42 biconvex lens ray diagram
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc... Convex lens ray diagram. When a ray passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond ...
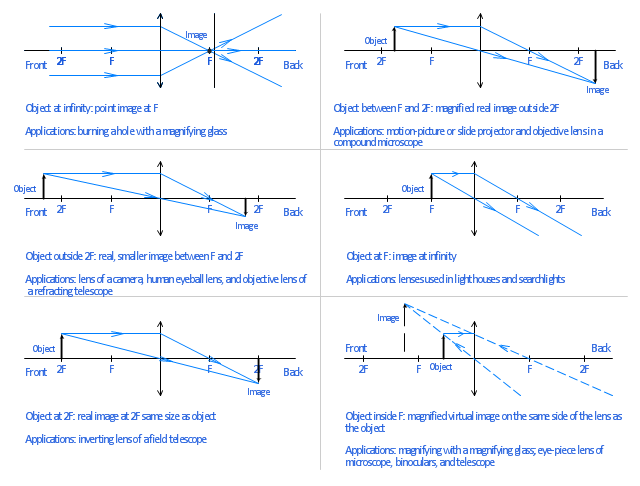
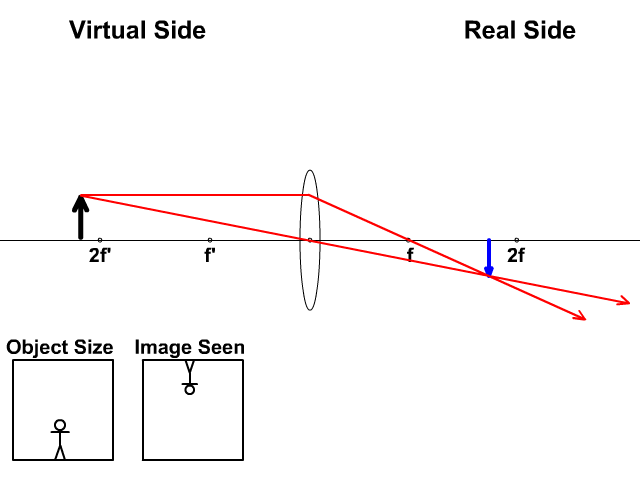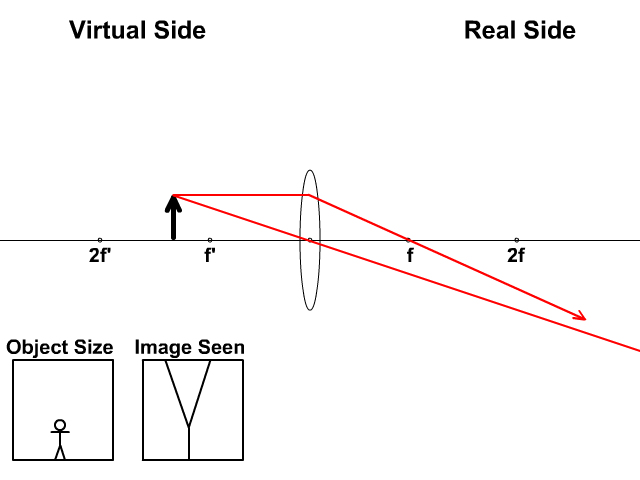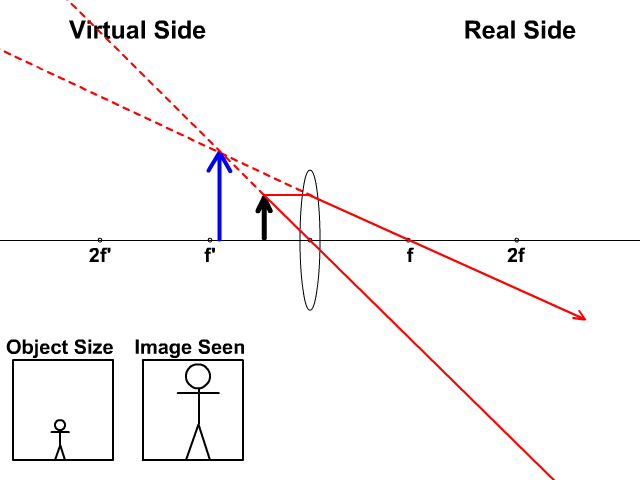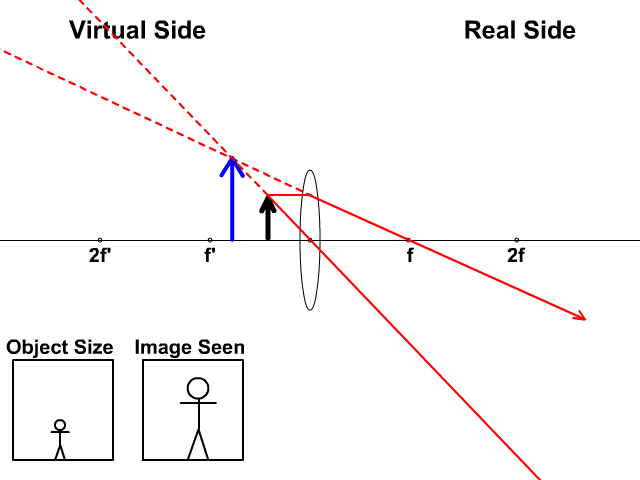
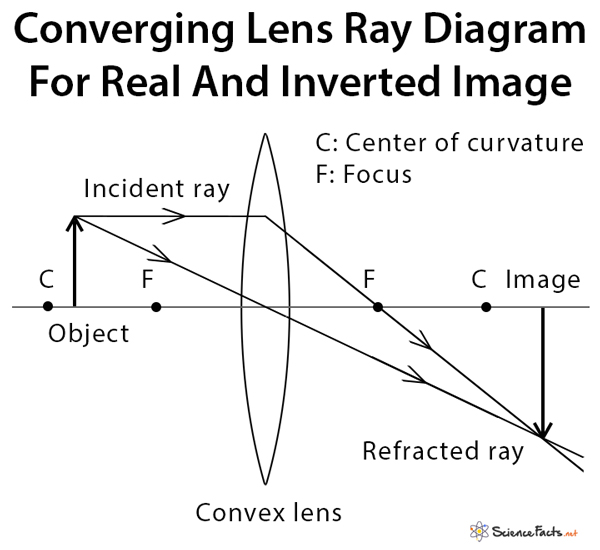
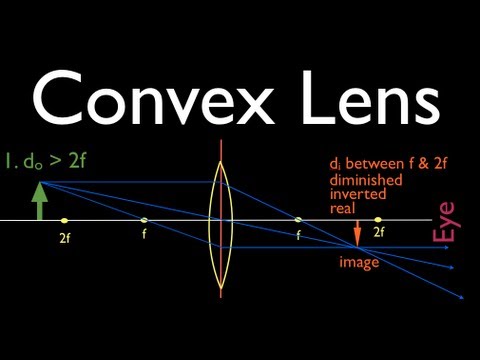
Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. In such cases, a real image is formed.
Biconvex lens ray diagram
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. A simple microscope consists of a convex lens of short focal length. Figure 3 shows the ray diagram which subsequently forms the image of an object (or we can say a source of light). Figure 3: Working of a Biconvex lens as a Magnifying glass. F is the focal length of the lens. A biconvex lens μ = 1. 5) of focal ... With help of suitable diagram, sign conventions and assumptions, derive Lens Make's formula for a convex lens. Hard. View solution > A biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 2 0 ...
Biconvex lens ray diagram. A lens is considered to be thin if its thickness t is much less than the radii of curvature of both surfaces, as shown in .In this case, the rays may be considered to bend once at the center of the lens. For the case drawn in the figure, light ray 1 is parallel to the optical axis, so the outgoing ray is bent once at the center of the lens and goes through the focal point. Lens Design I - Seminar 1 Warm-Up (20min) Setup a single, symmetric, biconvex lens for imaging a point object. The lens is made of the glass N-BK7, has a radius of curvature of R = 32.3 mm, and a thickness of t = 5 mm. The numerical aperture in object space has a value of NA = 0.05 and the corresponding object has a distance of s = 100 mm. Note that if the lenses are oriented the other way, then