45 in a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the
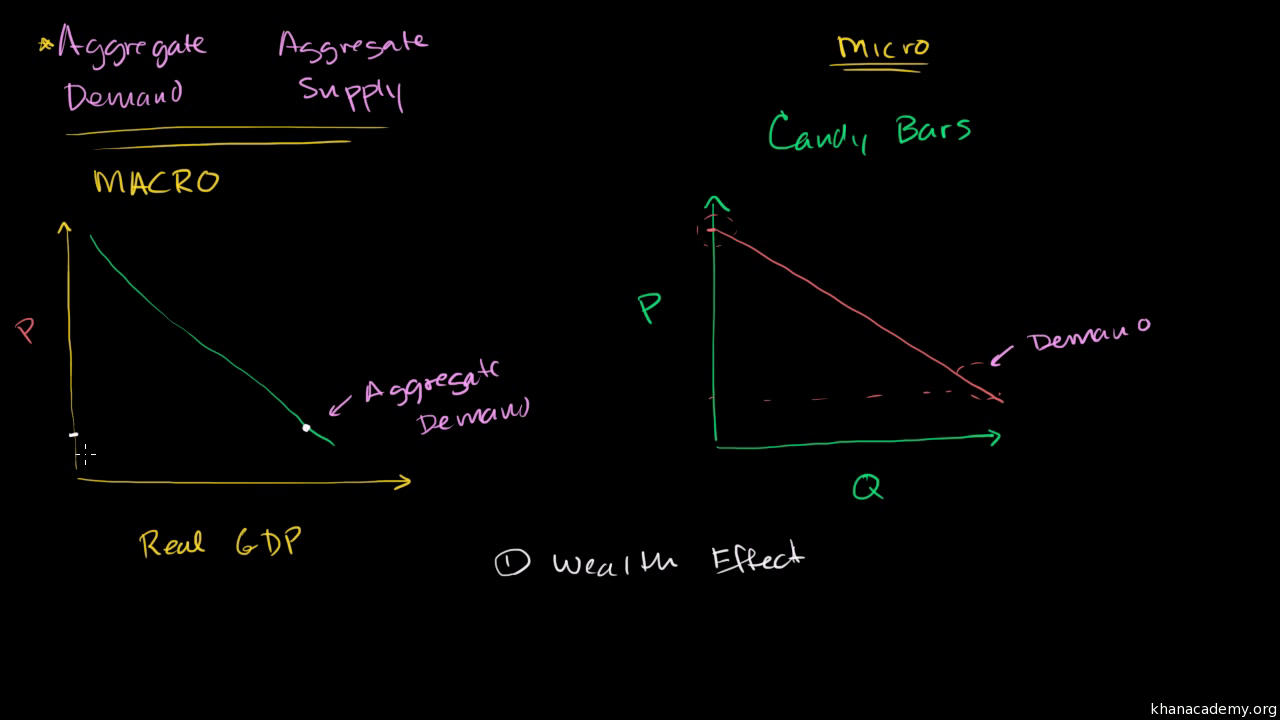
Aggregate demand (AD), like GDP(E), refers to the total level of spending in the economy. Consequently, when aggregate demand is measured it is the same as GDP(E). Aggregate demand includes household spending (also called consumption, C), investment by businesses and households (I), spending by the government (G) and net spending from overseas ... In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves,the GDP gap is measured as the B)Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the A) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the
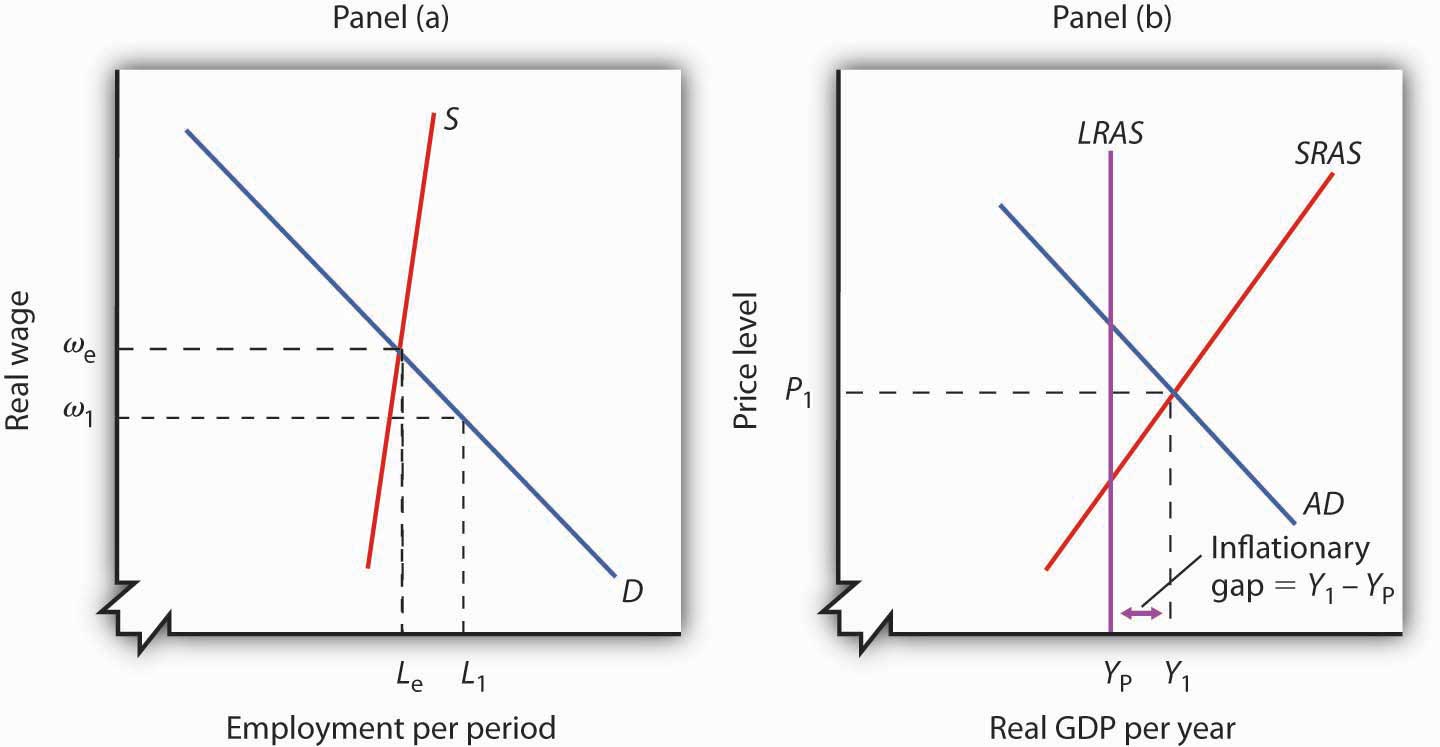
