43 diagram of brachial plexus
(PDF) Anatomy of the brachial plexus - ResearchGate The brachial plexus is a complex anatomical network of nerves that mainly supplies the upper limb. A thorough understanding of the anatomy of this region provides the clinician with valuable ... Brachial plexus quizzes and diagrams: Learn faster! | Kenhub The brachial plexus is the mysterious place from which all of the nerves of the upper extremity arise, facilitating motor and sensory innovation of the arm. You can think of it as the life support of the upper extremity. You can also think of it in sections, these being the roots, trunks, divisions, cords and branches.
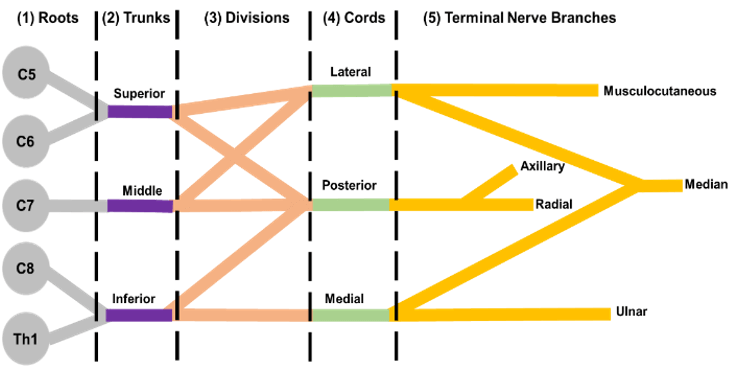
Brachial plexus schematic with distal targets (printable ... Brachial plexus schematic with distal targets (printable diagram) I've drawn the brachial plexus before showing more of its anatomical relationships (which is actually why the trunks and cords are named as they are). As I'm gearing up studying, I created this more schematic diagram of the plexus, including the distal targets (mostly the ...

Diagram of brachial plexus
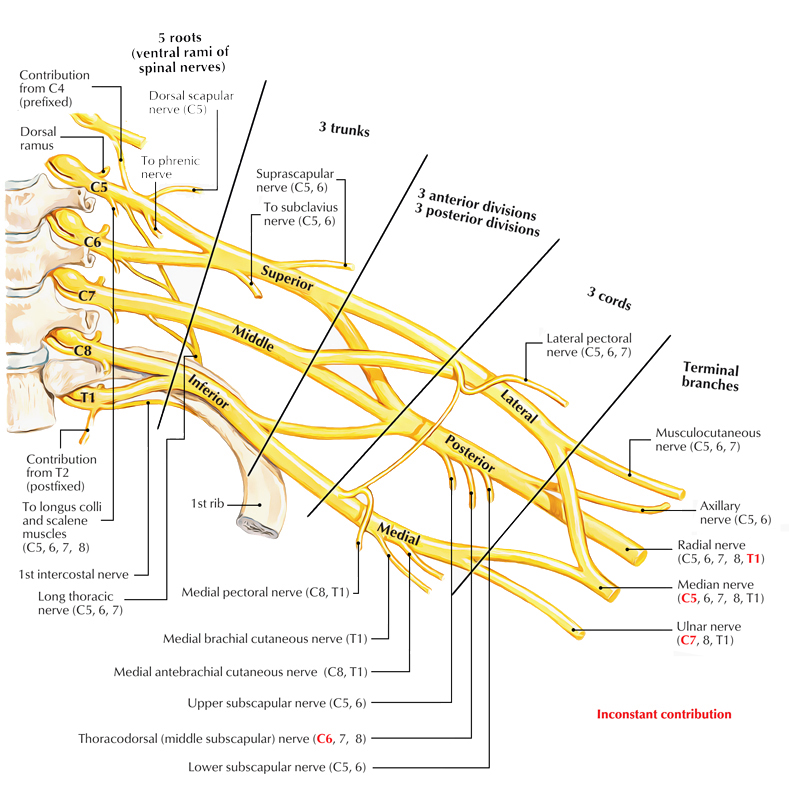
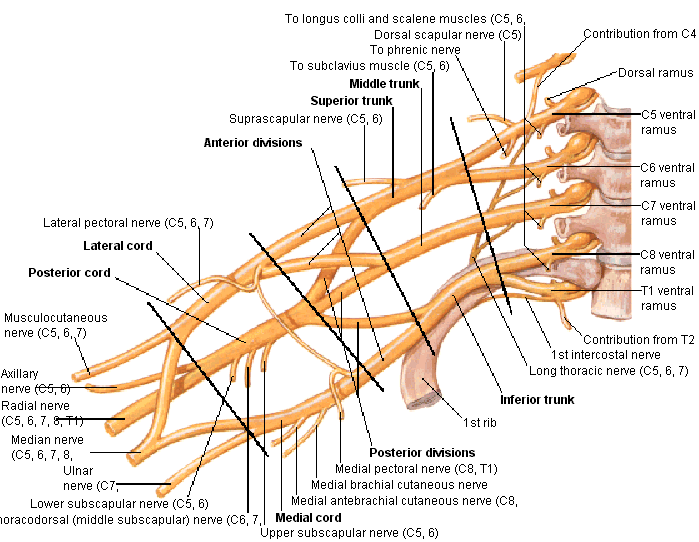
mnemonics for Brachial plexus | Anatomy made easy mnemonics The Brachial plexus consists of the spinal nerves of the anterior primary rami of C5, C6, C7, C8, so forth till T1. It also consists of the anterior primary rami of the C4 and T2 nerves. The Plexus extends from the spinal cord, passes through the cervico-axillary canal in the neck, over the first rib then into the armpit. Brachial plexus injury - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Overview. The brachial plexus is the network of nerves that sends signals from your spinal cord to your shoulder, arm and hand. A brachial plexus injury occurs when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or in the most serious cases, ripped