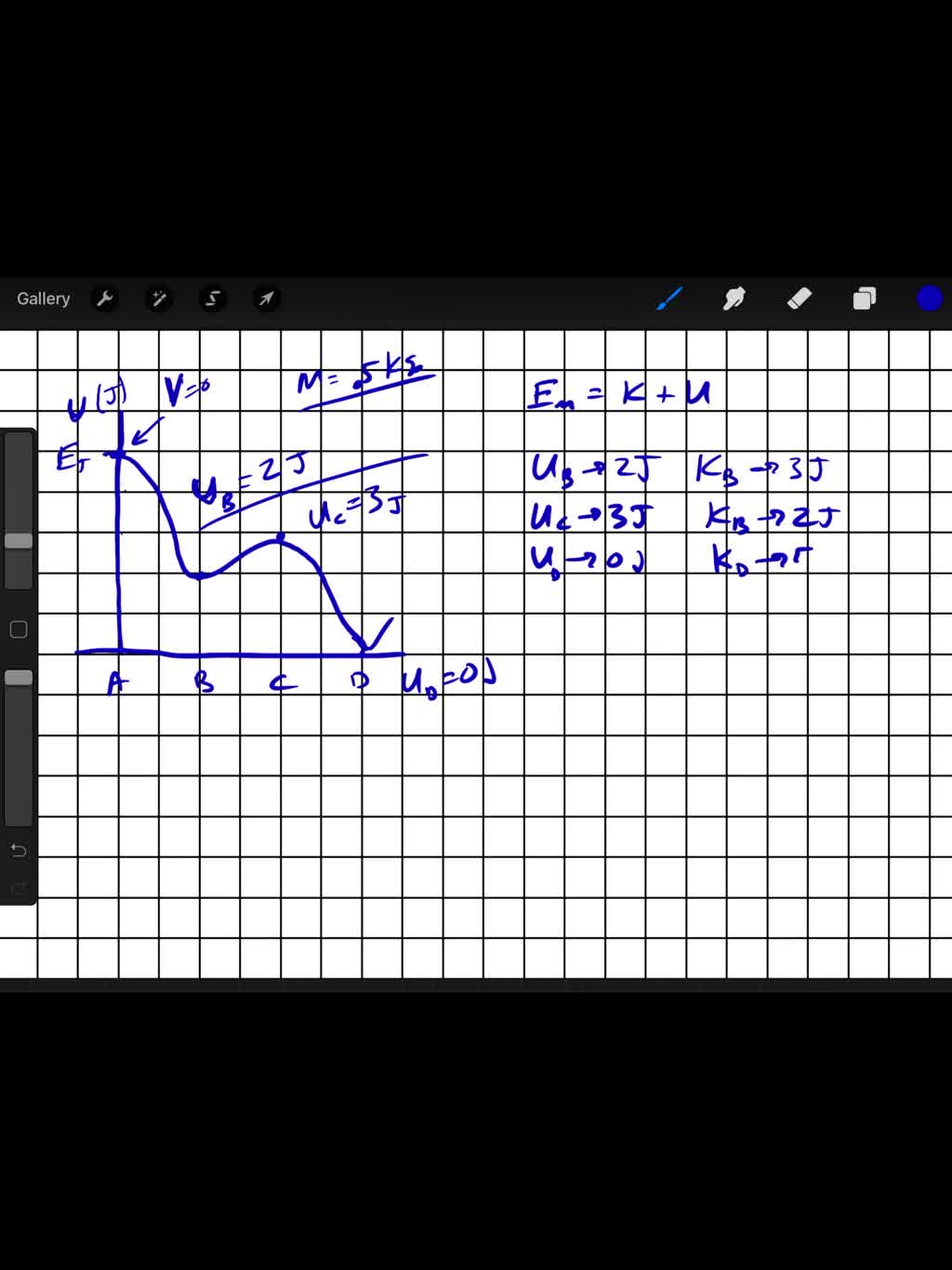
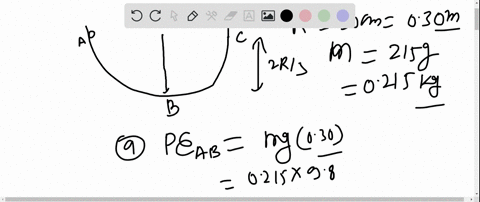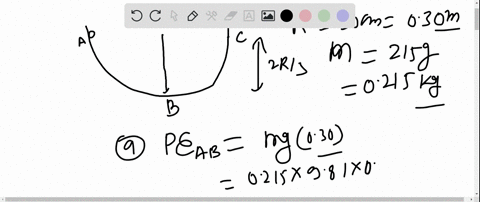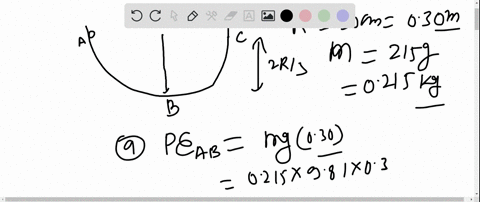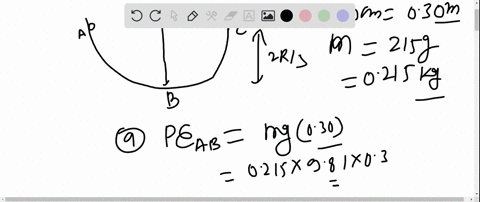
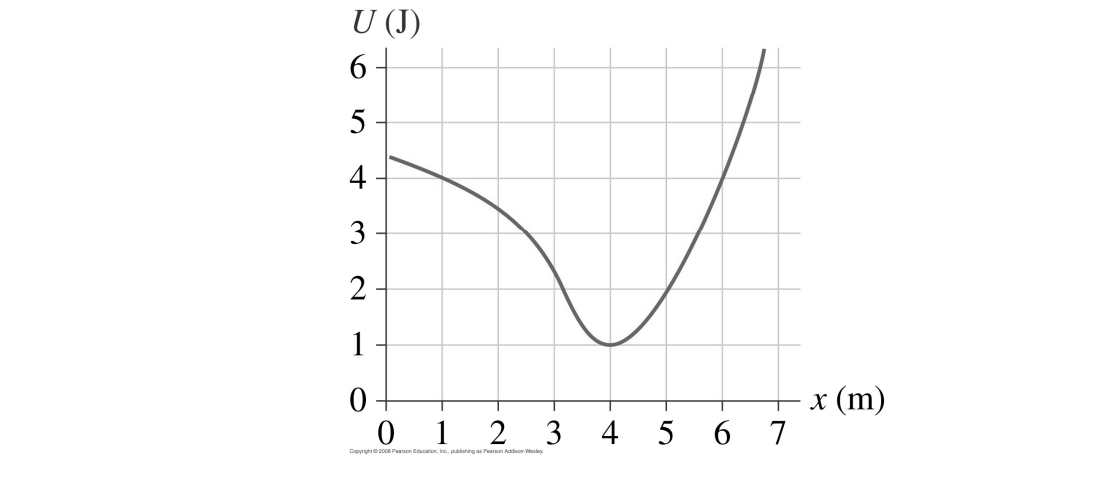
40 (figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a.
