40 airplane free body diagram
5%, which is equivalent to an amplification factor of Q=10. A similar tool is available for vibration. ... The free-body diagram is ... The aircraft will encounter aerodynamic buffeting as it accelerates through the transonic velocity. Note that shock waves begin to form on the aircraft as it approaches the This video introduces and explains both free body diagrams and objects on an inclined plane for A Level Physics.A free body diagram is used to display the fo...
Free Body Diagram - 941 Words | Cram. Show More. Check Writing Quality. Register to read the introduction…. Move the ramp to an angle of zero (horizontal) and draw a free body diagram of the cabinet here: On a horizontal plane, the normal force is _Perpendicular_______ to the weight. The cabinet has a mass of 100kg.
Airplane free body diagram
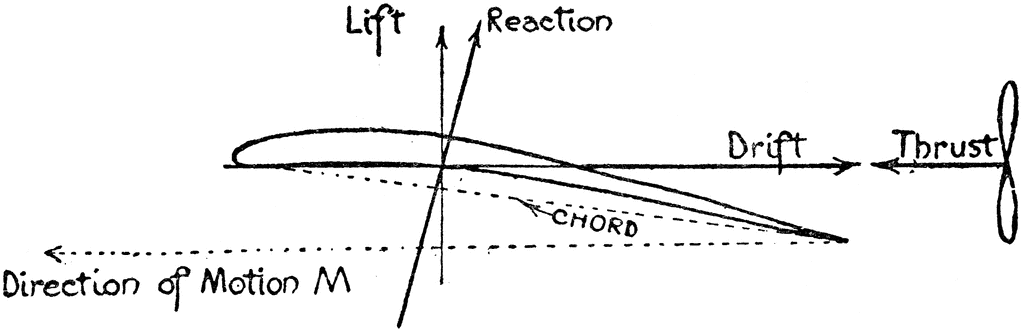
Feb 08, 2007 · Airplane Free-body diagram!! Homework Statement A plane with mass of 1090 kg is flying straight and level at an altitude of 1100 meters & a constant velocity of 200 kg/hr (55.55m/sec). Assuming that the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/sec^2, the force on the plane due to gravity is 10900 Newtons. Since the plane is in level flight, the net force in the y direction is 0 & the lifting force provided by the wings equals the weight of the plane. Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes. The Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes Concept Builder challenges a learner to utilize an understanding of force types in order to construct a free-body diagram for an object moving along an inclined plane. Learners select force arrows from an arrow bank and label the arrows with a force type. An airplane wing free body diagram illustrating forces acting on the wing. Keywords plane, planes, Aerodynamic of Aeroplane Wing, Airplane Wing Free Body Diagram, Aerodynamic Wing Free Body Diagram. Galleries Air Transportation. Source. H. Barber The Aeroplane Speaks (New York, NY: Robert M. McBride & Co, 1917)
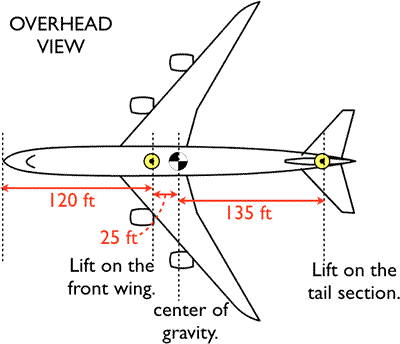
Airplane free body diagram. Draw a free-body diagram of the airplane. If these components have weights W_A = 43000lb , W_B = 8000 lb, and W_C = 6000 lb determine the normal reactions Question : Due to an unequal distribution of fuel in the wing tanks, the centers of gravity for the airplane fuselage A and wings B and C are located as shown. A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram: Free Body Diagram and Kinetic Diagram : Establish the r, q inertial coordinate system and draw the particle’s free body diagram. = maq ma r mg N s N OA 2q. ... When a pilot flies an airplane in a vertical loop of constant radius r at constant speed v, his apparent weight Download scientific diagram | Free body diagram of a fixed-wing aircraft during a pitching maneuver. from publication: A MAV that flies like an airplane and hovers like a helicopter | Near-earth ...
This physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acc... A free body diagram is a graphic, dematerialized, symbolic representation of the body (structure, element or segment of an element) in which all connecting "pieces" have been removed. A FBD is a convenient method to model the structure, structural element, or segment that is under scrutiny. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... Solution. Figure 11.7 A solid cylinder rolls down an inclined plane from rest and undergoes slipping. The coordinate system has x in the direction down the inclined plane and y upward perpendicular to the plane. The free-body diagram shows the normal force, kinetic friction force, and the components of the weight.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... The Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes Concept Builder includes a bank of 32 questions organized into 8 Question Groups and spread aross three difficulty levels. Each question provides a description of an object moving up or down an inclined plane. Learners must construct the free-body diagram for the situation. Free Body Diagram of an Inclined Plane in TikZ. In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inclined plane with a load resting on top of it in LaTeX using TikZ package. We will draw a triangle to represent the inclined plane, a rectangle for the load, then add arrows with labels to highlight different forces. 1.
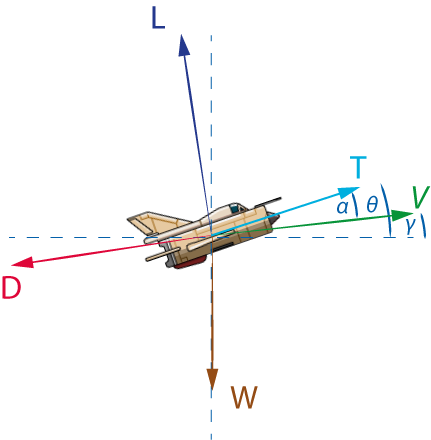
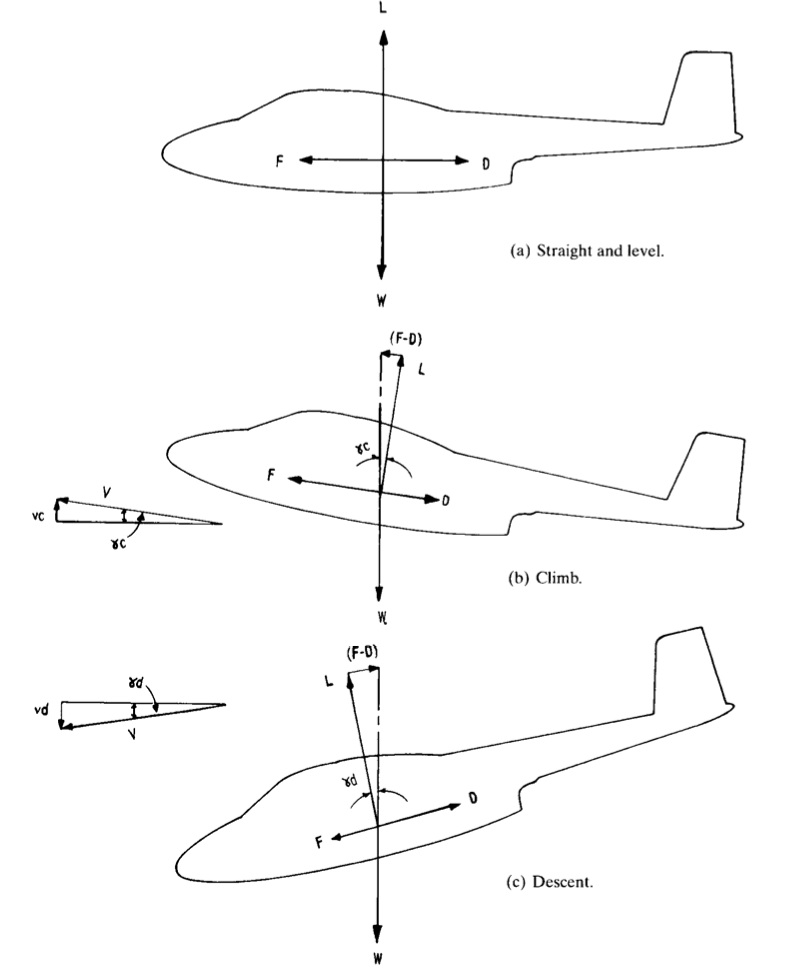
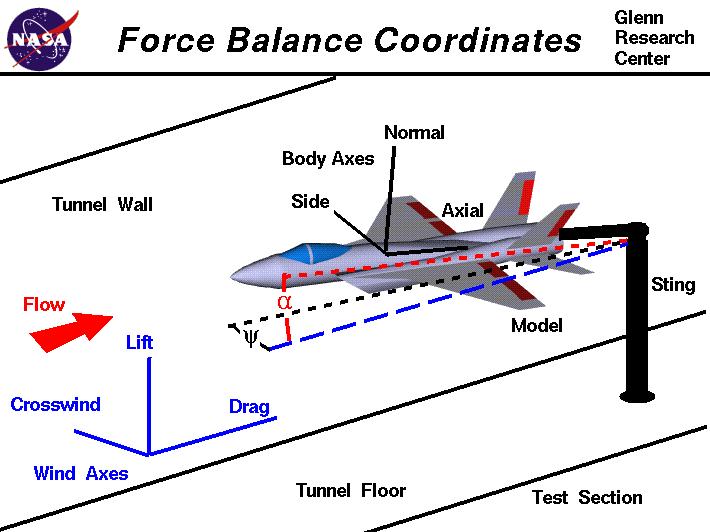
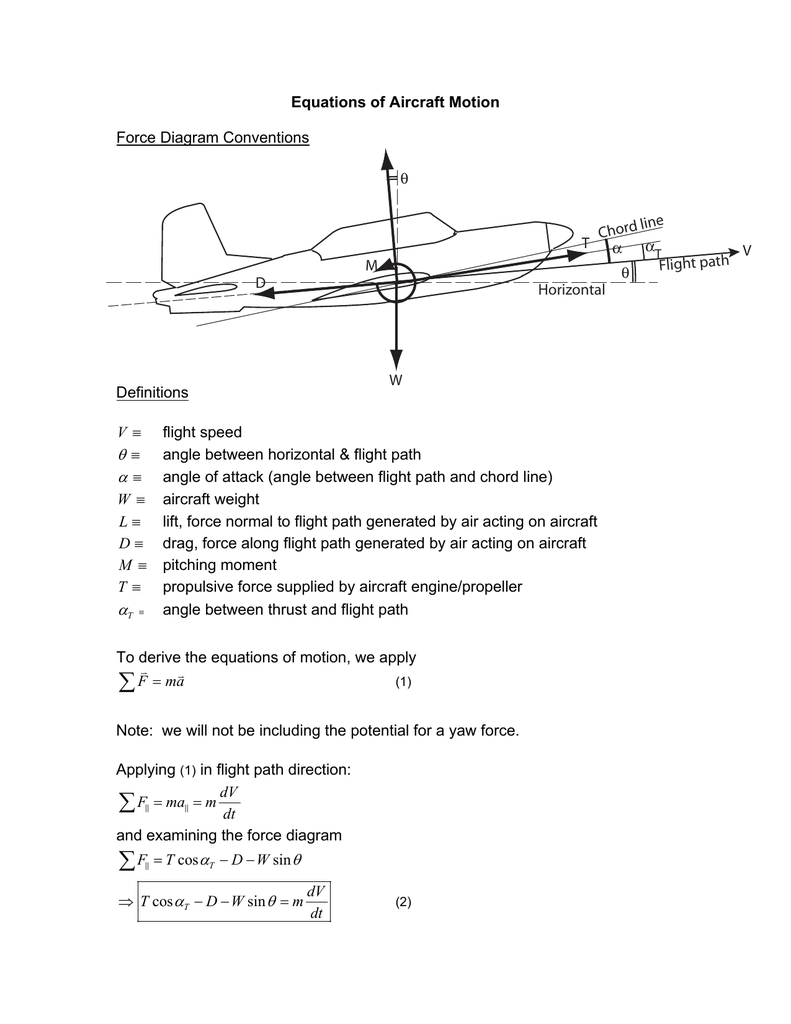
It is based on the dynamic diagram of Section 18.2.1, General two-dimensional free-body diagram for an aircraft, and Equations (18-1) and (18-2) (18-1) (18-2). However, it has been modified to represent level flight, yielding a form familiar to many pilots, in which L = W and T = D .
