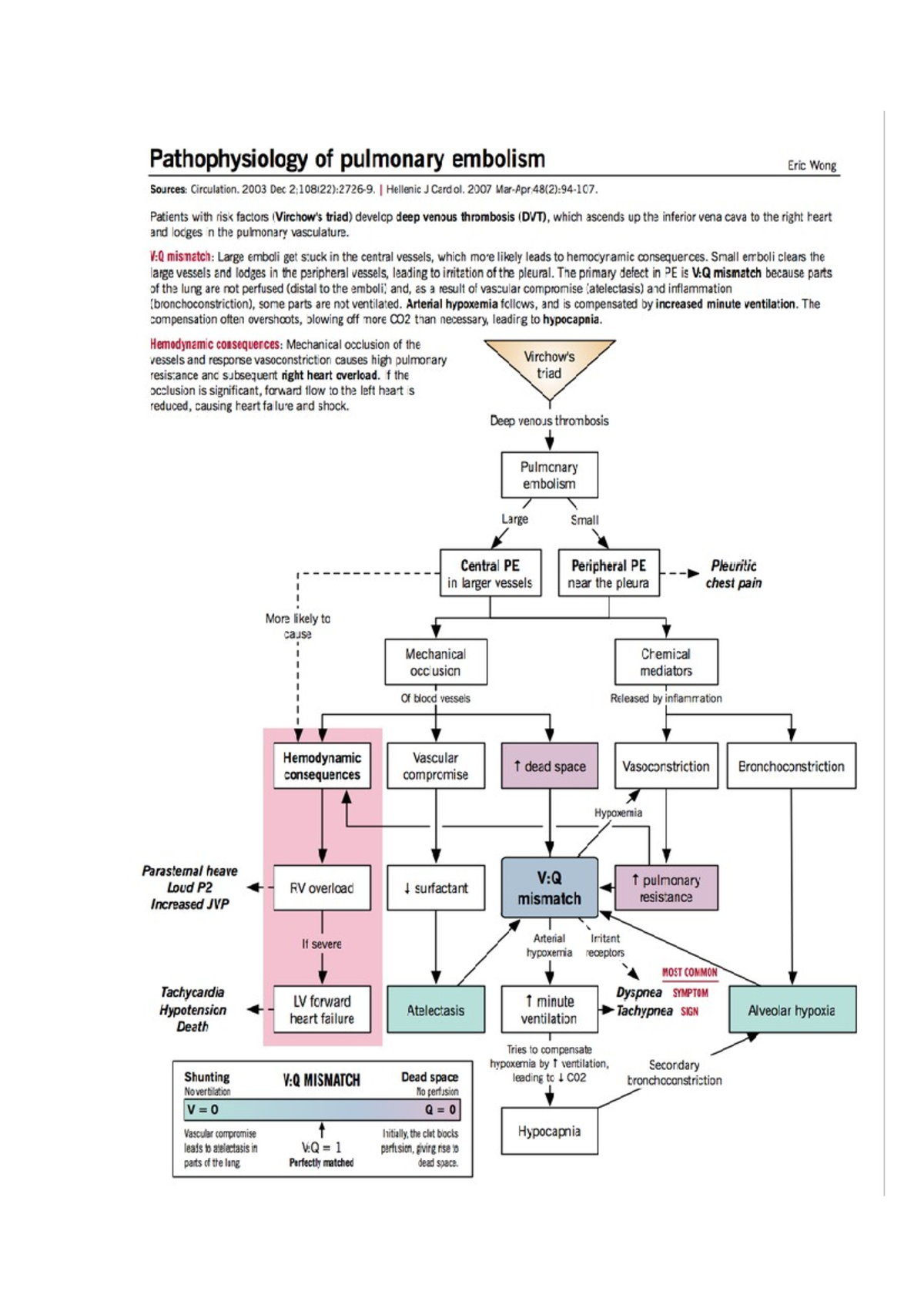
41 pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram
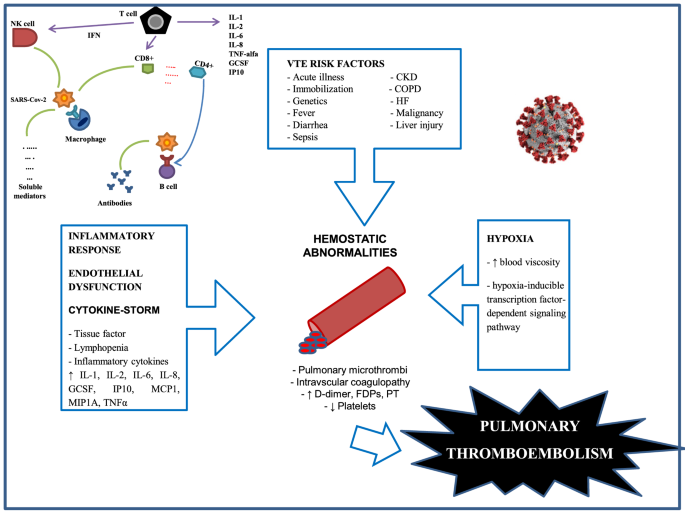
Современные проблемы патогенеза и диагностики... Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a frequent urgent cardiovascular conditions. The main cause of PE is thrombosis of deep veins of lower limbs. Key words: pulmonary embolism, pathophysiology, diagnostics. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary embolism symptoms; info | Patient Pulmonary embolism is a medical emergency. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a medical emergency. It may present with very few clinical signs and/or symptoms, making it easy to miss, and a high index of suspicion is warranted.
Nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism | European Respiratory Society Nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism (NTPE) is defined as embolisation to the pulmonary circulation of different cell types (adipocytes, haematopoietic, amniotic, trophoblastic or tumour), bacteria, fungi, foreign material or gas. The purpose of this article is to describe the clinical signs, pathogenesis...

Pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram
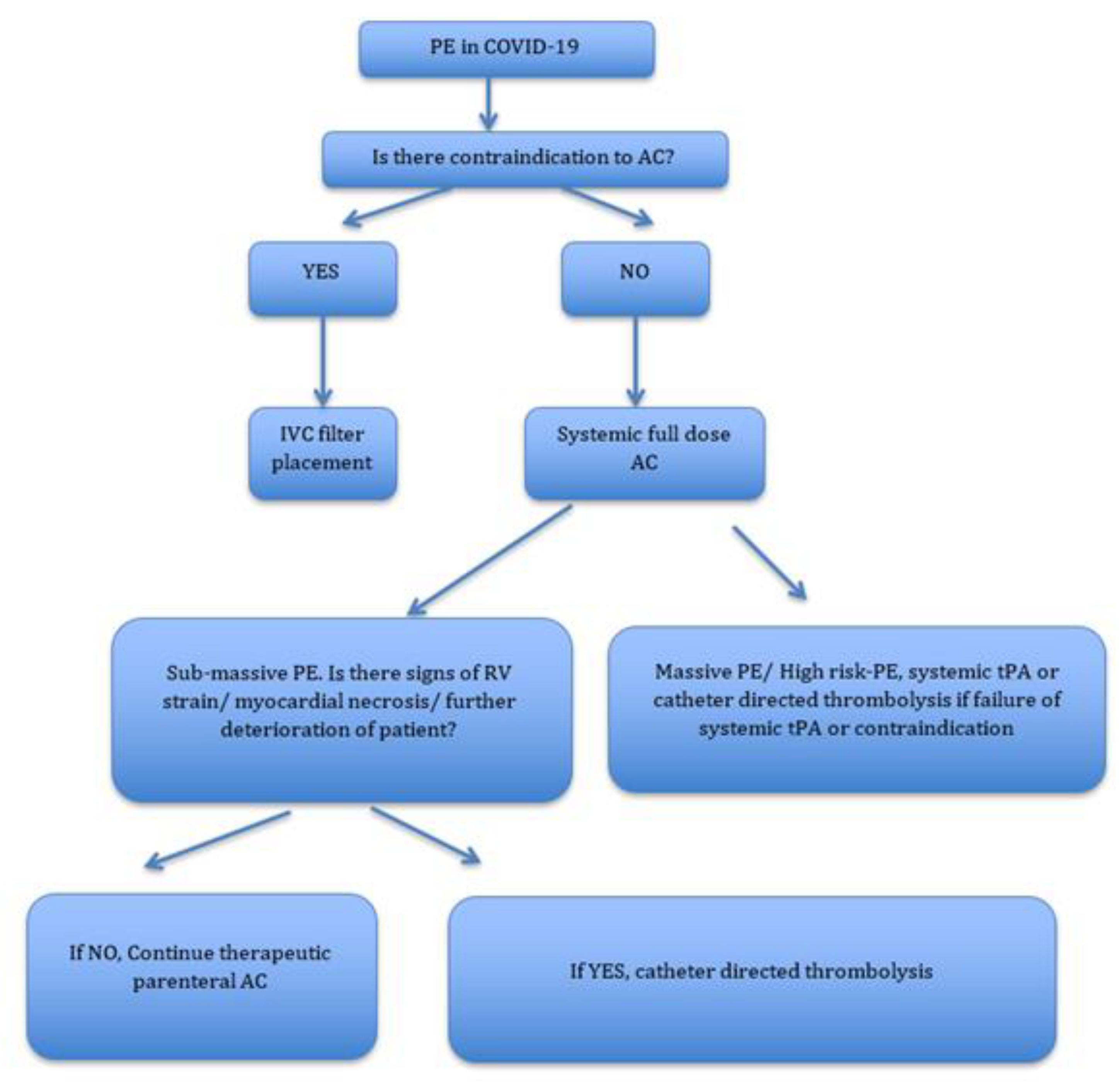
Pulmonary embolism: clinical guidelines of European Society Key words: recommendations, pulmonary embolism, venous thromboembolism, shock, hypotension, chest pain, dyspnea, heart failure, diagnosis, anticoagulants, thrombolysis. Natural history, pathophysiology, and diagnosis. Pulmonary Embolism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and sometimes fatal disease that continues to persist despite advances in This review will discuss