42 d flip flop state diagram
PDF Timing Diagrams: Example: Rising-Edge Triggered JK Flip-Flop... - Flip-Flops are synchronous devices that are edge-triggered - Edge-triggered devices update their outputs when the clock changes states Notes: This timing diagram ignores propagation delays. The resulting sums should be latched on the falling edge of the clock cycle. D Flip Flop design simulation and analysis using different software's Figure 17: Block Diagram of D Flip Flop. Truth table of synchronous D Flip-Flop which is clocked to the rising edge of input clock. TFF changes state on every rising clock edge can be created by adding feedback loop Qbar to data input. To establish one at output initially, we have to define an...
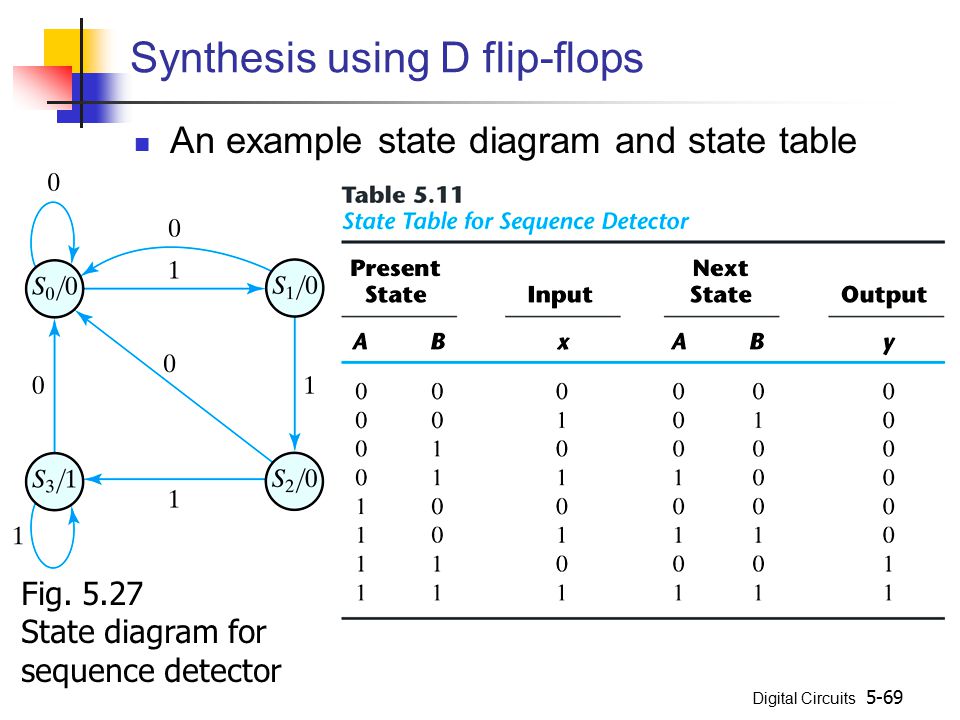
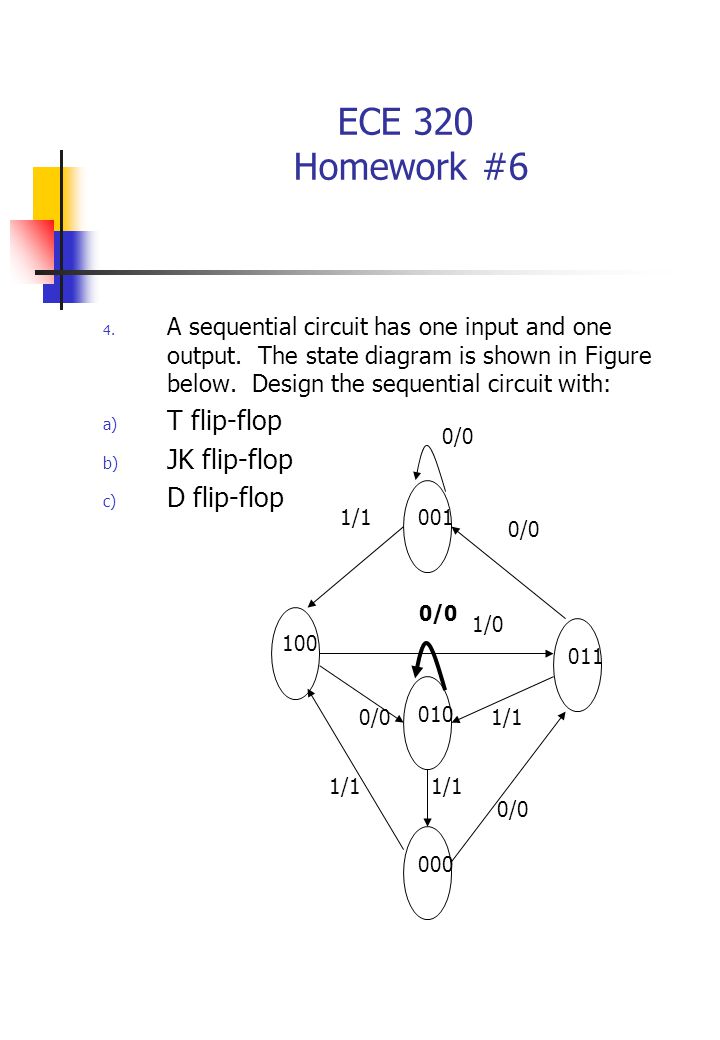
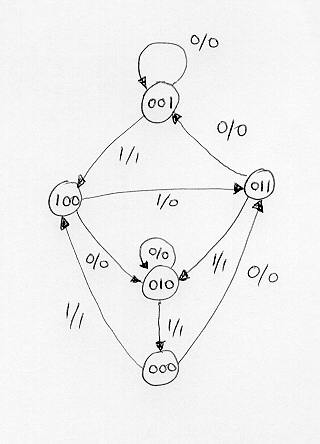
PDF Microsoft Word - Solution6_3rd_edition.doc Page: 5. The state diagram has two states State 0 : Output = Input State1 : Output = Complement of input PS Inp. NS Out A xAy 0 000 0 111 1 011 1 110 DA= A + x y=A⊕x. 5-19) A sequential circuit has three flip-flops A, B, C; one input x; and one output, y. The state diagram is shown in Fig.P5-19.
D flip flop state diagram
PDF PowerPoint Presentation | First: D-latch state function D-flip-flop state diagram. Slide Number 26. Synthesis of asynchronous circuits. Exemple: serial paritety circuit. • All flip-flops and latches are themselfes asynchronous state machines • They are useful to synchronize events in situations where metastability is/can be a problem. Flip flop's state tables & diagrams 7. The D flip-flop has the following state table ▪ Note that changes on clock edge are always assumed The corresponding state diagram is ▪ Again, transitions occurs only on a clock edge. 11. TheT flip-flop state table The State Diagram is Q Q(next) T 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0. D Flip Flop Explained in Detail - DCAClab Blog These flip flops use feedback concept to create sequential logic where the previous state affect future states (unlike combinational circuit). The D in the D flip flop represents the data (generation, processing, or storing) in the form of states. The two states are binary, 0 (Low) and 1 (High), set or...
