41 diffusion and osmosis diagram
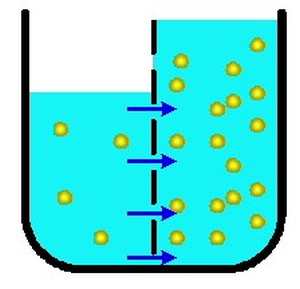
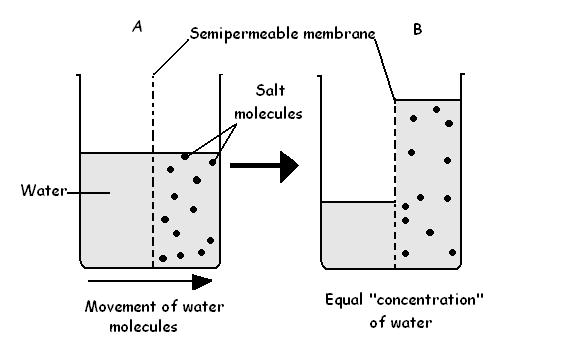
ADVERTISEMENTS: Process of Diffusion in Plant Cell (With Diagrams)! Diffusion: The movement of various substances into a plant, usually from the soil, out of which the green plant synthesises the numerous complex organic compounds, is accomplished, principally through the agency of the process known generally as diffusion. In some cases, however, the operation of the […] Share the following explanation with students, using the diagram on the board: • Tell