44 orbital diagram for hydrogen
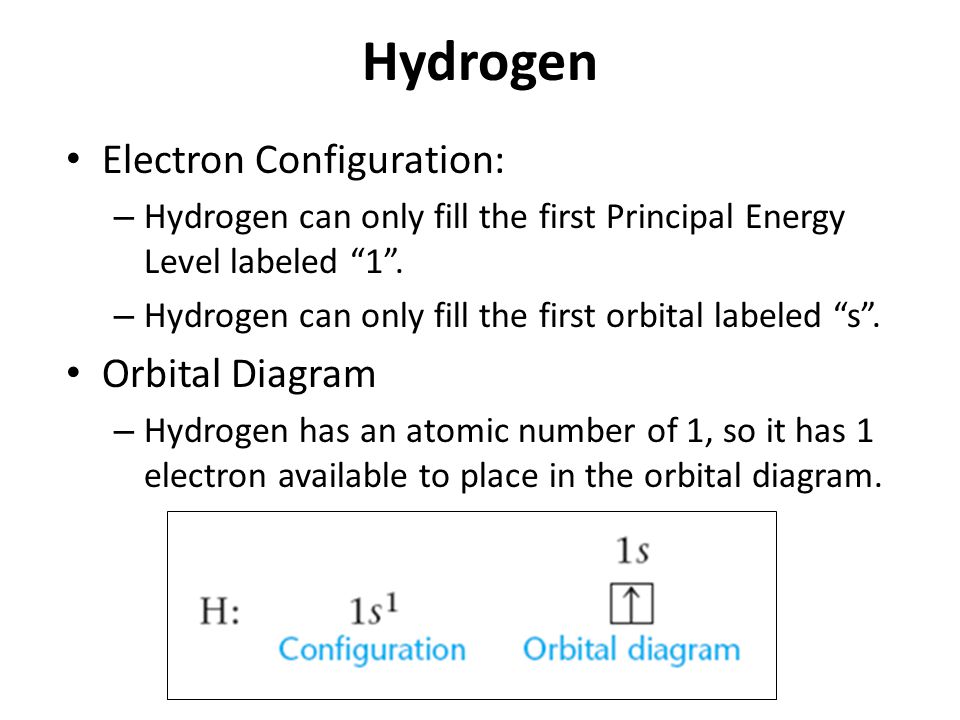
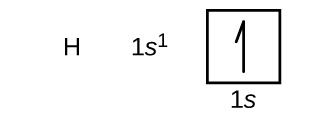
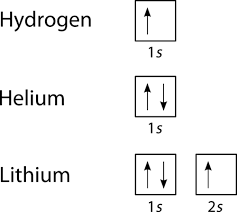
Atomic orbitals can be the hydrogen-like "orbitals" which are exact solutions to the Schrödinger equation for a hydrogen-like "atom" (i.e., an atom with one electron). Alternatively, atomic orbitals refer to functions that depend on the coordinates of one electron (i.e., orbitals) but are used as starting points for approximating wave functions that depend on the simultaneous coordinates of ... Hydrogen and Helium - The 1s Orbital . We start with hydrogen, which has only one electron. According to the Aufbau principle, this should be placed into the 1s orbital, which is the lowest energy orbital. The configuration of hydrogen is 1s 1.