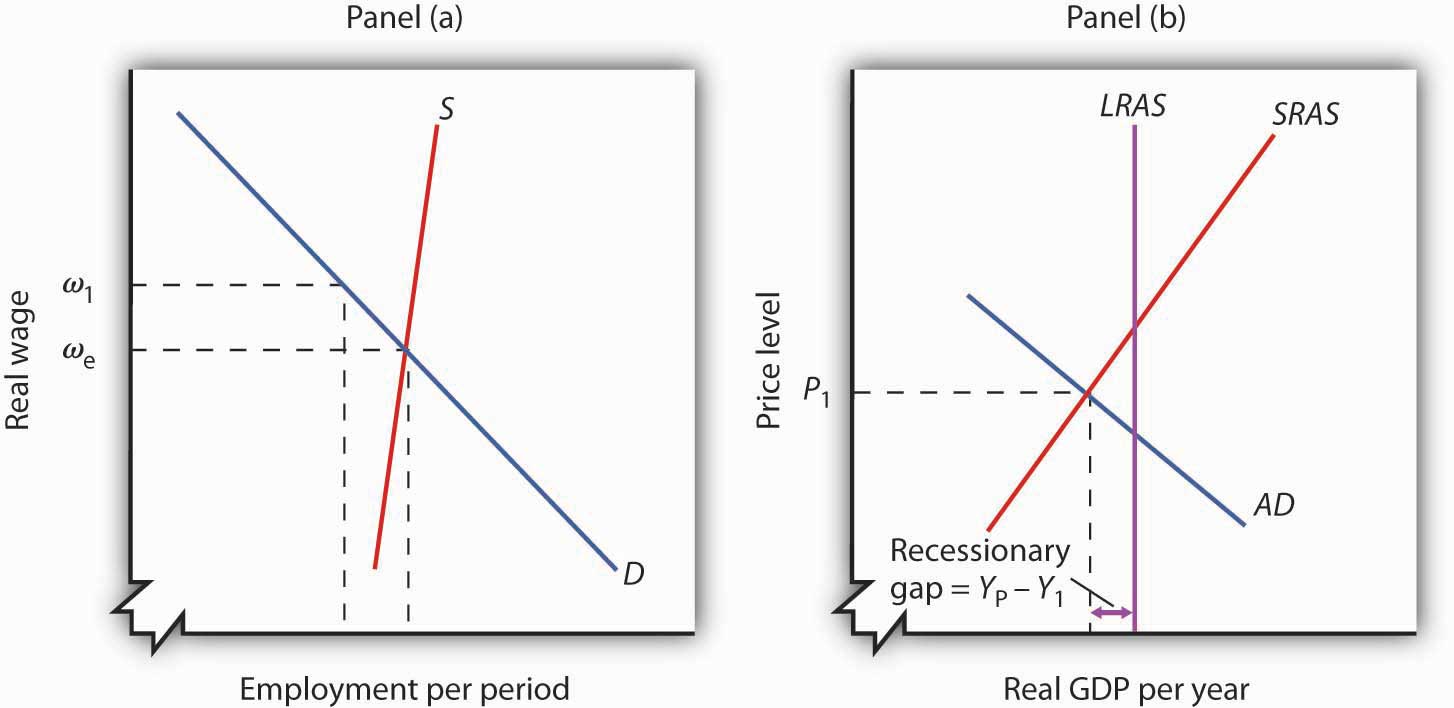
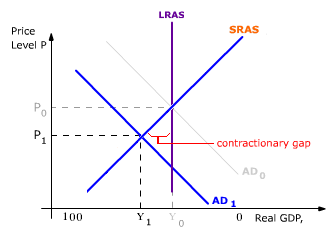
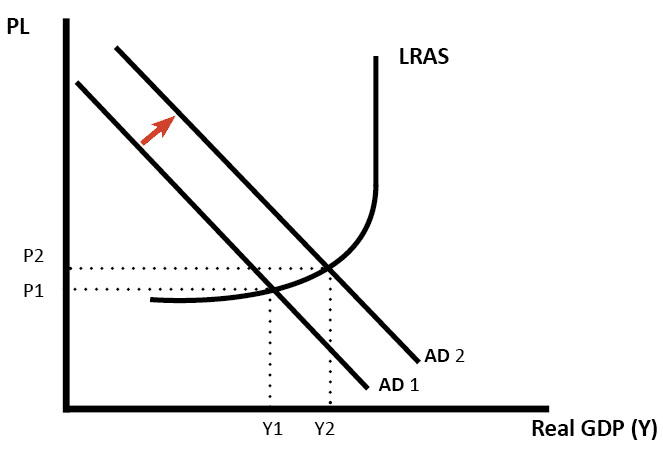
The aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves will intersect to the left of the long-run aggregate supply curve. Suppose an economy's natural level of employment is L e , shown in Panel (a) of Figure 22.13 ";A Recessionary Gap" . demand shock, the government needs to shift the AD curve to the right. Monetary policy that increases the money supply will shift the AD curve to the right and return the economy to P 1 and Yp. 5. For each of the following, describe the effect on the AD, SRAS, and LRAS curves, identify whether the effect causes a shift of