students to recall that diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Osmosis refers to the movement of water moleculesacross a membrane trying to achieve equilibrium.
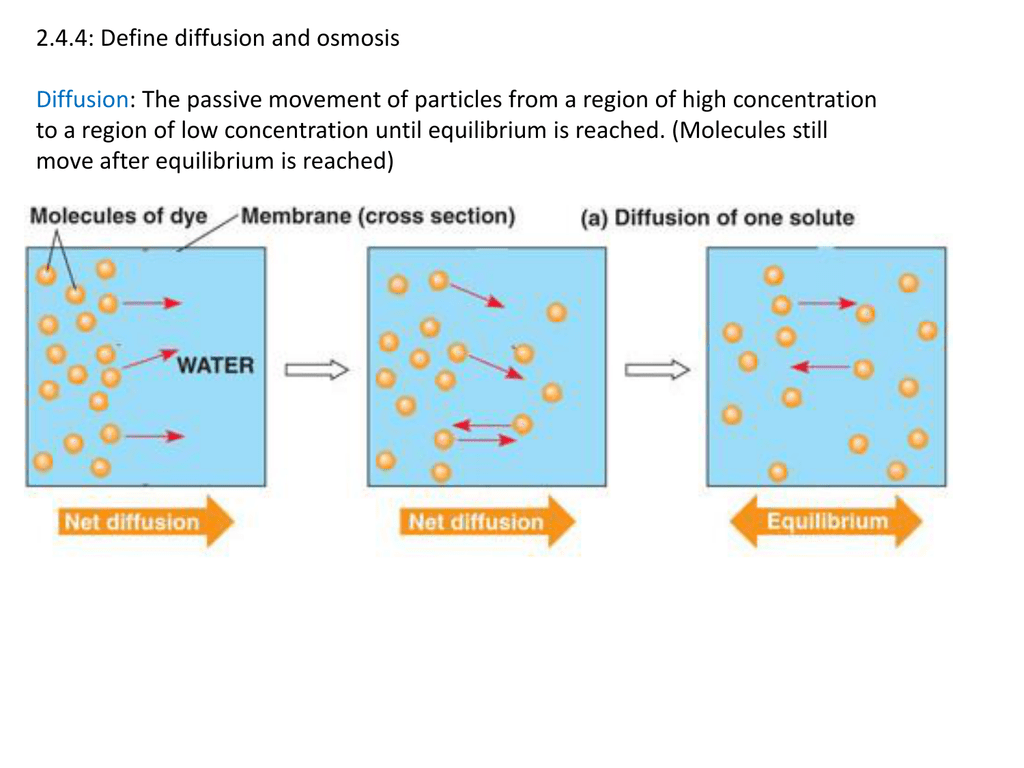
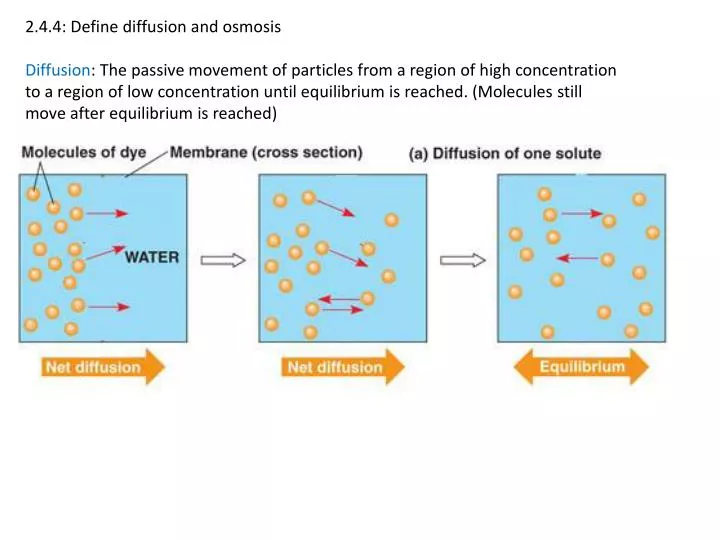
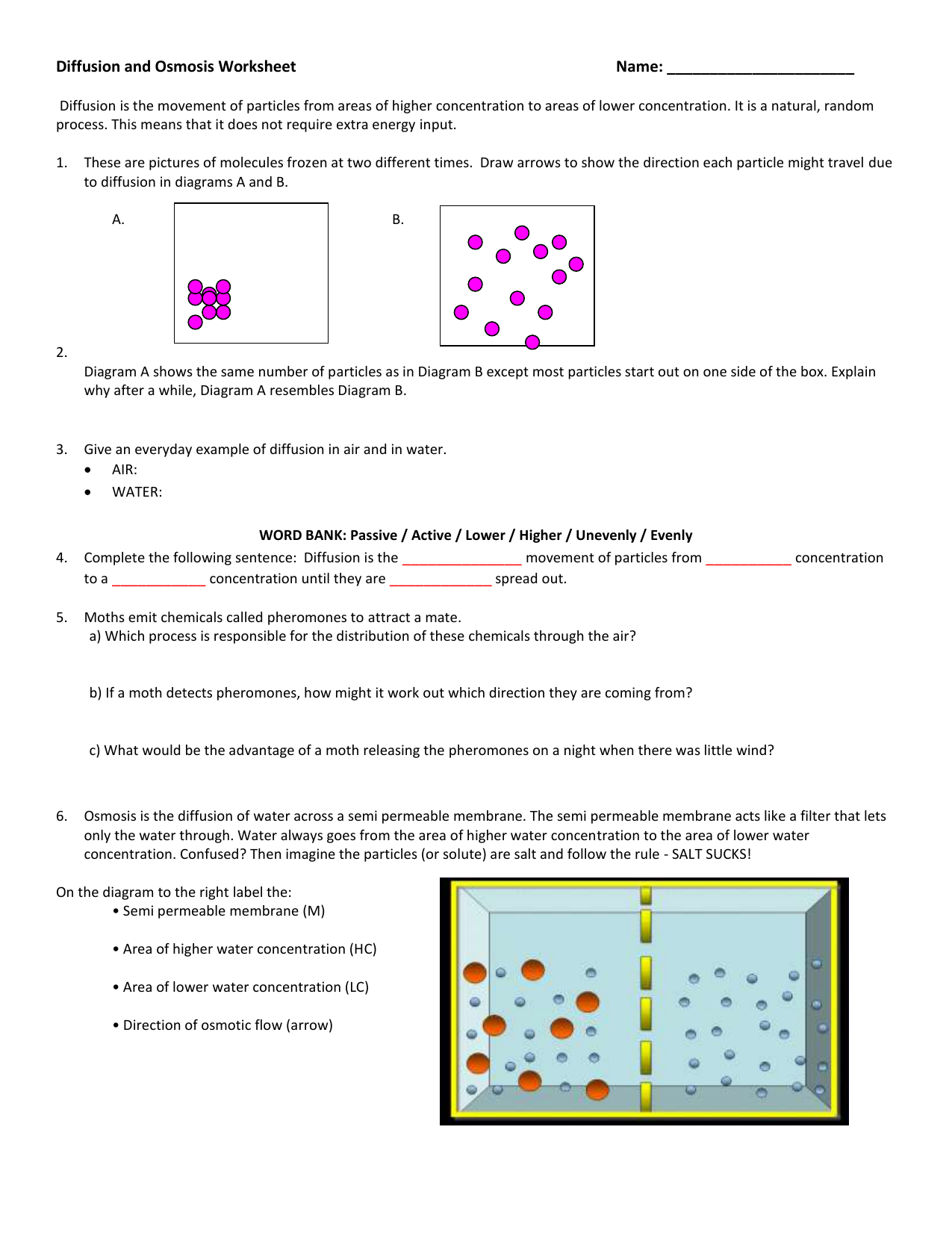
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet. Diffusion. is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. It is a natural, random process. This means that it does not require extra energy input. 1a. These are pictures of molecules frozen at two different times.
