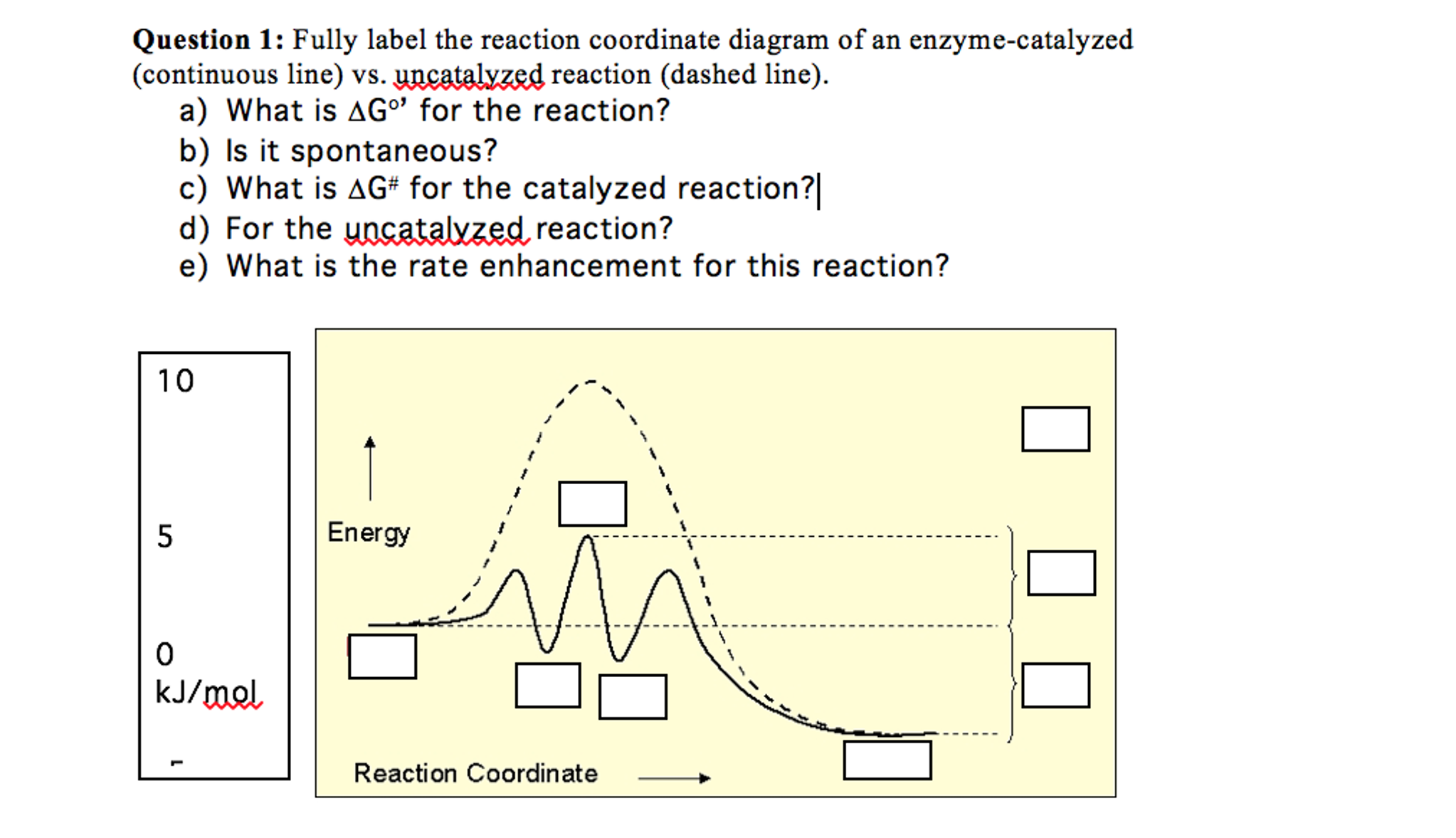
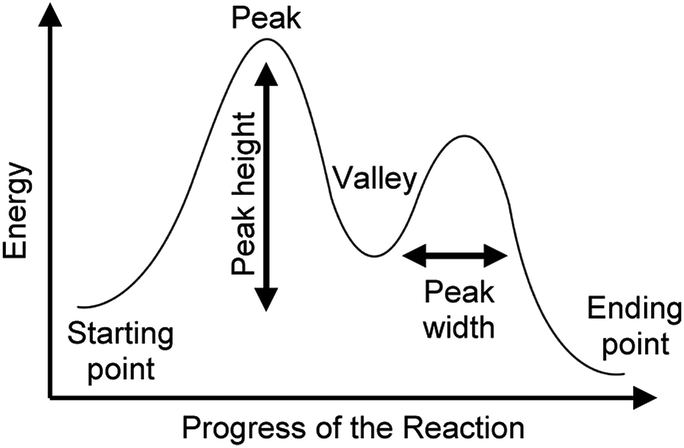
43 Enzyme Reaction Coordinate Diagram
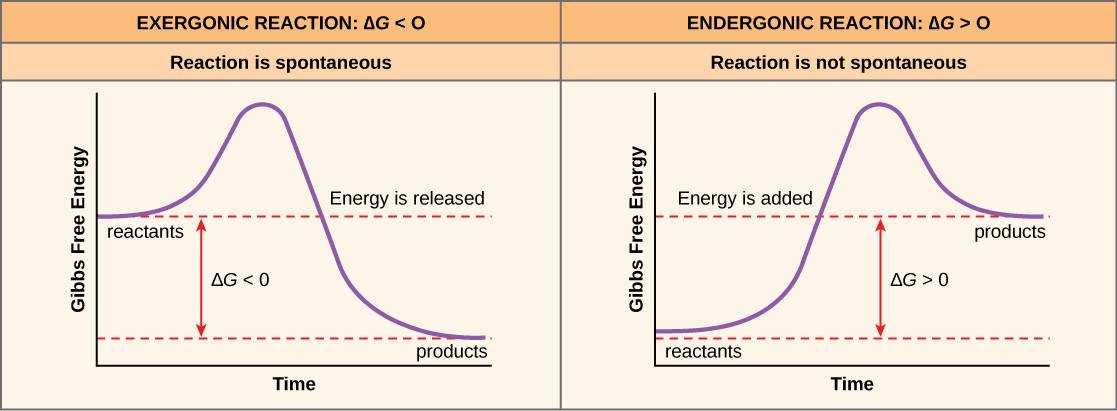
Chapter 6 Notes | PDF | Enzyme Inhibitor | Enzyme Reaction Coordinate Diagram. Enzymatic Catalysis Enzymes do not affect equilibrium (G) Slow reactions face significant activation barriers (G) that must be surmounted during the reaction Enzymes increase reaction rates (k) by decreasing G. PDF 05_02_Lecture_02_23_2018.pptx | A Reaction Coordinate Diagram A reaction coordinate diagram shows the energy changes that take place in each step of a reaction. Thermodynamics and Kinetics. Thermodynamics: • are products more stable than starting materials? • overall, are new bonds in products stronger than the old in starting materials? • deals with equilibria.
Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Download scientific diagram | Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. from publication: Design, synthesis and characterization of enzymeanalogue-built polymer catalysts as ... a simple enzyme-catalyzed reaction scheme (Figure 4), the reaction coordinate diagram shows that...

Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram
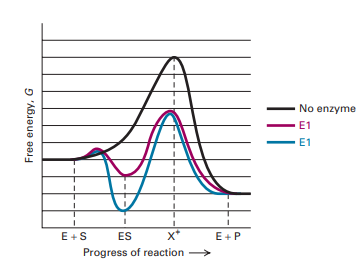
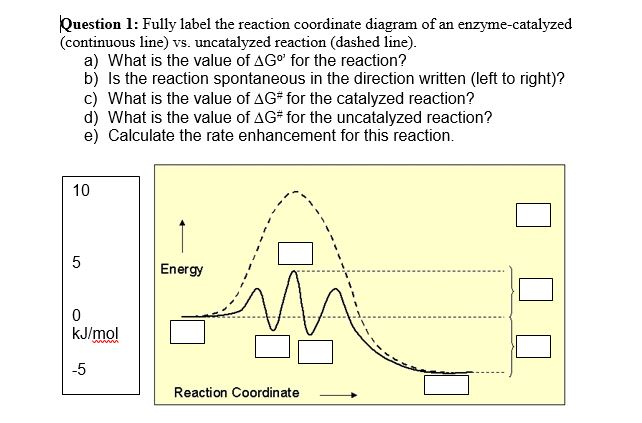
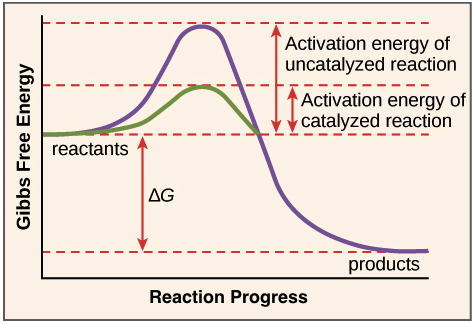
CHEM 440 - Enzyme kinetics Left: Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction representing the mechanistic model we are considering. The free energy of activation, ΔG‡, which for our present purposes can be considered as equivalent to activation energy, is much lower for the catalyzed reaction compared... chemistry-book/m51104.md at master · philschatz/chemistry-book A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction The study of enzymes is an important interconnection between biology and chemistry. BCHM Lecture 21 pt. 2 Flashcards | Quizlet What can a reaction coordinate diagram for enzymes be used for. Describe what creates the energy curve of enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams. Energy is required to go into the system to convert between substrate to product, and this energy input is reflected by the energy curve.
Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams - Isotope Effects FIGURE 3.24 A hypothetical reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed chemical reaction. Energetics of a two-step reaction: enzyme and substrate combine to form a E • S complex by way of a first transition state EX^, followed by turnover of the E S complex into E + Products. PDF Introduction to Enzymes | (3) Greater reaction specificity Reaction coordinate diagram for an overall reaction with two elementary reaction steps. - Transition state theory tells us the free energy difference between reactant and transition state reflect rate and the slowest step has the largest difference. - two cases - step 1 slow (green); step 2 slow (red). PDF CHAPTER 4 | Factors that Affect the Rate of Enzyme Reactions Enzymes are proteins, and their function is determined by their complex structure. The reaction takes place in a small part of the enzyme called the active site, while the rest of the protein acts as "scaffolding". This is shown in this diagram of a molecule of the enzyme trypsin, with a short length of... Enzyme function | Osmosis Enzymes are proteins that play a major role in the biochemical reactions happening every moment inside our bodies - everything from digesting a bowl of ramen noodles to Every biochemical reaction has a substrate and a product - so let's put them on this graph called a reaction coordinate diagram.
7.1 Concept Review for Enzyme Reactions Coordination of heme cofactors with their enzyme counterparts often involves electrostatic interactions with histidine residues as shown in the succinate Figure 7.16 Common Peptidase Reactions. Aminopeptidases (top diagram) and carboxypeptidases (middle diagram) remove the terminal amino... PDF Chemical Kinetics Reaction Coordinate Diagrams. • It shows the energy of the reactants and products (and, therefore, DE). • The high point on the diagram is the transition state. The substrate fits into the active site of the. enzyme much like a key fits into a lock. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College. Enzyme Catalysis - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Some enzymes can catalyse reactions without requiring cofactors. Other enzymes require the presence of metal ions for full catalytic activity : these ions can play Enzyme-catalyzed reactions do not obey the classical kinetic laws that relate to chemical reactions carried out in homogeneous media. PDF 12_13_14_15_16ab_17_Enzymes - Reaction coordinate written as a horizontal line - Substrates binding with arrow down; substrates are denoted in order A, B, C - Products released with Let's review what governs the rates of chemical reactions: the. look like using an enzyme? transition state energy Reaction Coordinate Diagram.