D flip flop state diagram. D Flip-Flop Circuit Diagram: Working & Truth Table Explained D Flip-flops are used as a part of memory storage elements and data processors as well. D flip-flop can be built using NAND gate or with NOR gate. Below we have described the various states of D type Flip-Flop using D flip flop circuit made on breadboard. Master Slave Flip Flop | Circuit Diagram and Timing ... Fig. Circuit diagram of Master Slave D flip flop designed with NAND gates. Master Slave edge triggered D Flip Flop. When the state of a flip-flop changes during the transition of a clock, the pulse is known as an edge-triggered flip-flop and these can be +ve edge-triggered, or -ve edge-triggered. The +ve Edge triggered flip flop means the state of it changed during the transition … The J-K Flip-Flop | Multivibrators | Electronics Textbook Conversely, a “reset” state inhibits input K so that the flip-flop acts as if J=1 and K=0 when in fact both are 1. The next clock pulse toggles the circuit again from reset to set. Logical Sequence of J-K Flip-Flop. See if you can follow this logical sequence with the ladder logic equivalent of … Flip Flop Conversion-SR to JK,JK to SR, SR to D,D to SR,JK ... That is, the values of S and R that are required to change the state of the flip flop from Qp to Qp+1 are written. SR Flip Flop to JK Flip Flop. JK Flip Flop to SR Flip Flop ; This will be the reverse process of the above explained conversion. S and R will be the external inputs to J and K. As shown in the logic diagram below, J and K will be the outputs of the combinational circuit. …
Flip Flop | Truth Table & Various Types | Basics for Beginners A flip flop is an electronic circuit with two stable states that can be used to store binary data. The stored data can be changed by applying varying inputs. In this circuit diagram, the output is changed (i.e. the stored data is changed) only when you give an active clock signal. Otherwise, even if the S or... PDF Lecture 1: Introduction to Digital Logic Design | Analysis with D Flip-flop • Draw the logic diagram with flip-flops and clock inputs. • Logic diagram may or may not include the combinational circuits. Two states are said to be equivalent, if for each member of the set of. inputs, they give exactly same output and send the circuit either to the same stare or to an equivalent state. Digital Circuits - Flip-Flops | Next State The circuit diagram of SR flip-flop is shown in the following figure. This circuit has two inputs S & R and two outputs Q(t) & Q(t)'. The operation of Next state of D flip-flop is always equal to data input, D for every positive transition of the clock signal. Hence, D flip-flops can be used in registers, shift... D Flip Flop: Circuit, Truth Table, Working, Differences, Diagrams D Flip Flop Introduction | D Flip Flop Theory. A flip flop is the fundamental sequential circuit element, which has two stable states and can store one bit at a time. The given circuit represents the D flip-flop circuit diagram, where the whole circuit is designed with the help of the NAND gate.
PDF Digital Logic Design Gate Level Minimization desired operation, derive a state diagram of the circuit 2. Assign binary values to the states 3. Obtain the binary-coded state table 4. Choose the type of flip-flop to be used 5. Derive the simplified flip-flop input and output. equations 6. Sketch the logic diagram. D Flip Flop (D Latch): What is it? (Truth Table & Timing Diagram) Learn what a D Flip Flop is, see the D Latch Truth Table, and a diagram of a D Flip Flop circuit. We also discuss a Gated D Latch ... This is why this type of single input Flip flop is known as a D-Flip Flop or D Latch. The basic logical representation (i.e. circuit diagram) of a D-flip flop is shown below. D Flip Flop State Diagram - Wiring Diagram Source Derive input equations 5. It can also be used for counting of pulses and for synchronizing variably timed input signals to some reference t... state diagram/state table/circuit diagram (using D-flip flop) - Digital... A method to solve combination of 3 or more 1(s) using state tables and the consequently applying principle of D flip flophope this video was helpful.
Edge-triggered Flip-Flop, State Table, State Diagram Edge-triggered Flip-Flop, State Table, State Diagram . Edge-triggered Flip-Flop • Contrast to Pulse-triggered SR Flip-Flop • Pulse-triggered: Read input while clock is 1, change output when the clock goes to 0. What happens during the entire HIGH part of clock can affect eventual output. • Edge-triggered: Read input only on edge of clock cycle (positive or negative) • Example …
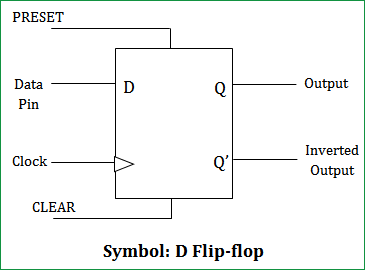
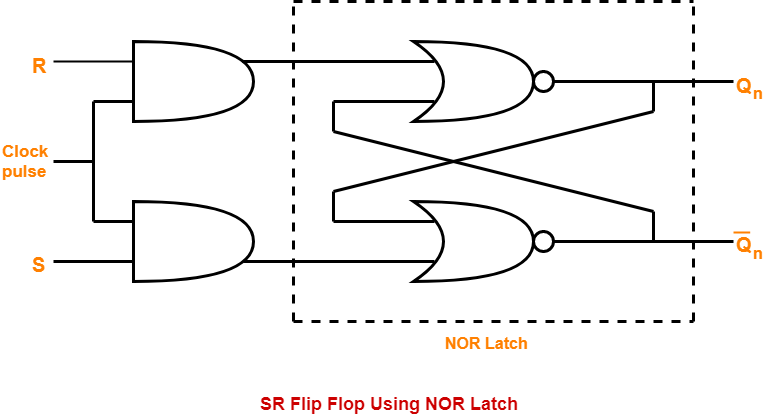
The flip flop is a basic building block of sequential logic circuits The output changes state by signals applied to one or more control inputs. The basic D Flip Flop has a D (data) input and a clock input and outputs Q and Q (the inverse of Q). Optionally it may also include the PR (Preset) and CLR (Clear) control inputs. The truth table and diagram.
