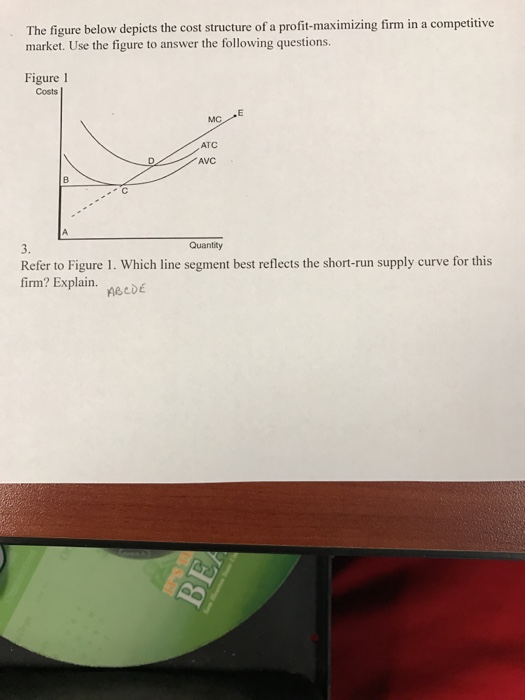
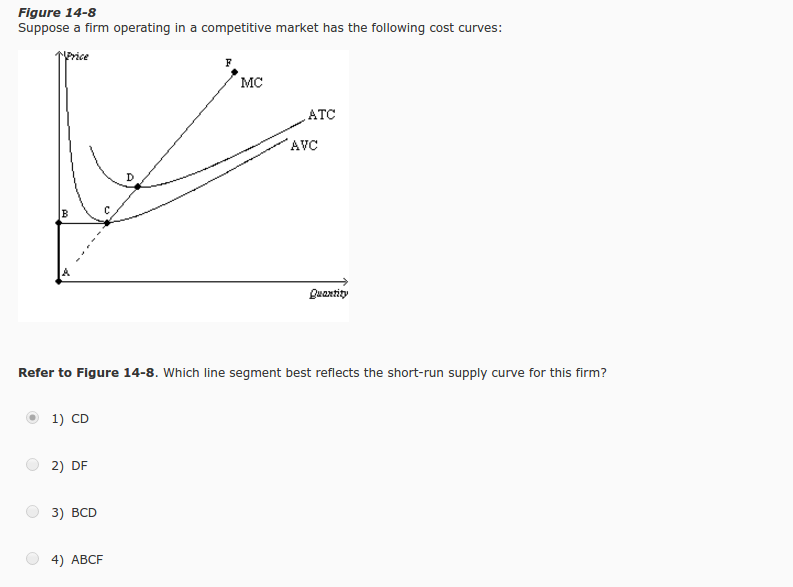
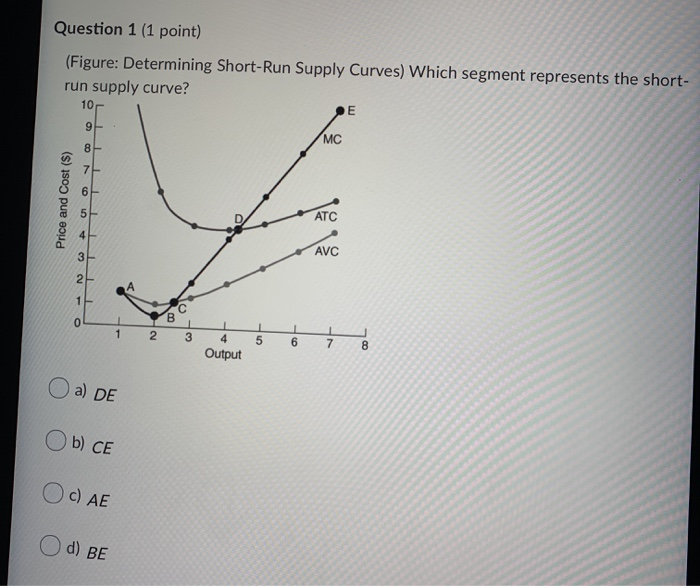
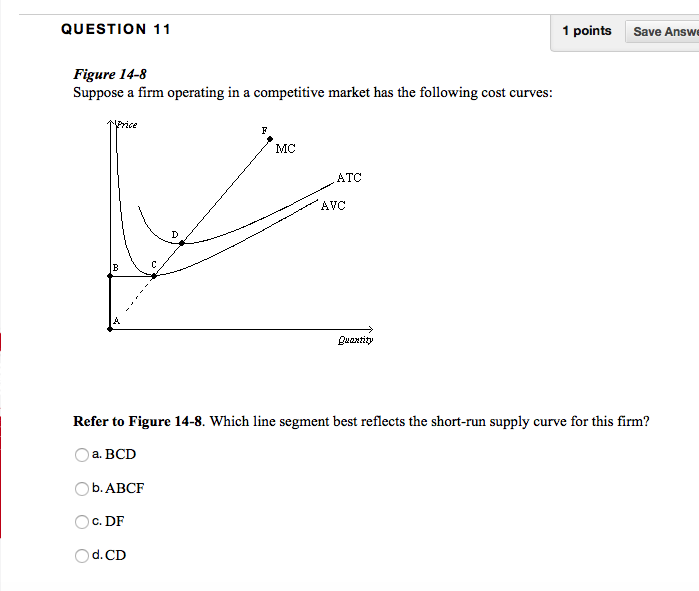
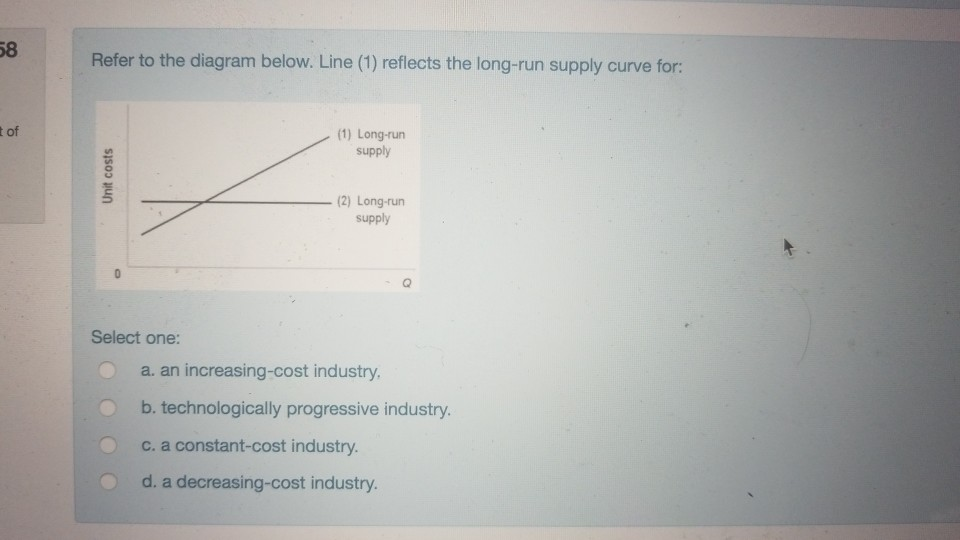
39 line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for
Describe the differences between changes in supply and changes in quantity supplied. A change in the quantity supplied refers to movement along the existing supply curve, S 0 . This is a Note that you will use the information provided in the first question for all of the questions on this page.
The _____ curve shows the negative relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output demanded in the economy. AD1 will shift to the right, reflecting a multiplied increase in the real GDP at every price level. Suppose that the stock market crashes.