apart or torn away from the spinal cord. PDF Brachial Plexus Anatomy: Normal and Variant Orebaugh and Williams: Brachial Plexus Anatomy TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 300-312 304 The scalene muscles, and the sometimes-elusive groove between them, are the chief landmarks for successful localization of the brachial plexus in ISB. However, the relationship between roots, trunks, and muscles is variable.
Diagram of brachial plexus. Cervical Nerves Diagram, Anatomy & Anatomy | Body Maps 19/01/2018 · The brachial plexus is a very complicated structure (akin to a busy freeway interchange in Los Angeles), with nerves splitting and recombining to provide nerve functions to the muscles and skin of ... Brachial plexus block - Wikipedia Brachial plexus block is a regional anesthesia technique that is sometimes employed as an alternative or as an adjunct to general anesthesia for surgery of the upper extremity.This technique involves the injection of local anesthetic agents in close proximity to the brachial plexus, temporarily blocking the sensation and ability to move the upper extremity. Superior sulcus tumors (Pancoast tumors) 16/06/2016 · Superior Sulcus Tumors, frequently termed as Pancoast tumors, are a wide range of tumors invading the apical chest wall. Due to its localization in the apex of the lung, with the potential invasion of the lower part of the brachial plexus, first ribs, vertebrae, subclavian vessels or stellate ganglion, the superior sulcus tumors cause characteristic symptoms, like arm or … Brachial Plexus Diagram | Quizlet Originates from the posterior cord. -Courses over anterior surface of the subscapularis muscle and the other supplying teres major muscle. Axillary Nerve. originates from the posterior cord. Courses inferiorly through the quadrangular space of the shoulder. -passes medial to the neck of the humorous. -innervates teres minor and deltoid muscles.
