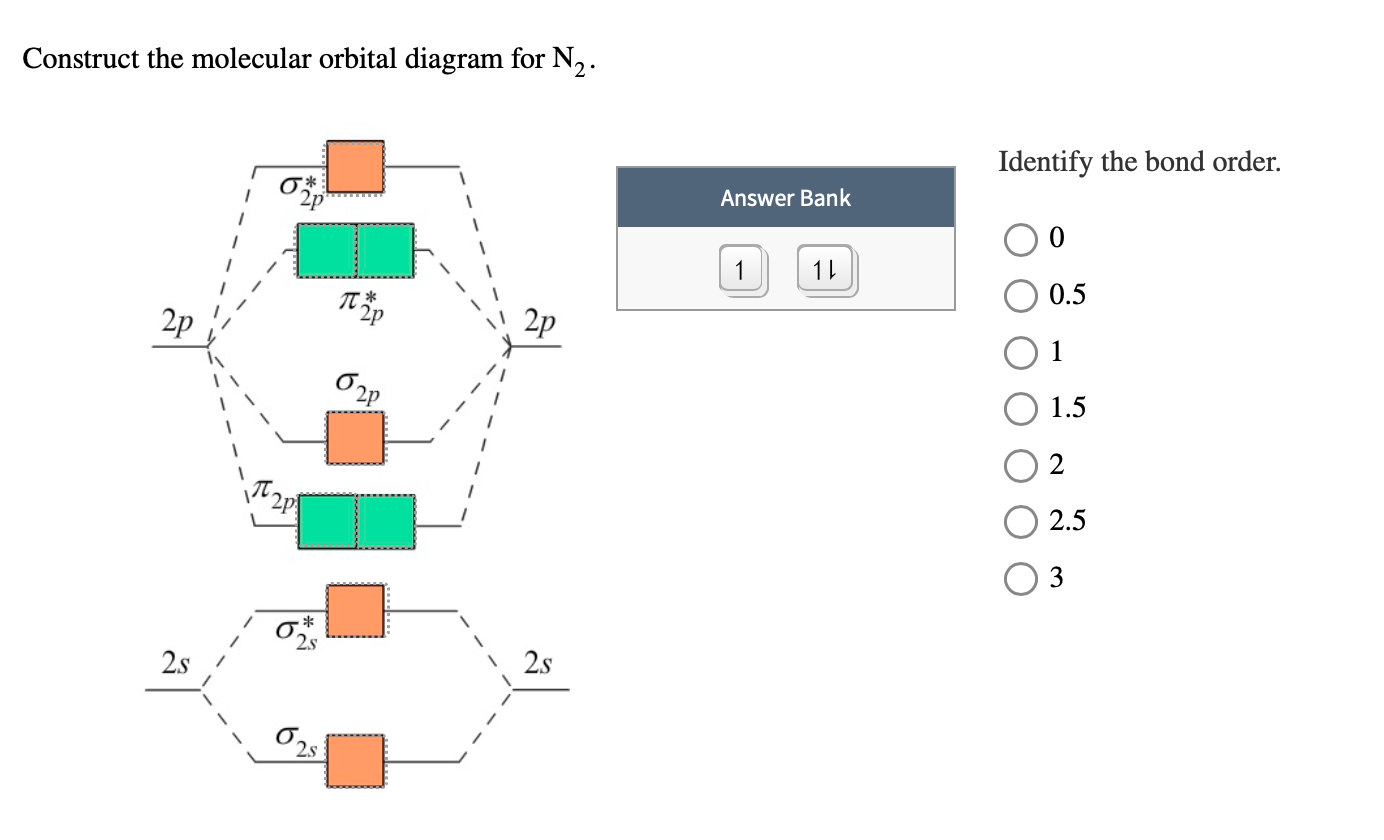
FREE Expert Solution. We can use the molecular orbital diagram to predict whether the molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. all the electrons are paired → diamagnetic . one or more electrons are unpaired → paramagnetic. Determine the number of valence electron. Group Valence Electrons. N 5A 2 x 5 e - = 10 e-. From +1 charge - 1 e-.
1) Mo Chit station to Saphan Mai: 11.4 km, 12 stations (N9–N20). 2) Saphan Mai to Khu Khot: 7.5 km, four stations (N21-N24). An 11.4 km, 12 station northern extension from Mo Chit station to Saphan Mai in Don Mueang District has been planned since the Sukhumvit Line opened. Originally, this extension was scheduled to be completed by 2008 ...
