44 stress and strain diagram
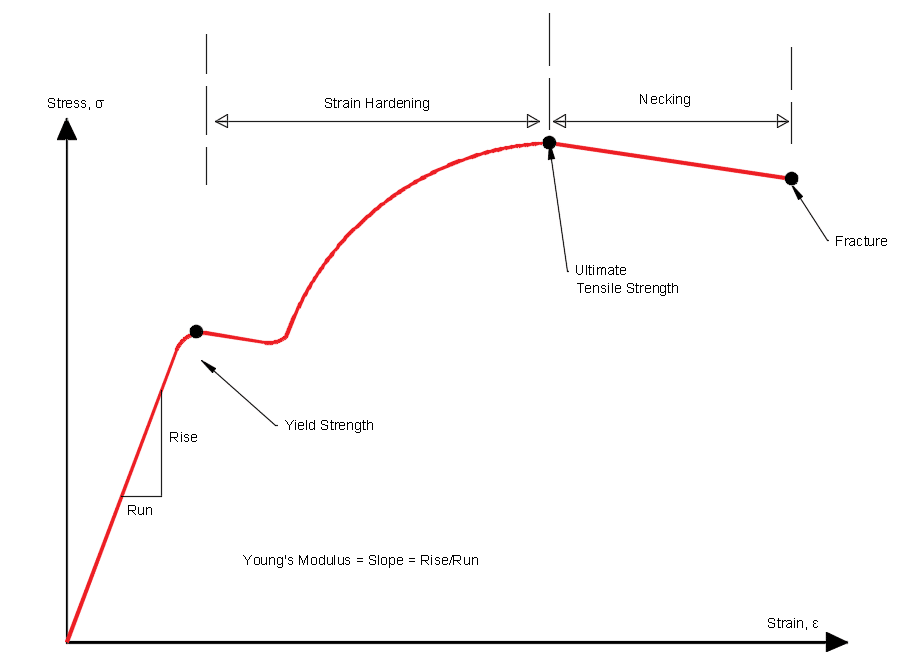
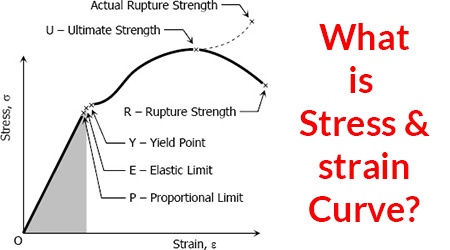
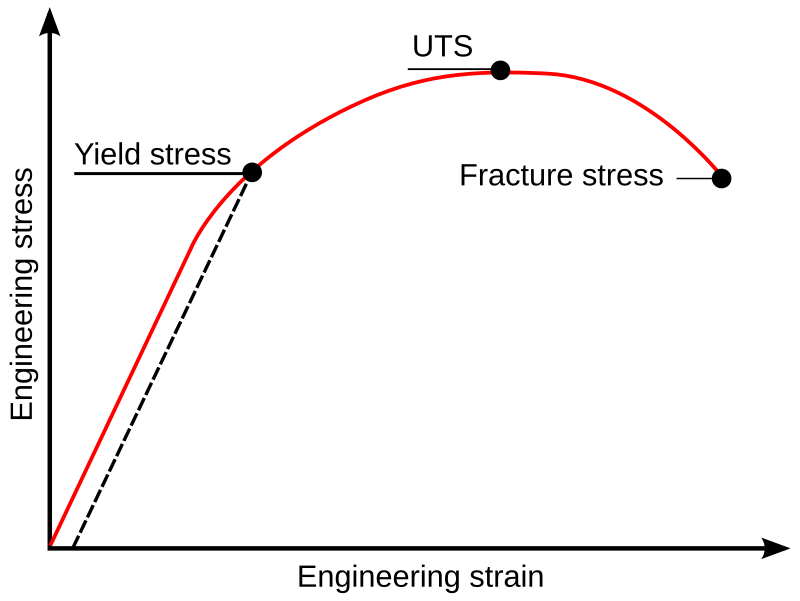
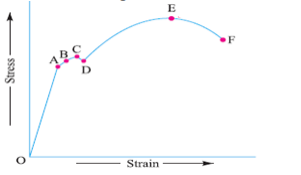
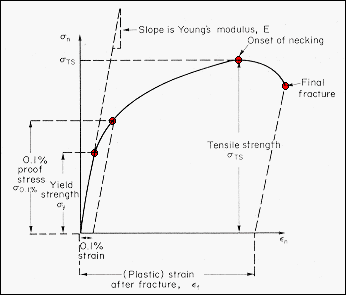
U: This point corresponds to the ultimate strength, S tu, which is the maximum value of stress on the stress-strain diagram. The ultimate strength is also referred to as the tensile strength . After reaching the ultimate stress, specimens of ductile materials will exhibit necking , in which the cross-sectional area in a localized region of the specimen reduces significantly. Concepts of Stress and Strain One of our principal concerns in this course is material behavior (Strength). But ... Consider the following free body diagram of a two-force member. Inasmuch as the stress σ acts in a direction perpendicular to the cut surface, it is referred to as a NORMAL stress. Thus, normal stressed may be either tensile or
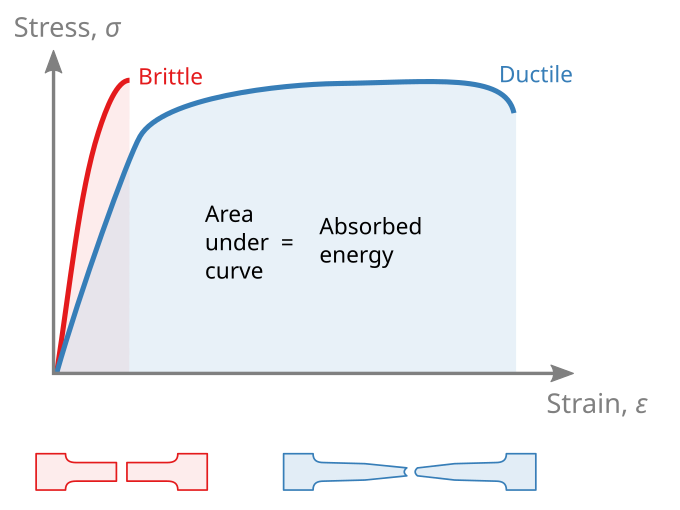
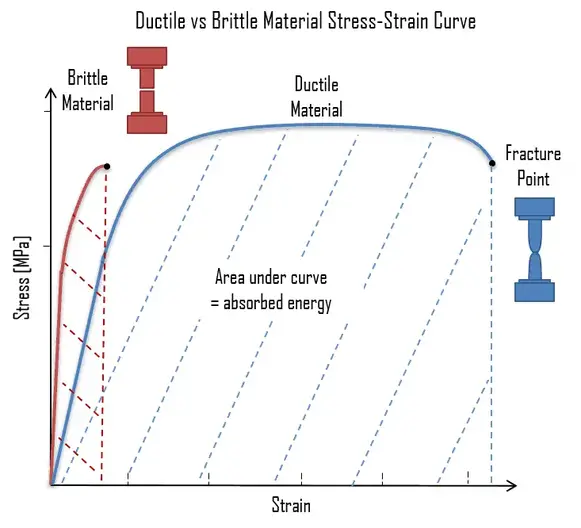
Toughness and strength. Toughness is related to the area under the stress–strain curve.In order to be tough, a material must be both strong and ductile. For example, brittle materials (like ceramics) that are strong but with limited ductility are not tough; conversely, very ductile materials with low strengths are also not tough. To be tough, a material should withstand both high stresses ...
Stress and strain diagram
Figure 5 shows a stress-strain relationship for a human tendon. Some tendons have a high collagen content so there is relatively little strain, or length change; others, like support tendons (as in the leg) can change length up to 10%. Note that this stress-strain curve is nonlinear, since the slope of the line changes in different regions. The maximum ordinate in the stress-strain diagram is the ultimate strength or tensile strength. Rapture Strength. Rapture strength is the strength of the material at rupture. This is also known as the breaking strength. Modulus of Resilience. Modulus of resilience is the work done on a unit volume of material as the force is gradually increased ... Stress and Strain Curves or Diagram: This curve is a behavior of the material when it is subjected to load. The stress-strain curve depends on two types of material. 1. Ductile Material: Ductile materials are materials that can be plastically twisted with no crack. They have the tendency to hold the deformation that occurs in the plastic region.