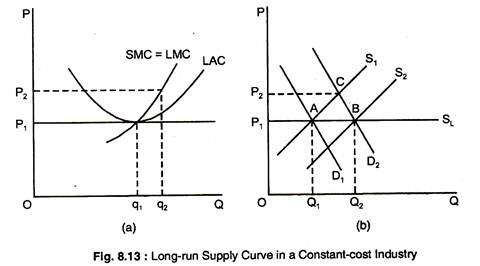
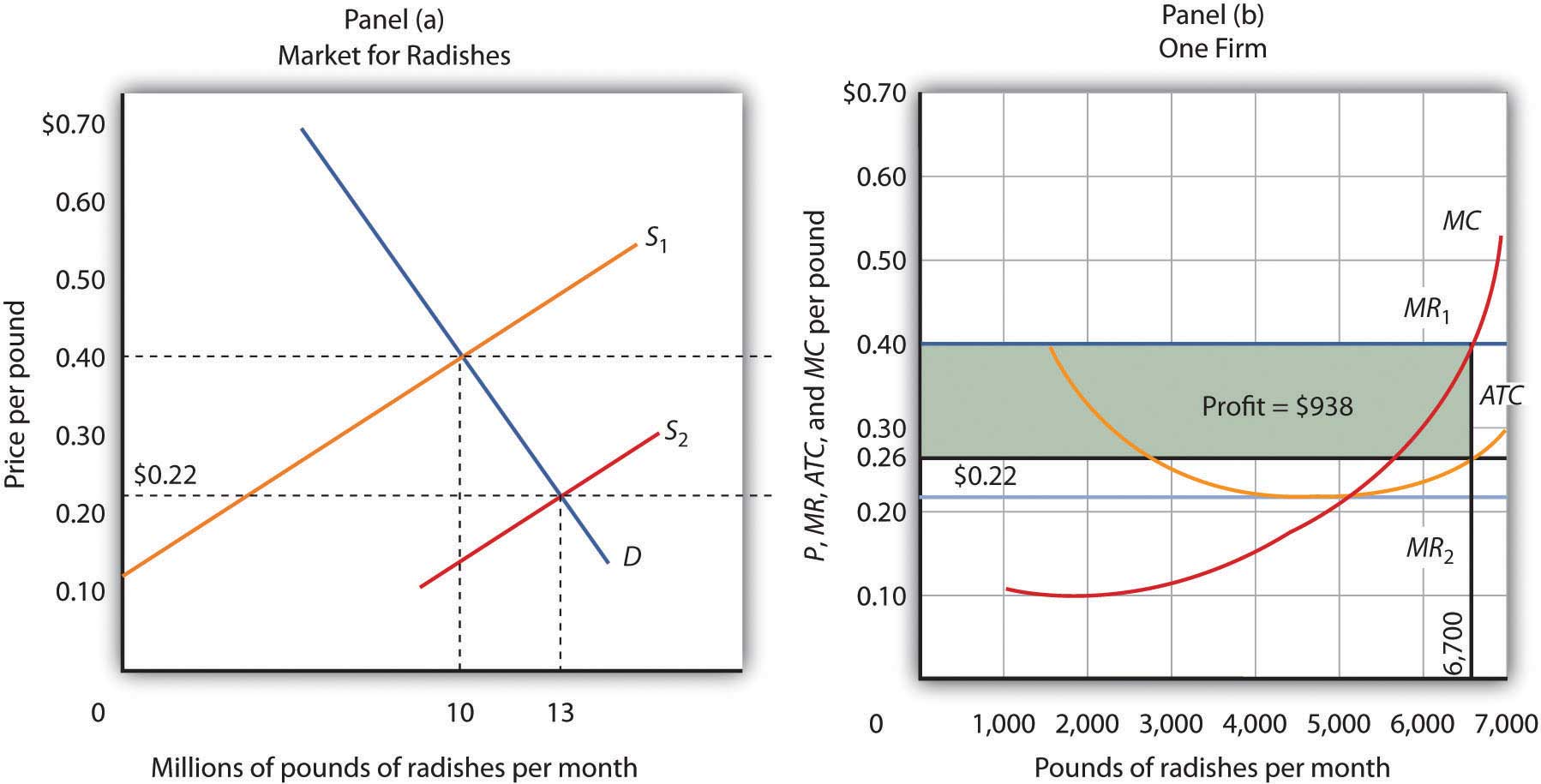
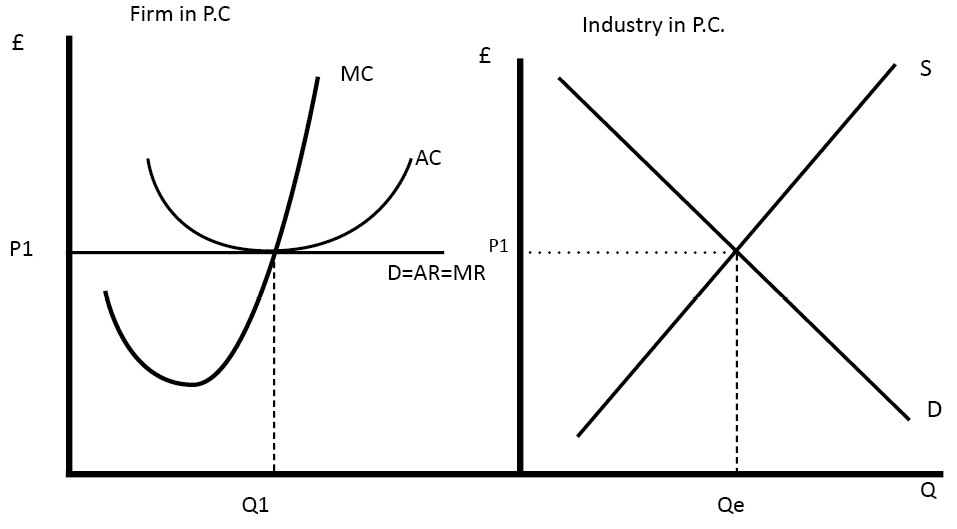
The long‐run equilibrium for an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market is illustrated in Figure . The profit maximizing level of output, where marginal cost equals The long‐run market supply curve is found by examining the responsiveness of short‐run market supply to a change in market demand.
Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for
In this diagram the supply curve shifts to the left. It leads to a higher price and fall in quantity demand. For example, if we run out of oil, supply will fall. However, economic growth means demand continues to rise. Increase in Demand.
This would shift the supply curve for butter to the right, resulting in a drop in the price of butter and an increase in the quantity of butter supplied. Long-run and short-run elasticities differ based on how rapidly consumers respond to price changes and how many substitutes are available.
The Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve(LRAS) is vertical on the graphic model representing the market for final goods and services(the AD-AS model). What Is Potential GDP and Why Does It Matter? "It reflects a world in which every worker is matched with the perfect job, every good idea is...
Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for.
The long-run Phillips curve is a vertical line that illustrates that there is no permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run. In the long-run the aggregate supply curve is perfectly vertical, reflecting economists' belief that changes in aggregate demand only cause a...
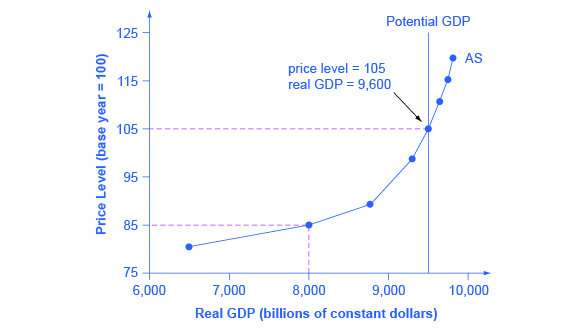
If the GDP deflator is 125 in the year that the output gap is identified, and two years later it is 150, is inflation becoming an issue? Draw a correctly labeled graph of the long-run aggregate supply, short-run aggregate supply, and aggregate demand curves.
Question: Show in a diagram the effect on the demand curve, the supply curve, the equilibrium price a. Draw the demand curve and the supply curve for Maine lobsters. He is close to breaking the major league record for home runs hit during one season, and it is widely anticipated that in the...
Derive the labour supply curve assuming that the maximum hours that can be worked is 24. As the utility function is a function of leisure and consumption, we can replace the hours in the budget constraint with leisure using our knowledge that workers have 24 hours that they split between leisure...
One of the most important long-run trends in the study of macroeconomics is for real GDP. The long-run trend of real GDP, which has historically Second, note that the short-run aggregate supply curve, labeled SRAS, has a positive slope. Aggregate real production that the business sector offers...
7.3 The Structure of Costs in the Long Run. The supply schedule and the supply curve are just two different ways of showing the same information. Because the graphs for demand and supply curves both have price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis, the demand curve...
In economics the long-run is a theoretical concept in which all markets are in equilibrium, and all prices and quantities have fully adjusted and are in equilibrium. The long-run contrasts with the short-run, in which there are some constraints and markets are not fully in equilibrium.