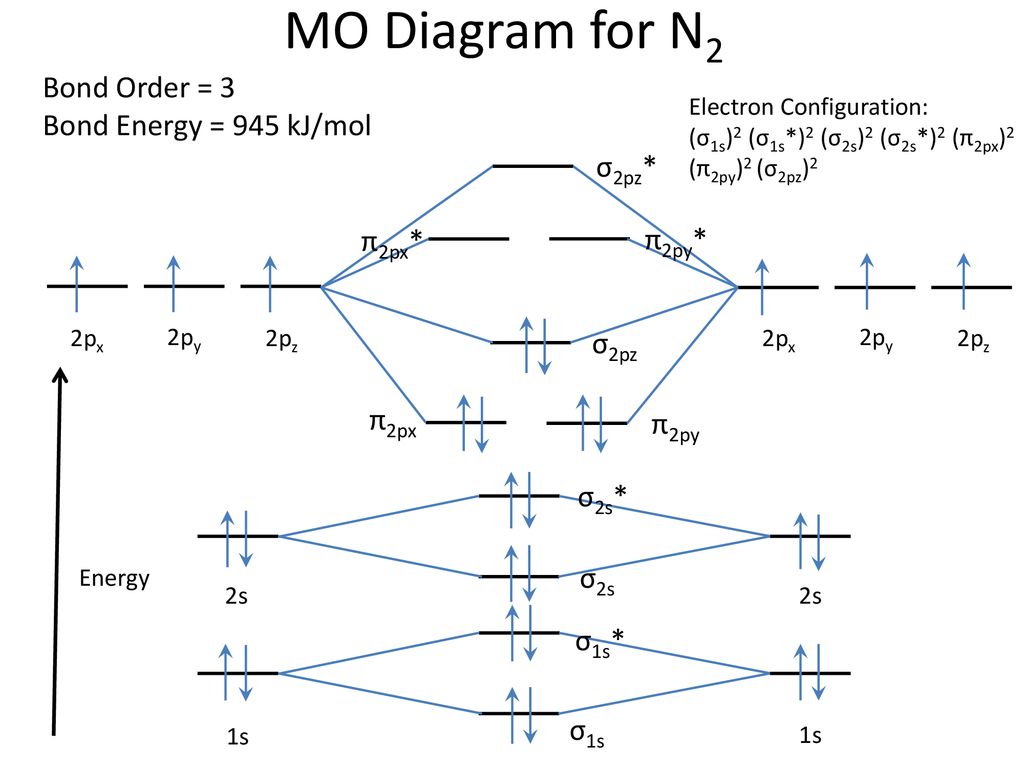
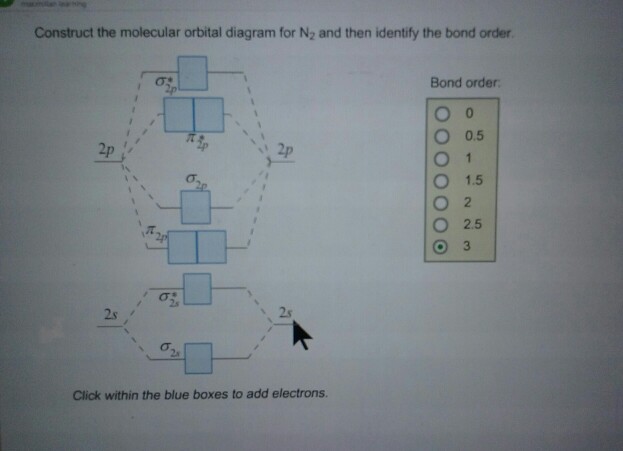
Answer (1 of 10): bond order = 3 Explanation = (1) no of electron in C = 6 (2) no of electron in O = 8 So, total no of electron = 14, so bond order = 3 Trick No. of electron = Bond order 12 = 2 13 = 2.5 14 = 3 15 = 2.5 16 = 2 17 =1.5 18 = 1
electronic configuration - Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^- - Chemistry Stack Exchange I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For $\ce{N2}$ the orbitals in increasing ene... Stack Exchange Network
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of $ {N_2}$ or $ {O_2}$ with magnetic behavior and bond order. Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond ...