Stress and strain diagram. A schematic diagram for the stress-strain curve of low carbon steel at room temperature is shown in figure 1. There are several stages showing different behaviors, which suggests different mechanical properties. To clarify, materials can miss one or more stages shown in figure 1, or have totally different stages. ... So now I want to plot stress-strain diagram to know the value of ultimate stress. So, can anyone guide me how to show total reaction force at the bottom edge then plot the stress-strain diagram? Material: Young's modulus, E = 200 GPa; Poisson's ratio m = 0.3, Reh = 690 Mpa. Answer (1 of 12): In structural engineering and strength of materials, a member or component may be subject to different types of forces/moments or a complex combination of them. These forces and moments or their combinations give rise to different types of stresses at different points in the me... Introduction to engineering stress-strain diagrams for metals. Made by faculty at the University of Colorado Boulder Department of Chemical and Biological En...
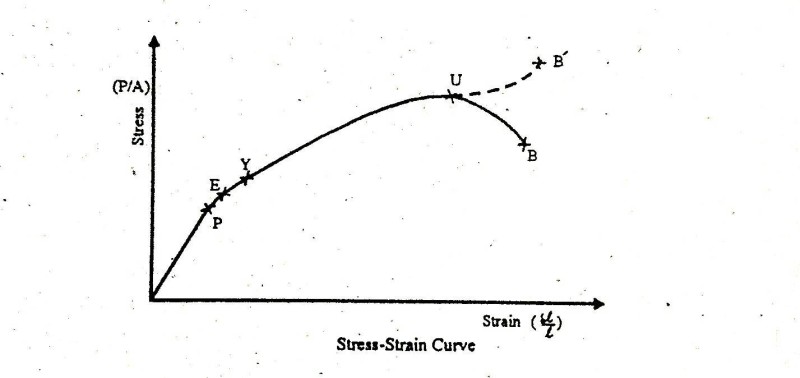
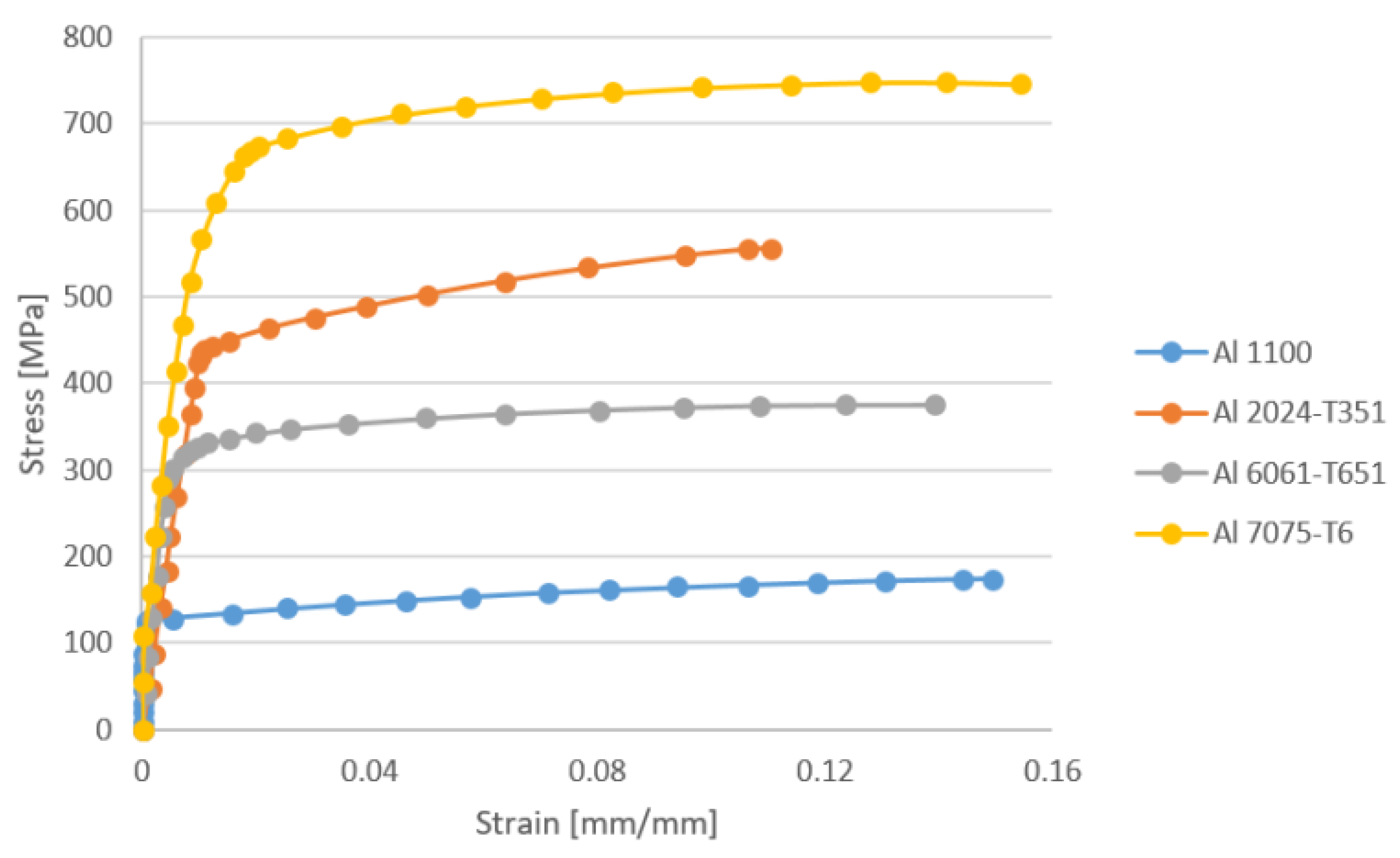
The stress-strain diagram for different material is different. It may vary due to the temperature and loading condition of the material. How to Draw Stress-Strain Curve or Diagram. A tensile test is done on the material for drawing the stress strain curve. A specimen of specific dimension is taken generally a circular rod. Answer to Solved (Stress - Strain Diagram for Median Carbon Structural 1. The stress-strain diagram. From the data of a tension test, it is possible to compute various values of the stress and corresponding strain in the specimen and then plot the result. The resulting curve is called