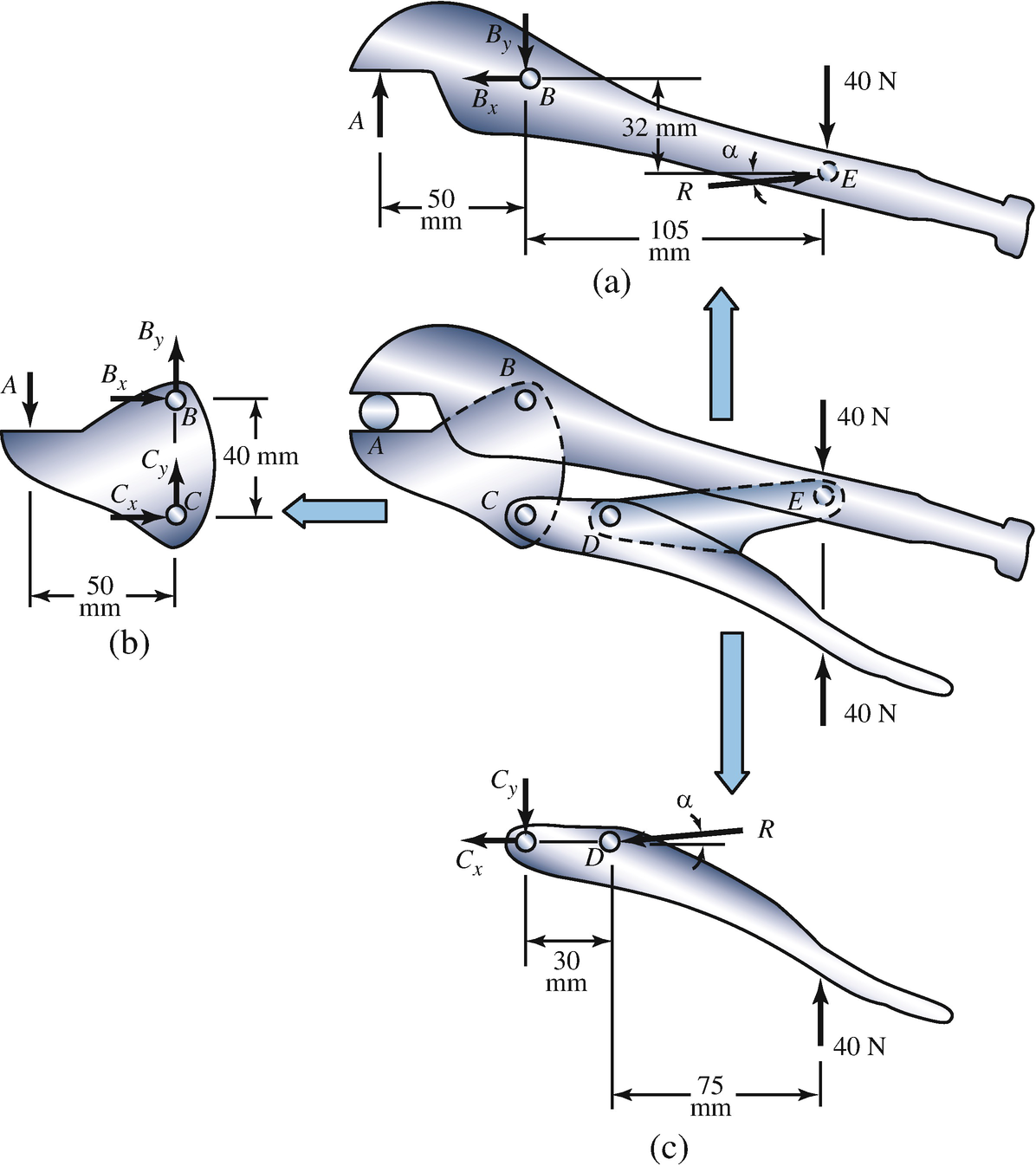
Know that the speed of the airplane decreases at a constant rate from 181 m/s at point A to 162 m/s at point C. 0.8 km B p=6 km Draw the free-body diagram of the pilot that is required to determine the magnitude of the abrupt change in the force exerted on a passenger as the airplane passes point B.
A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it. In physics and engineering , a free body diagram (force diagram, [1] or FBD) is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces , moments , and resulting ...