Complete the MO energy diagram for the N2+ ion by dragging the electrons , , and in the figure given below.. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
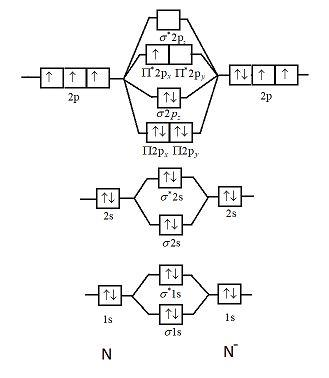
Why is the MO diagram different for N2 and N2-? I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For $\\ce{N2}$ the orbitals in increasing energy are: because it has 14 electrons. For $\\ce{N2-}$ there are 15 electrons.
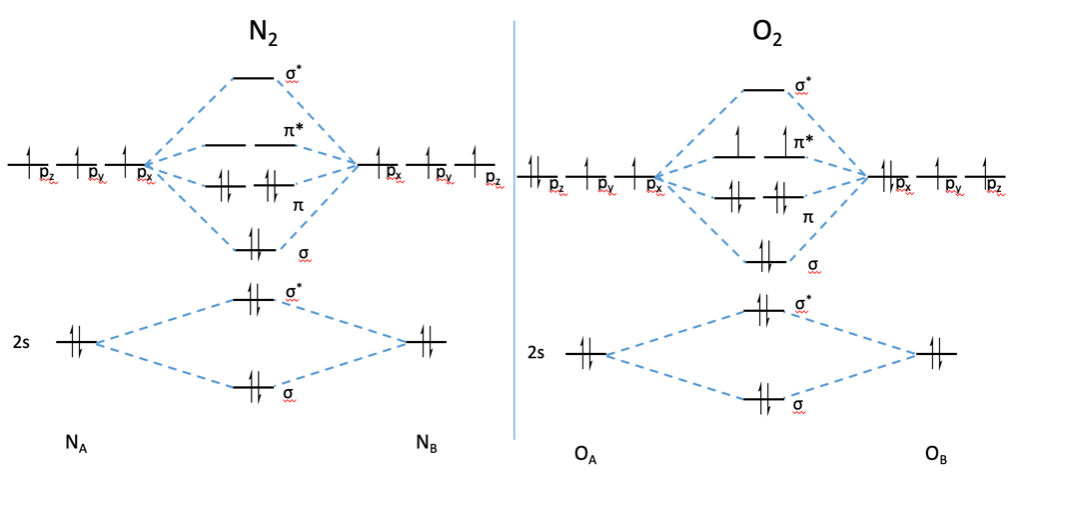
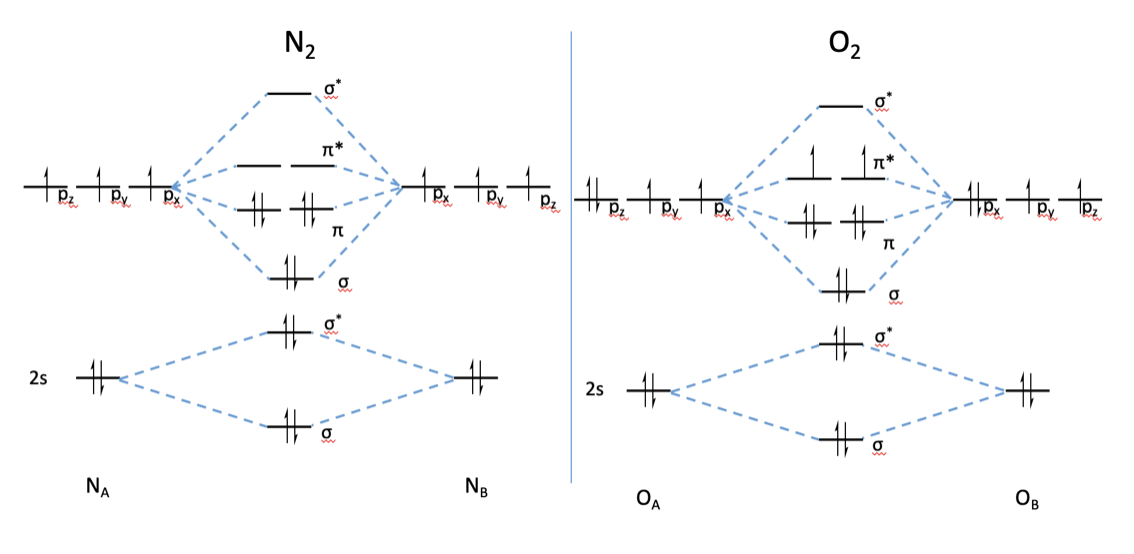
Why MO diagram of N2 and NO molecules differ from each other? S-p mixing is the primary cause of the difference in the molecular orbitals of nitrogen and oxygen, which is influenced by the initial atomic orbital energies. The more stabilized 2s orbital does not s-p mix as effectively, due to the greater energy difference between the 2s and 2p ...