What is a D Flip-Flop ??? (Using Discrete Transistors) A flip-flop is a 1 bit digital data storage unit. The latch is also done this work. In the above circuit diagram the 2 transistors make the latch circuit. It's working is same as latch which given in my D Flip-Flop Working. We already discussed the latch working in my previous 'LATCH BLOG'.
D-Latch AND D-FLIP FLOP (Introduction) : VLSI ... The working of D flip flop is similar to the D latch except that the output of D Flip Flop takes the state of the D input at the moment of a positive edge at the clock pin (or negative edge if the clock input is active low) and delays it by one clock cycle. That's why, it is commonly known as a delay flip flop. The D FlipFlop can be interpreted as a delay line or zero order hold. The advantage ...
D-Type Flip Flop Circuit Diagrams in... - The Engineering Projects "The D-Type Flip Flop is a type of Flip Flop that captures the value of D input for a specific time of the Clock edge and show the output according to the Recall that Flip Flops are the Logical Circuits that can hold and store the data in the form of bits and are important building blocks of many of electronic...
T Flip Flop Circuit Diagram, Truth Table & Working Explained 02.10.2017 · T Flip-flop Circuit diagram and Explanation: The IC power source V DD ranges from 0 to +7V and the data is available in the datasheet. Below snapshot shows it. Also we have used LED at output, the source has been limited to 5V to control the supply voltage and DC output voltage. We have used a LM7805 regulator to limit the LED voltage. Practical Demonstration of …
D Type Flip-flops | Timing Diagram Flip-flops, D-type flip-flops explained, Data latch, ripple-though, edge-triggering, synchronous and asynchronous operation. As can be seen from the timing diagram shown in Fig 5.3.2, if the data at D changes during this time, the Q output assumes the same logic level as the D.
Practical Electronics/Flip-flops - Wikibooks, open books for an open... A flip-flop is a circuit that exists in one of two states and so can store information. A simple flip-flop can be defined in terms of two NAND logic gates. Flip-flops are non-linear circuits, meaning the output from one of its gates is fed 'back' to be processed with the input signal.