Diffusion and osmosis diagram
Teaching Osmosis and Diffusion through Kidney Dialysis by Amanda Reasoner Introduction. The idea of an artificial kidney, or any artificial organ for that matter, seems like such a complex idea only to be understood by those that have specialized in fields such as nephrology or biomedical engineering. Diffusion. Osmosis. Gradient. Equilibrium. Selectively Permeable. Passive Transport. Active Transport. Isotonic. Hypertonic. Hypotonic. Contractile Vacuole. The below mentioned article explains about the osmosis and diffusion with the help of suitable diagrams. Diffusion: The movement of molecules of a solute in a solvent from higher to lower concentration is diffusion. The concentration of a solute in a solvent depends on the number of its molecule in a given volume of solvent.
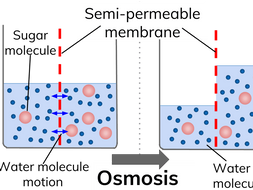
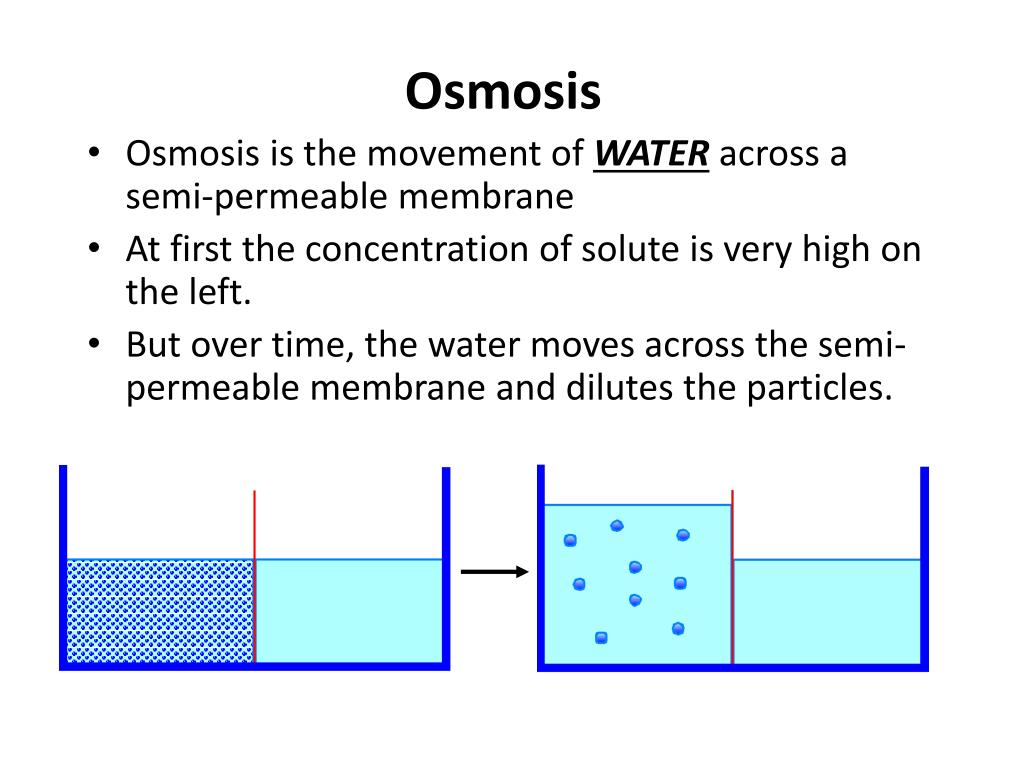
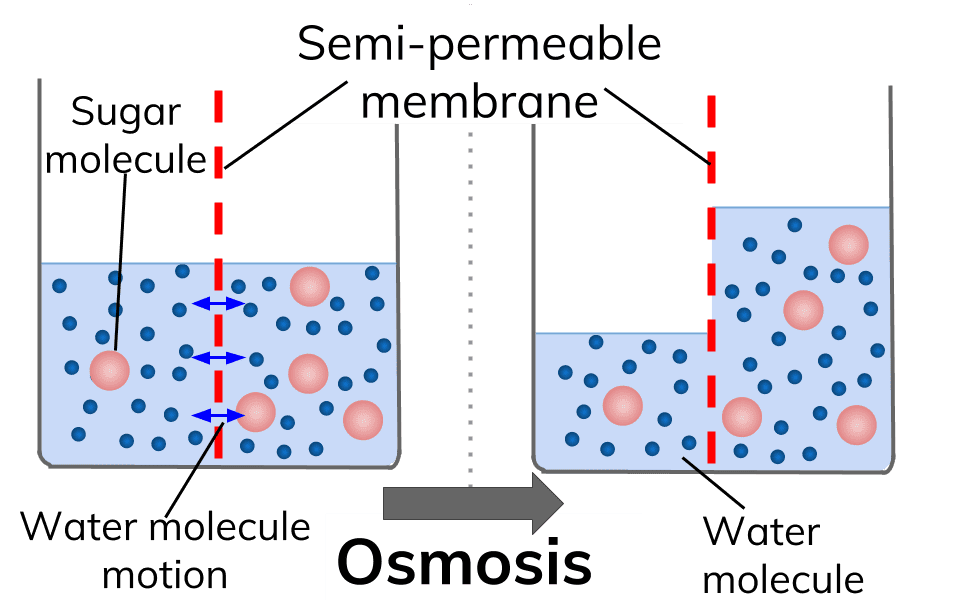
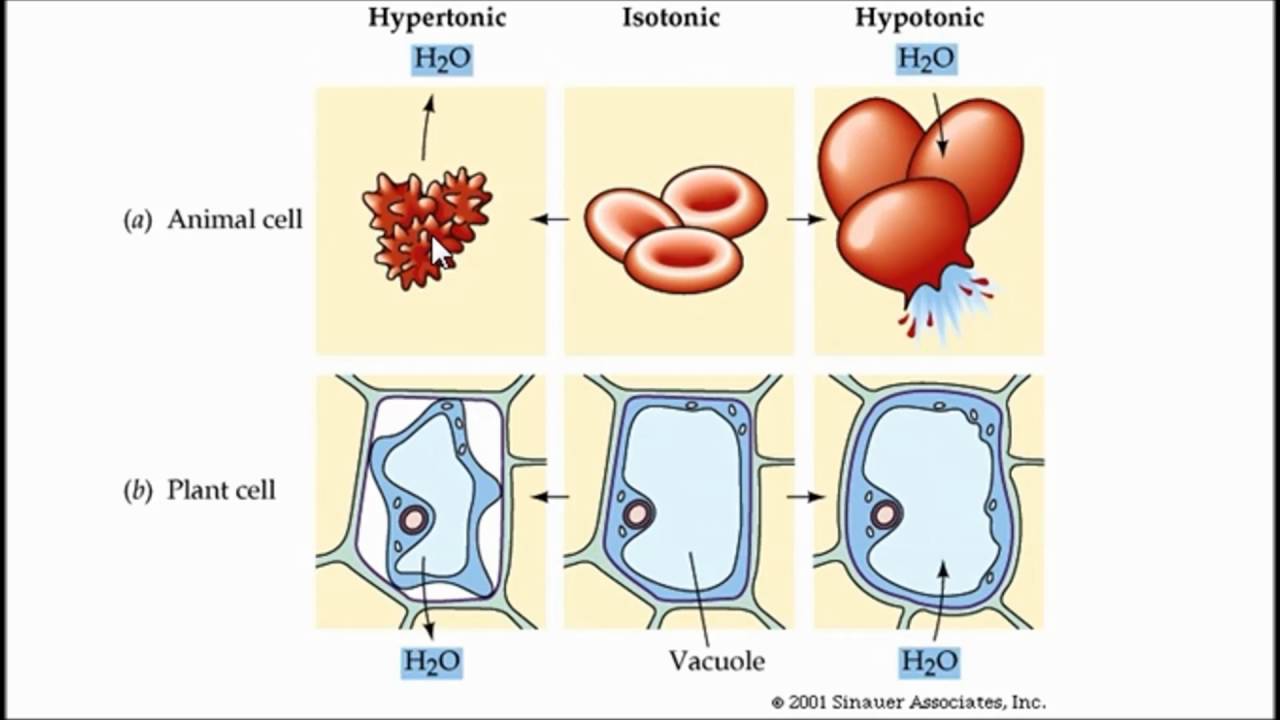
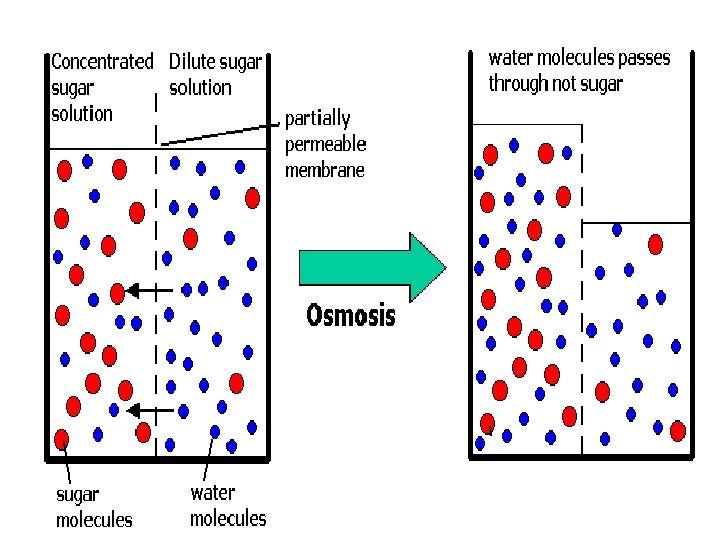