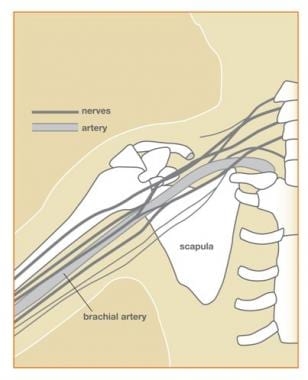
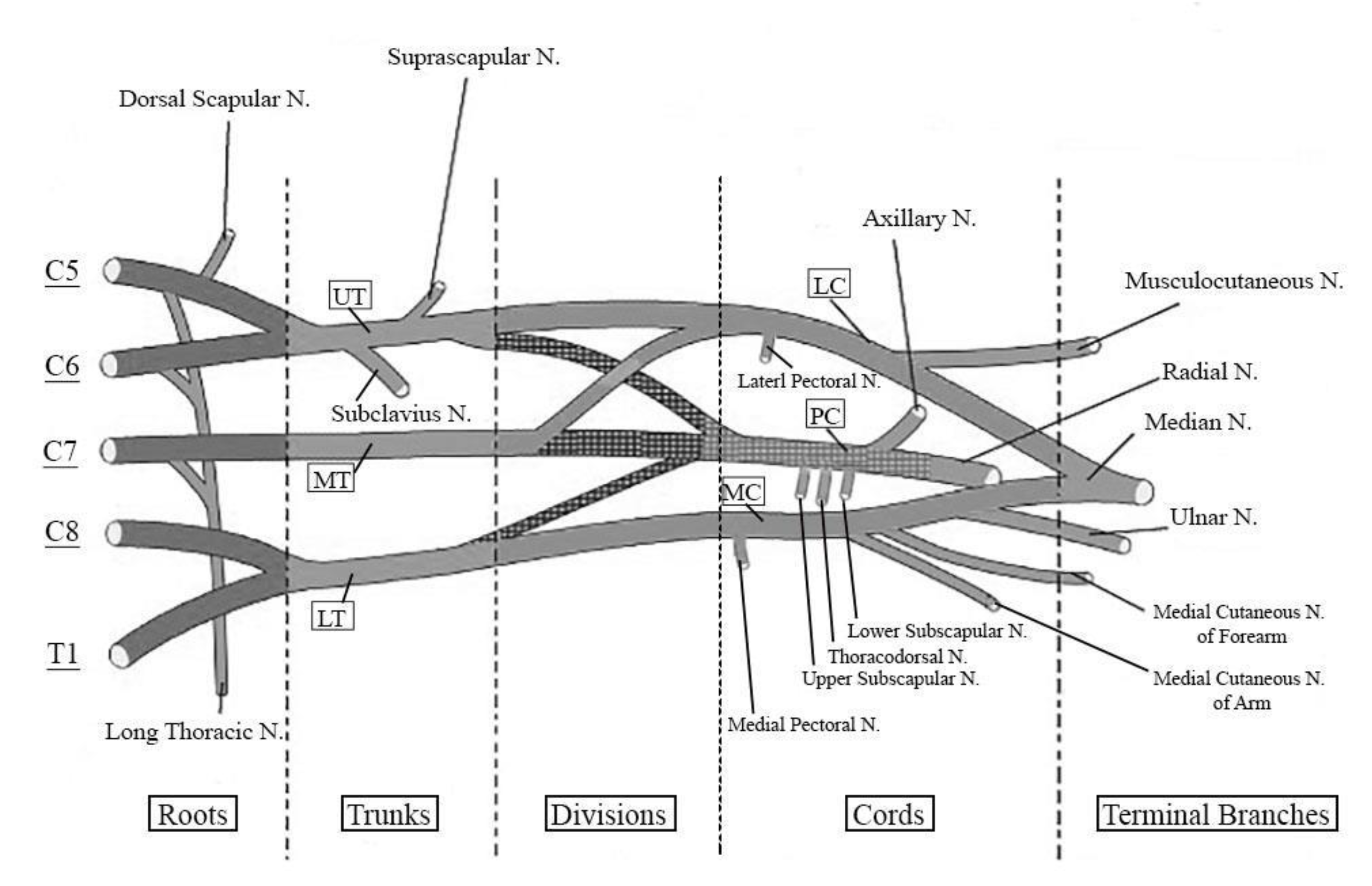
Brachial Plexus | How to Draw Simplified Line Diagram of ... Brachial Plexus AnatomyComplete Session with Applied Anatomy and MCQ'sVideo covers one of the most important topic of Upper LimbFind out, How to Draw Simplif... Brachial plexus (diagram) | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org Diagram. Long thoracic nerve. Lower subscapular nerve. From the case: Brachial plexus (diagram) Diagram. Lower subscapular nerve. Medial cutaneous nerve of the arm. From the case: Brachial plexus (diagram) Diagram. Brachial Plexus Injury | Johns Hopkins Medicine The brachial plexus is a network of nerves in the shoulder that carries movement and sensory signals from the spinal cord to the arms and hands. Brachial plexus injuries typically stem from trauma to the neck, and can cause pain, weakness and numbness in the arm and hand. Brachial plexus injuries often heal well if they aren't severe. 2 - Axilla and Brachial plexus Diagram | Quizlet Axilla contents (4) 1. axillary artery (major blood supply of arm) 2. axillary vein (major venous drainage of arm) 3. brachial plexus (nerve plexus supplying arm) 4. lymph nodes and fat. Axillary lymph nodes are of tremendous clinical importance.