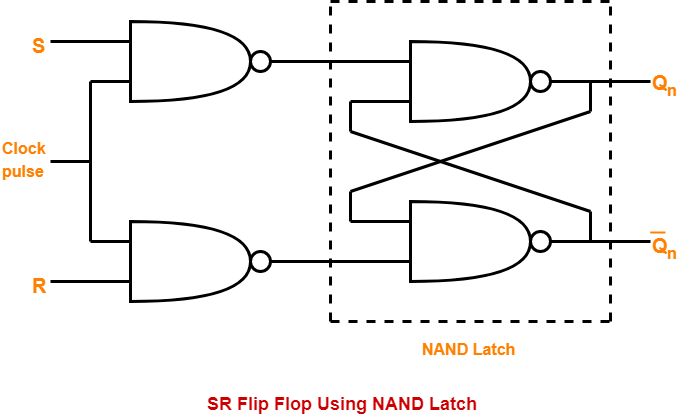
SR Flip-Flop Circuit Diagram with NAND Gates: Working ... 22.09.2017 · SR Flip-flop Circuit Diagram and Explanation: Here we have used IC SN74HC00N for demonstrating SR Flip Flop Circuit, which has four NAND gates inside. The IC power source has been limited to MAXIMUM OF 6V and the data is available in the datasheet. Below snapshot shows it. Hence, we have used a LM7805 regulator to limit the supply voltage and pin voltage …
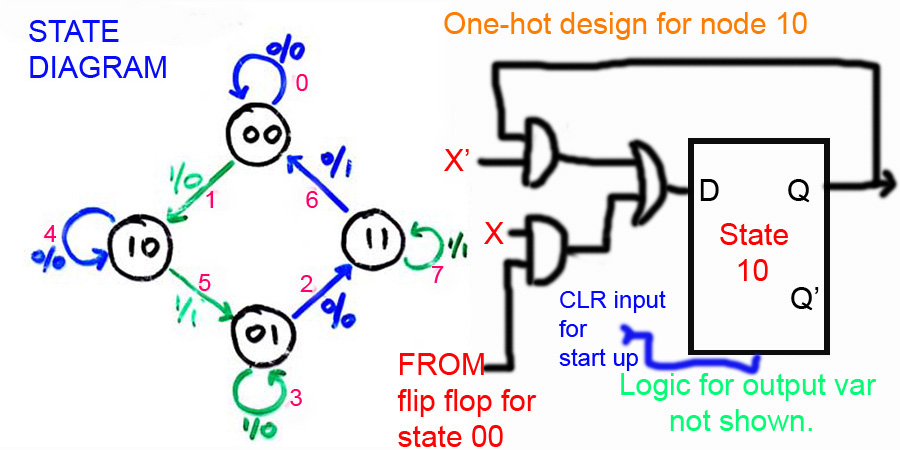
PDF Slide 1 | Symbols for Latch and D-Flip-Flops Draw a state diagram. Minimize states (see Section 9.1). The Huffman model, containing: Flip-flops for storing the state. Combinational logic to generate outputs and next state from inputs and present state.
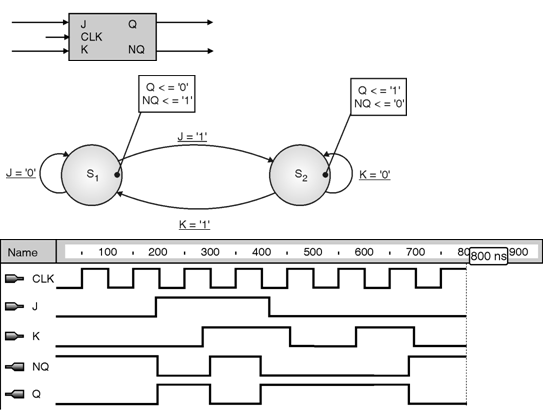
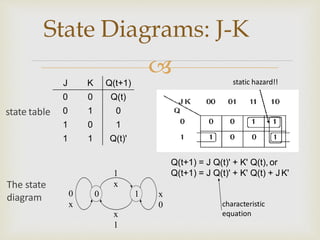
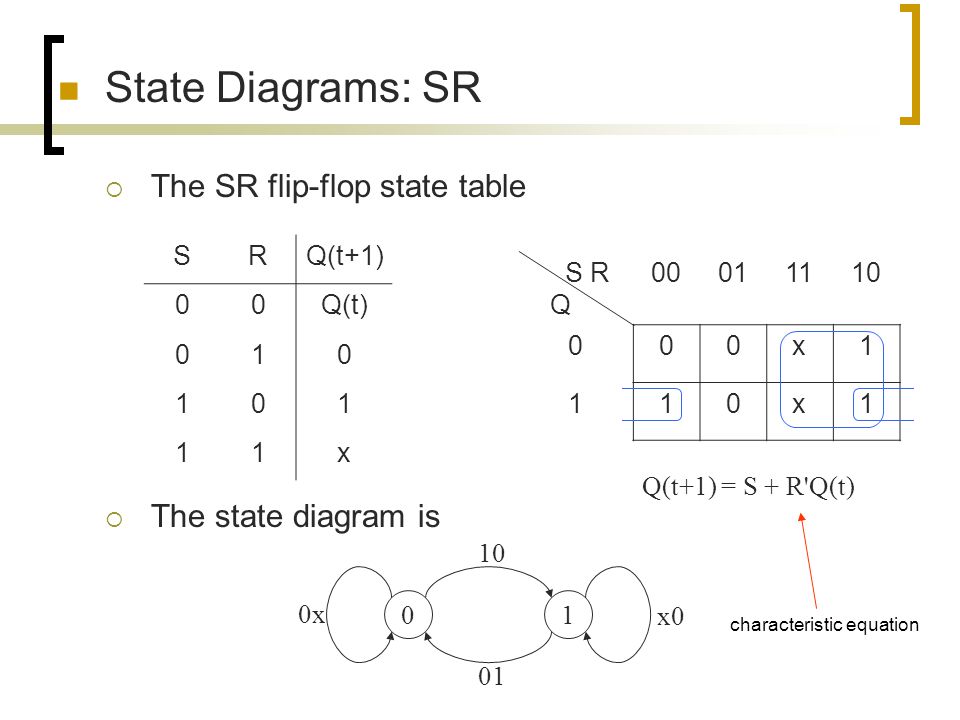
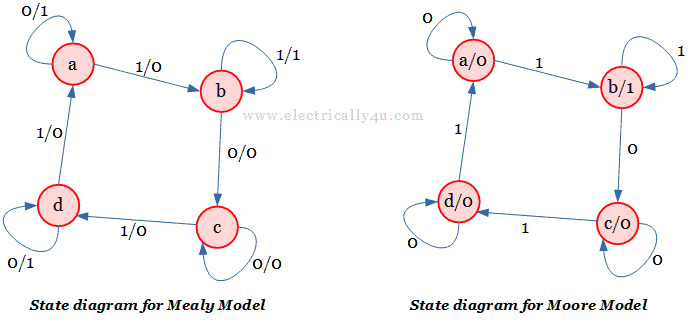
PDF Moore state diagram of an S-R flip-flop • A state diagram is used for a synchronous circuit. It shows: - the circuit state - the possible transitions between states - the values of the circuit outputs. • The assigned state table differs from the state table by showing the flip-flop outputs assigned to each state instead of the state label.
D-type Flip Flop Counter or Delay Flip-flop | Basic Electronics Tutorials This state will force both outputs to be at logic "1", over-riding the feedback latching action and The "D flip flop" will store and output whatever logic level is applied to its data terminal so long as the clock input Functional diagram of the 74LS373 Octal Transparent Latch. The D-type Flip Flop Summary.
How to draw a sequential circuit to detect an even number... - Quora I'll leave the state diagram as an exercise, after all you should contribute something to your own homework. Hint: it's trivial. Flip Flops are integral precisely because their current and next states can co-exist, in the parts of the logic that deal with them.