Diffusion and osmosis diagram. Diffusion also most commonly occurs between gas molecules, although it may also occur between solids and liquids or between liquids and gases. Osmosis on the other hand only occurs between two solvents. Osmosis also takes much less time to occur than diffusion. A Venn Diagram showing Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport. Osmosis in the human body diagram.Osmosis requires a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis Examples in Daily Life. In animals the concentration of body fluids blood plasma and tissue fluid must be kept within strict limits if cells lose or gain too much water by osmosis they do not function. 12. For each question use diagrams A-F above. Which cells have: a. Taken in water? b. Lost water? c. No change in water? The diagram above shows how cells can be altered due to osmosis. Water is constantly moving across cell membranes by random motion. The relative amount of water movement into and out of the cells is indicated by the size of ... Basic Characteristics of Osmosis. Requires a semipermeable membrane. A slow and spontaneous process. Occurs in liquid medium. Requires no energy expenditure and thus also called passive diffusion. Movement of water occurs from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential. The process continues until the concentration of ...
Pre/Post Test - Osmosis, Diffusion . 1. The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane is: A. homeostasis B. osmosis C. active transport D. equilibrium . 2. All matter is composed of very small particles called: A. molecules B. ions C. solutes D. isotopes . 3. Diffusion can occur in any mixture, including one that includes a semipermeable membrane, while osmosis always occurs across a semipermeable membrane. When people discuss osmosis in biology, it always refers to the movement of water. In chemistry, it's possible for other solvents to be involved. The primary differentiating factor between the two systems is the medium in which they are employed. Osmosis can only function in a liquid medium, but diffusion can occur in all three mediums (solid, liquid and gas). Furthermore, osmosis requires a semi-permeable membrane, while diffusion does not. A Venn Diagram showing Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport. You can edit this Venn Diagram using Creately diagramming tool and include in your. DIFFUSION. OSMOSIS. ACTIVE TRANSPORT. Place these features in the correct part of the Venn Diagram. Involves water only. Requires energy. Is passive.