Free-body diagram. "A free body diagram, sometimes called a force diagram, is a pictorial device, often a rough working sketch, used by engineers and physicists to analyze the forces and moments acting on a body. The body itself may consist of multiple components, an automobile for example, or just a part of a component, a short section of a beam for example, anything in fact that may be considered to act as a single body, if only for a moment.
An inclined plane is basically a ramp. It is a flat surface that is sloped rather than horizontal. When solving problems about objects on an incline, it is convenient to choose a coordinate system with axes ... Rotated free body diagram ...
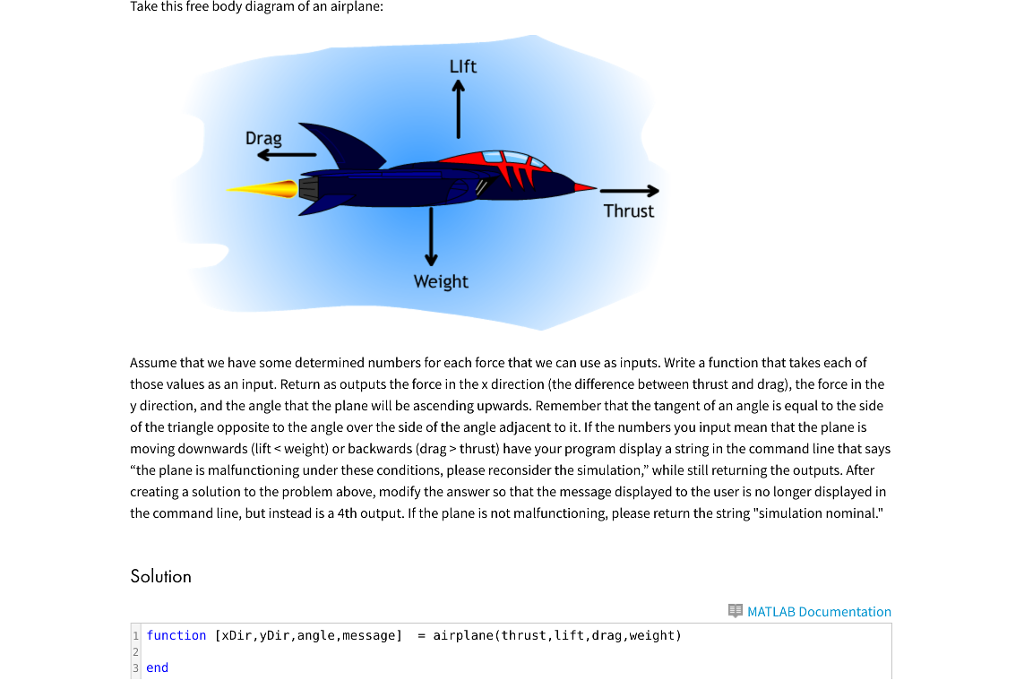
Paper Airplane Showdown and The Fundamentals of Flight 7 reate 3 free body diagrams for their plane design centered on the planes estimated center of mass ( 1 for the plane during launch, 1 for the plane during midflight, 1 for the plane upon landing). Test your new design again and record your new data below Trial 4 Trial 5 Trial 6
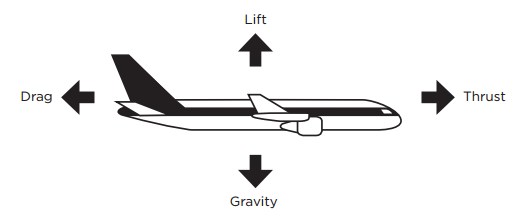
Four forces acting on an aircraft in straight-and-level, unaccelerated flight are thrust, drag, lift, and weight. How these forces work and knowing how to control them with the use of power and flight controls. Lift equation exemplifies this mathematically and supports that doubling of the airspeed will result in four times the lift. A limit to how far the AOA can be increased, if a stall is ...
Draw free-body diagrams that conform to the assumed displacement positions and their resultant reaction forces (i.e., tension or compression). c. Apply to the free body diagrams to obtain the governing equations of motion. The matrix statement of Eqs.(3.123) is The mass matrix is diagonal, and the stiffness matrix is symmetric.