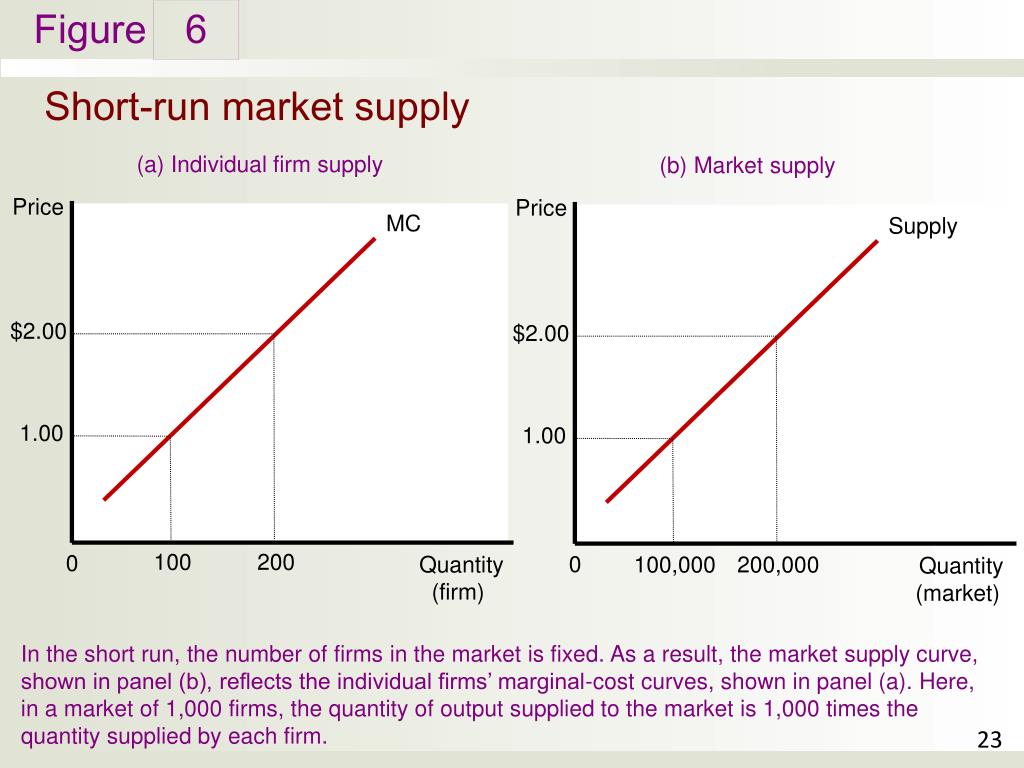
The long run differs from the short run in two ways: 1. Firms can adjust all inputs and fixed costs are not sunk. The long run market supply curve maps the quantity of output supplied for each given price. The supply of firms takes place after all long run adjustments of inputs and entry or exit of firms.
In the long run, the competitive firm's supply curve is the ? A factory operator bought a diesel generator set for P 10,000.00 and agreed to pay the dealer uniform sum at the end of each year for 5 years at 8% interest compounded annually, that the final payment will cancel the debt for principal...
Similar to short run, in the long run, an organisation must satisfy the condition of MR = MC to maximise its profit. Figure 4 shows the profit maximisation of an organisation Therefore, Pc and Qc are the equilibrium points for the organisations for a long period of time in imperfect competition.
15 Why is the supply curve perfectly elastic in the long run? Under perfect competition, there are many buyers and sellers, and prices reflect supply and demand. When the demand for the good increases, the long-run result is an increase in the number of firms and in the total quantity supplied...
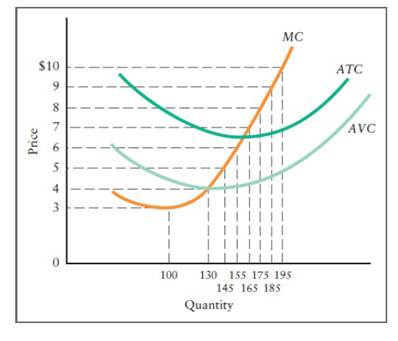
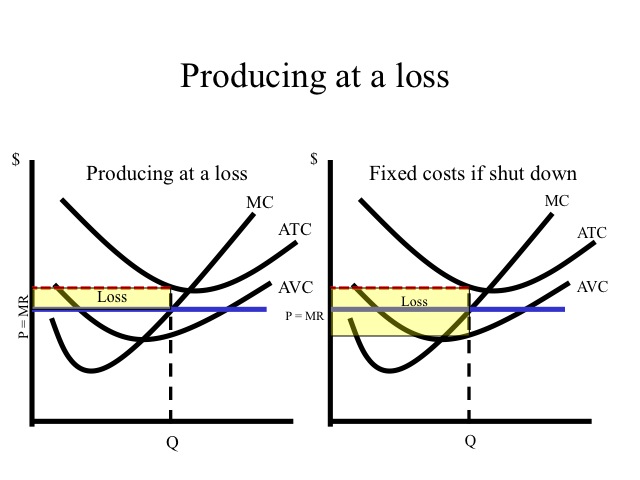
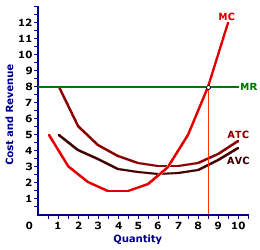
50. Allocative efficiency is achieved when the production of a good occurs where A. P = minimum ATC.B. P = MC.C. P = minimum AVC.D. total revenue is equal to TFC. 51. A firm is producing an output such that the benefit from one more unit is more than the cost of producing that additional unit.