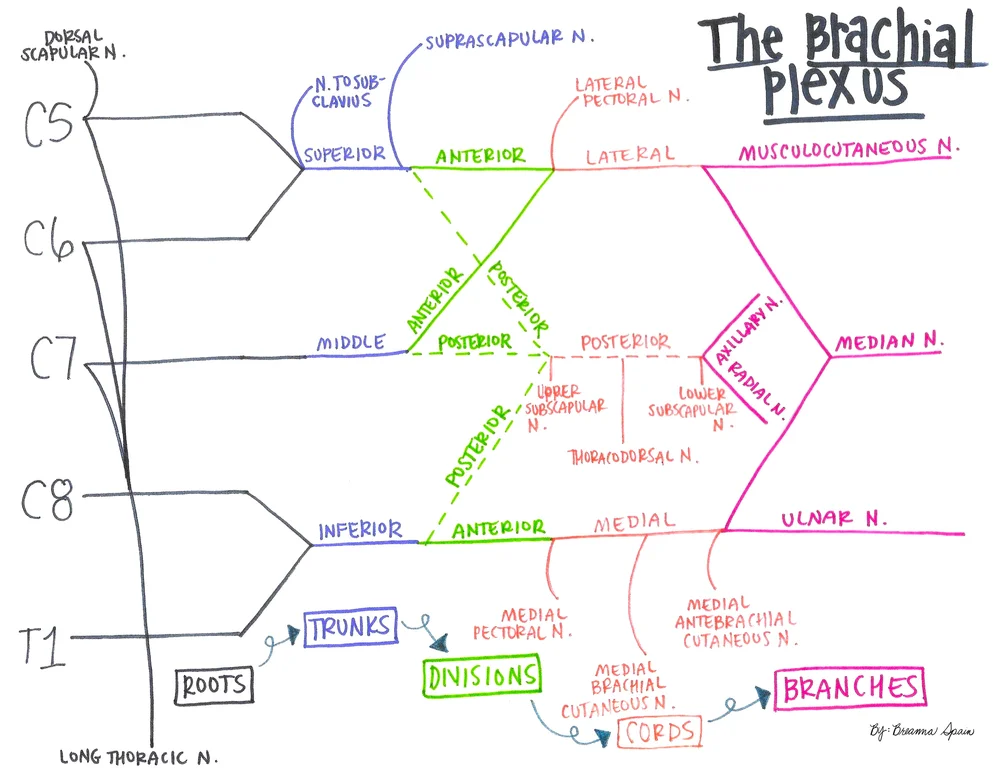
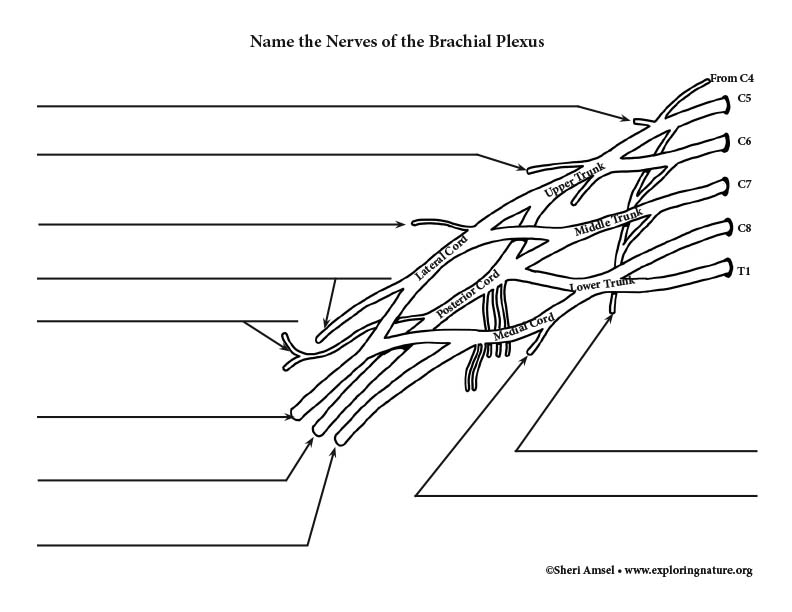
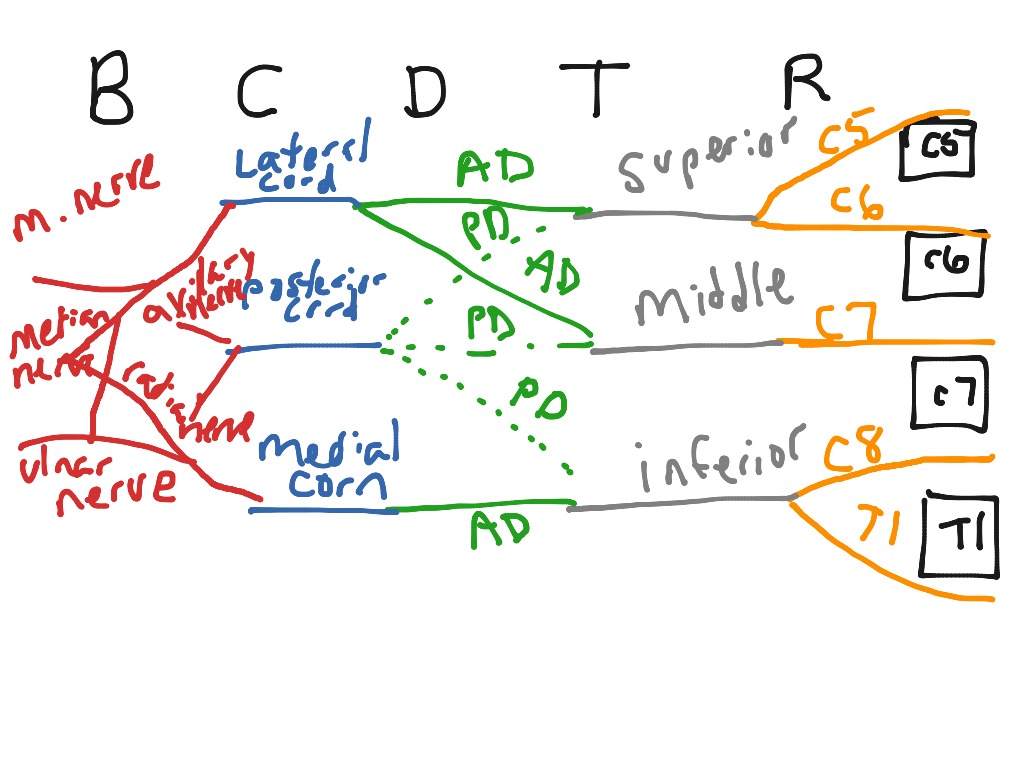
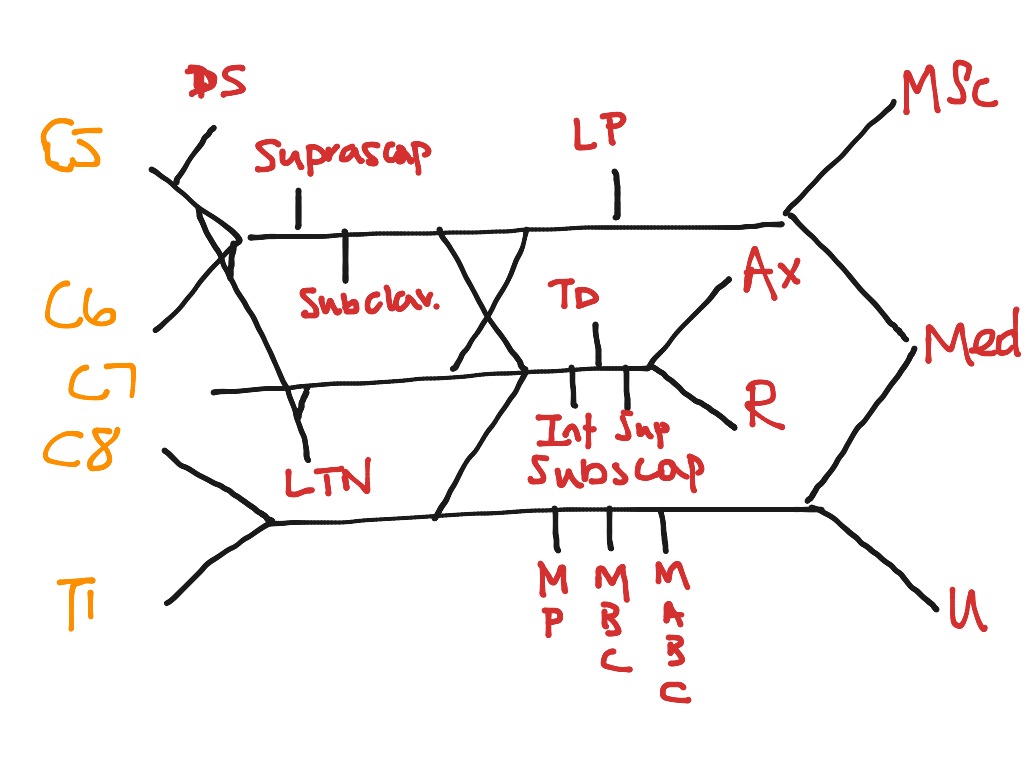
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Brachial Plexus - StatPearls ... The brachial plexus is formed by the anterior primary rami of C5 through T1 and provides sensory and motor innervation of the upper extremity. The brachial plexus is divided, proximally to distally into rami/roots, trunks, divisions, cords, and terminal branches. The trunks can be found within the posterior triangle of the neck, between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. Brachial Plexus of Ox Anatomy - Radial, Median and Ulnar ... The brachial plexus of ox derives from the ventral branches of the last three cervical and first two thoracic nerves.If you want to get the best guide to learn the anatomy of the brachial plexus of an ox, this article is for you. Here, I will show