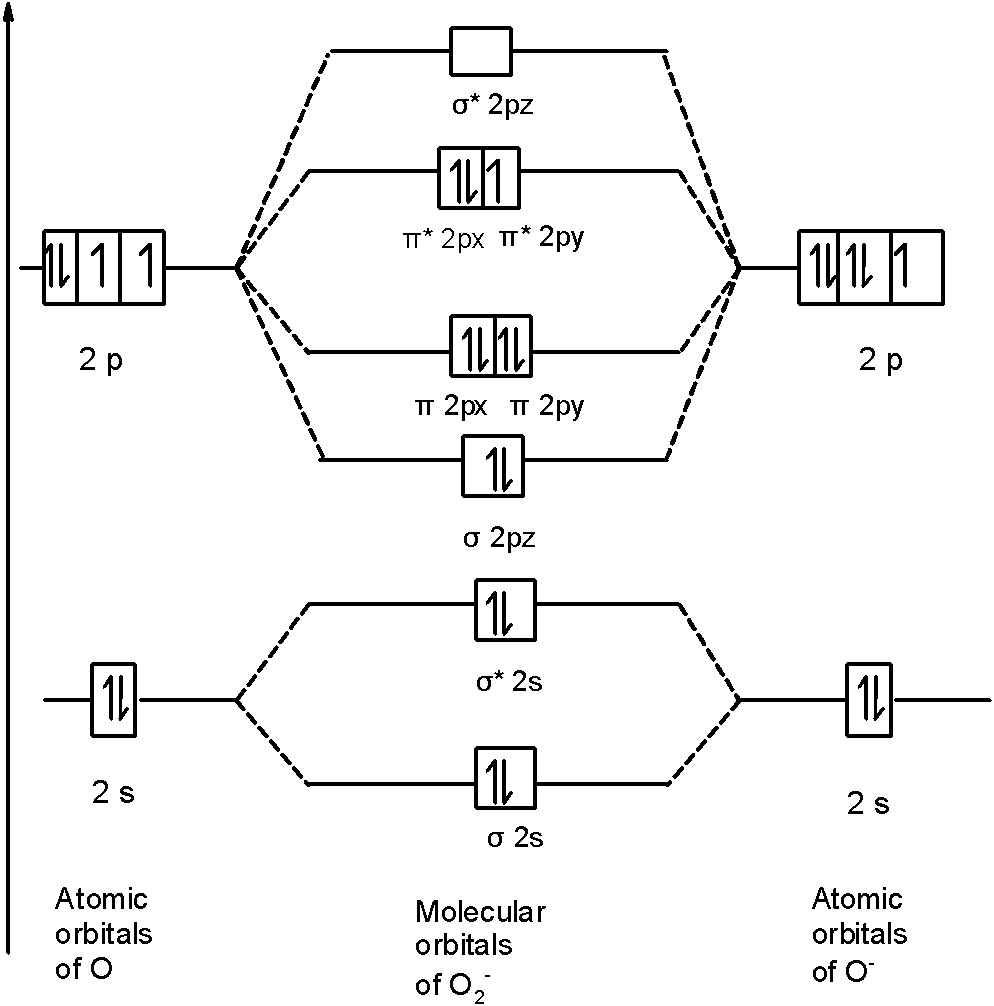
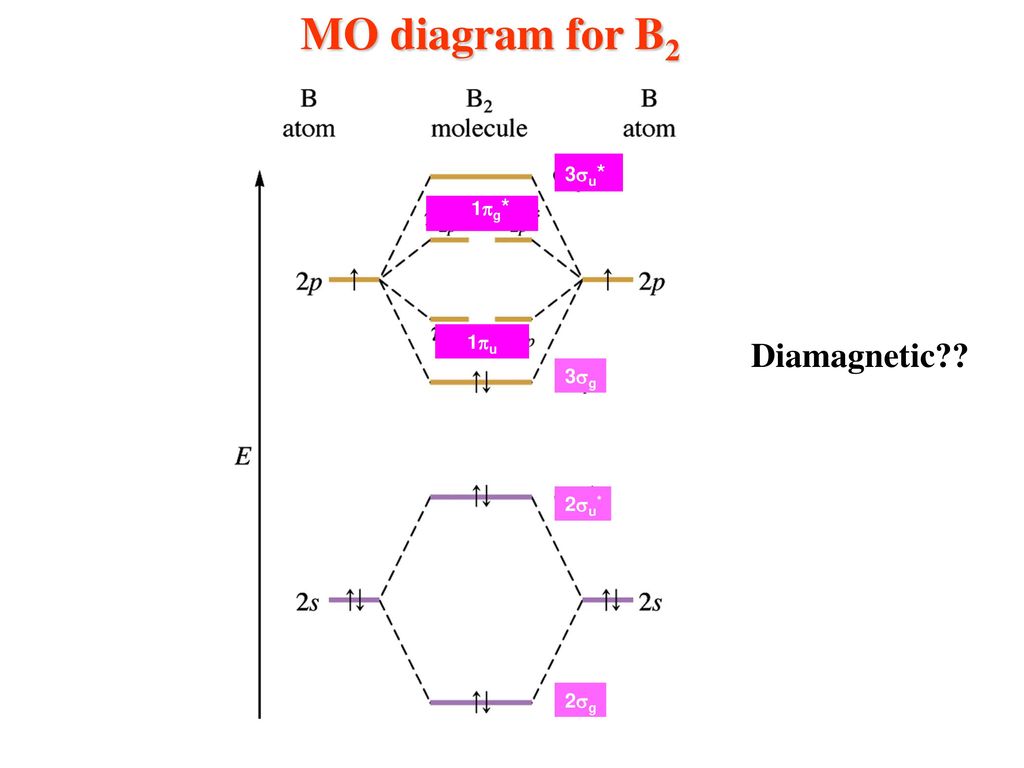
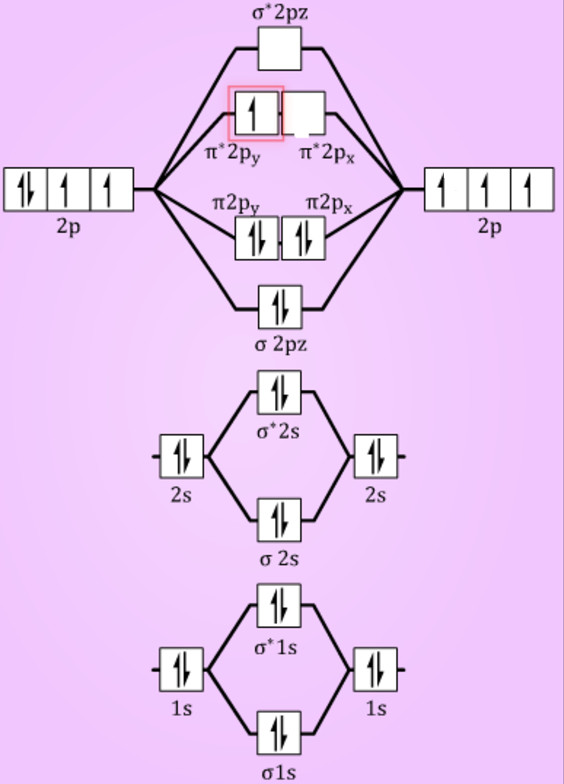
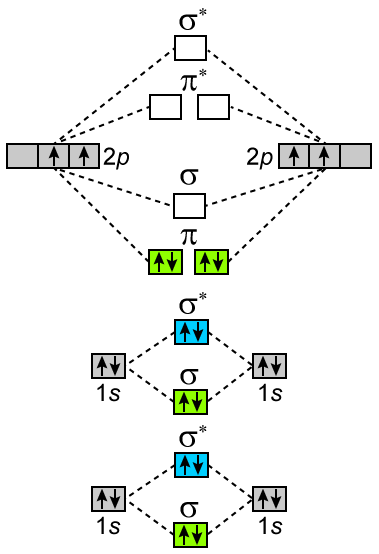
45 b2 2- molecular orbital diagram
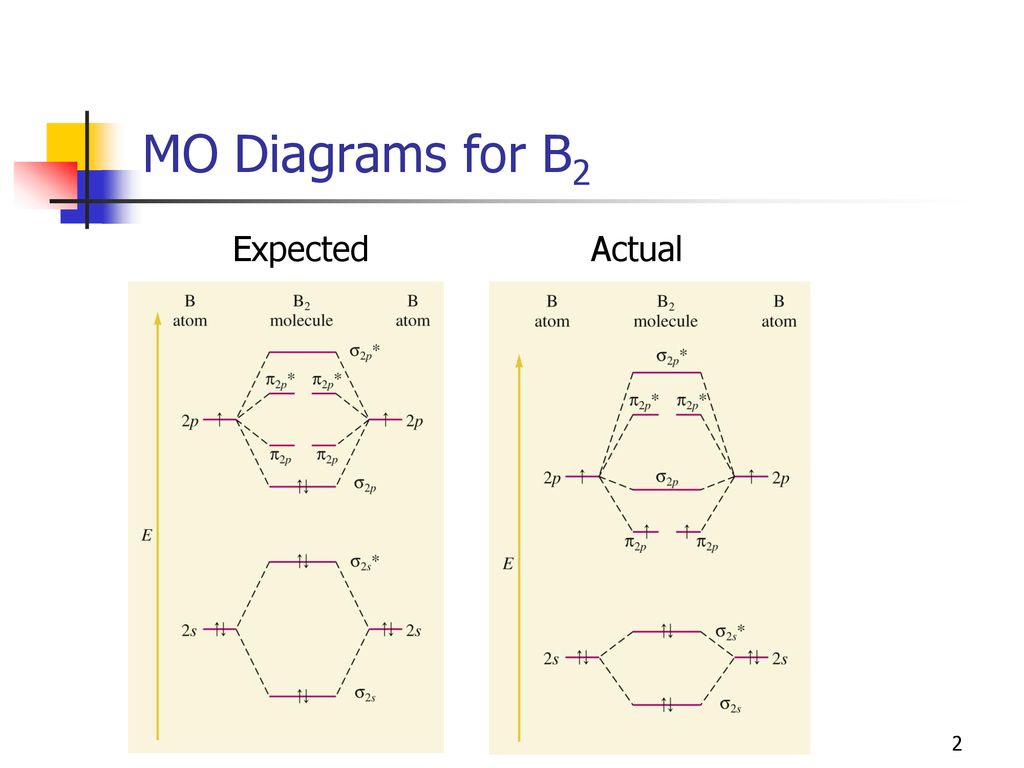
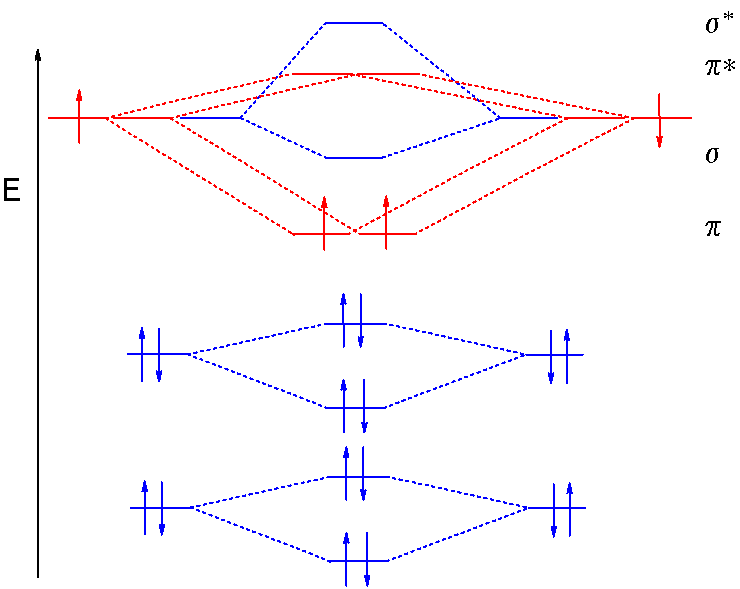
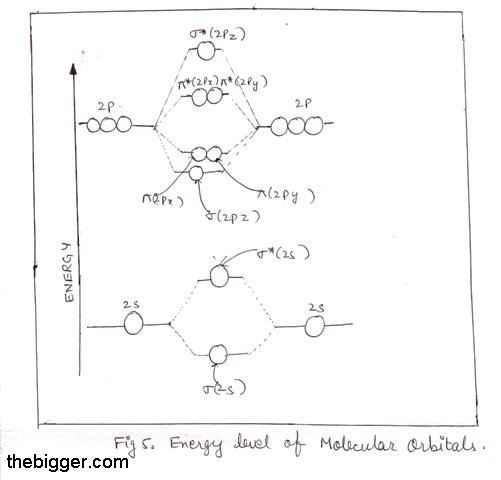
molecular orbital theory - Why is diboron (B2) paramagnetic? Before we get there it is worth while knowing a generic valence molecular orbital diagram where no s-p mixing occurs. This one pretty much applies to all main group elements heavier than nitrogen. This results in a triplet ground state. The finished valence molecular orbital diagram is pictured below. Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals) This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.
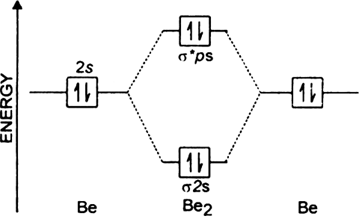
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding However, we can predict that the Be2 molecule and the Ne2 molecule would not be stable. We can see this by a consideration of the molecular electron...
B2 2- molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbital diagram of NO(nitric oxide) molecule Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12. PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and... Using the molecular orbital theory, why does a Be2 molecule not exist? The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels According to molecular orbital theory,molecular orbital diagram for helium molecule can be given as. From molecular orbital configuration,bond...
B2 2- molecular orbital diagram. PDF A qualitFaetIIive molecular orbital diagram SfAoLrC 'sferrocene (D5d) A qualitative molecular orbital diagram for ferrocene (D5d) FeII SALC's Fe. • The two benzene rings of Cr(h6‐C6H6)2 are ideally orientated in an eclipsed (D6h) conformation. B2g (6 nodes). anti-bonding. Molecular Orbital Theory The bonding molecular orbital concentrates electrons in the region directly between the two nuclei. Placing an electron in this orbital therefore stabilizes the H2 molecule. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms. Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry/Molecular Orbital Theory... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. PDF Chapter 5 | 5.2.2 Orbital Mixing Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In molecular orbital theory the symmetry properties and relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how these orbitals interact to form...