the stress-strain diagram. Stress s = applied Load P divided by the specimen s original cross-sectional Area A 0. STRESS-STRAIN DIAGRAM: The mechanical properties of a material are determined in the laboratory by performing test on the small specimens of the material. Most common material test is the Tension Test. In this test, loads are measured on the main dial of the machine while the elongations are measured with the help of extensometers. It consists of a cylindrical specimen having a diameter of 0.5 ...
The stress - strain diagram differs in form for various materials. Stress Strain Curve for Concrete and Steel Stress-strain diagram of a medium-carbon structural steel Exploring the Stress / Strain Curve for Mild Steel Metallic engineering materials are classified as either ductile or brittle materials. A ductile material is one having ... Allowable stresses are 80MPa and 140MPa in copper and steel, respectively; α = 18 × 10-6 K-1 for copper and 12 ×10-6K-1for steel. 5. A 3.5m long steel column of cross-sectional area 5000mm2 is subjected to a load of 1.6 MN. Determine the safety factor for the column, if the yield stress of steel is 550MPa. The stress-strain diagram provides a graphical measurement of the strength and elasticity of the material. Also, the behaviour of the materials can be studied with the help of the stress-strain diagram, which makes it easy with the application of these materials. The stress-strain diagram is generally accepted as the plotted results of a tensile test completed under carefully controlled conditions on a speciman of a metal. The stress-strain diagram important for design engineers in that it establishes the physical properties of the material under test including the yield strength, the ultimate strength ...