In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output If the recessionary GDP gap is $500, then the proper fiscal stimulus when faced with an upward-sloping AS curve is to Shift the AD curve rightward by more than $500
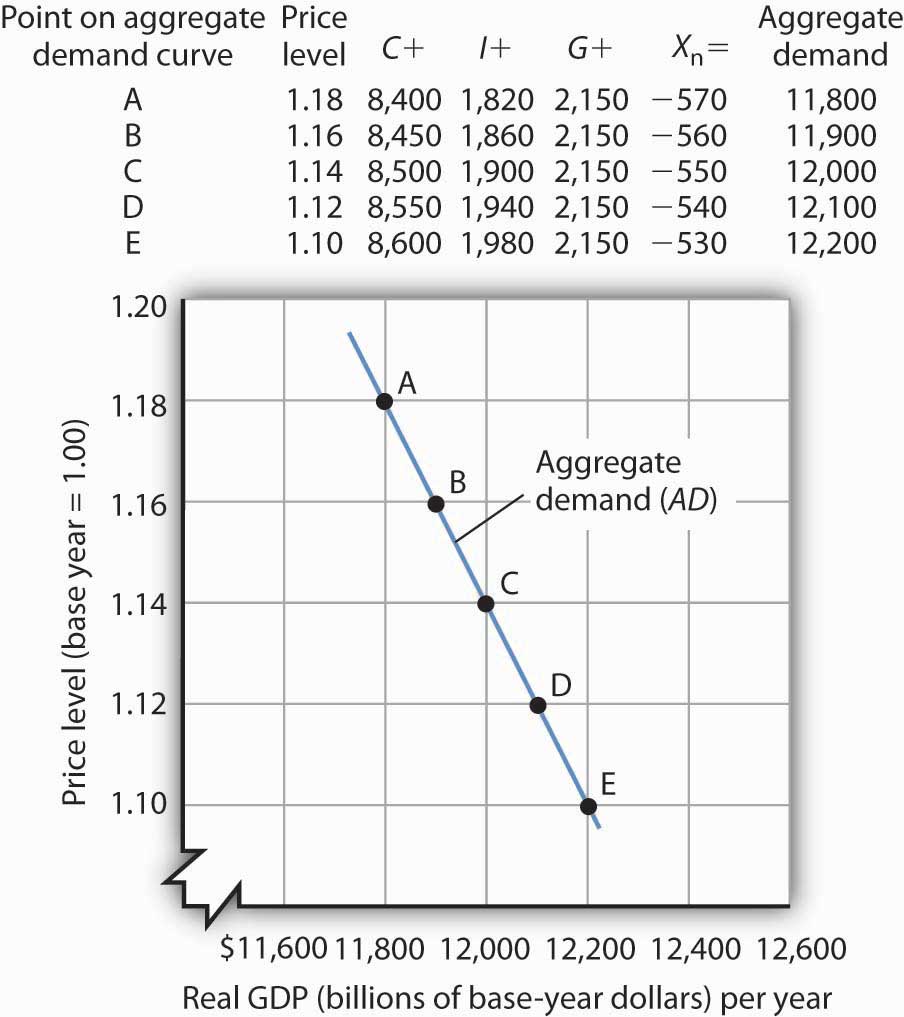
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the. Y = 100,000L, where Y is real GDP in US$, and L is the number of employed labor. P 9,500 Y in billions of US$ AD1 SRAS1. LRAS 100 AD2 102 A B 9,900 (a) Find the natural rate of unemployment. The natural rate of unemployment is the rate of unemployment at the long run equilibrium. Since aggregate demand curve (AD1), short-run aggregate supply Aggregate Demand: The term aggregate demand (AD) is used to show the inverse relation between the quantity of output demanded and the general price level. The AD curve shows the quantity of goods and services desired by the people of a country at the existing price level. In Fig. 7.2 the AD curve is drawn for a given value of the money supply M. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the a. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. Aggregate supply refers to the total amount of goods and services that producers are willing to supply within an economy at a given overall price level. An aggregate supply curve indicates the connection between different price levels and the amount of real GDP supplied and it is represented by an upward sloping curve.