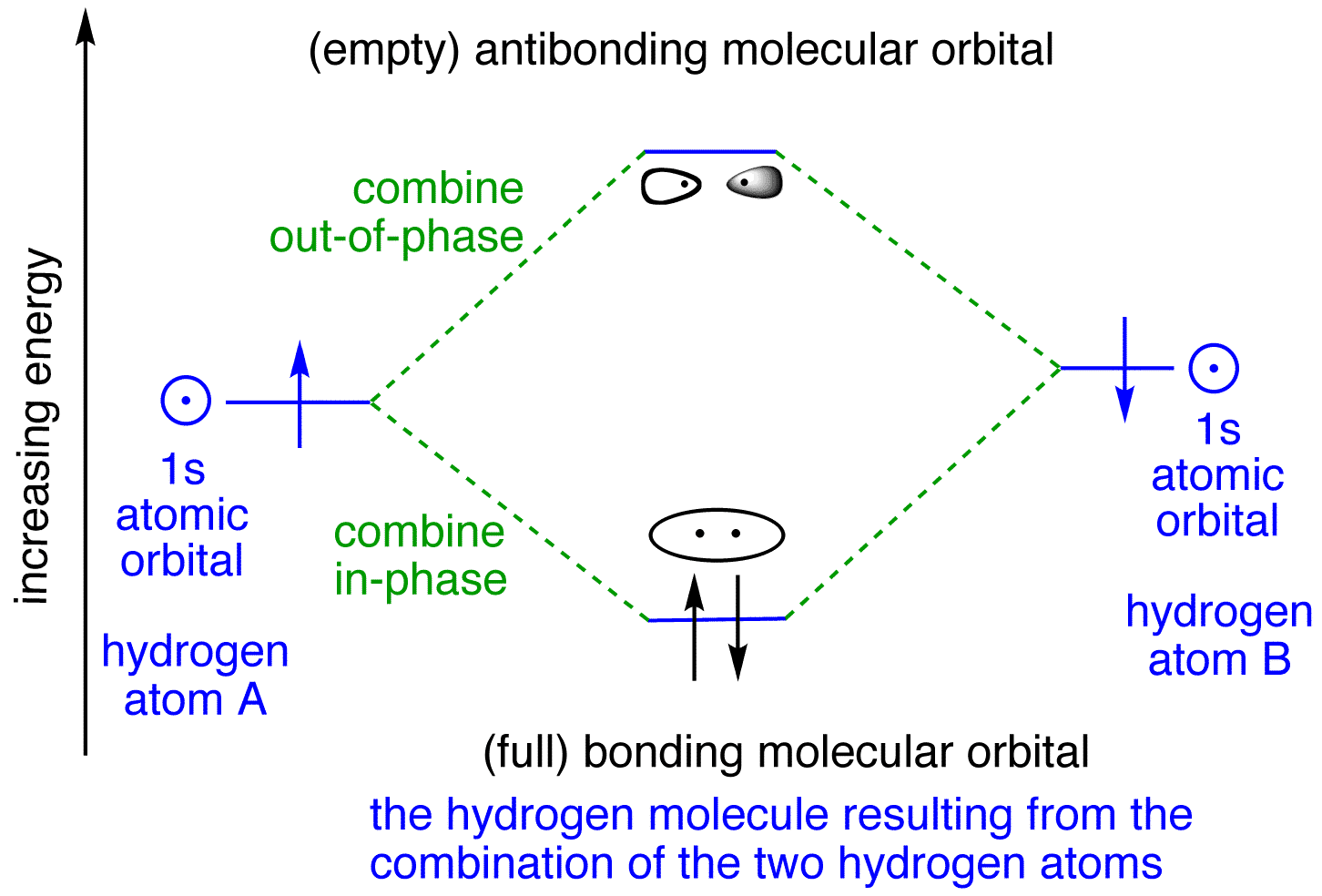
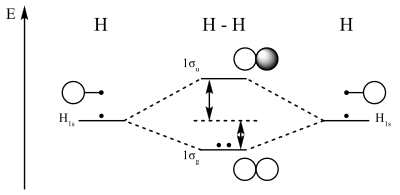
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem
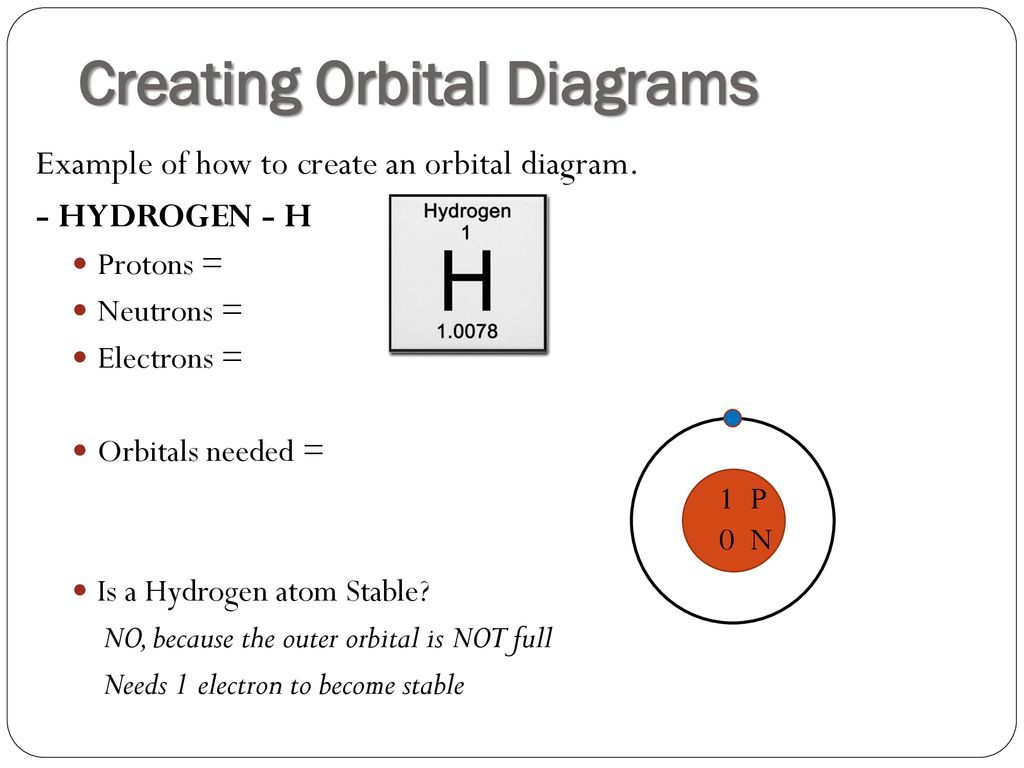
Orbital diagram for hydrogen
Hydrogen Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic hydrogen has 1 electron in a 1s orbital. Of course, there are 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, etc. empty orbitals at higher energy. Let's just consider the 1s orbitals. Remember that an orbital is a mathematical function that describes the probability of finding an electron in space. Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. CONTROLS . Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. See the diagram below: Now you can see that the central atom here is Carbon because it is easy for Carbon to become stable as it is the least electronegative of all. However, hydrogen is the least electronegative but it cant be a central atom because it has only one spare electron. The other two atoms H and N are attached to C by a single bond.
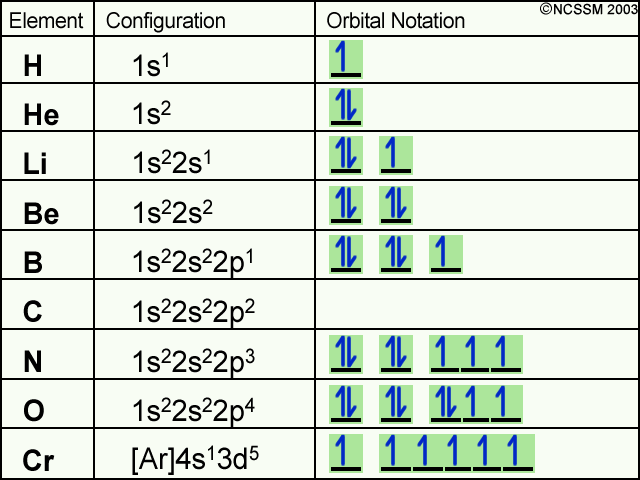
Orbital diagram for hydrogen. Hydrogen (H) Electron Configuration with Full Orbital Diagram. Hydrogen electron configuration is 1s 1. Hydrogen is a s-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of hydrogen, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of hydrogen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. 1. Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2. Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3. Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4. Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5. Answer (1 of 3): Hydrogen has only one electron, so the only relevant force (in a classical approximation) is between the one negatively charged electron and the positively charged nucleus. In a multi-electron atom, the negatively charged electrons repel each other. We call this effect "electron... The orbital diagram for hydrogen can be represented in the following way. This notation uses a box to represent the orbital, the label for the orbital and an arrow to represent the electron. The electronic configuration for hydrogen can be written as 1s 1. This is a short-hand notation which identifies the level, the sublevel and the number of ...
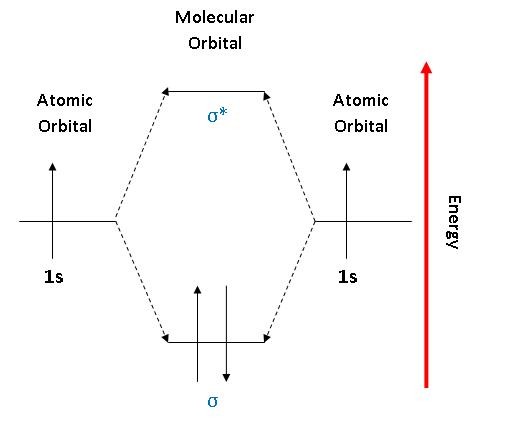
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ... Similar to atomic orbitals, we can write electron configuration energy diagrams for molecular orbitals (Figure 9.20 "Hydrogen molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagram"). Notice that the atomic orbitals of each atom are written on either side, and the newly formed molecular orbitals are written in the centre of the diagram. This question deals with the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of the simple diatomic hydrogen molecule. VSEPR theory describes this as two hydrogen atoms forming a single covalent bond. See below. Orbital diagrams are useful to show the number of electrons, number of electron shells, number of electron pairs, and electron spin directions in a particular atom/ion. Arrows represent electrons, and their spin is represented by which way they point (up or down). Two electrons can be paired into one shell (one little box) as one orbital.
