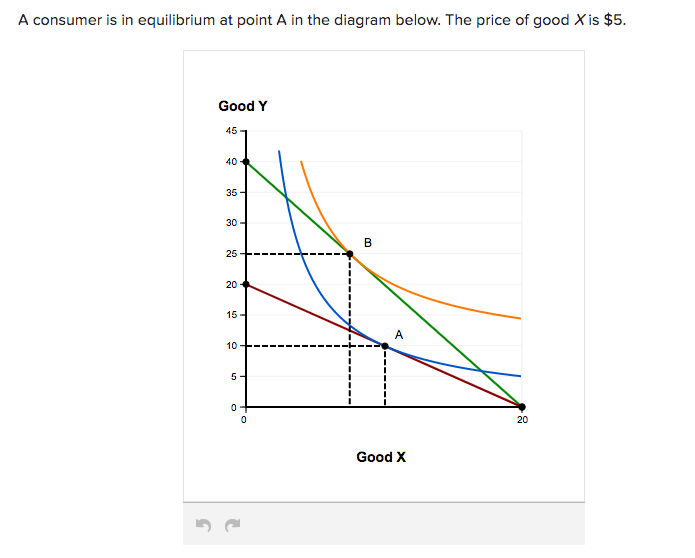
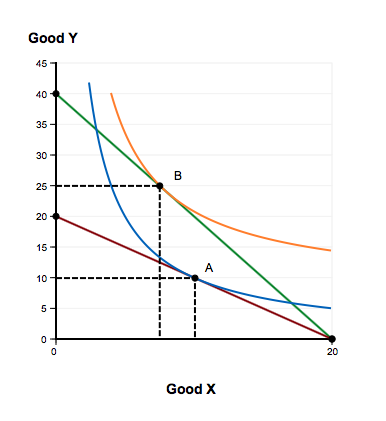
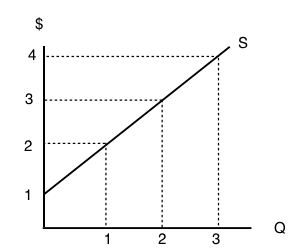
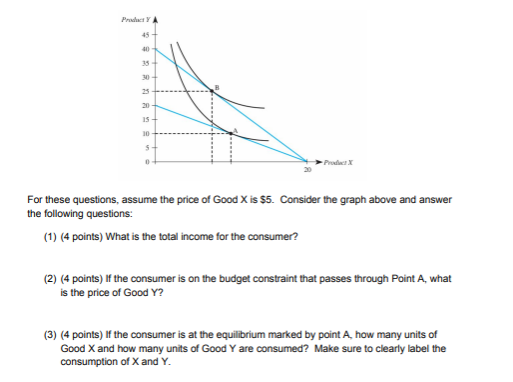
45 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
If the consumer demands less of good X after the rise in income, that good X is an inferior good for that consumer. Q.31. Explain the effect of increase in income of buyers of a 'normal' commodity on its equilibrium price. Ans. i. Increase in income increases demand at the given price. ii. This leads to excess demand. iii. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. ... Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium? The price of good Y decreased to $2.50. The price of good Y increased to $10.
At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? units. d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium? The price of good Y decreased to $2.50. The price of good Y increased to $10.
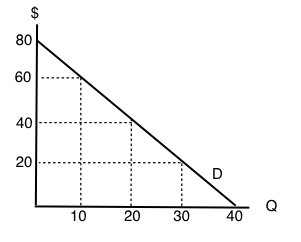
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
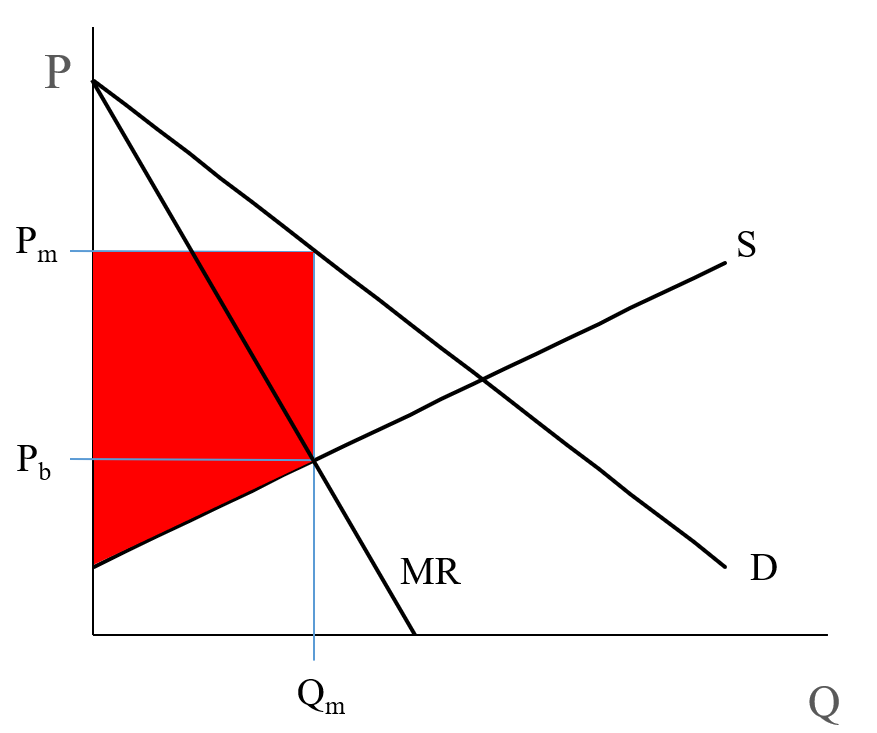
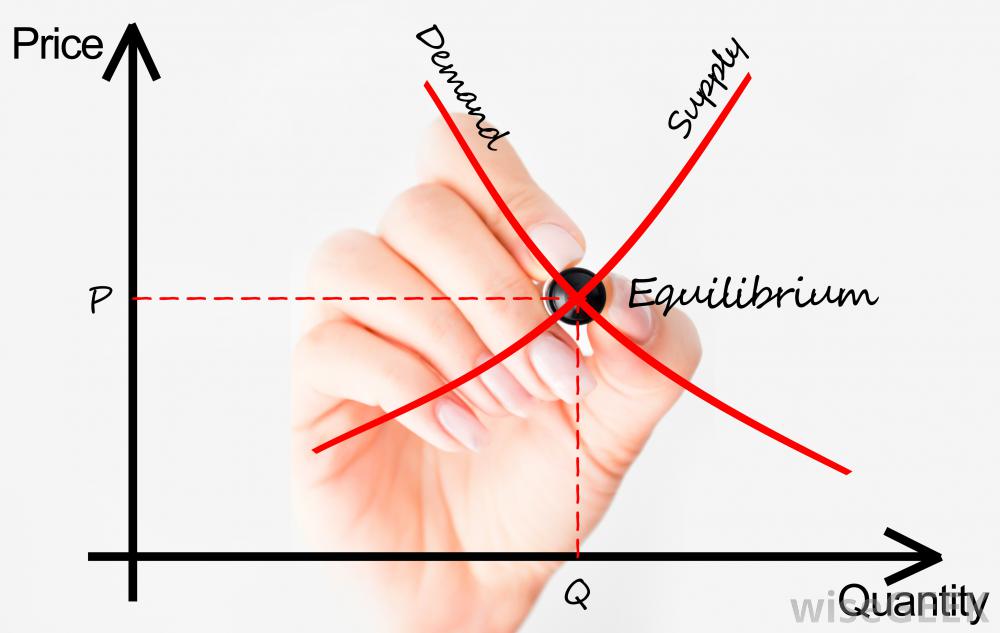
It can be seen from the given diagrams that Figure B is derived from Figure A. In figure A, initially, consumer equilibrium is attained at point E, where MU (10) = Price (10). Corresponding to point E, we derive point E 1 in figure B. Due to fall in price (suppose from 10 to 8), MU > Price at the given quantity. consumer surplus? A $0.15 B $0.85 C $0.90 D $1.35 13 A market is in equilibrium at price $5. Market supply changes from being inelastic at each price to become elastic at each price. The market equilibrium price does not change. What is the effect on consumer surplus and producer surplus? consumer ... At a price below the equilibrium, there is a tendency for the price to rise. Figure 3.7 The Determination of Equilibrium Price and Quantity When we combine the demand and supply curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.. 20) A relative price is the A) absolute price of a good. B) price of a substitute. C) price of one good multiplied by the price of another. D) price of a related good. E) price of one good divided by the price of another. 20) 21) Sue consumes oysters and clams. Pounds of oysters are measured on they-axis and pounds of clams on the x-axis. If ... 14.5 CONSUMER S EQUILIBRIUM IN CASE OF A SINGLE COMMODITY Consumer s equilibrium in case of a single commodity can be explained on the basis of the law of diminishing marginal utility. How does a consumer decide as to how much to buy of a good? It will depend upon two factors. (a) The price she pays for each unit which is given and Thus at the equilibrium point E,MRSXY=Price of good x/Price of good y= PX/PY The tangency between the given price line and an indifference curve is a necessary but not a sufficient