you the formation of brachial plexus, branches, and their innervation in an ox, sheep, and goat. Brachial Plexus | Roots | Trunks | Cords | Geeky Medics The brachial plexus is a complex intercommunicating network of nerves formed by spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1. The brachial plexus, frequently appears in examination questions. This guide will cover the brachial plexus and includes a summary diagram. One of the best ways to memorise the brachial plexus is by drawing it. How to Draw the Brachial Plexus | Study with an SPT Below are step by step diagrams that you can follow along to draw out the brachial plexus. If you've mastered that already, you can download my brachial plexus pdf with the nerve innervations and some mnemonics! Hope this tutorial was helpful! While its important to learn the structure and labels for this diagram, knowing what each nerve ...
The External Ear - Structure - Function - TeachMeAnatomy 16/08/2020 · The ear can be divided into three parts; external, middle and inner.This article will focus on the anatomy of the external ear – its structure, neurovascular supply and clinical correlations. The external ear can be divided functionally and structurally into two parts; the auricle (or pinna), and the external acoustic meatus – which ends at the tympanic membrane.
Brachial plexus - Physiopedia Brachial plexus injury can occur in a variety of ways and can occur as a result of shoulder trauma, tumours, or inflammation. The rare Parsonage-Turner Syndromecauses brachial plexus inflammation without obvious injury, but with nevertheless disabling symptoms. But in general, brachial plexus lesions can be classified as either traumatic or ...
Making Anatomy Simple - TeachMeAnatomy Containing over 700 vibrant, full-colour images, TeachMeAnatomy is a comprehensive anatomy encyclopedia presented in a visually-appealing, easy-to-read format.