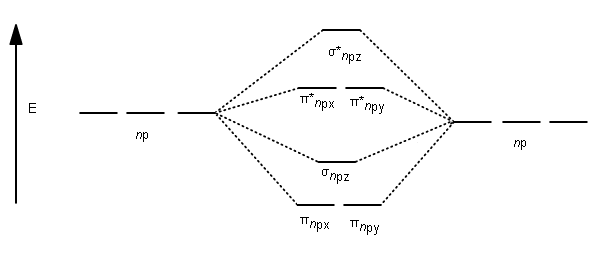
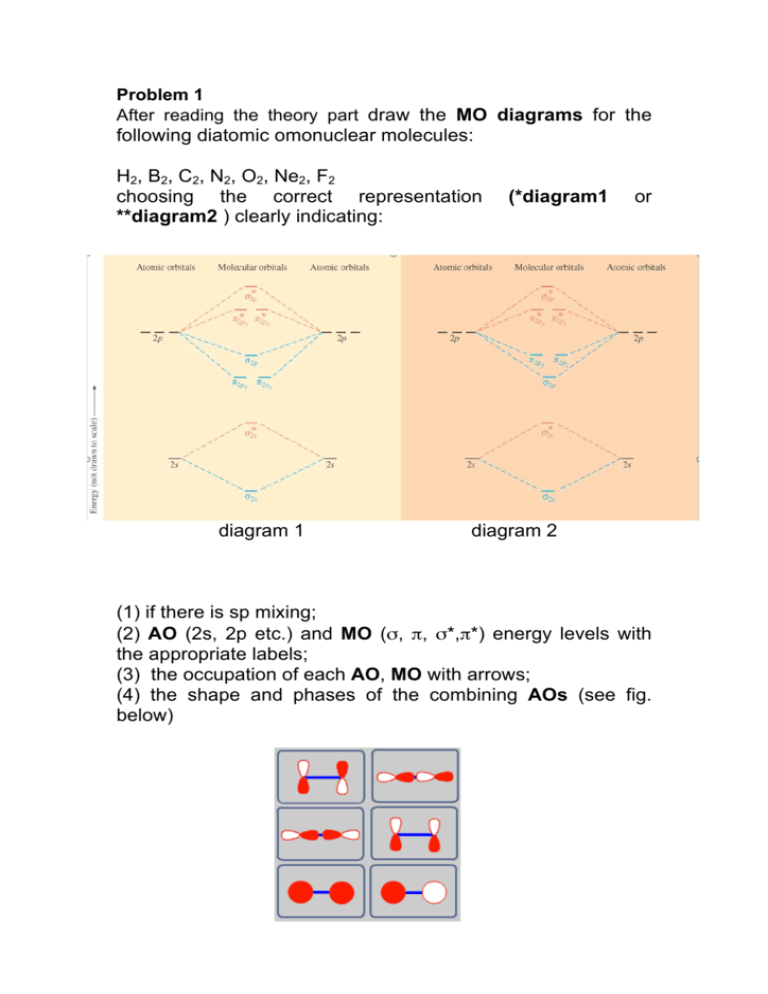
Molecular Orbitals: Molecular Orbital Theory | SparkNotes Figure %: Orbital correlation diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules other than B2, C2, and N2. To draw the correlation diagrams for heteronuclear diatomic molecules, we face a new problem: where do we place the atomic orbitals on an atom relative to atomic orbitals on other atoms? Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), Chemistry Study... | eMedicalPrep The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. For example, homonuclear diatomic molecules of second row elements like Li 2 , Be 2 , B 2 , C 2 , N 2 , the σ 2p z MOs is higher in energy than π 2px and π 2py MOs. PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory... Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in Molecular Orbital Theory - BH3. The BH3 molecule exists in the gas phase, but dimerizes to B2H6... Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
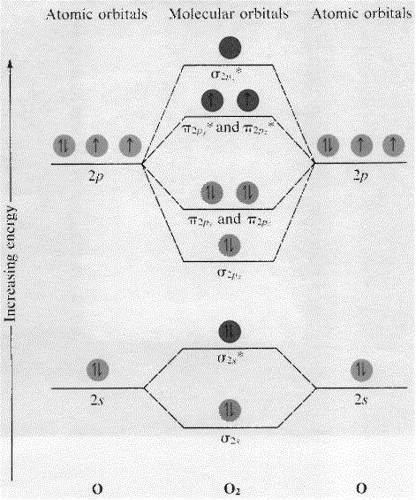
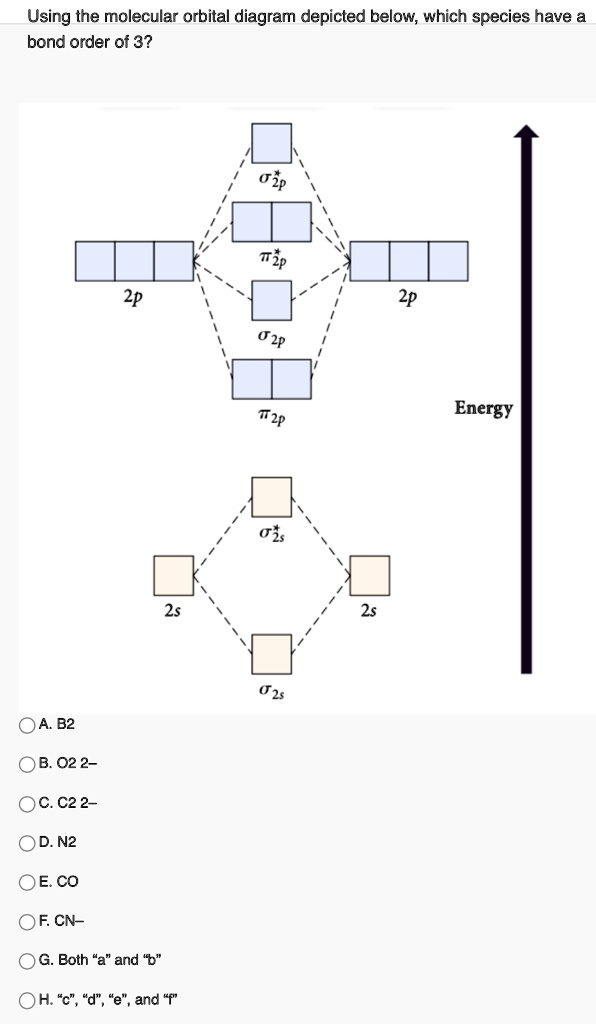
Figure 11. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that... Example 2: Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O2. Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples... PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.ppt... Lecture 4 Revision of hybridisation Molecular orbital theory and diatomic molecules. Prof G. W. Watson Lloyd Institute 2.05. watsong@tcd.ie. • Energy level diagram represents this interaction. - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular... Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules This energy diagram for the molecular orbitals is shown in Fig.1 However, experimental evidence for oxygen and heavier diatomic molecules have... PDF Microsoft Word - Chapter 1_6_SY.doc Draw molecular orbital diagrams for diatomic species. Figure 9.36 Molecular orbital diagram for H2 Notice the following features of the H2 molecular orbital diagram. The molecular orbital diagram for the second row homonuclear. Chapter 9. Theories of Chemical Bonding.