this arrangement will produce more spherical aberration than the bi-convex case. To answer your question specifically, the bi-convex lens is the best lens to use in the situation where the beam incident on the lens is diverging and the beam leaving the lens is converging symmetrically. Consider a thin lens in air. As shown above, the power of the lens is simply the sum of the powers of the individual surfaces. The diagram shows a biconvex lens but the derivation is valid for any type of thin lens. For air, n 1 ~1,use n = n 2 and define f by Ray Diagrams for Thin Lenses. To draw a ray diagram, apply the following rules
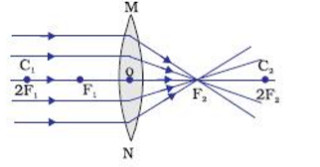
A ray diagram without the produced image is shown. A car acting as an object in front of a biconvex lens between F and 2 F on the object side of the lens. There is a light ray parallel to the principal axis that is bent through F on the image side of the lens. There is a ray straight through the center of the lens. Generally, bi-convex lenses perform with minimum aberrations at magnification factors between 0.2x and 5x. Convex lenses are primarily employed for focusing applications and for image magnification. Typical plano-convex lenses (Figure 1(b)) have one positive convex face and a flat (plano) face on the opposite side of the lens. A Ray Diagram is a simple picture using only 2 or 3 light rays reflected off an object to visualize how images are formed. For a converging lens, the following three rays are drawn: 1. Ray 1 is drawn parallel to the principal axis and then passes through the focal point on the back side of the lens 2. A biconvex lens is one that is convex on both sides of the lens, as shown below: Treating this and drawing ray diagrams for a biconvex lens is essentially two refractions (one on the way into the lens and the other on the way out) along curved surfaces. So let's look at the steps necessary to draw the ray diagram for light going through a lens.