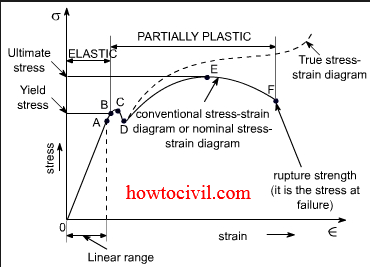
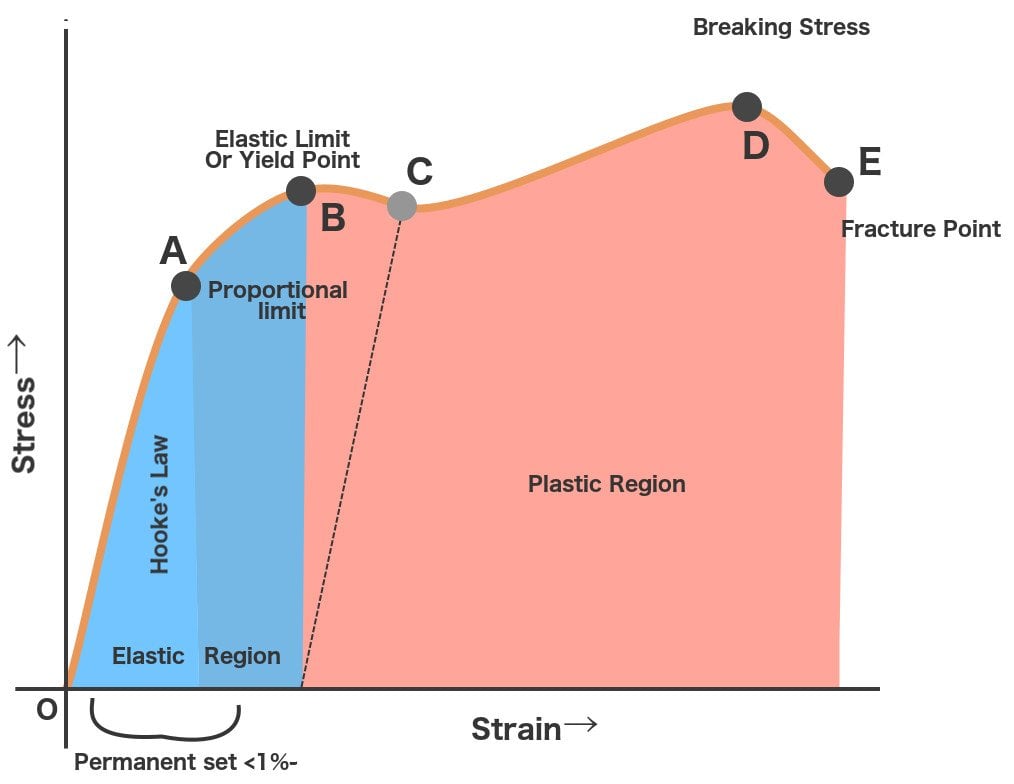
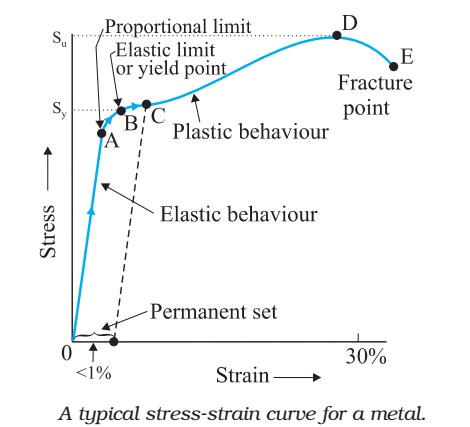
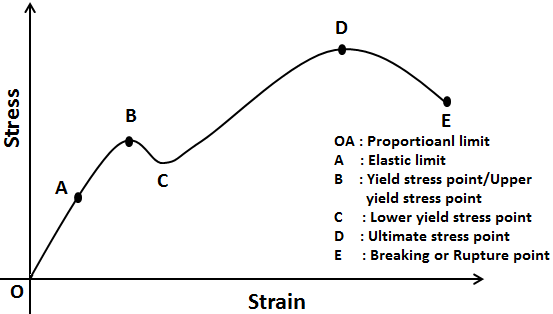
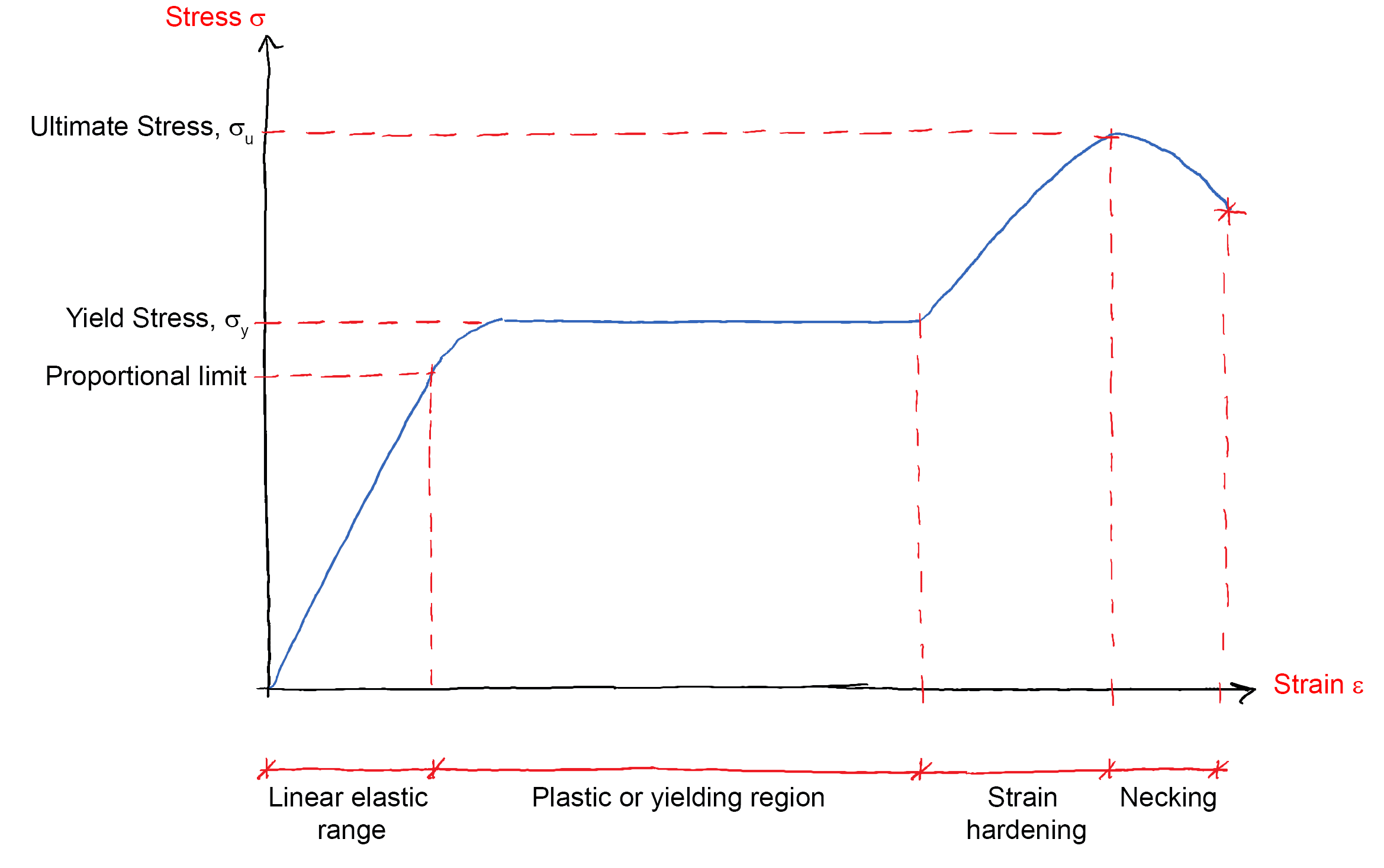
The line OA on a stress-strain diagram shows a proportional limit. Elastic limit. It is a limit up to which material (specimen) behaves elastically. However, the curve is not shown linear between elastic limit & proportional limit but the material is still elastic and if the load is removed within the elastic limit, the specimen will return to ...
Stress Strain Diagram for Brittle Materials: Above graph shows that gray cast iron exhibit less plastic region i.e it fractures just after elastic limit so it is a brittle material. Different Points On Stress Strain Curve:
Stress and Strain Curve for an Elastic Material: Suppose a wire of uniform cross-section is suspended from a rigid support. When the load at other side is increased gradually, then length of wire goes on increasing. If we plot the graph between stress and strain, then shape of the curve will be as shown in fig just below:
When stress causes a material to change shape, it has undergone strain ordeformation. Deformed rocks are common in geologically active areas. A rock’s response to stress depends on the rock type, the surrounding temperature, and pressure conditions the rock is under, the length of time the rock is under stress, and the type of stress.
With increasing stress, strain increases linearly. In the diagram above, this rule applies up until the yields strength indicator. Young's Modulus of Elasticity. It is defined as the ratio of longitudinal stress to strain within the proportional limit of a material. Also known as modulus of resilience, it is analogous to the stiffness of a ...
Stress-Strain Curve, as the name suggests, it's basically related to material's stress and strain. Stress strain curve is defined as the curve or a graphical representation of a material's stress and its strain and understood the relationship between stress and strain. Stress strain curve graph basic. Stress is represented along the Y-Axis.
If the stress-strain diagram varies from what the Young's Modulus equation tells us to expect, then we know that the material has yielded, and the object is now experiencing plastic deformation.
Explaining Stress-Strain Graph. The stress-strain diagram has different points or regions as follows: Proportional limit. Elastic limit. Yield point. Ultimate stress point. Fracture or breaking point (i) Proportional Limit. The region in the stress-strain curve that observes the Hooke's Law is known as the proportional limit. According to this ...