Diffusion sees molecules in an area of high concentration move to areas with a lower concentration, while osmosis refers to the process by which water, or other solvents, moves through a semipermeable membrane, leaving other bits of matter in its wake. Diffusion, osmosis & active transport venn diagram - Google Slides. Place these features in the correct part of the Venn Diagram. Involves water only. Requires energy. Is passive. Movement of particles. Needs a semi-permeable membrane. High to low concentration. Against a concentration gradient. Osmosis is the diffusion of a solvent through a differentially permeable membrane. In biological systems, the solvent will usually be water. Osmosis will occur whenever the water concentrations are different on either side of a differentially permeable membrane. Diffusion and osmosis involves the movement of materials from one region another. The main difference between osmosis and diffusion is that osmosis requires a semi permeable membrane. The movement of materials always occur in cells. This movement could occur by; Active transport Osmosis diffusion
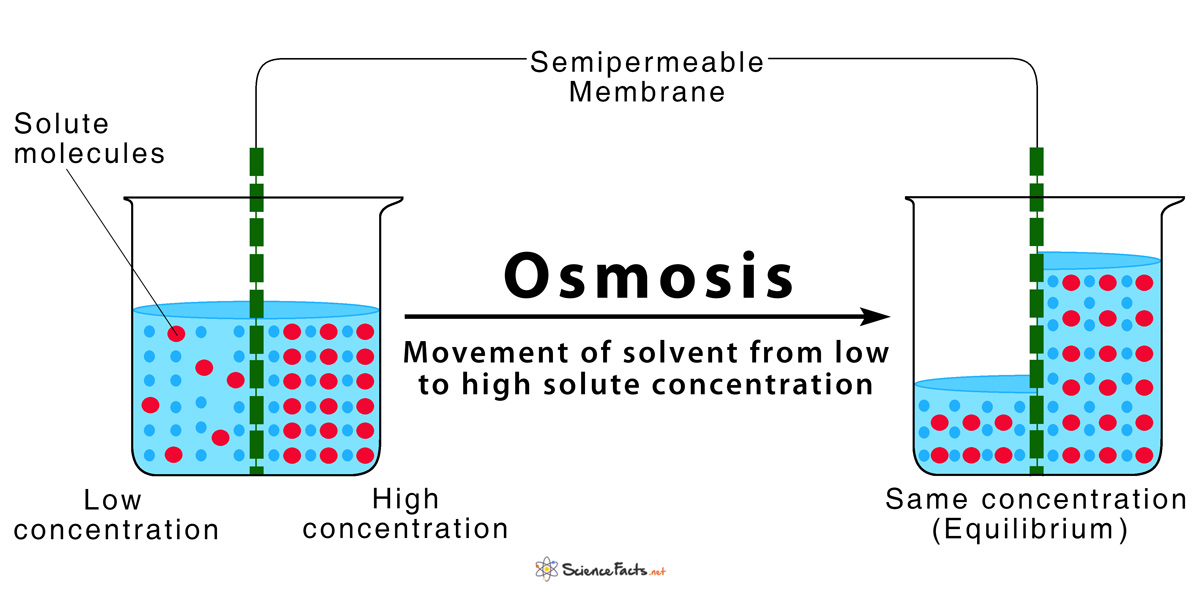
Osmosis (/ ɒ z ˈ m oʊ s ɪ s /, US also / ɒ s-/) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides.