Molecular Orbitals - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Figure 5. Molecular orbital diagram for a simple octahedral complex. This is qualitatively equivalent to the results of the simpler crystal field theory, which ignores orbital overlap with the ligand orbitals and uses just the electrostatic repulsion of the metal d-orbitals and the negative charges of the ligands.
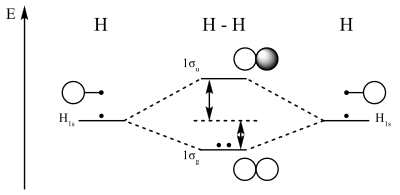
PDF Molecular Orbitals in | 9-2 Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. One is a bonding orbital, 1s (blue), resulting from addition of the wave functions of the 1s orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Theory: Explanation, Illustrations and... - Embibe Molecular Orbital Theory: To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Have you ever thought about how sigma and pi bonds are formed? What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic behaviour?
What is the molecular orbital diagram for B_2? | Socratic Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals.
Asked for: molecular orbital energy-level diagram, valence electron... A molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H2+.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical Bonding and... Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons. 3) If Nb = Na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified | by Megan A. Lim | Medium Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. However, we can predict that the Be2 molecule and the Ne2 molecule would not be stable. We can see this by a consideration of the molecular electron configurations (Table 8.3).
How to Make the Molecular Orbital Diagram for B2 (Bond Order...) This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the B2 (boron) molecule. The bond order of the boron molecule is also calculated and...
Using the molecular orbital theory, why does a Be2 molecule not exist? The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels According to molecular orbital theory,molecular orbital diagram for helium molecule can be given as. From molecular orbital configuration,bond...
PDF Figure 9.32: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and...
Molecular Orbital diagram of NO(nitric oxide) molecule Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.




















0 Response to "45 b2 2- molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment