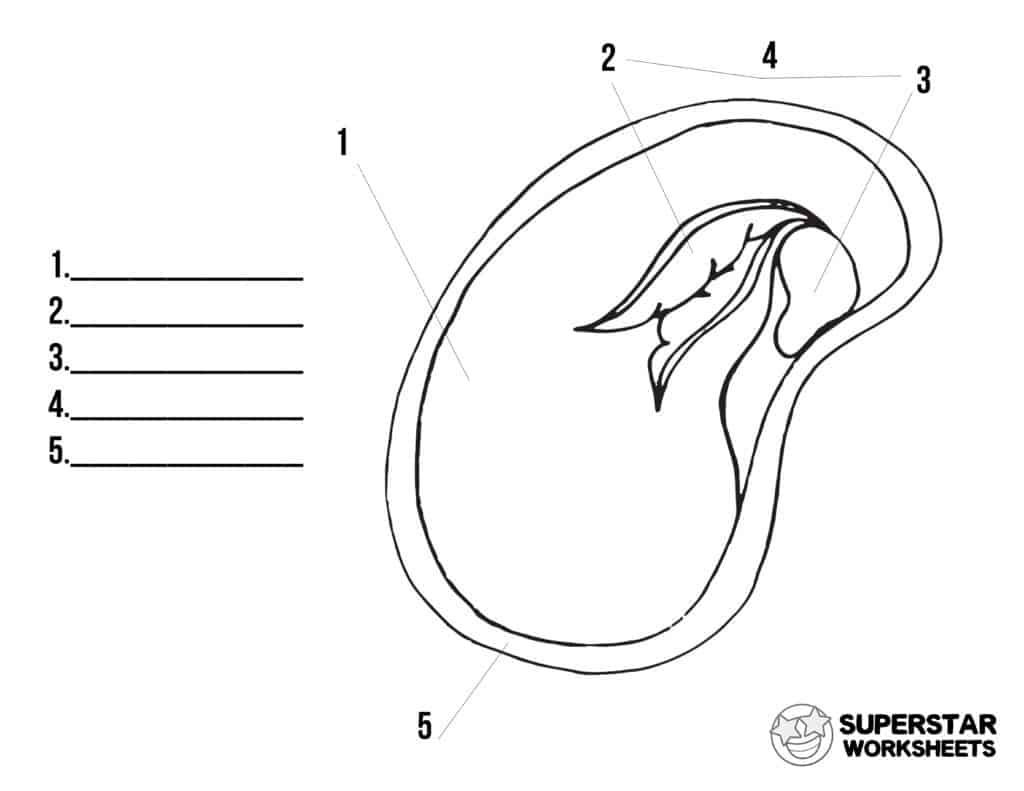
43 parts of a seed diagram
Every seed consists of three main parts: 1. Embryo is a tiny plant in the seed that may grow roots, stem, and leaves under proper conditions. 2. Food supply (called cotyledon in dicots like beans, endo-sperm in monocots like corn) surrounds the embryo and is the seed’s only source of nourishment as it pushes through the soil to grow. Feb 02, 2016 · Parts of a seed diagram. Find this Pin and more on Science by Sarah Price - Priceless Ponderings . Kindergarten Science. Elementary Science. Teaching Science. Science For Kids. Science And Nature. Science Education. Earth Science.