Digital Flip-Flops - SR, D, JK and T Flip-Flops - Sequential Logic... Flip-flop's truth table consists of current and next states. It shows the output state of flip-flop after a clock cycle. Enable pin enables the D flip-flop to hold its last state without considering the clock signal. It does not matter if there is a clock edge, the flip-flop will hold its state if it is disabled.
Flip-flop types, their Conversion and Applications - GeeksforGeeks Flip-flop is a circuit that maintains a state until directed by input to change the state. A basic flip-flop can be constructed using four-NAND or four-NOR gates. Draw K-Maps using required flipflop inputs and obtain excitation functions for sub-flipflop inputs. Construct logic diagram according to the...
Flip-flop (electronics) - Wikipedia In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information – a bistable multivibrator.The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic.Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital ...
Edge-triggered Latches: Flip-Flops - InstrumentationTools In the second timing diagram, we note a distinctly different response in the circuit output(s): it only responds to the D input during that brief moment of Otherwise, the flip-flop's outputs latch in their previous states. It is important to note that the invalid state for the S-R flip-flop is maintained only for...
PLC Latch (Flip-Flop) Logic Function - EEP Let’s put some light on Latch/Unlatch Logic (or Flip/Flop) PLC Function. Latches // A latch is like a sticky switch – when pushed it will turn on, but stick in place, it must be pulled to release it and turn it off. A latch in ladder logic uses one instruction to latch, and a second instruction to unlatch, as shown in Figure 1 below. The output with an L inside will turn the output D on ...
FLIP-FLOPS - California State University, Northridge "D" flip-flop. • Explain and use a 'T' flip-flop. • Explain the difference between synchronous and asynchronous circuits. -• Describe some common applications of flip-flops. • Explain what a One-shot is. "". " . ', L ~ 5.2 DISCUSSION In . the introduction:to this chapter. it was stated that 'a latch can . be . made from paired logic 'gates. While this, istrue, Ci ' simple latch . can ...