[Free body diagram. Wikipedia] The free-body diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Free Body Diagram On An Inclined Plane
A free-body diagram is a useful means of describing and analyzing all the forces that act on a body to determine equilibrium according to Newton's first law or acceleration according to Newton's second law. ... Draw a free-body diagram on a coordinate plane for this situation. Show Solution.
zontal force on it. The force T exerted by the airplane's propeller is horizontal. (a) Draw the free-body diagram of the airplane. Deter-mine the reaction exerted on the nose wheel and the total normal reaction on the rear wheels (b) when T =0, (c) when T = 250 lb. W T A B 5 ft 4 ft 2 ft Solution: (a) The free body diagram is shown. (b) The ...
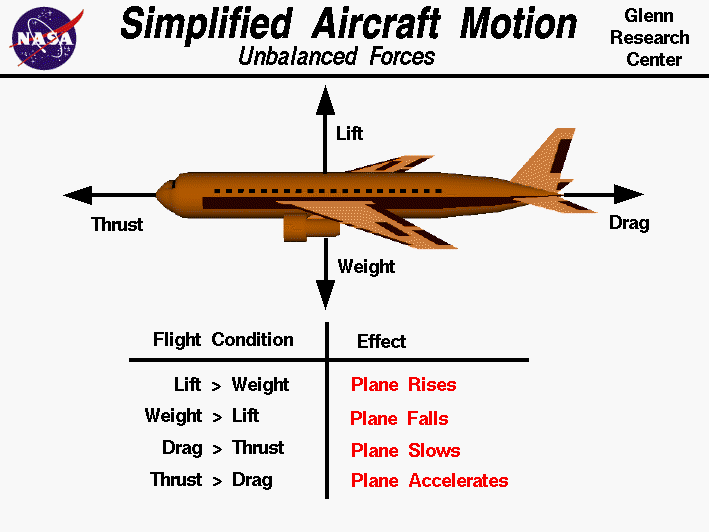
A force may be thought of as a push or pull in a specific direction. A force is a vector quantity so a force has both a magnitude and a direction. When describing forces, we have to specify both the magnitude and the direction.This slide shows the forces that act on an airplane in flight.. Weight Weight is a force that is always directed toward the center of the earth.

Hw 5 Solutions Docx Mmet 275 Mechanics For Technologists Hw 5 Solutions Chapters Sections 4 2 4 4 4 9 5 1 5 2 Short Questions 5 Points Each Steps Course Hero
B) free body diagram of point P; three forces (upper part of figure below) 1) Tension T 1 2) Tension T 2 3) Tension T 3 Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W 1 exerted by the earth on the box.
The aircraft experiences a 9G upward load; knowing the data described above, one should be able to acquire the shear and bending moment distributions along the wing of the spitfire aircraft. STEP 1: Make a cut and draw a Free body diagram with all of the external forces acting on the body.
Weight. Weight is also known as the force of gravity, and it the gravitational force due to the acceleration of gravity on the airplane, as with any mass. Weight can increase due to maneuvers performed in flight. A stylized free body diagram for the forces acting on an airplane in staight and level flight.
An airplane wing free body diagram illustrating forces acting on the wing. Keywords plane, planes, Aerodynamic of Aeroplane Wing, Airplane Wing Free Body Diagram, Aerodynamic Wing Free Body Diagram. Galleries Air Transportation. Source. H. Barber The Aeroplane Speaks (New York, NY: Robert M. McBride & Co, 1917)
Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes. The Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes Concept Builder challenges a learner to utilize an understanding of force types in order to construct a free-body diagram for an object moving along an inclined plane. Learners select force arrows from an arrow bank and label the arrows with a force type.
Feb 08, 2007 · Airplane Free-body diagram!! Homework Statement A plane with mass of 1090 kg is flying straight and level at an altitude of 1100 meters & a constant velocity of 200 kg/hr (55.55m/sec). Assuming that the acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/sec^2, the force on the plane due to gravity is 10900 Newtons. Since the plane is in level flight, the net force in the y direction is 0 & the lifting force provided by the wings equals the weight of the plane.



















0 Response to "40 airplane free body diagram"
Post a Comment