Brachial plexopathy following herpes zoster infection: two ... MRI of the brachial plexus demonstrated T2 hyperintensity and contrast enhancement in the part of the brachial plexus that was compatible with both the clinical symptoms and the electrophysiological findings. Especially, MR imaging reflected the functional impairments more accurately than electrophysiological studies in the acute phase, during ...
Brachial Plexus Anatomy: Overview, Gross Anatomy, Blood ... The brachial plexus (plexus brachialis) is a somatic nerve plexus formed by intercommunications among the ventral rami (roots) of the lower 4 cervical nerves (C5-C8) and the first thoracic nerve (T1). The plexus, depicted in the images below, is responsible for the motor innervation of all of the muscles of the upper extremity, with the exception of the trapezius and levator scapula.
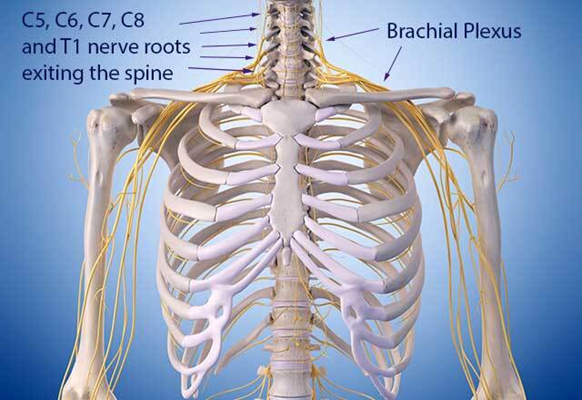
PDF BRACHIAL PLEXUS CENTER - St. Louis Children's The brachial plexus is a complex arrangement of nerves that controls the muscles of the shoulder, arms and hands. It is located on the side of the neck above the collarbone (see diagram 1). The nerves of the brachial plexus branch off the spinal cord (see diagram 2). THE CAUSE OF BIRTH BRACHIAL PLEXUS PALSY Brachial plexus injury occurs when ...
Brachial plexus anatomy. | Download Scientific Diagram Download scientific diagram | Brachial plexus anatomy. from publication: Reducing the Risk and Impact of Brachial Plexus Injury Sustained From Prone Positioning-A Clinical Commentary ...
Brachial plexus - Wikipedia The brachial plexus is a network of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1).This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit.It supplies afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand.
Brachial plexus - Operative Neurosurgery The brachial plexus is a network of nerve s, running from the spine, formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve (C5-C8, T1). The brachial plexus passes through the cervico-axillary canal in the neck to reach the axilla (armpit region), and into the arm including the hand, innervating these regions.
Draw the Brachial Plexus in 10 seconds! - YouTube An easy way to draw the basic components of the brachial plexus. On paper, it's pretty easy to draw the brachial plexus using this method in around 10 secon...
Lower subscapular nerve - Wikipedia Structure. The lower subscapular nerve contains axons from the ventral rami of the C5 and C6 cervical spinal nerves. It is the third branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It gives branches to 2 muscles: subscapularis muscle. It usually gives 4 branches to innervate the subscapularis, and can give up to 8 branches.
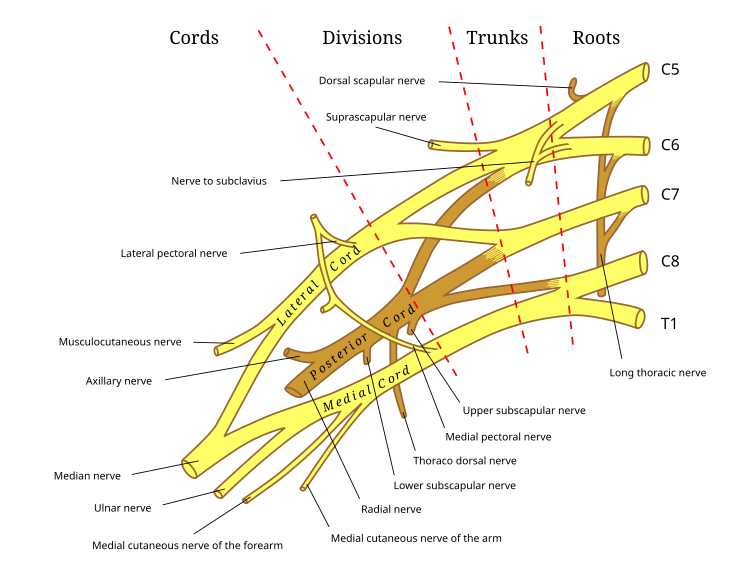
Brachial Plexus - SmartDraw Brachial Plexus. Anterior view of the nerves that make up the brachial plexus. Central rami, superior, middle and inferior trunks, lateral posterior and medial cords, axillary nerve, musculocutaneus nerve, radial nerve, median nerve and ulnar nerve). Branches of the ventral rami.