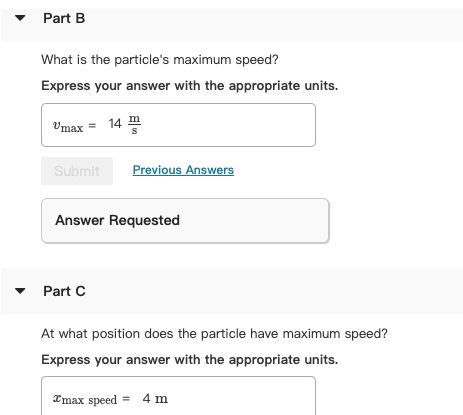
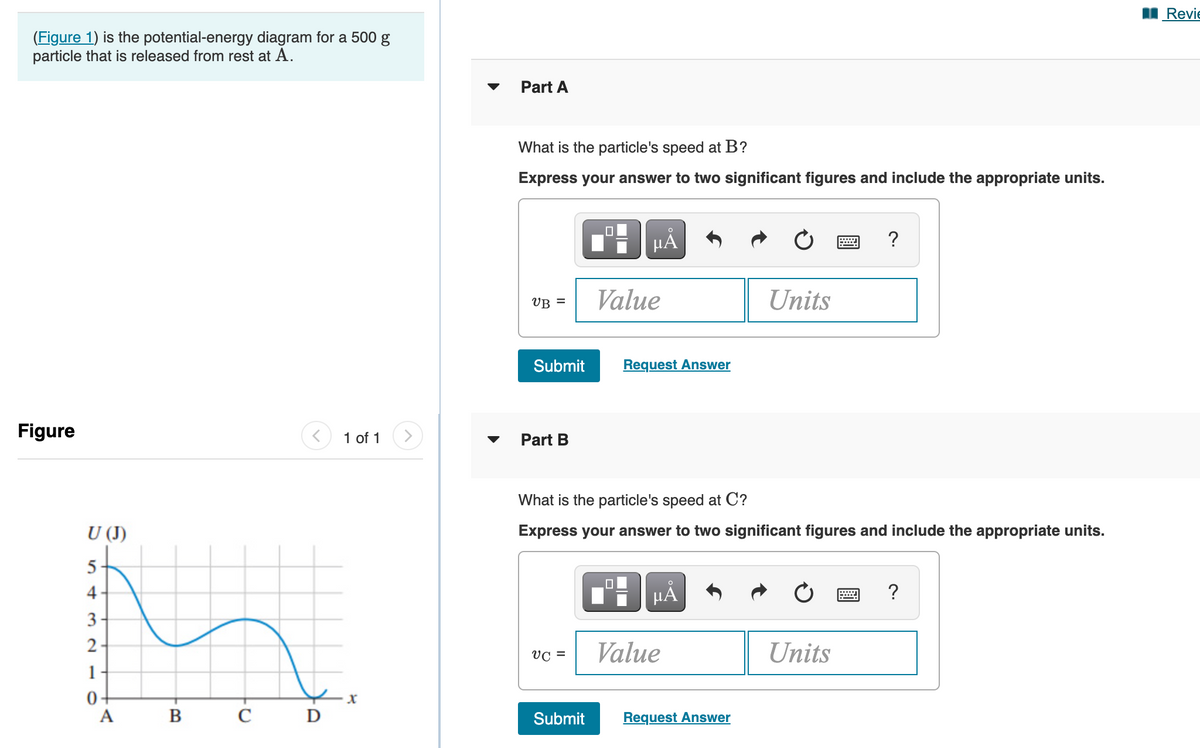
Potential-energy diagram help. I am given a potential-energy diagram with the vertical axis is potential-energy and the horizontal axis is x. The mass of the particle is 500g. They are asking the velocities of b, c, and d. The following image is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. (a) What is the particles speed at B? (b) What is the particles speed at C? (c) What is the particles speed at D?
Is the Potential-energy Diagram for A 500 G Particle that is Released From Rest at A. help with physics the figure is the potential energy then initial potential energy is 5j potential energy at b=2j loss in p e =gain in kinetic energy k e =1 2 m v 2 putting the values of mass =0 5kg k e at various points b c d we speed at b=12m s speed at c=8m s speed at d=20m s solved the figure is the ...
(figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a.
Exam No. 1 Solutions . I. (20 pts) Three positive charges q1 = +2 μC, q2 = +1 μC, and q3 = +1 μC are arranged at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 2 m as shown in the diagram. Calculate: a) The force exerted on q1 by the other charges. Answer: Because charges q2 and q3 are equal, and q1 lies on the line bisecting the two charges ... The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 450g particle that is released from rest at a image is in link http. Is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a. The energy of the particle when it is released e 5 j at a the potential energy at b ub 2 j. Problem: The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D?1 answer · Top answer: From the equation of kinetic energy:K.E = (1/2)mv2At point B:The potential energy is 2J. The kinetic energy is (5 - 2) = 2 J.[readmore]Therefore, 3 = (1/2)(500 ...
(figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a.. The figurefigure 1 is the potential energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x10m. 100 27 ratings or. What are the particles speeds atb c and d. The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a. The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particlethat is released from rest at a. The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a. Section 106 energy diagrams 25 figure ex1025 is the poten tial energy diagram from phys 009 at university of cincinnati. G) n = m r G 2 F t = m (a G) t = m r G M G = I G Since the body experiences an angular acceleration, its inertia creates a moment of magnitude I G equal to the moment of the external forces about point G. Thus, the scalar equations of motion can be stated as: When a rigid body rotates about a fixed axis perpendicular to the plane of the body at The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a. I am given a potential energy diagram with the vertical axis is potential energy and the horizontal axis is x. Chapter 7 Potential Energy And Energy Conservation Motion Of A Mass On A Spring Chemical Potential Wikipedia Energy System
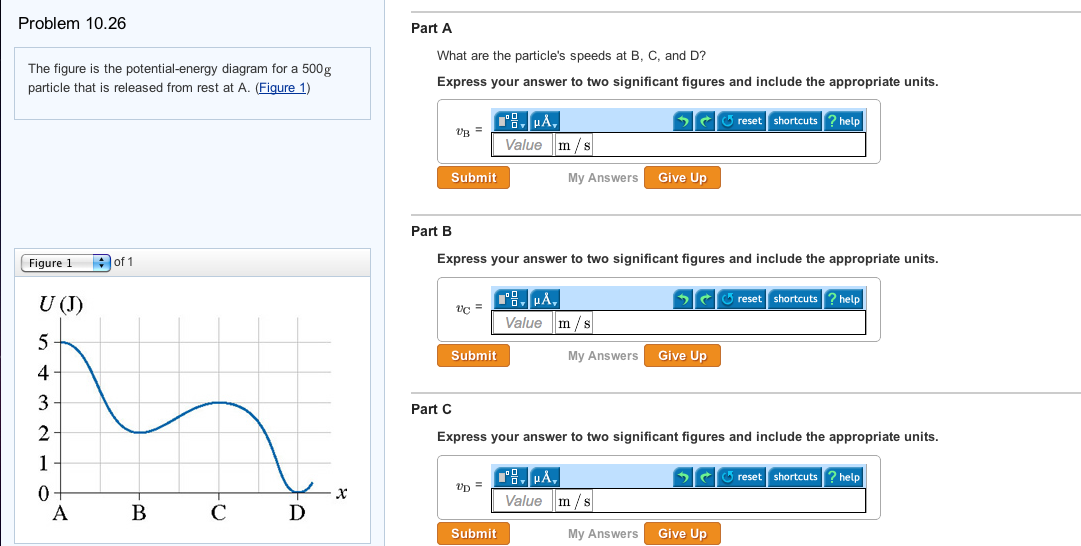
The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particlethat is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds atB, C, and D? 1. The figure gives the potential energy function of a particle . Rank regions AB, BC, CD, and DE according to the magnitude of th e force on the particle, greatest first. If multiple regions rank equally, use the same rank f or each, then exclude the intermediate ranking (i.e. if objects A, B, and C must be ranked, and A and B must both be views, students are given a potential energy diagram and told the particle is released from rest at x = 23 m. They are then asked to describe the subsequent motion of the particle. In order to answer, students can recognize that since the particle is released from rest, the total energy is equal to the potential energy at that position (i.e., 2 J). From Equation 29-12, the energy required to reverse the orientation of a proton's magnetic moment from parallel to antiparallel to the applied magnetic field is ΔU = 2µB = 2(1.41 ×10 −26 A ⋅ m2)( 7.0 T) = 1.97 × 10−25 J = 1.23× 10−6 eV. (This amount of energy is characteristic of radio waves of frequency 298 MHz, see Chapter 39 ...
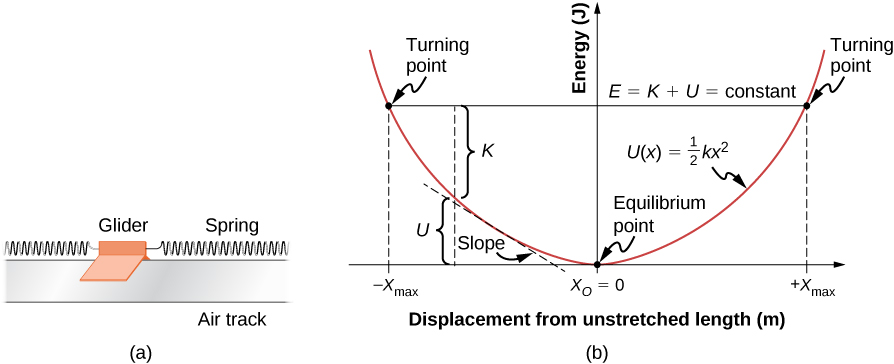
Solution for (Figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. Part A What is the particle's speed at B? A block of mass 500 g is attached to a spring of spring constant 80 N/m (see the following figure). The other end of the spring is attached to a support while the mass rests on a rough surface with a coefficient of friction of 0.20 that is inclined at angle of 300. This potential energy calculator enables you to calculate the stored energy of an elevated object. The full name of this effect is gravitational potential energy because it relates to the energy which is stored by an object as a result of its vertical position or height. Interpreting a one-dimensional potential energy diagram allows you to obtain qualitative, and some quantitative, information about the motion of a particle. At a turning point, the potential energy equals the mechanical energy and the kinetic energy is zero, indicating that the direction of the velocity reverses there.