The lithium 1s orbital is the lowest-energy orbital on the diagram. Because this orbital is so small and retains its electrons so tightly, it does not contribute to bonding; we need consider only the 2 s orbital of lithium which combines with the 1 s orbital of hydrogen to form the usual pair of sigma bonding and antibonding orbitals. The bonding picture is essentially the same as for the hydrogen molecule, except that each helium atom brings two electrons to the molecular orbitals. There would be four electrons to fill into our molecular orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ... Theories of covalent bonding and shapes of molecules 04:How to construct Molecular orbital diagram for Hydrogen molecule and helium molecule and bond order a...
6. There is one p orbital on boron but there is no adjacent atom with another p orbital. Add it to the molecular orbital diagram as a non-bonding molecular orbital. 7. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. sp Hybrid Orbitals in BeH2 1.
In a methane molecule, the 1s orbital of each of the four hydrogen atoms overlaps with one of the four sp 3 orbitals of the carbon atom to form a sigma (σ) bond. This results in the formation of four strong, equivalent covalent bonds between the carbon atom and each of the hydrogen atoms to produce the methane molecule, CH 4 .
The energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. If noticed, the energy gap in successive shells decreases with the energy. The orbitals get closer and closer as we move higher. The electron will mostly spend time in 1s orbital since it is the most stable condition. It can jump to an excited state from the ground state by absorbing energy.
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
Quantum Mechanics: The Hydrogen Atom 12th April 2008 I. The Hydrogen Atom In this next section, we will tie together the elements of the last several sections to arrive at a complete description of the hydrogen atom. This will culminate in the de nition of the hydrogen-atom orbitals and associated energies.
Oxygen electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4.The period of oxygen is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen(O) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles. The eighth element in the periodic table is oxygen.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ...
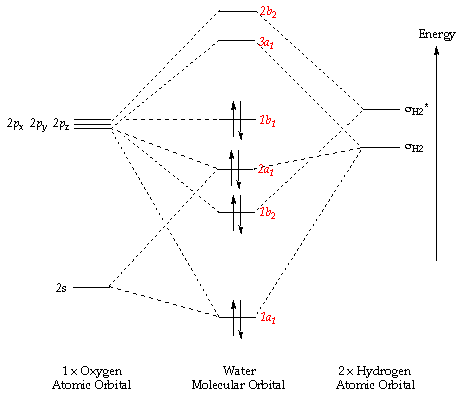
Even though you find complex names on other molecules, everyone calls H2O "water". Water is made up of two hydrogen (H) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom. The formula for water is H 2 O. The hydrogen atoms have filled orbitals with two electrons and the oxygen atom has a filled second orbital with eight electrons.
1. Hydrogen molecule, H 2. It is formed by the combination of two hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom in the ground state has one electron in 1s orbital. Therefore, in all there are two electrons in hydrogen molecule which are present in lower most s 1s molecular orbital.
Explain about the molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule. chemical bonding; class-11; Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. 1 Answer +1 vote . answered Dec 22, 2020 by Taashi (15.8k points) selected Dec 24, 2020 by Aashi01 . Best answer. 1. Electronic ...
See the diagram below: Now you can see that the central atom here is Carbon because it is easy for Carbon to become stable as it is the least electronegative of all. However, hydrogen is the least electronegative but it cant be a central atom because it has only one spare electron. The other two atoms H and N are attached to C by a single bond.
Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. CONTROLS . Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
Hydrogen Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic hydrogen has 1 electron in a 1s orbital. Of course, there are 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, etc. empty orbitals at higher energy. Let's just consider the 1s orbitals. Remember that an orbital is a mathematical function that describes the probability of finding an electron in space.
























0 Response to "44 orbital diagram for hydrogen"
Post a Comment