condition consumer's equilibrium .The second condition for consumer's equilibrium is convexity of indifference curve to the origin . The price of x is $0.50 and the price of good y is $0.75, and the bundle x = 10 and y = 10 uses up all the consumers income. The consumer's preferences are strictly convex. Which of the following is TRUE? a) To maximize utility the consumer should buy more x and less y. b) To maximize utility the consumer should buy less x and more y.
The consumer's income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $50X + $100Y. When the consumer is given a $50 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a ... 5 UCLES 2004 9708/01/O/N/04 [Turn over 12 In the diagram, point X shows the equilibrium price and quantity for a fruit drink. The government announces that the ingredients used in the drink can be harmful. A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y and is in equilibrium. Show that when the price of good X rises, the consumer buys less of good X. Use utility analysis. [AI 2014] Answer: As, we know condition for consumer equilibrium is, Necessary Condition Marginal utility of last rupee spend on each commodity is same. 3) 4) In the below figure, a consumer is initially in equilibrium at point C. The consumer's income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $100 X + $200 Y. When the consumer is given a $100 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a new equilibrium at point D. Explanation a. P x = $100, P y = $200 ...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the accompanying figure. The price of good X is $5.. a. What is the price of good Y? b. What is the consumer's income? c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium? 5. A consumer will start buying less of good-X and more of Good-Y, when: (a) MUx/Px = MUm (b) MUx/Px<MUy/Py (c) MUy/Py = MUm (d)MUx/Px>MUy/Py 6. According to IC approach, at the point of equilibrium: (a) slope of IC > slope of price line (b) slope of IC < slope of price line (c) Slope of IC # slope of price line (d) slope of IC = slope of price ... The consumer's equilibrium is shown in the diagram below. In the diagram, there are four indifference curves - IC 1, IC 2, IC 3 and IC 4 and a budget line PQ. Which of the points from A to D is an optimal, utility maximizing, optimum choice? Point B is not optimal. A is better than B since A is on a higher indifference curve. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y?$ b. What is the consumer's income?$ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium?
4 In the indifference curve diagram point M is the consumer’s initial equilibrium and MN is the substitution effect of a fall in the price of good X. If good X is a Giffen good which point will be the consumer’s new equilibrium point after the fall in