the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of PE. Pulmonary Embolism. Douglas P. Zipes MD, in Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of... Pulmonary Embolism and Other Pulmonary Artery... | Radiology Key Pulmonary embolism CT scanning may identify other lesions responsible for chest pain or acute dyspnea presentations. Pulmonary Artery Anatomy. Normally, there are 17 bronchopulmonary segments, any of which may develop an embolism.
Pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram. lungs.thecommonvein.net › histologyHistology | Lungs - The Common Vein 1. Pulmonary Circulation. The pulmonary circulation is set apart from the other systemic circulations by the fact that has a smaller amount of smooth muscle and less surrounding tissue, thus making it more distensible and increasing its capacitance. The pulmonary circulation can be divided into 2 on the bases of the connective tissue ... Lund and Browder chart - Wikipedia The Lund and Browder chart is a tool useful in the management of burns for estimating the total body surface area affected. It was created by Dr. Charles Lund, Senior Surgeon at Boston City Hospital, and Dr. Newton Browder, based on their experiences in treating over 300 burn victims injured at the Cocoanut Grove fire in Boston in 1942.. Unlike the Wallace rule of nines, the … Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism... Pulmonary embolism (PE) is not a disease by itself but may have a venou s thrombotic. source and is therefore more precise if cl assified as venous patients without shock. Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary. Embolism Focusing on Thrombolysis - New approaches. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Pleural_effusionPleural effusion - Wikipedia A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.01 millilitre per kilogram weight per hour, and is cleared by lymphatic absorption leaving behind only 5–15 millilitres of fluid, which helps to maintain a functional ...
Pulmonary Embolism - Pulmonary - Medbullets Step 2/3 Amniotic fluid embolism. Pathophysiology. occlusion of the pulmonary vasculature results in hypoxemia and subsequent pulmonary the increased pulmonary constriction causes an increase in pulmonary vascular resistance, which decreases right ventricular stroke volume leading to. › content › 370Pulmonary embolism: update on management and ... - The BMJ Aug 05, 2020 · Pulmonary embolism is a common and potentially fatal cardiovascular disorder that must be promptly diagnosed and treated. The diagnosis, risk assessment, and management of pulmonary embolism have evolved with a better understanding of efficient use of diagnostic and therapeutic options. The use of either clinical probability adjusted or age adjusted D-dimer interpretation has led to a ... Pulmonary Embolism: Overview and More Pulmonary Embolism Guide. Overview. Symptoms. A smaller pulmonary embolism causes less significant symptoms but is still a medical emergency that can be Bĕlohlávek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A. Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology... Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy The pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism. Although pulmonary embolism can arise from anywhere in the body, most commonly it arises from the calf veins. The venous thrombi predominately originate in venous valve pockets (inset) and at other sites of presumed venous stasis.
Pulmonary Embolism - pathophysiology - NURS 7320... - StuDocu Pulmonary Embolism Definition: Blockage of 1 or more pulmonary arteries by a thrombus, fat or air embolus, or tumor tissue. The word embolus derives from the Greek word meaning "plug". A PE that gains access to the venous system and then to the pulmonary circulation. Pulmonary Embolism - Physiopedia Original Editor Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka. Top Contributors - Uchechukwu Chukwuemeka, Karen Wilson, Kim Jackson and Rachael Lowe. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. In most cases, a deep venous thrombosis (DVT) forms in the leg. Pulmonary Embolism • LITFL • CCC Respiratory Pulmonary embolism (PTE, PE) ranges from asymptomatic to a life threatening catastrophe. PE occurs when a deep vein thrombosis migrates to the pulmonary arterial tree. those with none of the above severe features are non-massive or low risk PEs. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis | Anesthesia Key Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Vascular Occlusion. The pulmonary vascular tree normally has a low resistance to fluid flow, and young persons without Classic Risk Factors and Physiologic Findings for Pulmonary Embolism. DVT, deep vein thrombosis; PE, pulmonary embolism...
[PDF] Pulmonary embolism: pathophysiology... | Semantic Scholar Pulmonary embolism: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment. @article{Kostadima2007PulmonaryEP, title={Pulmonary embolism: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment.}, author={Eleni Kostadima and Epaminondas G Zakynthinos}, journal={Hellenic journal of...
Pulmonary Embolism - Pathophysiology Flashcards | Quizlet Pathophysiology. Thrombus formation Occlude pulmonary circulation Decreased surfactant production - clot prevents alveoli from producing surfactant - harder If a D-Dimer is ordered it means the physician is considering a Pulmonary Embolism as one of their Differential Diagnoses (DDx).
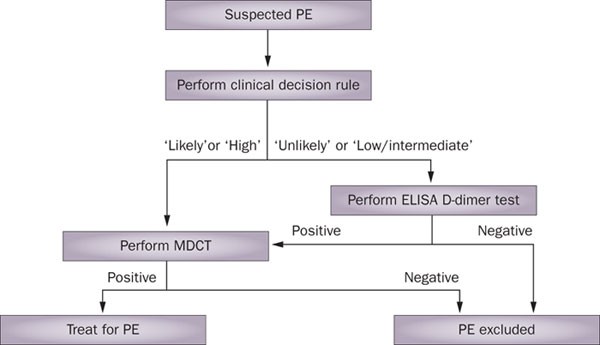
PDF Op-ehea190412 1..61 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration 8 3.2 Predisposing factors . . ... . 9 3.3 Pathophysiology and determinants of 18 5 Assessment of pulmonary embolism severity and the risk of early...
Acute pulmonary embolism 1: pathophysiology, clinical... | Heart Fatal pulmonary embolism occurs in 0.5-0.8% of unprotected patients older than 40 years undergoing major abdominal surgery. About one in 20 patients after Pathophysiology and clinical presentation. The effects of an embolus depend on the extent to which it obstructs the pulmonary circulation, the...
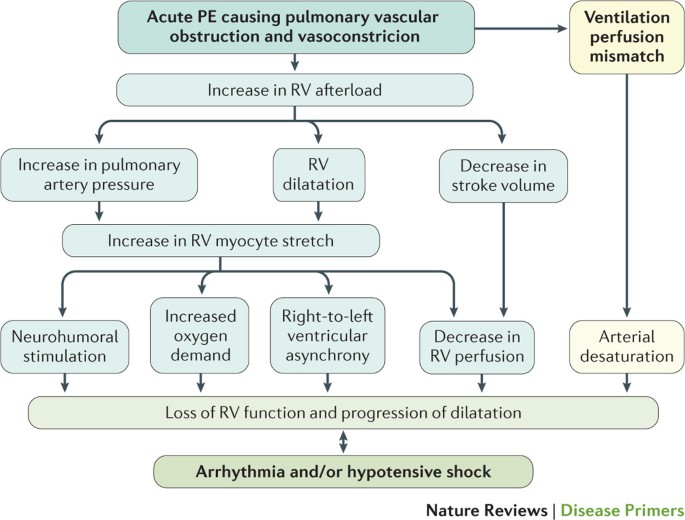
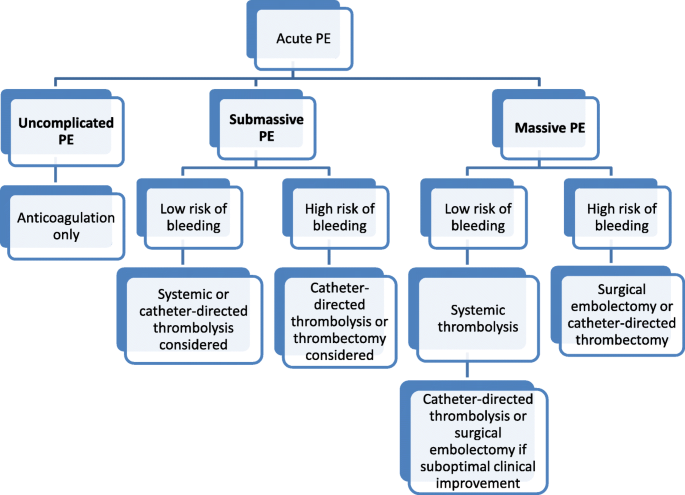
PDF untitled | 2.5 Clinical classication of pulmonary embolism severity management of acute pulmonary embolism. 2.4 Pathophysiology. Acute PE interferes with both the circulation and gas exchange. Right ventricular (RV) failure due to pressure overload is considered the primary cause of death in severe PE.
› contents › chronic-obstructiveChronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Definition, clinical ... Nov 16, 2021 · Cardiovascular-pulmonary interaction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with special reference to the pathogenesis and management of cor pulmonale. Med Clin North Am 1990; 74:571. Iyer AS, Wells JM, Vishin S, et al. CT scan-measured pulmonary artery to aorta ratio and echocardiography for detecting pulmonary hypertension in severe COPD.
Page: American Journal of Cardiology Impact of Multidisciplinary Pulmonary Embolism Response Team Availability on Management and Outcomes Chaudhury et al. American Journal of Cardiology, Vol.124, No.9, p1465-1469
Pulmonary Embolism - Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis... Pulmonary embolism causes, risk factors, prevention, signs and symptoms, diagnosis & treatment. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery that is usually caused a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ThrombusThrombus - Wikipedia A thrombus, (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis.There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein.
Pulmonary Embolism Nursing Care and Management: Study Guide Pulmonary embolism refers to the obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by a thrombus that originates somewhere in the venous system or in the right side of the heart. What is Pulmonary Embolism? Classification. Pathophysiology. Statistics and Epidemiology. Causes.
Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: Pathology... | Osmosis Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT and pulmonary embolism, or PE are a spectrum of clinical manifestations that result Okay, so large emboli that occlude the pulmonary trunk place tremendous amounts of sudden pressure on Okay, now let's tie the pathophysiology to the clinical presentation.
Pulmonary Embolism l Diagnosis l Basic Testing l Treatment Pulmonary embolism is serious disease of human beings. But now a day we can easily diagnose it by its sign and symptoms..... Anticoagulation. Thrombolytic therapy. Prognosis for pulmonary embolism. Prevention. Nursing care plan. References.
UNUSUAL CAUSES OF CUTANEOUS ULCERATION Cholesterol embolism (CE) (Figure 6B [E1]) Patients present with varied skin manifestations such as livedo reticularis, purpura, cyanosis, blue toes, digital gangrene, painful subcutaneous nodules, renal failure; interestingly, arterial hypertension is very uncommon. Patients may also have fever, weight loss, myalgia, and anemia. Large vessels ...
Pulmonary embolism differential diagnosis - wikidoc Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. The APEX Trial Investigators; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Rim Halaby, M.D. Pulmonary embolism must be distinguished from other life-threatening causes of chest pain including acute myocardial infarction, aortic dissection...