The resulting stress-strain curve or diagram gives a direct indication of the material properties. Note: Stress-strain diagrams are typically based upon the original cross sectional area and the initial gage length, even though these quantities change continuously during the
On stress-strain diagram, these materials don't have yield point and value of E is small. 6- Toughness The toughness of a material is ability to withstand both plastic and elastic deformations. It is a highly desirable quality for structural and machine parts to withstand to shock and vibration. ...
STRESS-STRAIN CURVES David Roylance Department of Materials Science and Engineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 August 23, 2001
Stress-Strain Diagram is determined by tensile test. Tensile tests are conducted in tensile test machines , providing controlled uniformly increasing tension force, applied to the specimen. The specimen's ends are gripped and fixed in the machine and its gauge length L 0 (a calibrated distance between two marks on the specimen surface) is ...
Stress Strain Diagram For mild Steel and Concrete and copper. Welcome to howtocivil.From This article, you will find three stress-strain diagrams for Mild Steel, Concrete, and Copper.. The Stress Strain Diagram For mild Steel
Ans: The stress-strain diagram provides an estimate of the strength and elasticity of the material. It also tells about the behaviour of the materials with the application of load. Q.5. What is the elastic limit? Ans: It is the point on the stress-strain curve after which material deforms plastically. Up to this point, the material returns to ...
In both cases, the tensile stress-strain diagrams exhibit a break or knee at strain values in the range of 0.25-0.3%. The failure strain for both SMCs is less than 2%. For SMC-R25, the stress-strain diagram is slightly non-linear below the knee, but becomes linear at strain values higher than 0.5%.
Developing a Stress-Strain Diagram After performing a tension or compression test and determining the stress and strain at various magnitudes of the load, we can plot a diagram of stress versus strain Stress-strain diagrams were originated by: Jacob Bernoulli (1654-1705) and J. V. Poncelet (1788- 1867) Developing a Stress-Strain Diagram
A stress strain diagram or stress strain curve is used to illustrate the relationship between a material's stress and strain. A stress strain curve can be constructed from data obtained in any mechanical test where load is applied to a material and continuous measurements of stress and strain are made simultaneously.
12.6.2021 · Shear strain definition Shear Strain is define as ,it is starin that produces due parallel or tangential force and this produce strain (deformation) is called as shear strain. Shear strain is defined to be, it is a ratio of the horizontal displacement to the hight of …
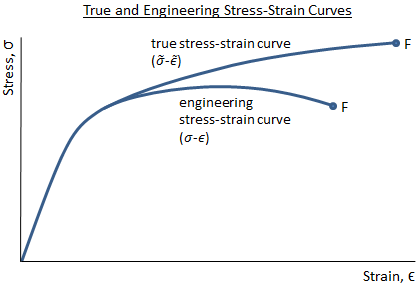
A stress-strain diagram that takes the instantaneous values of cross-sectional area and length to determine stress and strain is referred to as a "true stress-strain diagram." For most applications, the engineering stress-strain diagram is sufficient, since the differences between the engineering and true versions are very small below the ...
The stress-strain curve is the most reliable and complete source for the evaluation of mechanical properties of any fibre. The stress-strain curve is produced by plotting the applied stress on the fibre axis and the elongation produced due it. The stress-strain curve of a model fibre is shown in Fig. 3.1.
Stress and Strain Curves or Diagram: This curve is a behavior of the material when it is subjected to load. The stress-strain curve depends on two types of material. 1. Ductile Material: Ductile materials are materials that can be plastically twisted with no crack. They have the tendency to hold the deformation that occurs in the plastic region.
The maximum ordinate in the stress-strain diagram is the ultimate strength or tensile strength. Rapture Strength. Rapture strength is the strength of the material at rupture. This is also known as the breaking strength. Modulus of Resilience. Modulus of resilience is the work done on a unit volume of material as the force is gradually increased ...
Figure 5 shows a stress-strain relationship for a human tendon. Some tendons have a high collagen content so there is relatively little strain, or length change; others, like support tendons (as in the leg) can change length up to 10%. Note that this stress-strain curve is nonlinear, since the slope of the line changes in different regions.


























0 Response to "44 stress and strain diagram"
Post a Comment