According To The Figure Below If The Price Of X Is 5 What Combination Of X And Y Will A Utility Maximizing Consumer Choose A 80x 20y B 120x 620y C 120 X
Therefore, he reaches the equilibrium at point Q on curve IC 3. Notice that at this point, the budget line PL is tangential to the indifference curve IC 3. Also, in this position, the consumer buys OM quantity of X and ON quantity of Y. Since point Q is the tangent point, the slopes of line PL and curve IC 3 are equal at this point. Further ...

Managerial Economics A Consumer Is In Equilibrium At Point A In The Accompanying Figure The Price Of Good X Is 5 Homeworklib
Is There Consumer Surplus At Equilibrium? A supply and demand diagram shows consumer surplus above the equilibrium price of the good and below the demand curve (usually a triangular area). Market equilibrium refers to the point at which prices stabilize, so that consumers and producers receive ...
The point at which a consumer reaches optimum utility, or satisfaction, from the goods and services purchased given the constraints of income and prices. This is based on the assumption that consumers attempt to get maximum utility from their purchases and that competition exists for the item ...
Check Pages 151 - 200 of MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS STRATEGY in the flip PDF version. MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS STRATEGY was published by MyDocSHELVES DIGITAL DOCUMENT SYSTEM on 2017-10-19. Find more similar flip PDFs like MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS STRATEGY.
In the diagram on the right the consumer's original budget line is L1, and the consumer buys the amount of good X at point A. Then the price of good X decreases dramatically so that the consumer's new budget line shifts to L2. After the price decrease the consumer buys the amount of good X at point C.
A consumer must divide $250 between the consumption of product X and product Y. The relevant market prices are Px = $5 and Py = $10.a. Write the equation for the consumer's budget line.b. Illustrate the consumer's opportunity set in a carefully labeled diagram.c. Show how the consumer's... View Answer.

Week 2 Chapter 4 Problems Docx Chapter 4 Question 1 A Consumer Has 300 To Spend On Goods X And Y The Market Prices Of These Two Goods Are Px 15 And Course Hero
19 Jan 2021 — The price of good X is $5. a.... 1 answer below ». A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the accompanying figure. The price ...1 answer · Top answer: Ans: a) Since the slope of teh line through A is -20/20=-1 and price of X is $5, then the price of Y is also $5 b) With all her income, the consumer ...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of good Y? $_____ B. What is the consumer's income? $_____ C. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? _____ units. D. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.