Pulmonary embolism | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org Pulmonary embolism (PE) refers to embolic occlusion of the pulmonary arterial system. The majority of cases result from thrombotic occlusion, and therefore the condition is frequently termed pulmonary thromboembolism which is what this article ma...
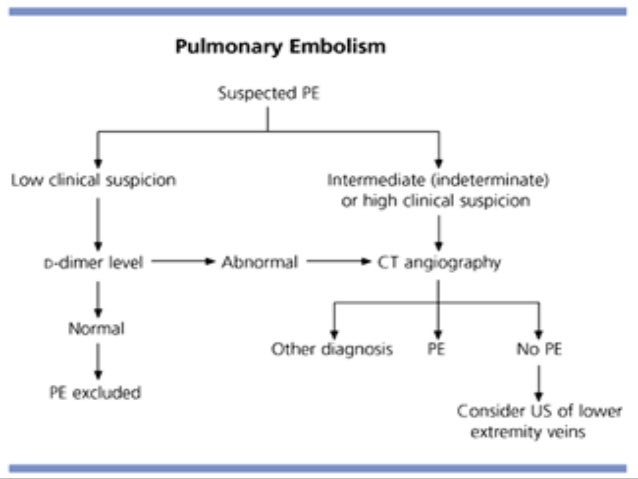
Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism Pulmonary Embolism (PE) - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the MSD Manuals - Medical Professional Version. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is most commonly accomplished with CT angiography, although ventilation/perfusion scanning is sometimes...
› 36280928 › Pathophysiology_of(PDF) Pathophysiology of Disease - An Introduction to ... Pathophysiology of Disease - An Introduction to Clinical Medicine, 7th Ed . × Close Log In. Log in with Facebook Log in with Google. or. Email. Password. Remember me on this computer. or reset password. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. ...
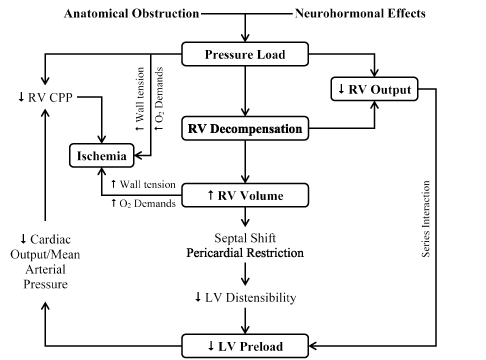
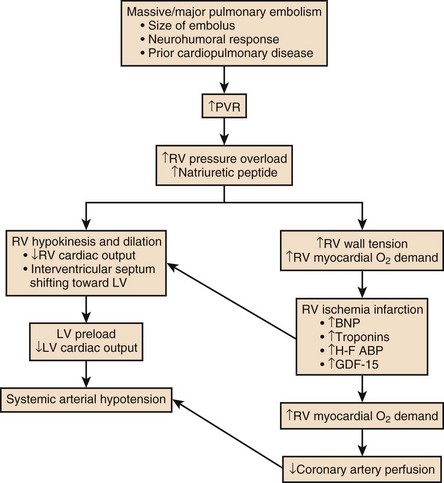
[Pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism] [Pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. Massive pulmonary embolism causes an acute pressure overload for the right ventricle associated with a drop in cardiac output leading, if untreated, to cardiogenic shock.
Pulmonary Embolism | Etiology, Pathophysiology... - YouTube Pulmonary Embolism | Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Treatment. Смотреть позже. Поделиться.
Right axis deviation - Wikipedia The pathophysiology depends on the specific cause of right axis deviation. Most causes can be attributed to one of four main mechanisms. Most causes can be attributed to one of four main mechanisms. [14] [15] These include right ventricular hypertrophy , reduced muscle mass of left ventricle, altered conduction pathways and change in the position of the heart in the chest.
Pulmonary Embolism | Concise Medical Knowledge Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a potentially fatal condition that occurs as a result of intraluminal obstruction of the main pulmonary artery or its branches by material (e.g., thrombus, air, amniotic fluid, or fat). Pulmonary Embolism: Risk Factors. Pathophysiology.