Reaction Coordinate Diagram Enzymes enhance... | Course Hero of catalytic functional groups on enzyme (Enzymes: induced fit) Rate enhancement by entropy reduction o Induced Fit o Induced Fit mechanism is most Regulation of Enzyme Catalytic Activity o Modification of protein structure leads to modification of protein activity Covalent Modification... PDF Part II Structure and Catalysis James Sumner 1887-1955 Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme- catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. In the reaction P, the ES and EP intermediates occupy minima in the energy progress curve of the plexes are intermediates (Eqn 8-1); they occupy valleys in the reaction co- ordinate diagram (Fig. Enzymes and Reaction Rates Enzymes and Reaction Rates. Chemical reactions occur when molecules interact and chemical bonds between them are formed or broken. In biology, chemical reactions are often aided by enzymes, biological molecules made of proteins which can be thought of as facilitators or catalysts. Description of the Reaction Coordinate - YouTube Explains the energy versus reaction coordinate diagram. Relates the activation energies for the forward and reverse reactions of an exothermic reaction to...
Thermodynamic framework for identifying free energy... | PNAS 2. (C) Reaction coordinate diagram for the enolization of androstene (S) to the dienolate intermediate (I), either in KSI (black) or in solution (red). (1981) Calculations of enzymatic reactions: Calculations of pKa, proton transfer reactions, and general acid catalysis reactions in enzymes.
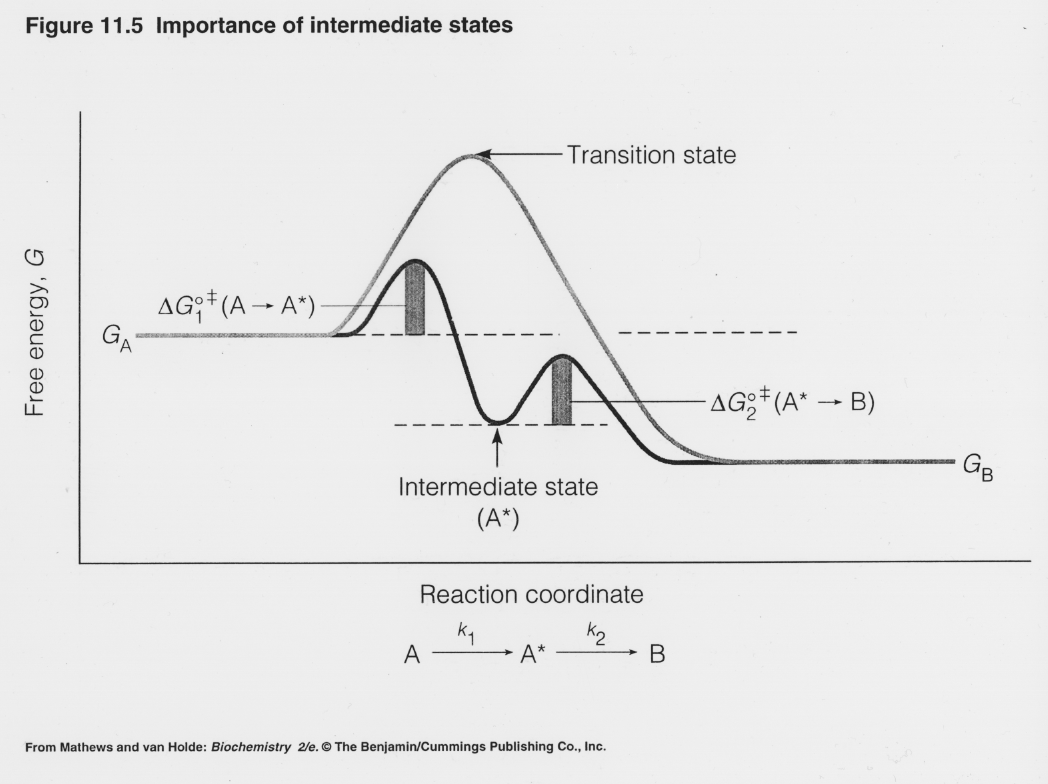
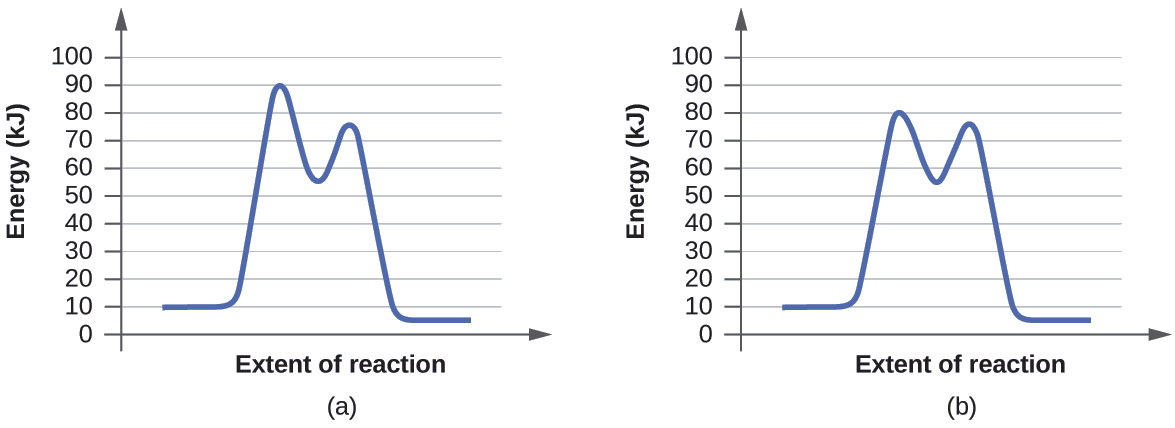
6. Reaction Coordinate Diagram Given the following reaction, sketch a reaction coordinate graph. The reaction involves two steps, step 1 is the slowest step and step 2 is the fastest step. Both steps are exothermic. Indicate on the diagram the overall enthalpy change of the reaction, the reaction for the transition states and...
Reaction coordinate diagram enzyme - Big Chemical Encyclopedia Figure 3. Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. Figure 8.58 Schematic illustration of reaction coordinate diagram of Triose Phosphate Isomerase (TIM) enzyme illustrating near perfect energy landscape pathway allowing for near perfect 1 1 1...