Draw A Budget Constraint And Indifference Curves For Pepsi And Pizza For Given Consumer Both Goods Are Normal Show What Happens To The Budget Constraint And The Consumer S Optimum When The
6 A consumer demands two goods, X and Y. The indifference curve diagram shows the effect of a change in the price of one of these goods on the consumer’s equilibrium. good Y good X O I2 I1 Which demand curve is consistent with the diagram? A price of good Y quantity of good Y O O B price of good Y quantity of good Y C price of good X quantity ...

Graded Hw 2 Ch 4 Docx 1 A Consumer Is In Equilibrium At Point A In The Diagram Below The Price Of Good X Is 5 A What Is The Price Of
The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? b. What is the consumer's income? c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment ...

Ii Structural Reform And Macroeconomic Adjustment In Industrial Countries In World Economic And Financial Surveys
A consumer is in equilibrium and is spending income in such a way that the marginal utility of product X is 40 units and that of Y is 16 units. If the unit price of X is $5, then the price of Y must beA) $1 per unit. B) $2 per unit. C) $3 per unit. D) $4 per unit.
You are watching: A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5. economics 0 0 Add a comment Next > Sortanswers by oldest Homework Answers recommended Answer See more: Which Of The Following Is True Of Enzymes And Substrates, Which Of The Following ...
A consumer is said to be in equilibrium when he feels that he “cannot change his condition either by earning more or by spending more or by changing the quantities of thing he buys”. A rational consumer will purchase a commodity up to the point where price of the commodity is equal to the marginal utility obtained from the thing.
March 2, 2016 - ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about Consumer’s Equilibrium. After reading this article you will learn about: 1. Meaning of Consumer’s Equilibrium 2. Assumptions 3. Conditions 4. Corner Solutions. Meaning of Consumer’s Equilibrium: A consumer is in equilibrium when given ...

Chapter 4 Hw Docx Chapter 4 Hw 1 A Consumer Is In Equilibrium At Point A In The Diagram Below The Price Of Good X Is 5 2 A Consumer Must Divide 600 Course Hero
1. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ 5 5 Correct b. What is the consumer's income? $ 100 100 Correct c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? 10 10 Correct units d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
Here, MU meets the price level at two different points A and B. At point A (2 nd unit), the marginal utility intersects the price level on a rising trend. A consumer derives a higher utility from additional consumptions of the 3 rd and 4 th units. On the 5 th unit, it intersects the price level at point B. Any additional consumption beyond this point shows a lower marginal utility than such ...
In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X.
11 Dec 2019 — Get the detailed answer: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of ...
Suppose the equilibrium price of good X is $10 and the equilibrium quantity is 60 units. If the price of good X is $4: a) The quantity demanded will be less than 60 units. b) The quantity supplied will be more than 60 units. c) There will be an excess demand for good X. d) There will be an excess supply of good X. 14.
1. A consumer's equilibrium is always formed at a point on the given budget line. 2. A consumer's equilibrium will shift to a higher indifference curve with an increase in consumer's income. Answer: 1. Budget line shows all possible combinations of the two goods that a consumer can buy, given income and prices of commodities.
5)A consumer will start buying less of good-X and more of Good-Y, when: (a)MUx/Px = MUm (b)MUx/Px < MUy/Py (c)MUy/Py = MUm (d)MUx/Px>MUy/Py 6) According to IC approach, at the point of equilibrium: (a) slope of IC > slope of price line (b) slope of IC < slope of price line (c) Slope of IC # slope of price line (d) slope of IC = slope of price line
At a price below the equilibrium, there is a tendency for the price to rise. Figure 3.7 The Determination of Equilibrium Price and Quantity When we combine the demand and supply curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
consumer surplus? A $0.15 B $0.85 C $0.90 D $1.35 13 A market is in equilibrium at price $5. Market supply changes from being inelastic at each price to become elastic at each price. The market equilibrium price does not change. What is the effect on consumer surplus and producer surplus? consumer ...
It can be seen from the given diagrams that Figure B is derived from Figure A. In figure A, initially, consumer equilibrium is attained at point E, where MU (10) = Price (10). Corresponding to point E, we derive point E 1 in figure B. Due to fall in price (suppose from 10 to 8), MU > Price at the given quantity.

Chapter 4 Hw Docx Chapter 4 Hw 1 A Consumer Is In Equilibrium At Point A In The Diagram Below The Price Of Good X Is 5 2 A Consumer Must Divide 600 Course Hero

Managerial Economics A Consumer Is In Equilibrium At Point A In The Accompanying Figure The Price Of Good X Is 5 Homeworklib

















0 Response to "45 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5."
Post a Comment