Q P S R Which parts labelled on the diagram indicate that this is a plant cell? A P and R B P and S C Q and R D Q and S PMT. 4 ... 12 The table shows four substances and the parts of the plant to which they are transported. substance part of plant 1 amino acids flower buds 2 carbon dioxide leaf cells
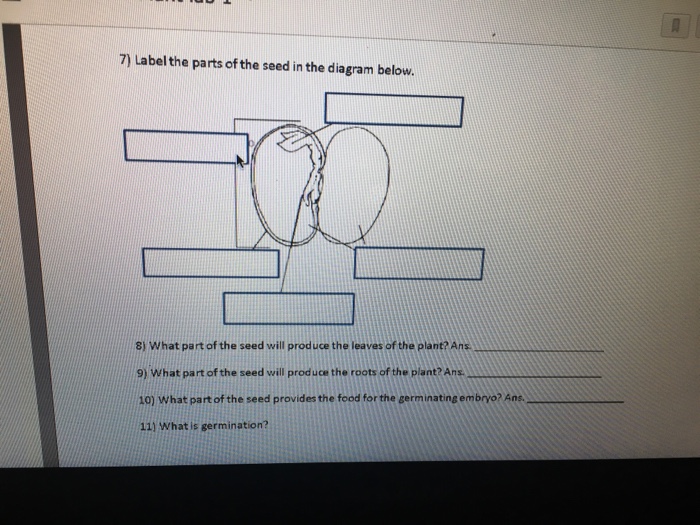
Parts of a seed diagram
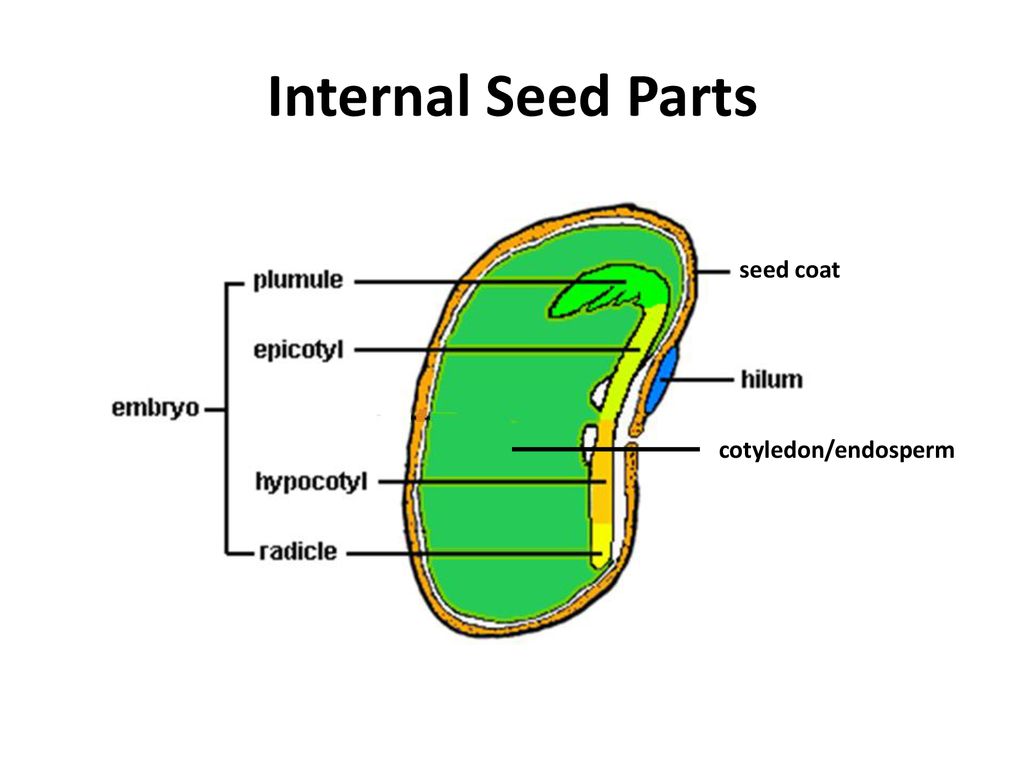
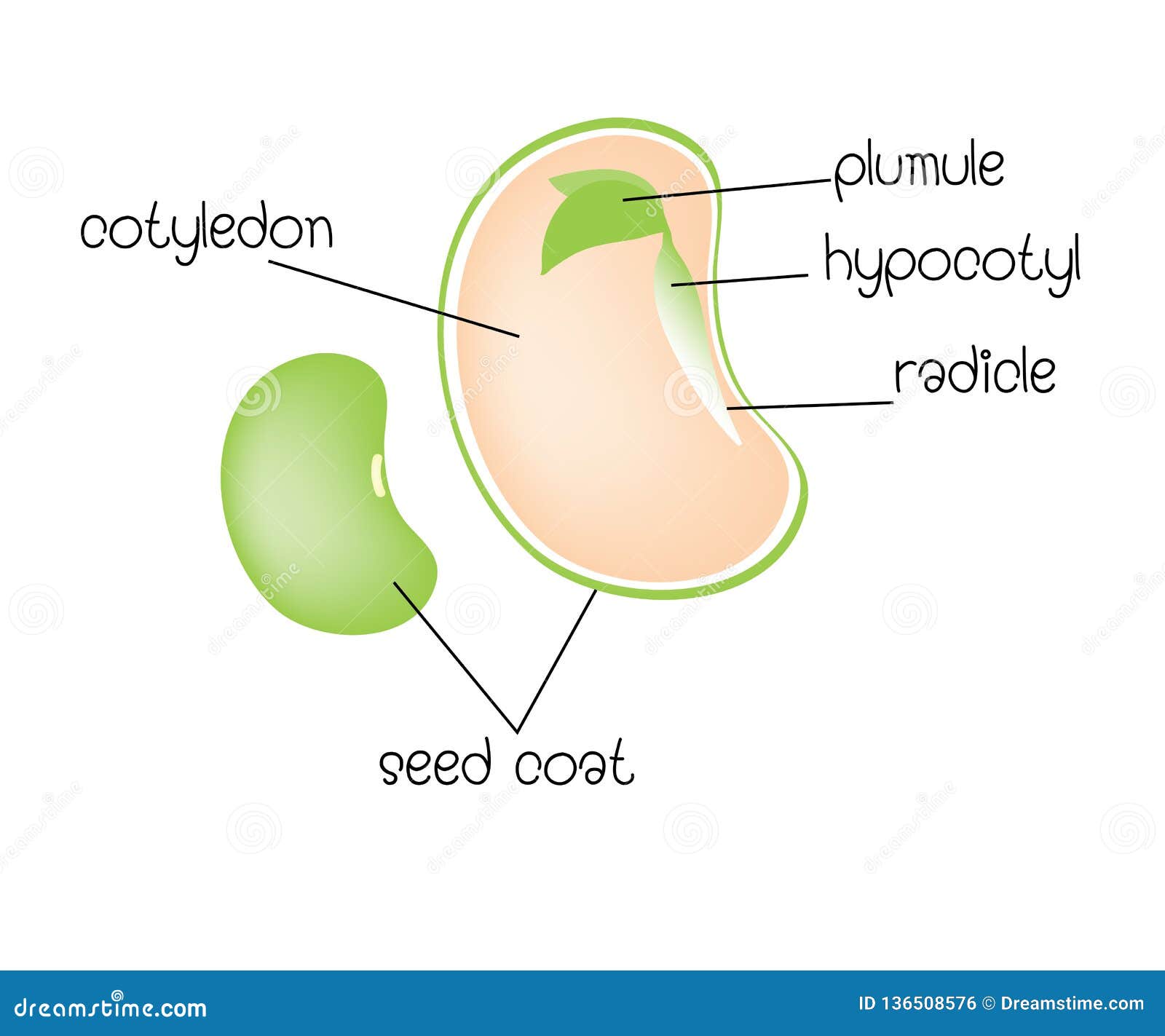
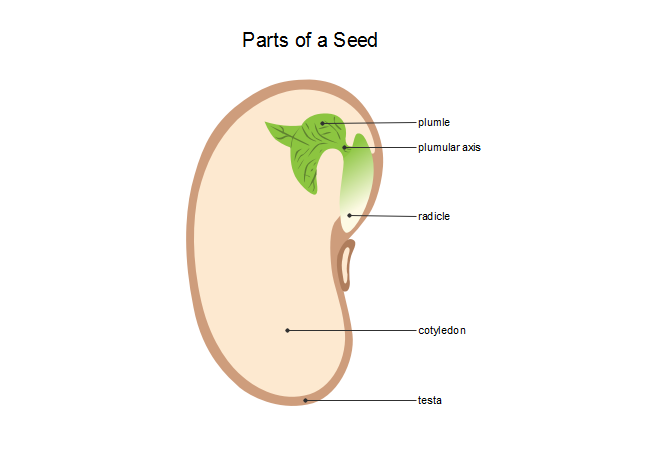
1. Dicotyledons, having embryos with two cotyledons, and. 2. Monocotyledons, with only one cotyledon. A maize grain is a single-seeded fruit in which the seed coat and the fruit wall are un-separable. On one side of the grain a small, opaque, whitish, deltoid area is seen to be distinctly marked out from the region. The embryo: It is basically a miniature plant, from the upper part of the embryo the leaves and the stem will emerge, and from the lower part the roots of the future plant will be formed; the embryo constitutes a small part of the seed, in the seeds of almost all the plants, the embryo stops growing when it is very small and enters a state of ... growth and development of a new plant. The three primary parts of a seed are the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The embryo is the young multicellular organism before it emerges from the seed. The endosperm is a source of stored food, consisting primarily of starches. The seed coat consists of one or more protective layers that encase the seed.