I'm casting a set of rays into an asymmetric bi-convex lens and applying Snell's law to each ray to trace them through the lens. I then calculate the expected focus using the following equation: 1 f = ( n − 1) [ 1 R 1 − 1 R 2 + ( n − 1) d n R 1 R 2] I've plotted this point, as well as the rays exiting the lens, and I'm seeing that they ... Biconvex lens are used as a magnifying or condensing lenses. These are utilized in many imaging systems such as the telescopes, monocular, microscopes, binoculars, cameras, projectors, etc. These are used in producing the virtual image in case of a human eye and a real image in case of the photographic films or an optical sensor. Derive the lens formula, 1/f = 1/v - 1/u for a concave lens, using the necessary ray diagram. Two lenses of power 10 D and −5 D are placed in contact. (i) Calculate the power of the new lens. (ii) Where should an object be held from the lens so as to obtain a virtual image of magnification 2? lens, the lens equation is the same but the value of fis nownegative. Ray diagrams for such lenses are drawn using: a ray from the top of the object through the middle of the lens; a ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis which the lens refracts so it seems to come from the focal point. V W F
Converging: Biconvex, planoconvex, and positive meniscus lenses focus light. Diverging: Biconcave, planoconcave, and negative meniscus lenses diverge light. Meniscus lenses are the type used in eyeglass and contact lenses. Positive meniscus lenses are thicker at the center than the edges.
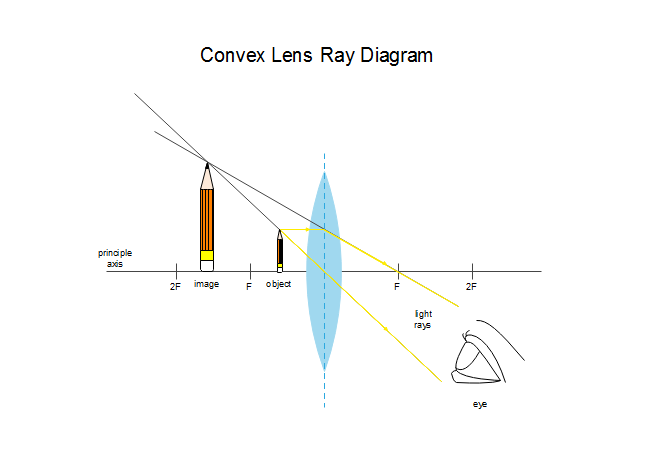
A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a lens. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were drawn in a previous part of Lesson 5. In this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for double concave lenses.