What is the MO diagram and bond order for N2 ( in Urdu / Hindi) Nitrogen (N 2) molecule: Nitrogen atom has electronic configuration 1s2, 2s2, 2p3. Two p-atomic orbitals (one from each nitrogen) atom combine to form two molecular orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital σ2px and antibonding molecular orbital σ*2px.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
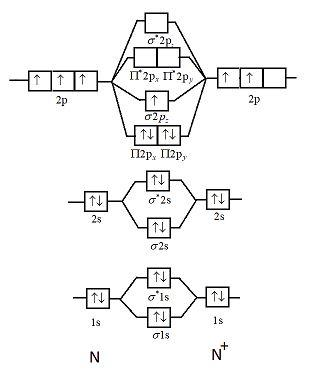
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order. Asked by sonkarshiva009 | 13th Mar, 2019, 05:47: PM. Expert Answer: Electronic configuration of N-atom(Z=7) is ...
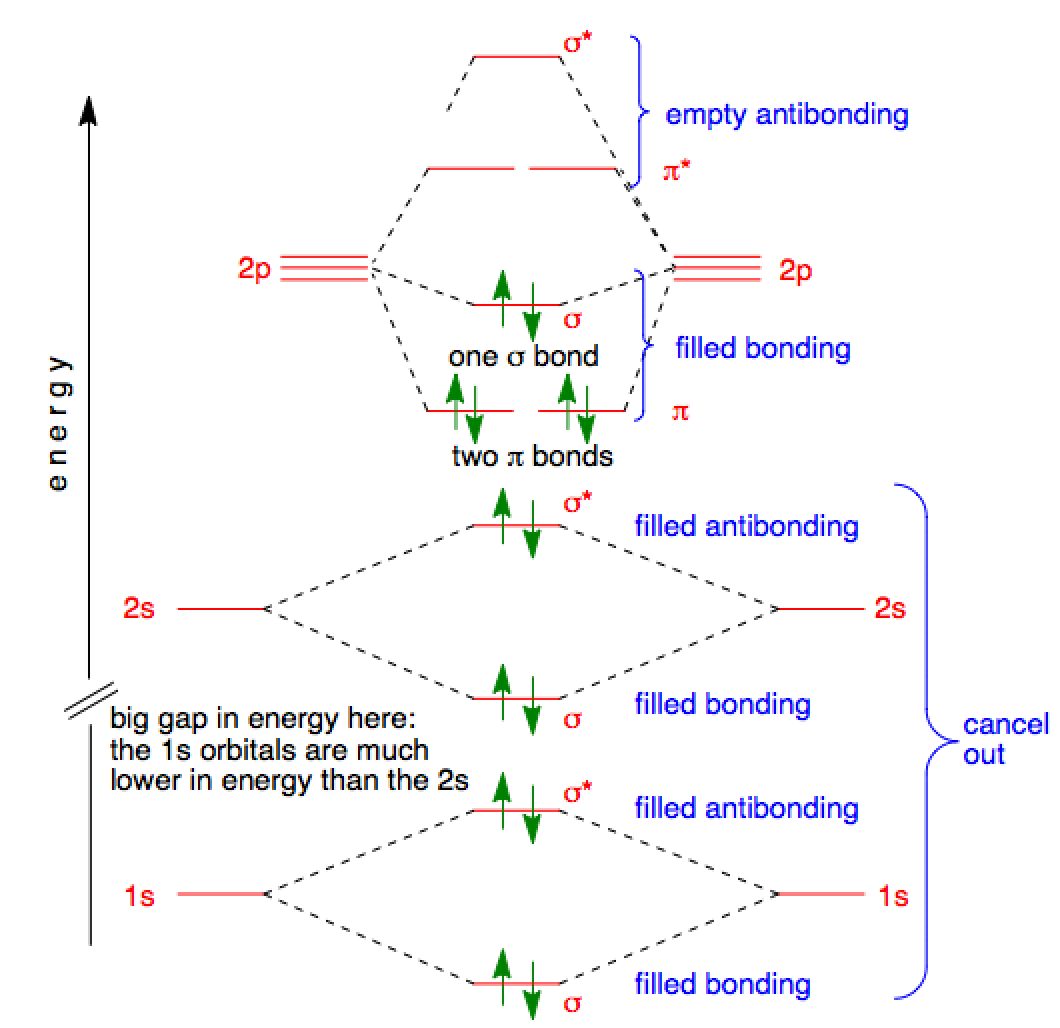
This diagram actually applies to this problem and to the next. Note that we need different diagrams here since the energies of the s and p 2p orbitals are reversed for case (a) vs. case (b) above. (With N2 it does seem strange in any event that the two p bonds would form before the s bond. Do you think this is right?)