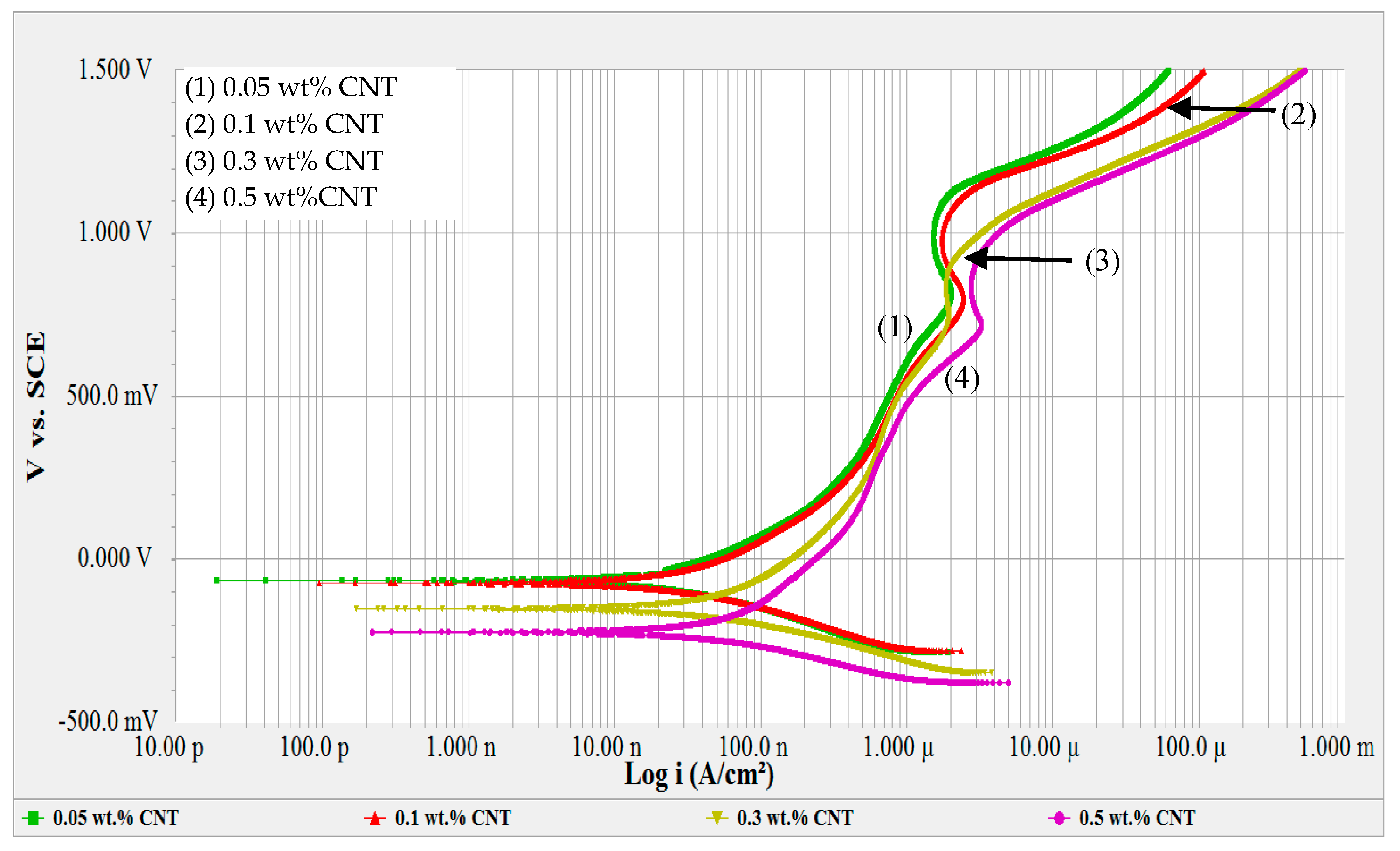
Materials Free Full Text Corrosion Evaluation Of 316l Stainless Steel In Cnt Water Nanofluid Effect Of Cnts Loading Html
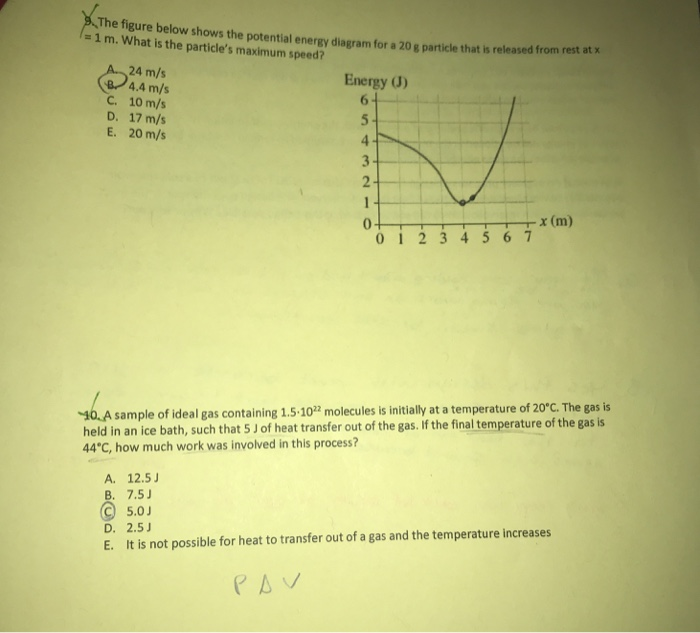
6. Figure shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of a 2.0 kg particle that can move along x-axis. The graph has the these values: UA = 9.0 J, Uc = 20.0 J and UD = 24.0 J. The particle is released at position x = 5.0m with kinetic energy 4.0 J where the potential energy is UB = 12.0 J, (a)What is the kinetic energy of the particle
The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle speeds at point B, C and D?
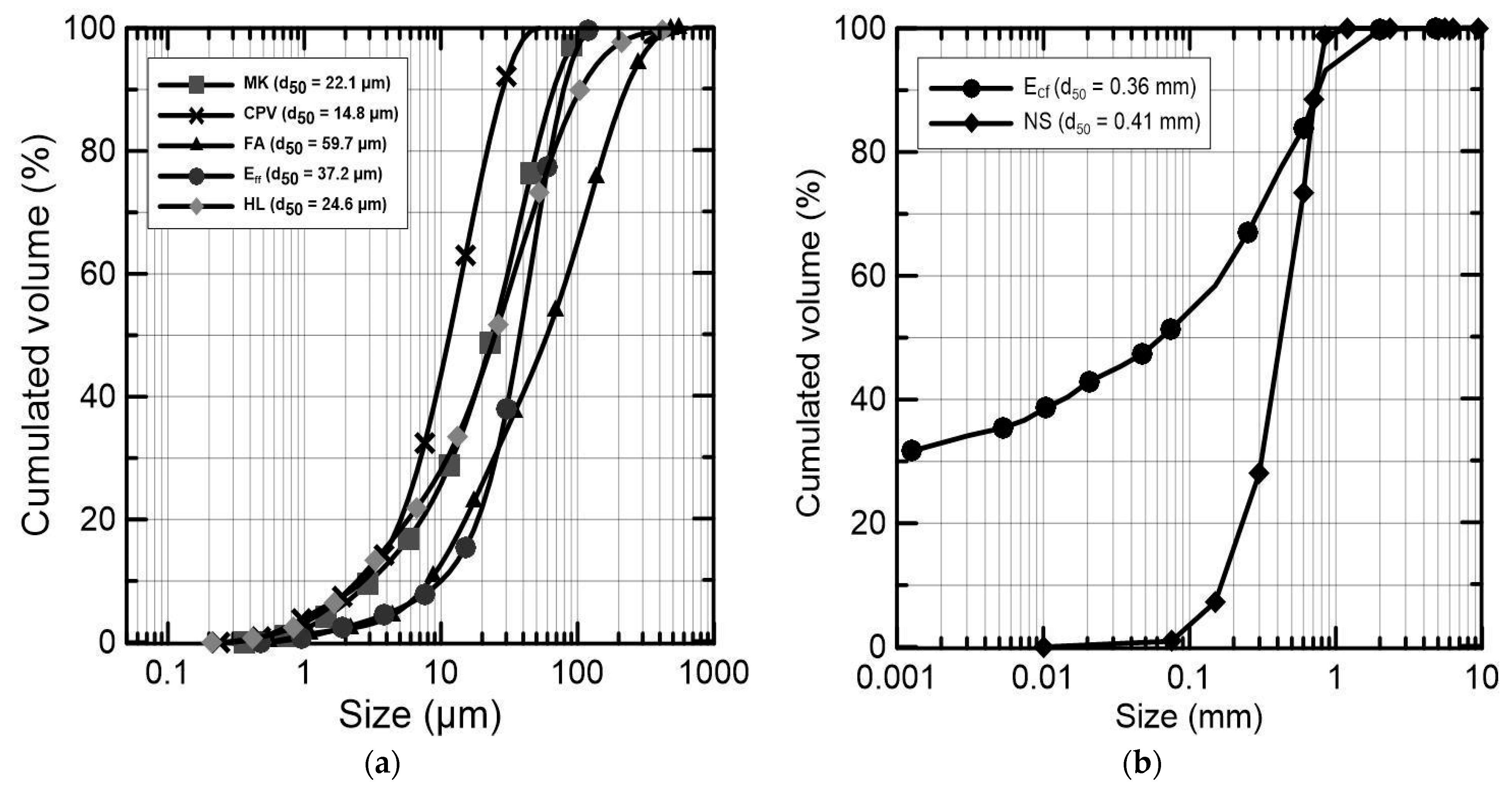
Sustainability Free Full Text Thermal Energy Analysis And Life Cycle Ghg Emissions Assessments Of Innovative Earth Based Bamboo Plastering Mortars Html
Physics questions and answers. Item 6 Part A (Figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A What is the particle's speed at B? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units UValue Units Submit Part B What is the particle's speed at C? Express your answer to two ...

Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A Wiring Site Resource
3,1,2. The potential energy of a .20kg particle moving along the x axis is given by U (x) = (8.0J/m^2)x^2 + (2.0J/m^4)x^4. -40 m/s. Object A and B interact with each other via both conservative and nonconservative forces. Let KA and KB be kinetic energies, U be potential energy, and E int be thermal energy.
Solved Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A What Are The Particle S Speeds At B C And D
The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle speeds at point B, C and D?
(b) The turning points for the particle with total energy (TE) shown are at 2 mx = and 8 mx =. (c) The particle could remain at rest in stable equilibrium at 3 mx = and 6 mx =. The particle could also remain at rest in unstable equilibrium at 1 mx = and 4 mx =. 10.14. The problem can be divided into three parts: (1) from when the first ball is ...
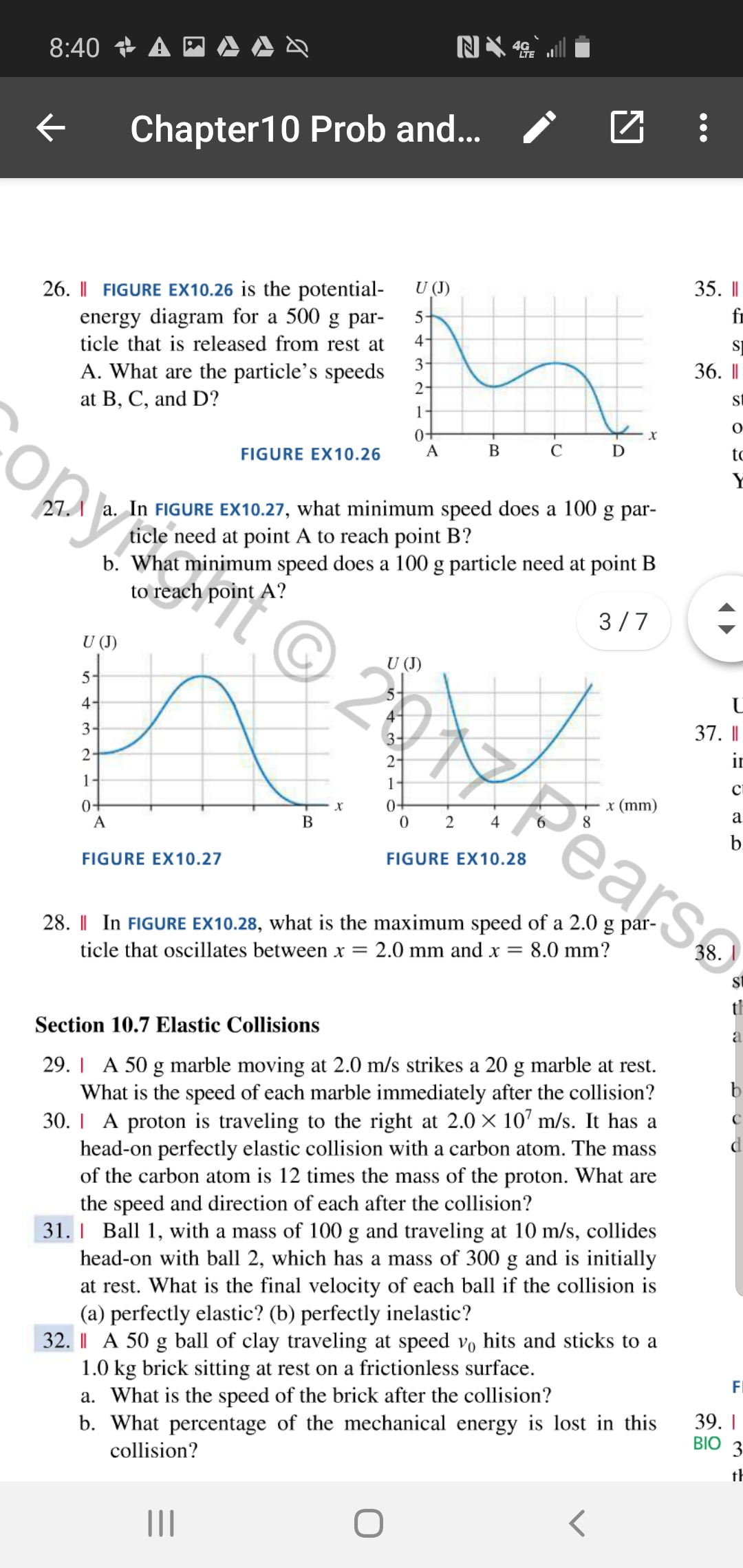
Figure EX10.26 is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D? Solution ...1 answer · Top answer: ?Solution 26E Step 1az: We are going to find the speed of the particle at the points B, C, and D. The mass of the particle m = 500 g = 0.5 kg The energy ...
Model:For an energy diagram, the sum of the kinetic and potential energy is a constant. Visualize: The particle with a mass of 500 g is released from rest at A. That is, at A. Since we can draw a horizontal TE line through The distance from the PE curve to the TE line is the particle's kinetic energy.