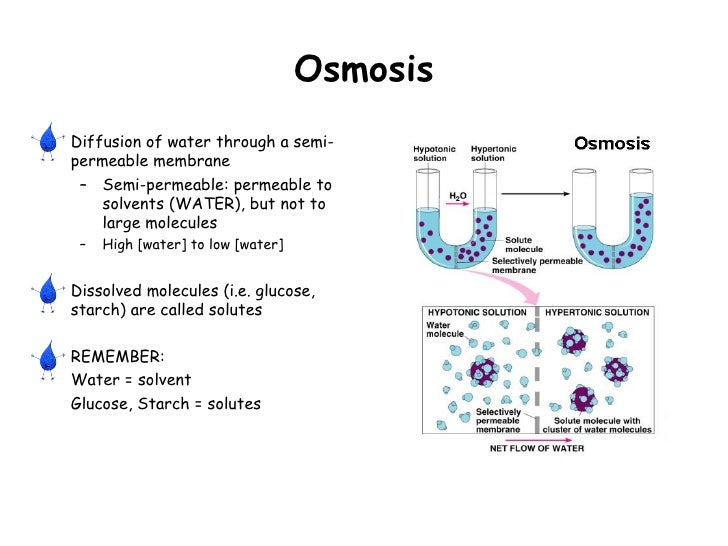
Osmosis Osmosis is a special example of diffusion. It is the diffusion of water through a partially permeable membrane from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution - down the water potential gradient) Note: diffusion and osmosis are both passive, i.e. energy from ATP is not used.
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules or solvent from a higher concentration area to a lower concentration area through a semipermeable membrane. While diffusion refers to the process in which substances get transported from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without any semi-permeable membrane.
DIFFUSION & OSMOSIS CHALLENGE KEY The following questions refer to the diagram below. The solutions in the two arms of the U-tube are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. At the beginning of the experiment the volumes in both arms are the same, and the level of the liquid is therefore at the same height.
13 Diffusion and Osmosis Mr. C. Biology 5 October 24, 2013 Osmosis Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. In the diagram the fluid tries to balance out its concentration of sugar.
The movement is through a semipermeable membrane and so the experiment shows the phenomenon of osmosis. 3. The force, with which the solution level in the tube increases, arises from the pressure exerted by the diffusion of water molecules into the tube. This pressure is called osmotic pressure. 4.
diffusion, as it was he who developed the theory of Brownian motion. Another example of diffusion is a mylar balloon that is filled with helium. As time passes, helium atoms diffuse through the wall of the balloon, and the balloon gradually deflates. Osmosis The process of osmosis involves the diffusion of molecules of a solute through a
Osmosis and diffusion are related processes that display similarities. Both osmosis and diffusion equalize the concentration of two solutions. Both diffusion and osmosis are passive transport processes, which means they do not require any input of extra energy to occur. In both diffusion and osmosis, particles move from an area of higher
Place the following labels in the diagram: high concentration, low concentration, and an arrow showing the direction that the molecules would travel before equilibrium is reached. The video clip explains that you can also look at water as moving to a _____ 2. Osmosis is a type of diffusion, but it involves the movement of water.
Diffusion and Osmosis. The cell membrane plays the dual roles of protecting the living cell by acting as a barrier to the outside world, yet at the same ...
Jun 18, 2019 — Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion; it is the passage of water from a region of high water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane ...
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Name: _____ Diffusion. is the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. It is a natural, random process. This means that it does not require extra energy input. These are pictures of molecules frozen at two different times.
DIFFUSION. • MOVEMENT OF MOLECULES FROM. HIGH CONCENTRATION TO LOW. CONCENTRATION. OSMOSIS. • MOVEMENT OF WATER THROUGH A. SEMIPERMEABLE MEMBRANE FROM.14 pages
This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Digestion and Absorption essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Digestion and Absorption by visiting the associated Learn Page.
What is Osmosis? By definition, osmosis is the movement of any solvent through a selectively permeable membrane into an area of higher solute concentration, the result of which will be an equalizing of solute concentration on either side of the membrane.. This equilibrium is important for the efficient and optimized function of cells; as mentioned before, balance is the preferred state in a ...
The below mentioned article explains about the osmosis and diffusion with the help of suitable diagrams. Diffusion: The movement of molecules of a solute in a solvent from higher to lower concentration is diffusion. The concentration of a solute in a solvent depends on the number of its molecule in a given volume of solvent.
Diffusion. Osmosis. Gradient. Equilibrium. Selectively Permeable. Passive Transport. Active Transport. Isotonic. Hypertonic. Hypotonic. Contractile Vacuole.
Teaching Osmosis and Diffusion through Kidney Dialysis by Amanda Reasoner Introduction. The idea of an artificial kidney, or any artificial organ for that matter, seems like such a complex idea only to be understood by those that have specialized in fields such as nephrology or biomedical engineering.












0 Response to "41 diffusion and osmosis diagram"
Post a Comment