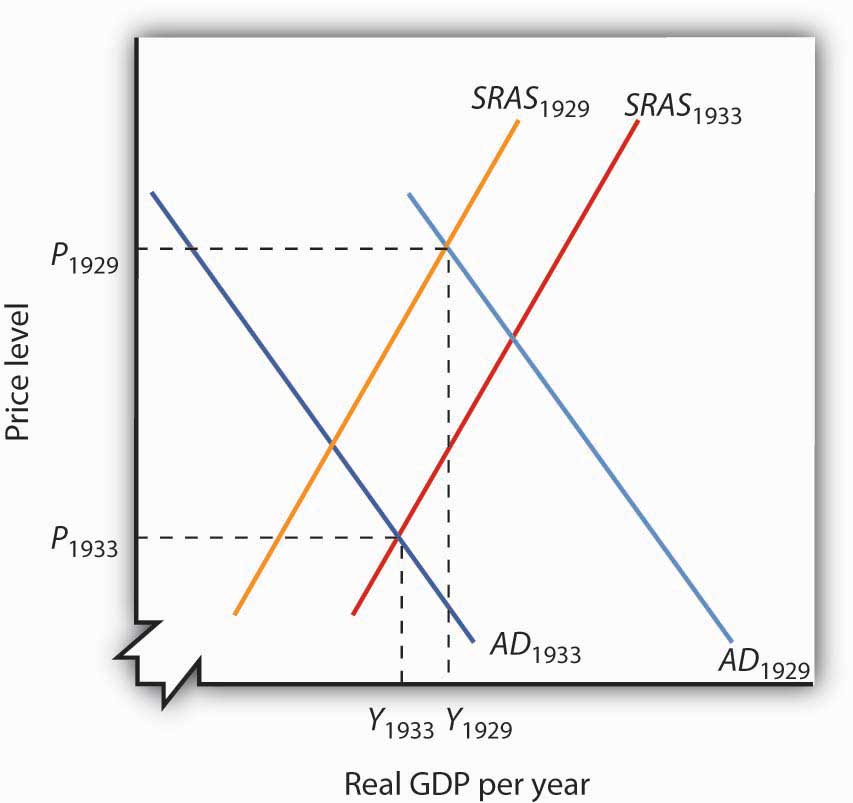
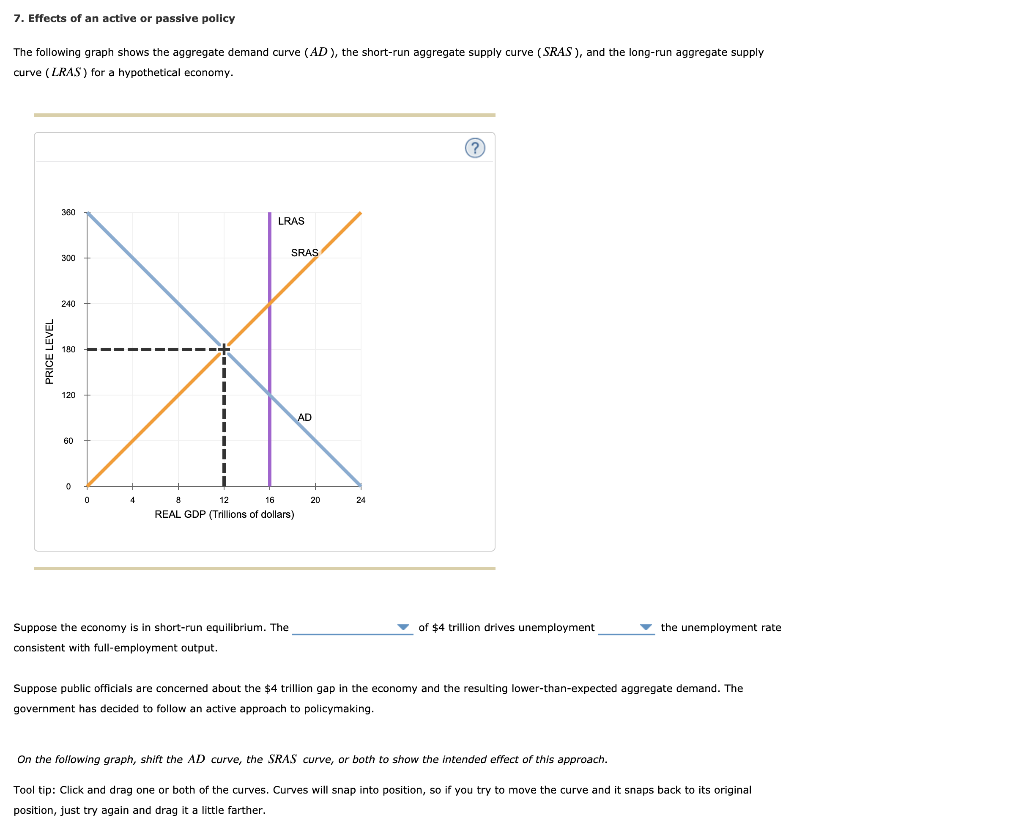
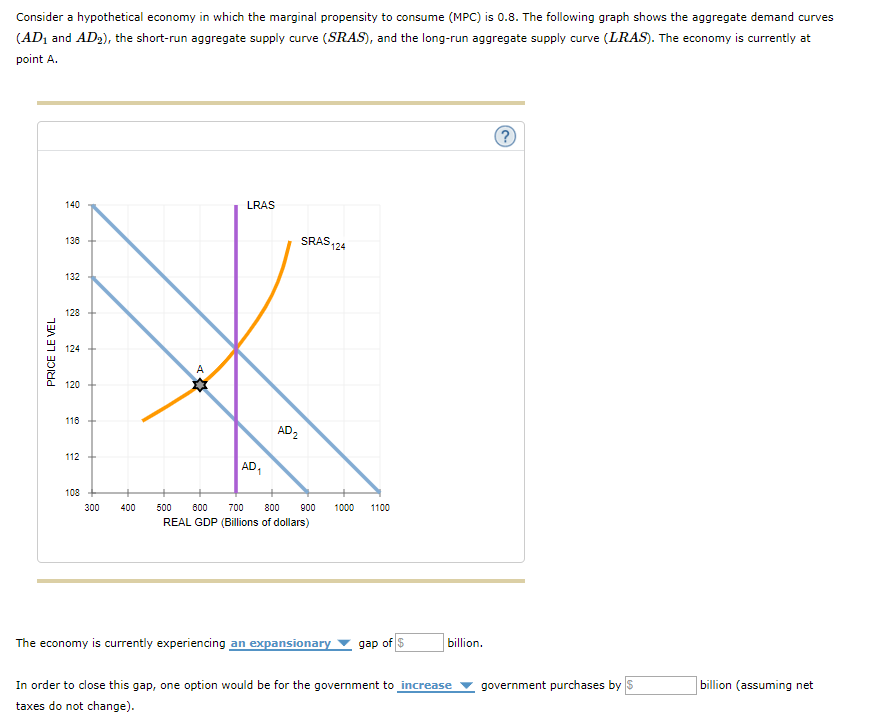
If aggregate demand exceeds the aggregate value of output at the full employment level, there will exist an inflationary gap in the economy. Aggregate demand or aggregate expenditure is composed of consumption expenditure (C), investment expenditure (I), government expenditure (G) and the trade balance or the value of exports minus the value of ... The horizontal axis of a microeconomic supply and demand curve measures the quantity of a particular good or service. In contrast, the horizontal axis of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram measures GDP, which is the sum of all the final goods and services produced in the economy, not the quantity in a specific market. The intersection of short-run aggregate supply curve 2 and aggregate demand curve 1 has now shifted to the upper left from point A to point B. At point B, output has decreased and the price level has increased. This condition is called stagflation. This is also the new short- run equilibrium. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the A. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output.
The Aggregate Demand Curve (AD) represents, in that sense, an even more appropriate model of aggregate output, because it shows the various amounts of goods and services which domestic consumers (C), businesses (I), the government (G), and foreign buyers (NX) collectively will desire at each possible price level. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the a) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves,the GDP gap is measured as the A)Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. B)Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. Gross domestic product is a way to measure a nation's production or the value of goods and services produced in an economy.Aggregate demand takes GDP and shows how it relates to price levels.
Figure 11.7 The Expenditure-Output Diagram The aggregate expenditure-output model shows aggregate expenditures on the vertical axis and real GDP on the horizontal axis. A vertical line shows potential GDP where full employment occurs. The 45-degree line shows all points where aggregate expenditures and output are equal.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the: a. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. b. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. c.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the: Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment ...Government Expenditures: $10 billionTax Revenues: $5 billion1 answer · Top answer: 4. A GDP gap is the difference be...
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the a) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment.
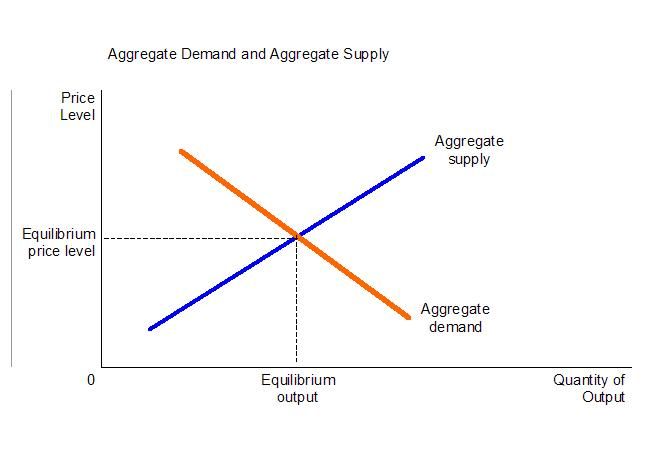
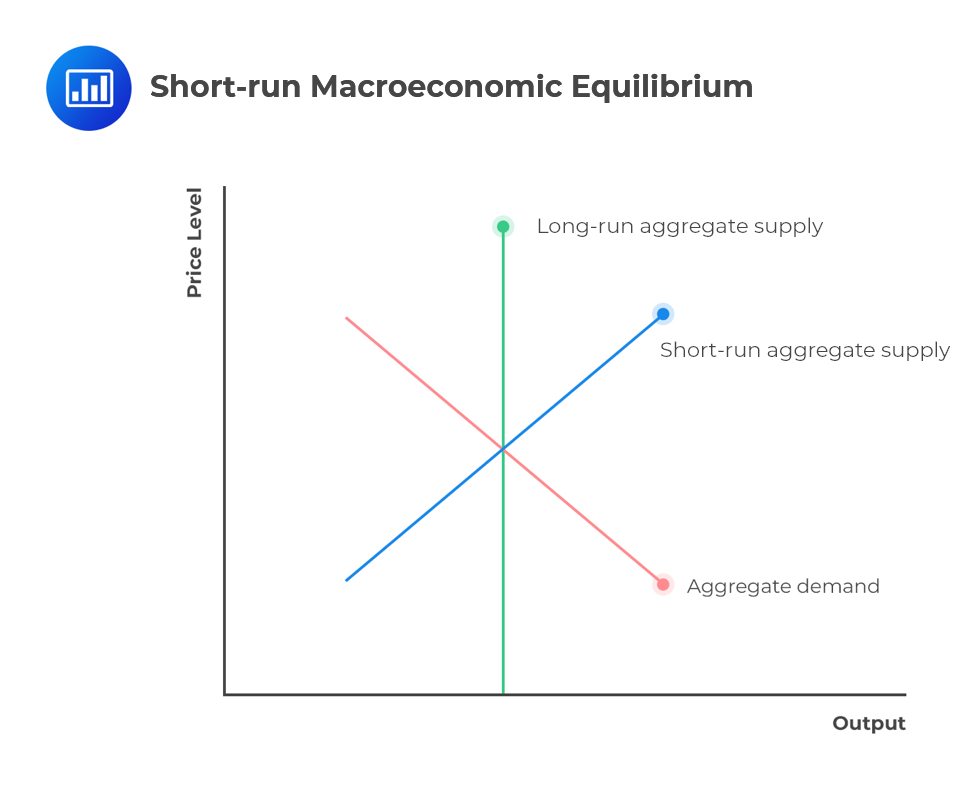
Aggregate supply, or AS, refers to the total quantity of output—in other words, real GDP—firms will produce and sell. The aggregate supply curve shows the total quantity of output—real GDP—that firms will produce and sell at each price level. The graph below shows an aggregate supply curve.