The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a. Figure ex1026 is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g par ticle that is released from rest. That is k 0 at x 10 m. A block sliding along a horizontal frictionless surface with speed collides with a spring and compresses it by 20 cm.
Solved Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A What Are The Particle S Speeds At B C And D
Answer to: The figure shows the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. a. What is the particle's speed at...

The Figure Below Shows A Graph Of Potential Energy U S Verses Position X For A Particle Executing On Edimensional Motion Along The X Axis The Total Mechanical Energy Of The System Is
Jul 1, 2021 — The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, ...

Recent Development In Defects Engineered Photocatalysts An Overview Of The Experimental And Theoretical Strategies Zafar Energy Amp Environmental Materials Wiley Online Library
The particle is released from rest at x 10 m. Start studying physics ch 8. The figurefigure 1 is the potential energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x10m. Figure ex1025 is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a.
Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A Wiring Site Resource
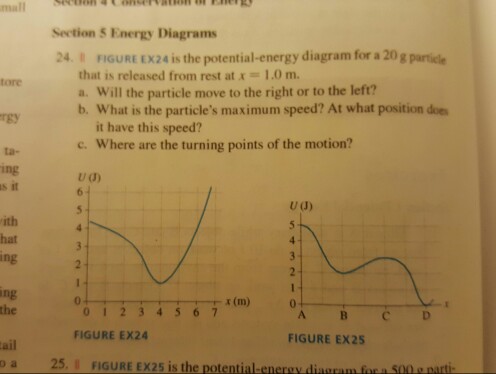
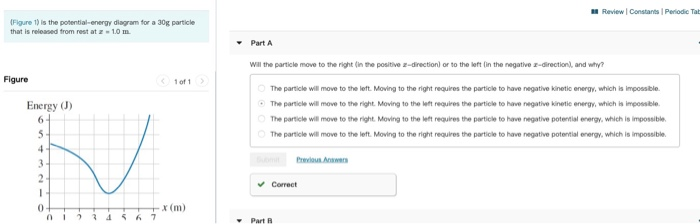
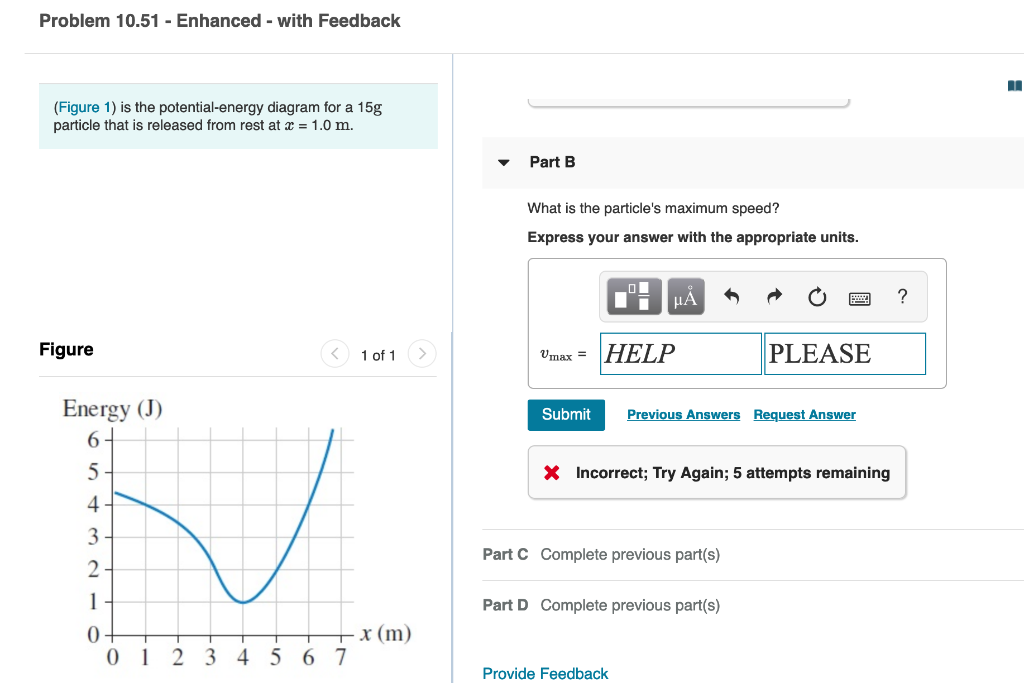
Answer to FIGURE EX10.24 is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m.a. Will the particle move to the right ... Rating: 4 · 4 reviews
is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. ... we will consider the following situation as depicted in the diagram (Figure 1): A block of mass m slides at a speed v along a horizontal, smooth table. ... Suppose the potential energy of the block at the table is given by mgh/3. This implies that ...
Jul 29, 2019 — What are the particles speeds at b c and d. The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a. A ...
equilibrium position and released from rest. It then experiences simple harmonic motion. When the object is . A /2 from the equilibrium position how is the energy divided between spring potential energy and the kinetic energy of the object? Assume mechanical energy is conserved. 1. The energy is 25% spring potential energy and 75% kinetic. 2.
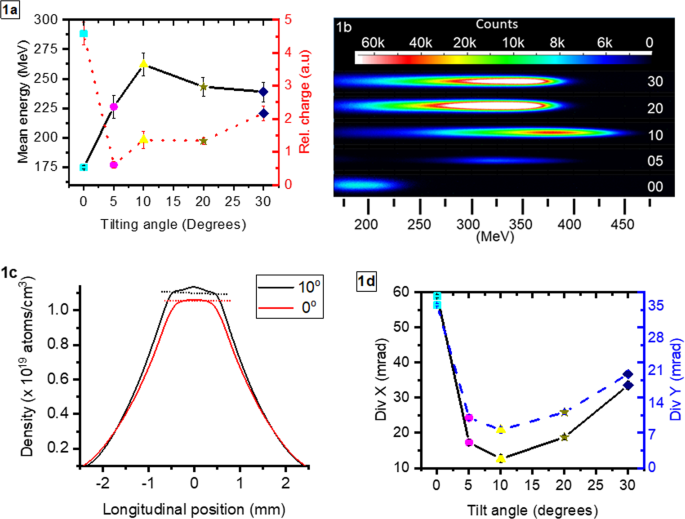
Electron Energy Increase In A Laser Wakefield Accelerator Using Up Ramp Plasma Density Profiles Scientific Reports
change as no potential energy change takes place: E = 1 2 m(V2 cf V 2 ci) + 1 2 M(V2 tf V 2 ti) = 1 2 1240 (182 252) + 1 2 8100(21:0722 202) = 8301J c) Most of the energy was transformed to internal energy with some being carried away by sound. 0.9 A 9.6-g bullet is red into a stationary block of wood having mass m = 4.90 kg. The bullet imbeds ...
is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B,C, and D?Jun 14, 2020
Problem: The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D?1 answer · Top answer: From the equation of kinetic energy:K.E = (1/2)mv2At point B:The potential energy is 2J. The kinetic energy is (5 - 2) = 2 J.[readmore]Therefore, 3 = (1/2)(500 ...