The more that the curve hugs the top left corner of the plot, the better the model does at classifying the data into categories. We can use the following code to calculate the AUC of the model and display it in the lower right corner of the ROC plot
Imagine the scenario: you arrive at the market to stock up on fruit, but it's been a bad year for apples, and supplies are low. In this article, we'll explore the relationship between supply and demand using simple graphs and tables, to help you make better pricing and supply decisions.
The isocost curve, therefore, is steeper than the isoquant, and the firm only hires capital (at point A) To determine how an increase in the price of capital changes the demand for labor, suppose initially The direction of the shift in the demand curve for labor, therefore, will depend on which effect is...
Plot the first 2 lines on a graph in the first quadrant (like shown below). The optimal feasible solution is achieved at the point of intersection where the budget & man-days constraints are active. This means the point at which the equations X + 2Y ≤ 100 and X + 3Y ≤ 120 intersect gives us the optimal solution.
Using the definitions at the beginning of the article, the short run is the period in which a company can increase production by adding more raw materials and more labor but not another factory. Conversely, the long run is the period in which all inputs are variable, including factory space, meaning that there...
Use the demand curve diagram below to answer the following TWO questions. 1. What is the own-price elasticity of demand as price decreases from $8 If doing so results in an increase in revenues raised, which of the following could be the value of the own-price elasticity of demand for ferry rides?
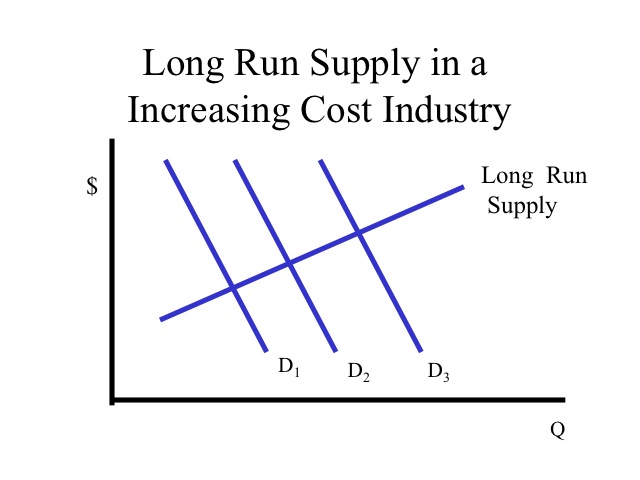
The long-run is supposed to be a period sufficiently long to allow changes to be made both in the size of The external diseconomies outweigh the external economies. The increased demand for the This means that the long-run supply curve LSC slopes upwards to the right as the output supplied...
When the quantity of the commodity supplied changes due to change in non-price factors, the supply curve does not extend or contract but shifts entirely. For an instance, the introduction of improved technology in industries helps in reducing the cost of production and induces production of more units...
Describe the three possible effects on the costs of the factors of production that expansion or contraction of a perfectly competitive industry may have and illustrate the resulting long-run industry supply curve in each case. Explain why under perfection competition output prices will change by...
If the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping, which of the following will cause inflation? The demand for money will decrease and nominal interest rates will decrease. long-run Phillips curve to shift to the right. actual inflation rate to fall below the expected inflation rate.
in the short run, prices are fixed but output may be above, below, or equal to potential output. In an aggregate supply and aggregate demand diagram, the long-run aggregate supply curve is We have Millions of practices for you to explore. Get millions of various questions with their answers.
The burden of the tax is reflected in the price of the good. 5. The following table shows the demand curve facing a monopolist a. On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two factories, the average and marginal revenue The supply curve is equivalent to the average expenditure curve.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/supply_curve_final-465c4c4a89504d0faeaa85485b237109.png)
/Supplyrelationship-c0f71135bc884f4b8e5d063eed128b52.png)












/producer_surplus_final-680b3c00a8bb49edad28af9e5a5994ef.png)



0 Response to "39 line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for"
Post a Comment