14+ N2 Mo Diagram. With mo diagrams, we can predict the number of bonds in diatomic molecules. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (n2) use aufbau and hund to fill with 10 valence electrons you get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2). N2 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram — UNTPIKAPPS from www.untpikapps.com Thus if we know…
Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^- $-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction moving from $\ce{Li2}$ to $\ce{F2}$. The $\mathrm{s}$-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction is the bonding interaction between the $\mathrm{2s}$ orbital of one atom and the $\mathrm{2p_{z}}$ orbital of another atom which (among other things) increases the energy of the $\mathrm ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) N2 Molecular Orbital Diagram.
focused subbeam is sent to a 10× micro-objective (MO) and detected by a CCD camera to obtain the far-field image for phase-prediction algorithms. Fig. 1. The structure of N-elements CBC system. (N=19 in this diagram). On the emission plane, the subapertures are usually arranged in the shape of regular hexagon. This is
Ni-Cr-Mo alloy construction • Operating pressures from 125 psig (9 bar) to 3,000 psig (207 bar) • LOTO and indicating switch options • Flow capacity 0.23 to 0.29 Cv • Surface finish 15 Ra max / 10 Ra avg (10, 7 & 5 Ra max options) • FA option 1.125 inch C-seal • Constant bleed option 5, 8 and 15 slpm of N2 @ 80 psig (5.5 bar) refer ...
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc) . One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen. The correlation diagrams for nitrogen and carbon monoxide and the first are nearly parallel to the corresponding orbital energy curves.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of N2. Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron configuration in terms of a sigma bond and pi bond. According to molecular orbital theory, it tells about magnetic nature, stability order, and the number of bonds in a molecule.
This website makes extensive use of JavaScript. The top menus will not function without it and most tools will also not work. If you do not know how to enable JavaScript in your web browser, you should be able find instructions by searching the web for "enable javascript in …
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric. Explain What is the relationship between bond order and the dissociation energy of a molecule? ...
The MO diagram for "NO" is as follows (Miessler et al., Answer Key): (The original was this; I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels. For further discussion on the orbital energy ordering being "N"_2-like, see here and comments.) Quick overview of what the labels correspond to what MOs: 1a_1 is the sigma_(2s) bonding MO. 2a_1 is the sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO. 1b_1 is the pi_(2p ...
#3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron.
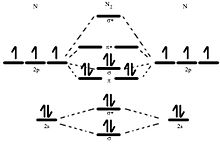
Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for N2. Now we add the 10 electrons, 5 from each nitrogen atom. Note that the bottom sigma symmetry orbital is strongly bonding, the top one is strongly antibonding, and the 2 in the middle are only weakly bonding and antibonding, respectively.
The diagram "progress of the computation" shows the three-state busy beaver's "state" (instruction) progress through its computation from start to finish. On the far right is the Turing "complete configuration" (Kleene "situation", Hopcroft–Ullman "instantaneous description") at each step. If the machine were to be stopped and cleared to blank both the "state register" and …
Use the molecular orbital energy level diagram to show that N 2 would be expected to have a triple bond, F 2 , a single bond and N e 2 , no bond. Hard View solution
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2.
Basic structure of molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen is: Electrons of nitrogen are to be filled in this diagram. Left side represents the configuration of one atom of nitrogen molecule and the right side represents the second atom of nitrogen molecule. Atomic number of nitrogen is seven. Therefore in N 2 there are a total fourteen electrons.










![Best Answer] draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d20/b492acf8cb9ff01954c3929a3b7a93c7.jpg)








0 Response to "43 mo diagram for n2"
Post a Comment