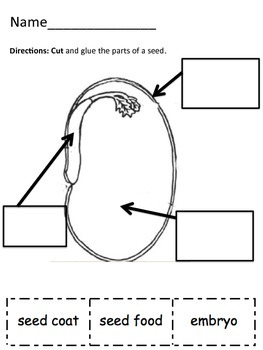
Parts of a seed diagram. Cotyledon, seed leaf within the embryo of a seed. Cotyledons help supply the nutrition an embryo needs to germinate and become established as a photosynthetic seedling and may themselves be a source of nutritional reserves or may aid the embryo in metabolizing nutrition stored elsewhere in the seed. sandisfunstuff. S. Sandi S. Seed Diagram Template This seed component diagram template is designed for botanical teaching which might be popular in middle and high school biology course. The template is available to edit free in vector format. parts of a plant diagram parts of a plant flower fruits and seeds diagram the flower the flower is the reproductive unit of some plants parts of the flower include petals sepals one or more carpels and stamens fruit the fruit is that part of a plant which is in charge of protecting the seeds and guarantee their dispersal A seed coat has the following four parts: a) Micropyle – the small opening present at one end of the seed coat, b) Funiculus – the seed stalk with which the seed is attached to the fruit body, the integument, c) Hilum – the region from which the seed breaks off from the fruit, leaving a scar, and d) Raphe – the base of the funiculus ...
The growth of the plant from a seed is known as germination. A seed has three parts: Seed Coat; Endosperm; Embryo; Seed Coat. A seed coat protects the internal parts of a seed. The seed coat has two layers. The outer layer is thick and known as the testa. The inner layer is thin and known as tegmen. A thick seed coat protects the seed from sunlight and water. A typical diagram of a plant body consists of three parts: 1) roots, 2) stems, and 3) leaves, each having specialized functions. Apart from these basic parts, a flowering plant also contains 4) flowers and 5) fruits. The root system covers the underground parts of a plant, which include the roots, tubers, and rhizomes, whereas the shoot system ... growth and development of a new plant. The three primary parts of a seed are the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The embryo is the young multicellular organism before it emerges from the seed. The endosperm is a source of stored food, consisting primarily of starches. The seed coat consists of one or more protective layers that encase the seed. The embryo: It is basically a miniature plant, from the upper part of the embryo the leaves and the stem will emerge, and from the lower part the roots of the future plant will be formed; the embryo constitutes a small part of the seed, in the seeds of almost all the plants, the embryo stops growing when it is very small and enters a state of ...
1. Dicotyledons, having embryos with two cotyledons, and. 2. Monocotyledons, with only one cotyledon. A maize grain is a single-seeded fruit in which the seed coat and the fruit wall are un-separable. On one side of the grain a small, opaque, whitish, deltoid area is seen to be distinctly marked out from the region.






























0 Response to "43 parts of a seed diagram"
Post a Comment