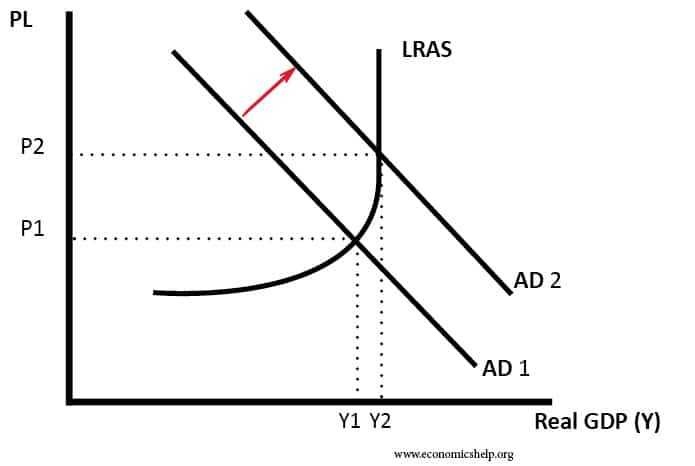
When the aggregate demand (AD) decreases, the equilibrium moves from point A to point B; the real GDP drops from Y2 to Y1 and prices from P1 to P2. The recession is measured between Y1 and Y2, which is the amount by which the real GDP is below GDP. Inflationary Gap
The aggregate demand curve represents the total quantity of all goods (and services) demanded by the economy at different price levels.An example of an aggregate demand curve is given in Figure .. The vertical axis represents the price level of all final goods and services. The aggregate price level is measured by either the GDP deflator or the CPI.
With aggregate demand at AD 1 and the long-run aggregate supply curve as shown, real GDP is $12,000 billion per year and the price level is 1.14. If aggregate demand increases to AD 2 , long-run equilibrium will be reestablished at real GDP of $12,000 billion per year, but at a higher price level of 1.18.
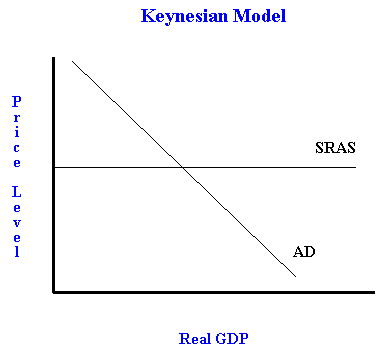
Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply Practice Question - Set-Up. This framework is quite similar to a supply and demand framework, but with the following changes: Instead of "price" on the Y-axis, we have "price-level". Instead of "quantity" on the X-axis, we have "Real GDP";, a measure of the size of the economy.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output If the recessionary GDP gap is $500, then the proper fiscal stimulus when faced with an upward-sloping AS curve is to Shift the AD curve rightward by more than $500
demand shock, the government needs to shift the AD curve to the right. Monetary policy that increases the money supply will shift the AD curve to the right and return the economy to P 1 and Yp. 5. For each of the following, describe the effect on the AD, SRAS, and LRAS curves, identify whether the effect causes a shift of
The aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves will intersect to the left of the long-run aggregate supply curve. Suppose an economy's natural level of employment is L e , shown in Panel (a) of Figure 22.13 ";A Recessionary Gap" .




















0 Response to "45 in a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the"
Post a Comment