The Interaction Of Climate Change And Methane Hydrates Ruppel 2017 Reviews Of Geophysics Wiley Online Library
The figure is the potential energy diagram for a 450g particle that is released from rest at a image is in link http. Is the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a. The energy of the particle when it is released e 5 j at a the potential energy at b ub 2 j.
Exam No. 1 Solutions . I. (20 pts) Three positive charges q1 = +2 μC, q2 = +1 μC, and q3 = +1 μC are arranged at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 2 m as shown in the diagram. Calculate: a) The force exerted on q1 by the other charges. Answer: Because charges q2 and q3 are equal, and q1 lies on the line bisecting the two charges ...

Migration Deposition Characteristics Of Exogenous Particles Near The Injection Well In A Groundwater Heat Pump System Sciencedirect
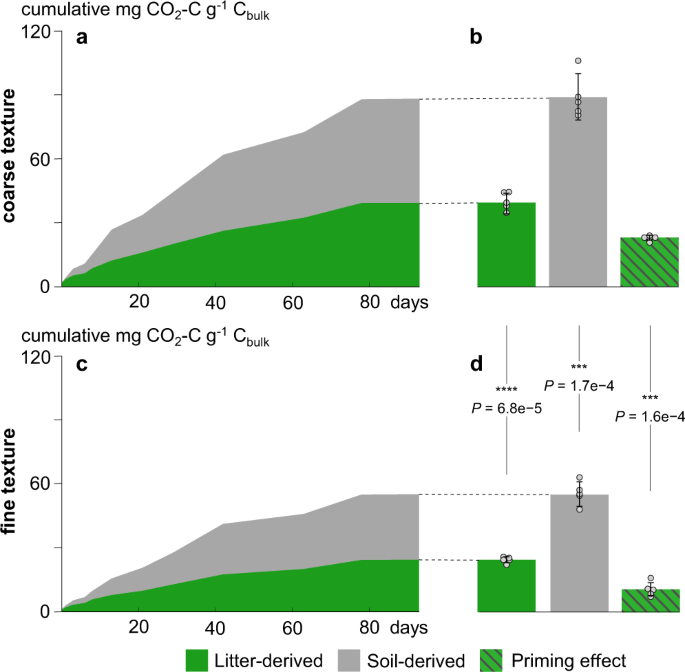
Particulate Organic Matter As A Functional Soil Component For Persistent Soil Organic Carbon Nature Communications
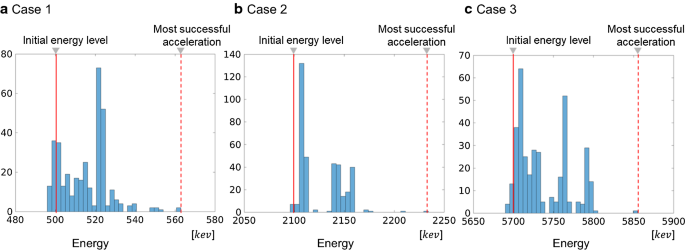
Acceleration Mechanism Of Radiation Belt Electrons Through Interaction With Multi Subpacket Chorus Waves Earth Planets And Space Full Text