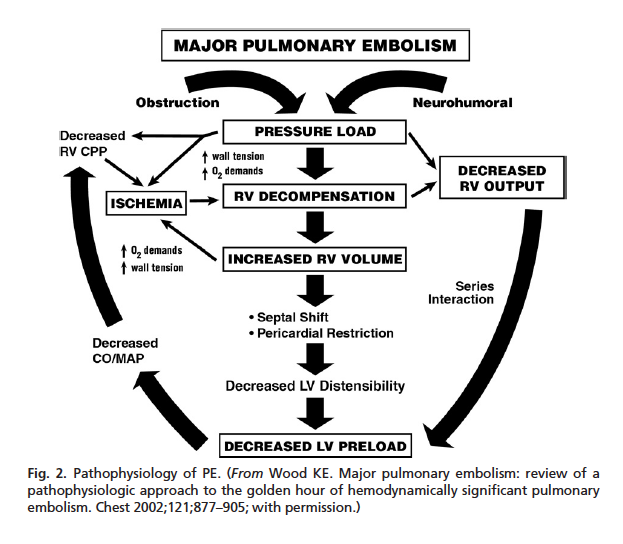
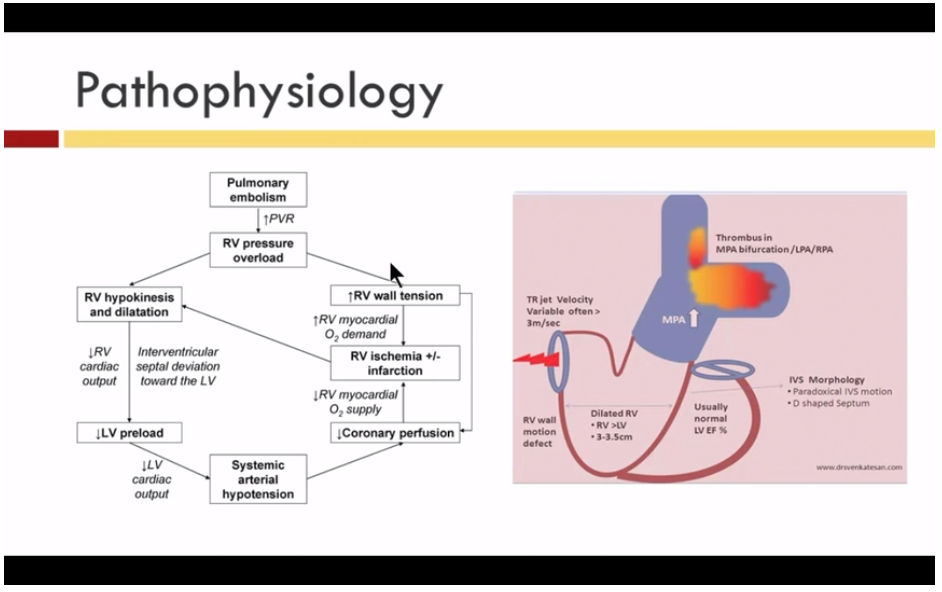
Pathophysiology of right ventricular failure in acute pulmonary... Pulmonary embolus (PE) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular death with more than We review here the pathophysiology of right ventricular (RV) failure in acute massive and Wood KE (2002) Major pulmonary embolism: review of a pathophysiologic approach to the golden hour of...
Pulmonary Embolism and Other Pulmonary Artery... | Radiology Key Pulmonary embolism CT scanning may identify other lesions responsible for chest pain or acute dyspnea presentations. Pulmonary Artery Anatomy. Normally, there are 17 bronchopulmonary segments, any of which may develop an embolism.
Pulmonary Embolism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and sometimes fatal disease that continues to persist despite advances in This review will discuss the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of PE. Pulmonary Embolism. Douglas P. Zipes MD, in Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of...
Pulmonary embolism: clinical guidelines of European Society Key words: recommendations, pulmonary embolism, venous thromboembolism, shock, hypotension, chest pain, dyspnea, heart failure, diagnosis, anticoagulants, thrombolysis. Natural history, pathophysiology, and diagnosis.

























0 Response to "41 pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram"
Post a Comment