D Flip Flop Explained in Detail - DCAClab Blog These flip flops use feedback concept to create sequential logic where the previous state affect future states (unlike combinational circuit). The D in the D flip flop represents the data (generation, processing, or storing) in the form of states. The two states are binary, 0 (Low) and 1 (High), set or...
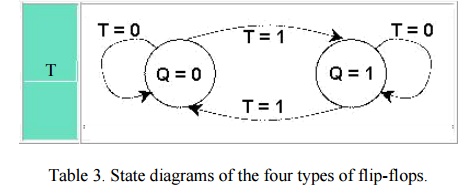
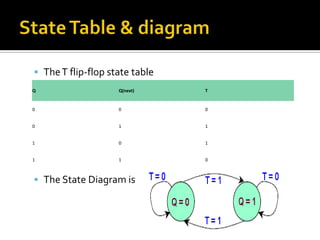
Flip flop's state tables & diagrams 7. The D flip-flop has the following state table ▪ Note that changes on clock edge are always assumed The corresponding state diagram is ▪ Again, transitions occurs only on a clock edge. 11. TheT flip-flop state table The State Diagram is Q Q(next) T 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0.
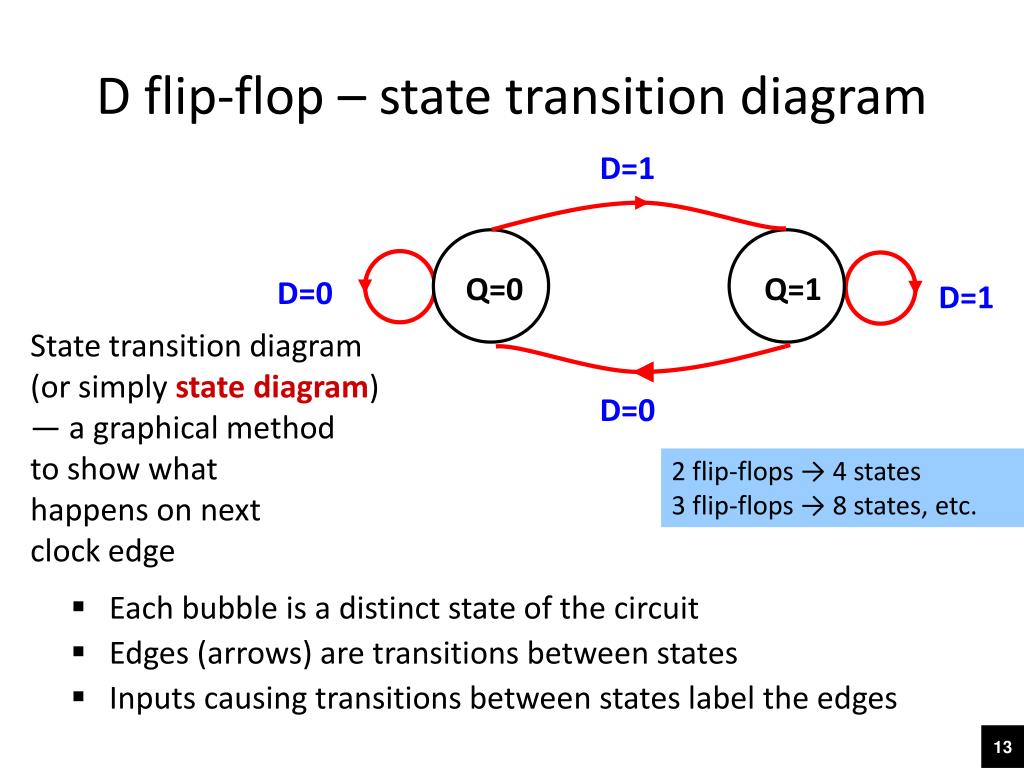
PDF PowerPoint Presentation | First: D-latch state function D-flip-flop state diagram. Slide Number 26. Synthesis of asynchronous circuits. Exemple: serial paritety circuit. • All flip-flops and latches are themselfes asynchronous state machines • They are useful to synchronize events in situations where metastability is/can be a problem.