An Expression For The Angle Of Repose Of Dry Cohesive Granular Materials On Earth And In Planetary Environments Pnas
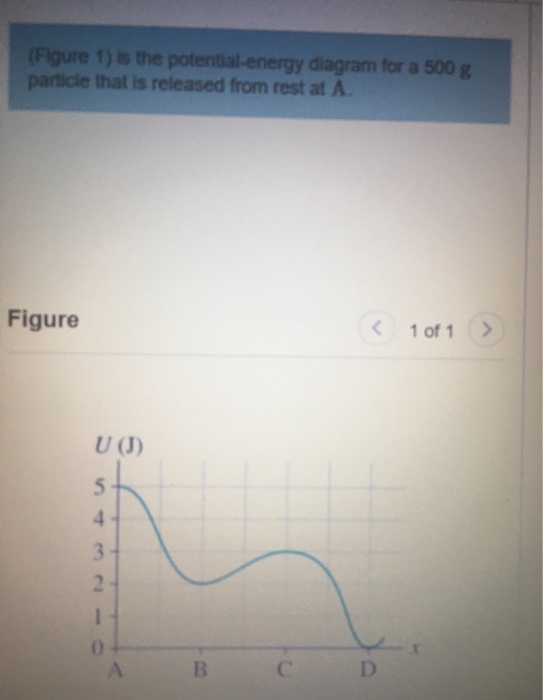
Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A Wiring Site Resource
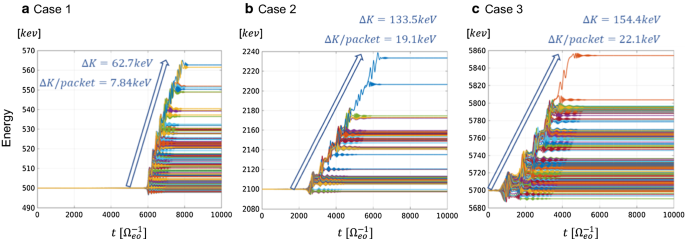
Acceleration Mechanism Of Radiation Belt Electrons Through Interaction With Multi Subpacket Chorus Waves Earth Planets And Space Full Text
Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A Wiring Site Resource
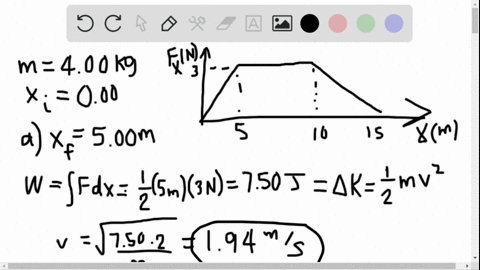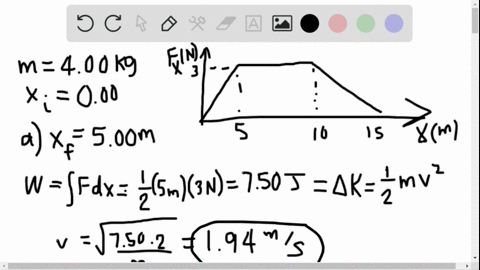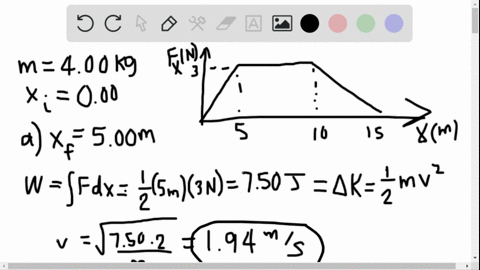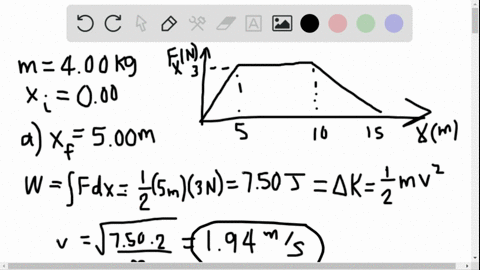
Solved Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A What Are The Particle S Speeds At B C And D
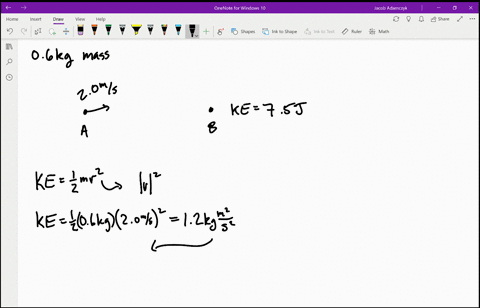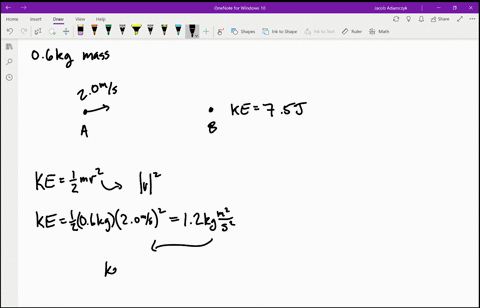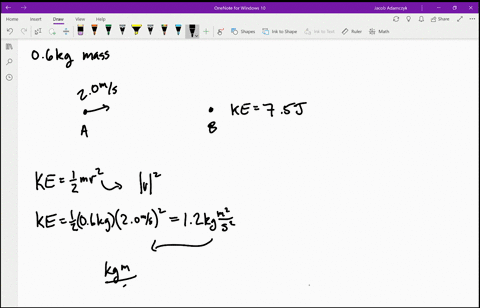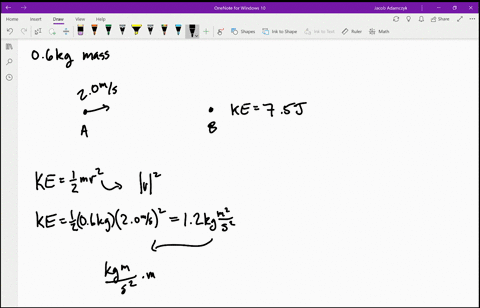
Solved Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A What Are The Particle S Speeds At B C And D

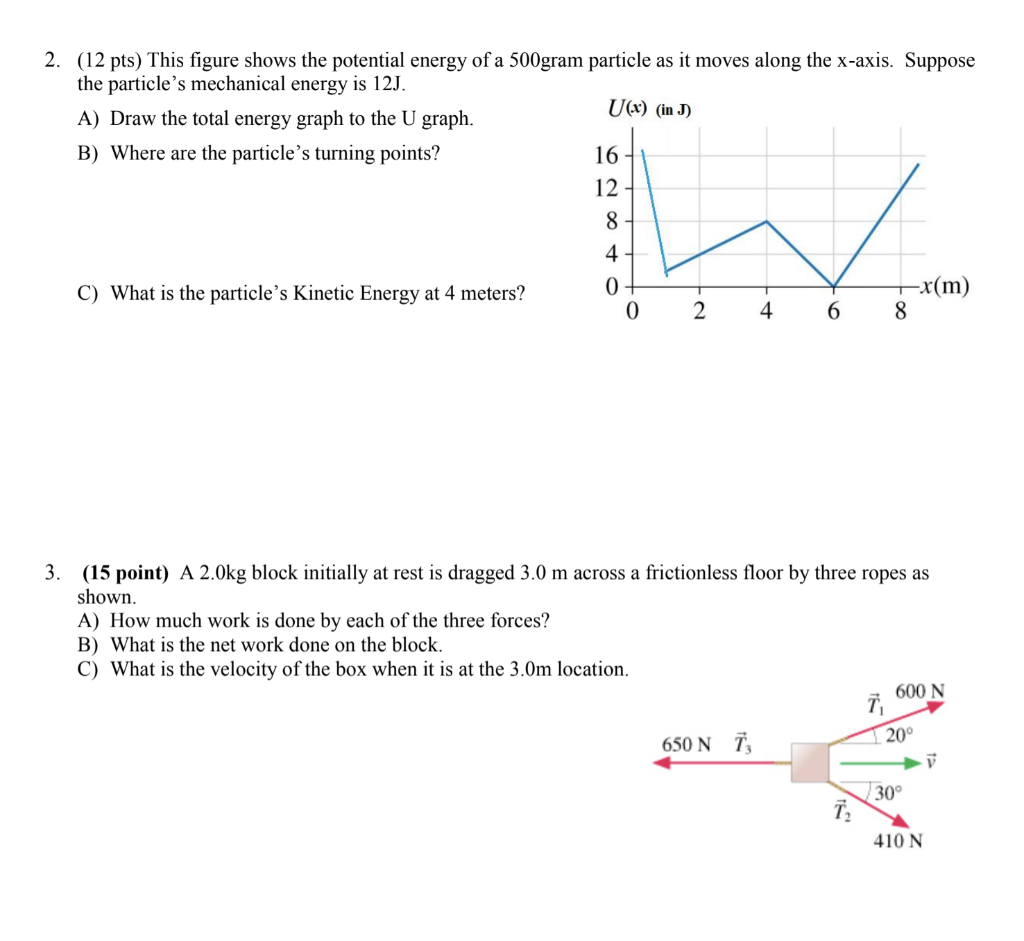







0 Response to "40 (figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a."
Post a Comment