Shoulder Pain Diagram: Diagnosis Chart - Shoulder Pain Exp Brachial Neuritis. Brachial neuritis is a rare condition caused by inflammation of a group of nerves known as the brachial plexus that control the shoulder and arm. Brachial neuritis usually develops very quickly, often at night, causing intense shoulder and arm pain. It can affect people at any age but is most common in young/middle aged adults.
Brachial plexus: Anatomy, branches and mnemonics | Kenhub The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that gives rise to all the motor and sensory nerves of the upper extremity.This plexus arises from the anterior rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 that undergo several mergers and splits into trunks and divisions, until they finally give rise to their terminal branches.These terminal branches are responsible for motor and sensory innervation of the upper ...
The Brachial Plexus - Sections - Branches - TeachMeAnatomy The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibres that supplies the skin and musculature of the upper limb. It begins in the root of the neck, passes through the axilla, and runs through the entire upper extremity. The plexus is formed by the anterior rami (divisions) of cervical spinal nerves C5, C6, C7 and C8, and the first thoracic spinal nerve, T1.
Brachial plexus Injury, Diagram, Roots, Trunks, Divisions ... Brachial plexus is a major network of nerves that innervate or supply the upper limbs - most nerves in the upper limb arise from the brachial plexus; there is one brachial plexus on the left and another on the right, both supplying the two upper limbs. The Brachial plexus starts in the lateral cervical region (posterior triangle) and extends ...
Brachial Plexus: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that originate in the spinal cord in the neck, travel down the neck (via the cervicoaxillary canal) and into the armpit. It contain the nerves that, with only a few exceptions, are responsible for sensation (sensory function) and movement (motor function) of the arms, hands, and fingers.
File:Brachial plexus color.svg - Wikipedia The brachial plexus with the courses of the spinal nerves shown in color. Based on an unpublished illustration by Jane Phillips-Conroy for the course Principles of Human Anatomy and Development (L48 4581) at Washington University in St. Louis. Known discrepancies with Brachial plexus article:
PDF Brachial Plexus Anatomy: Normal and Variant Orebaugh and Williams: Brachial Plexus Anatomy TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 300-312 304 The scalene muscles, and the sometimes-elusive groove between them, are the chief landmarks for successful localization of the brachial plexus in ISB. However, the relationship between roots, trunks, and muscles is variable.
Brachial plexus injury - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Overview. The brachial plexus is the network of nerves that sends signals from your spinal cord to your shoulder, arm and hand. A brachial plexus injury occurs when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or in the most serious cases, ripped apart or torn away from the spinal cord.
mnemonics for Brachial plexus | Anatomy made easy mnemonics The Brachial plexus consists of the spinal nerves of the anterior primary rami of C5, C6, C7, C8, so forth till T1. It also consists of the anterior primary rami of the C4 and T2 nerves. The Plexus extends from the spinal cord, passes through the cervico-axillary canal in the neck, over the first rib then into the armpit.
![brachial_plexus [Operative Neurosurgery]](https://operativeneurosurgery.com/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=brachial_plexus.png)





















:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/2896/0DMe5CzwfLDHjx2Q0fq2Lw_Brachial_plexus_-_Main_divisions.jpg)
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/plexus-brachialis-3/xRmvDWlAjDQcOaxVBhGrzw_Brachial_plexus.png)




0 Response to "43 diagram of brachial plexus"
Post a Comment