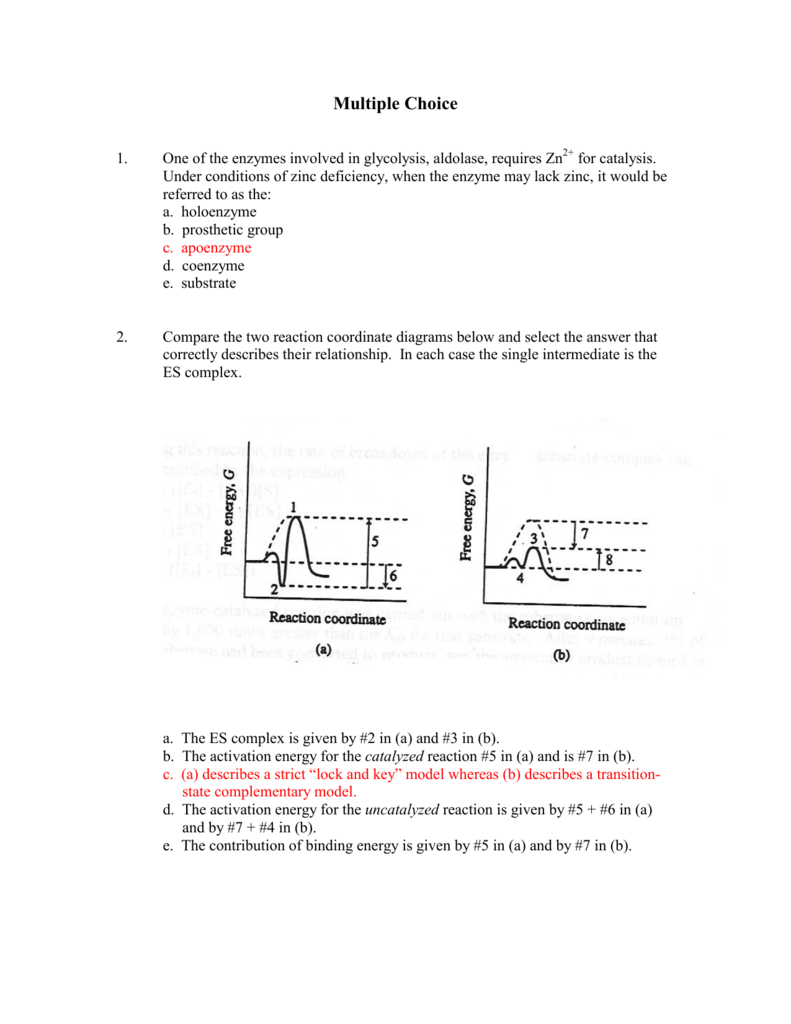
Solved Use the reaction coordinate diagram of an enzyme ...diagram of an enzyme catalyzed reaction shown below to answer Questions 5 through 10 From this diagram you can conclude: (A) The forward reaction is (D) the enzyme binding P. (E) the release of P from the enzyme. The point El on the reaction coordinate diagram corresponds to: (A) a dead end.
Energy profile (chemistry) - Wikipedia For a chemical reaction or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical representation of a single energetic pathway, along the reaction coordinate, as the reactants are transformed into products.
4.6: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, ...Oct 17, 2019 · Uploaded by Layne Morsch
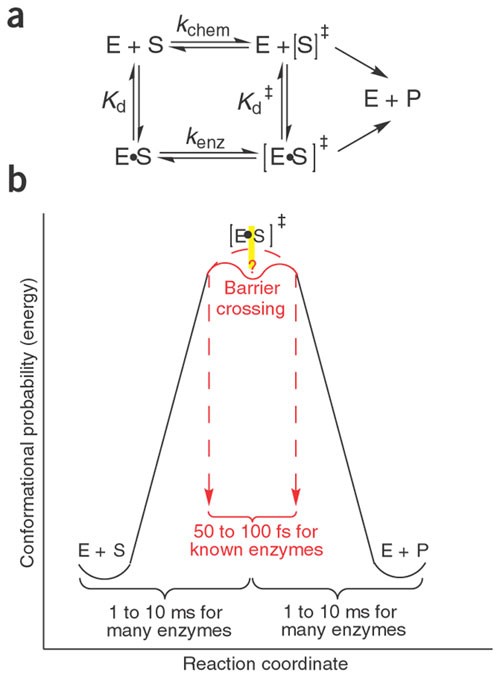
Dynamical origins of heat capacity changes in enzyme-catalysed... This has general implications for understanding enzyme catalysis and demonstrating a direct connection between functionally important microscopic dynamics and macroscopically measurable quantities. Heat capacity changes affect the temperature dependence of enzyme catalysis, with...
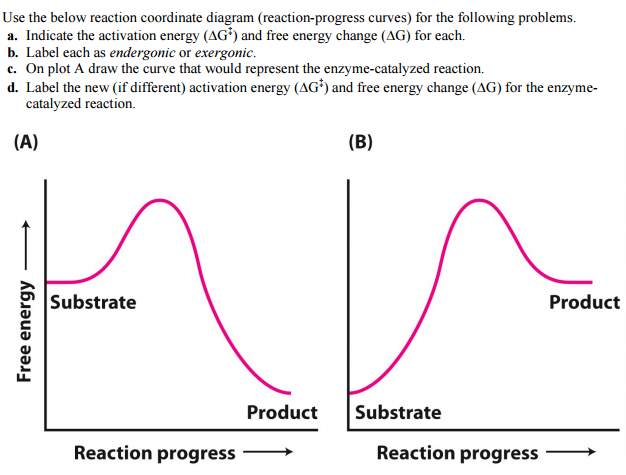
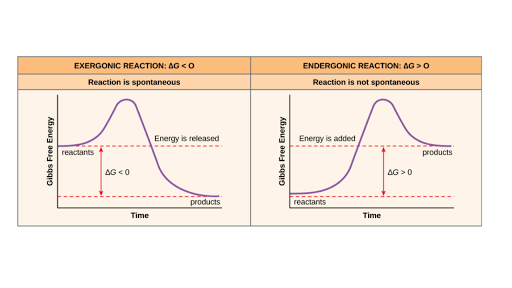
6.6: Reaction Coordinate Diagrams - Chemistry LibreTexts 6.6: Reaction Coordinate Diagrams. Last updated. Save as PDF. The energy diagram for a typical one-step reaction might look like this: Despite its apparent simplicity, this energy diagram conveys some very important ideas about the thermodynamics and kinetics of the reaction.
PDF Compare and contrast the reaction coordinate diagrams for chemical... ABSTRACT Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to relate the free energy changes that occur during the progress of chemical processes to the rate and equilibrium constants of the process. Here I briefly review the application of these diagrams to the thermodynamics and kinetics of the generation...
PDF Measurement of β -Galactosidase Reaction Coordinate Diagram comparing enzyme catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. The catalyst offers an alternate reaction pathway (shown in red) where the activation energy (Ea) for the overall process is lower when the enzyme catalyzes the reaction.
Enzyme Kinetics - Structure - Function - Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Enzyme Function. Enzymes provide an alternative pathway for a reaction, which has a lower activation energy (Ea) - the minimum energy input needed for The rate-limiting step of any reaction is its slowest step, and this is what sets the pace of the entire reaction. In enzymatic reactions, the...
PDF Voet_chapt_11.ppt reaction coordinate 3. Catalytic mechanism 4. Lysozyme 5. Serine proteases. Enzyme act with great speed and precision. Introduction. Reactants approach one another along a path of minimal free energy = reaction coordinate. Transition state diagram/reaction coordinate diagram: Plot of free...
Six types of enzymes (video) | Biomolecules | Khan Academy Enzymes are often named for their reactions, and you can often discern the function of an enzyme from its name. We will learn about six types of But before we do that, let's review the idea that enzymes make biochemical reactions go faster. And if you look at a reaction coordinate diagram...
BCHM Lecture 21 pt. 2 Flashcards | Quizlet What can a reaction coordinate diagram for enzymes be used for. Describe what creates the energy curve of enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams. Energy is required to go into the system to convert between substrate to product, and this energy input is reflected by the energy curve.
chemistry-book/m51104.md at master · philschatz/chemistry-book A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) Identify which diagram suggests the presence of a catalyst, and determine the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction The study of enzymes is an important interconnection between biology and chemistry.
CHEM 440 - Enzyme kinetics Left: Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction representing the mechanistic model we are considering. The free energy of activation, ΔG‡, which for our present purposes can be considered as equivalent to activation energy, is much lower for the catalyzed reaction compared...

.png)















0 Response to "43 Enzyme Reaction Coordinate Diagram"
Post a Comment