![Solved] Question 2 [50pts]: Design the sequential circuit ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/questions/2020/05/5eb5746534feb_ScreenShot20200508at18.01.09.png)
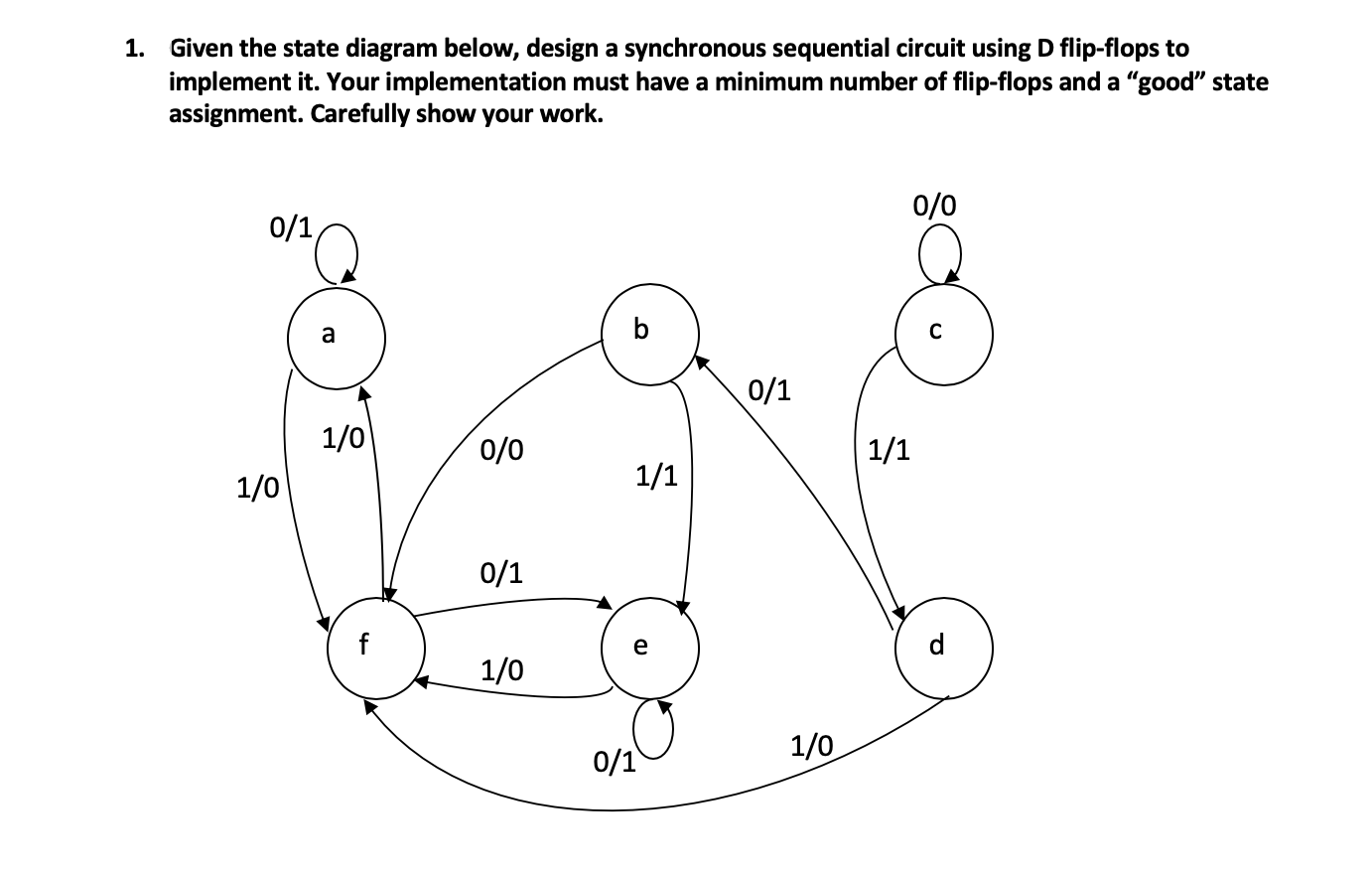
![2. (8 marks] Design a sequential circuit specified by the ...](https://img.homeworklib.com/questions/2ee667c0-be7f-11eb-aafc-2fe27e414092.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,w_560)







0 Response to "42 d flip flop state diagram"
Post a Comment