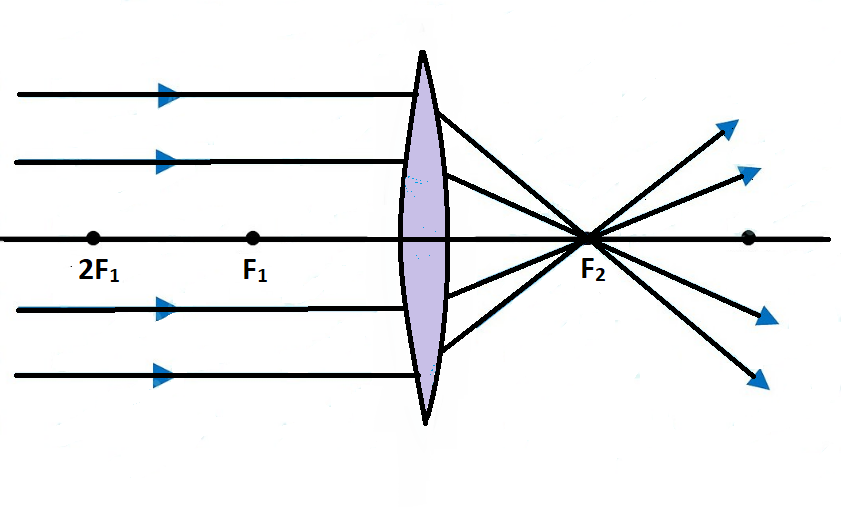
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
We can use biconvex lenses as burning glasses. Biconvex lenses are found in the natural camera viz: the human eye, where they produce virtual images. Biconvex lenses are positive lenses, and they are best-used for converging beams that are diverging in nature. We find the applications of biconvex lens industries and also in image relays.
The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ...
Ray Tracing Diagram For Convex Lens Physics Diagrams Optics Vector Stencils Library Ray Diagram Lenses
Wikipedia] The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray Diagram Of Biconvex Lens. ...
Wilson S Quarter Century In Photography A Collection Of Hints On Practical Photography Which Form A Complete Text Book Of The Art Radiating Point Then The Circle Of Aberration Becomes The More
For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
భౌతిక రసాయన శాస్త్రం 10 వ తరగతి క్విజ్ 4 ఐదవ ప్రశ్న జవాబు వివరణPhysical sciences 10th Class Quiz 4 ...
We draw another ray which passes through Center of Curvature. So, the ray will go back along the same path after reflection. Where both reflected rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between Pole (P) and Focus (F) We can say that. Image is behind the Mirror (Virtual Image) Image is Erect.
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
Draw A Ray Diagram And Show How A Convex Lens Is Used As A Magnifying Glass Physics Topperlearning Com 2jppsyaa
Single lenses capable of forming images (like the bi-convex lens) are useful in tools designed for simple magnification applications, such as magnifying glasses, eyeglasses, single-lens cameras, loupes, viewfinders, and contact lenses. This interactive tutorial explores how a simple bi-convex lens can be used to magnify an image.
A biconvex lens μ = 1. 5) of focal ... With help of suitable diagram, sign conventions and assumptions, derive Lens Make's formula for a convex lens. Hard. View solution > A biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 2 0 ...
A simple microscope consists of a convex lens of short focal length. Figure 3 shows the ray diagram which subsequently forms the image of an object (or we can say a source of light). Figure 3: Working of a Biconvex lens as a Magnifying glass. F is the focal length of the lens.
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
Explain With The Help Of A Diagram Why The Convex Lens Is Also Called Converging Lens Physics Topperlearning Com Rv8ec6gpp

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes
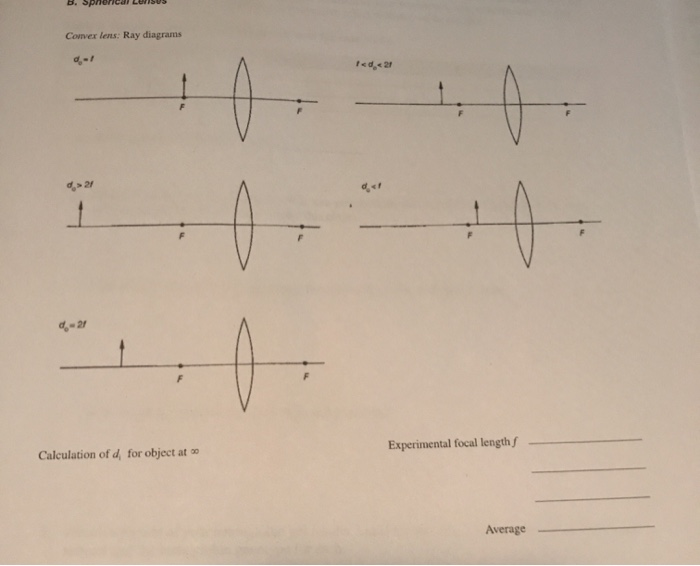










---teachoo.png)










0 Response to "42 biconvex lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment