39 the pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem solving tool.
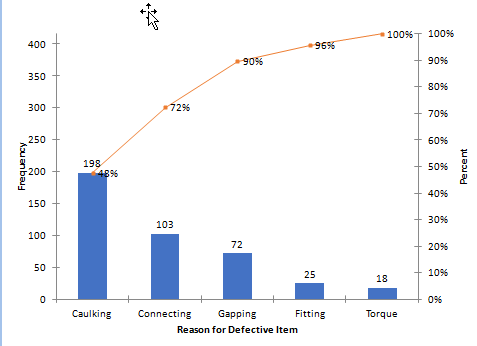
A Pareto Chart named after the Italian Economist Vilfredo Pareto. It is a type of chart which contain both bars and line graph, where the individual values represent in bar graph in descending order (largest to smallest value) and cumulative percentage is represented in the line graph. Click here to know "How to Plot Pareto Chart In Excel".
Pareto Chart (also known as Pareto Analysis or Pareto Diagram) is one of the seven basic tools of quality which helps to determine the most frequent defects, complaints, or any other factor. It is a visual tool widely used by professionals to analyze data sets related to a specific problem or an issue. From this aspect, it can be used as an ...
Pareto chart c. fishbone diagram d. scatter diagram ... The XY chart, which is a problem-solving tool, is sometimes called a scatter diagram. a. True b. False . b. False . The first section of a typical preliminary investigation report is the case for action. a. True b. False ...
The pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem solving tool.
problem-solving c. steering d. auditing Answer: c _. Which of the following generally is not a factor influencing of how organizations are structured? ... control chart. c. scatter diagram. d. Pareto diagram. Answer: a _. A quality improvement tool useful for determining the relationship between two variables is the a. check sheet. b. control ...
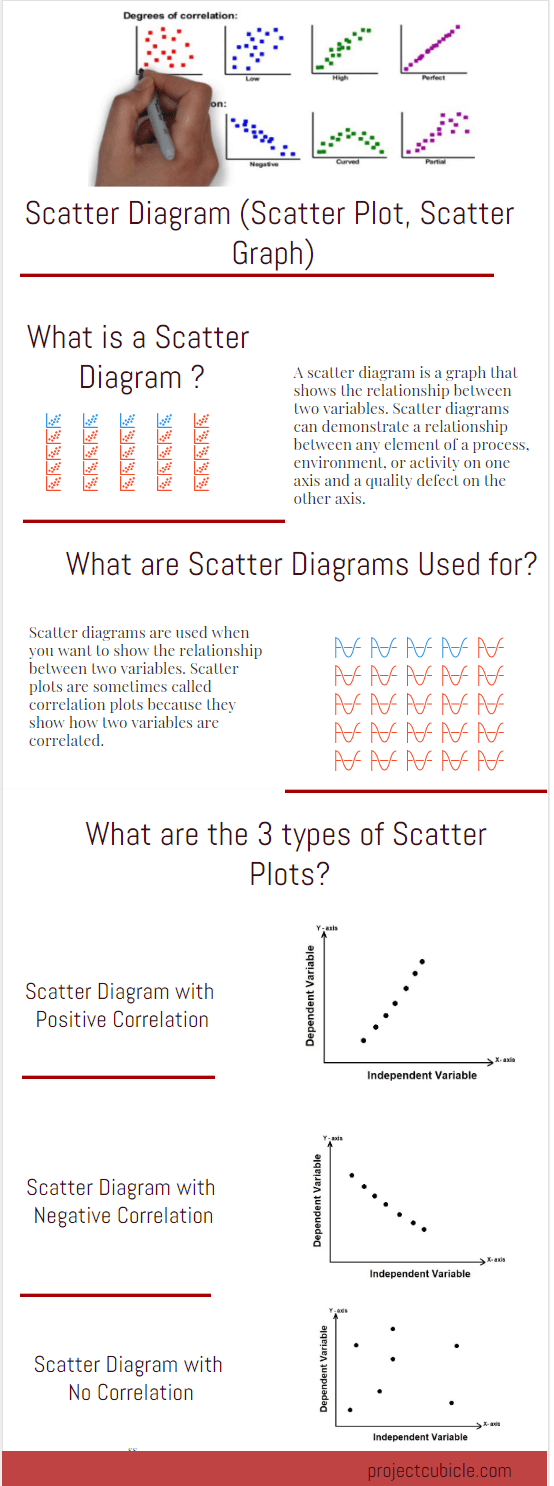
Pareto chart: A bar graph that shows which factors are more significant. Scatter diagram : Graphs pairs of numerical data, one variable on each axis, to look for a relationship. Stratification : A technique that separates data gathered from a variety of sources so that patterns can be seen (some lists replace stratification with flowchart or ...
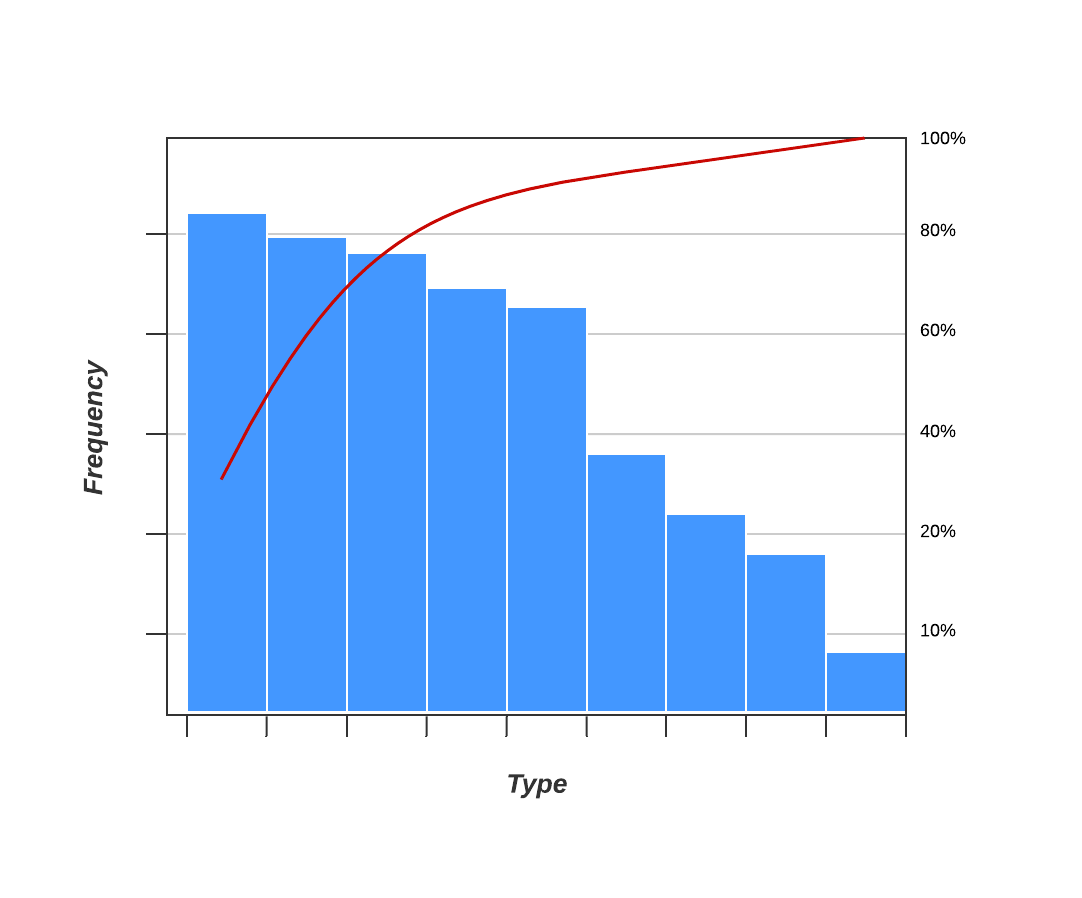
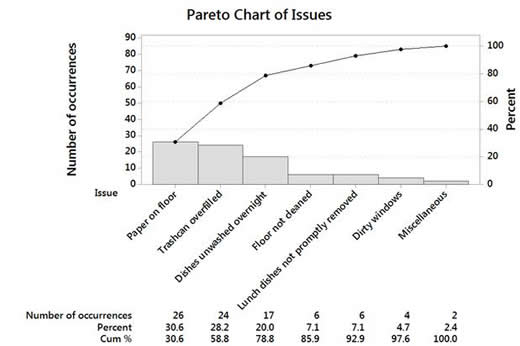
Quality Glossary Definition: Pareto chart. Also called: Pareto diagram, Pareto analysis. Variations: weighted Pareto chart, comparative Pareto charts. A Pareto chart is a bar graph. The lengths of the bars represent frequency or cost (time or money), and are arranged with longest bars on the left and the shortest to the right.
The pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem solving tool..
A. Pareto Diagram B. Scatter diagram C. Histogram D. All of above. 5. Discrete variables are also called A. Frequency distribution B. Continuous variables C. Discontinuous Invariables D. None of the above. 6. Pareto Analysis cannot be used A. To generate a list of problems B. To evaluate performance after implementation of solutions C. To ...
Pareto chart is also called a Pareto diagram and Pareto analysis. It is named for the Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, who described Pareto principle, according to which roughly 80% of the outcomes come from 20% of the conditions, for many events. This assumption is used in calculations of business profit or population of any country.
a) Pareto chart. b) Check Sheet. c) Scatter Diagram. d) 2 k factorial design. Answer: d. Clarification: Pareto chart, check sheet, and scatter diagram are all parts of the 7 problem solving tools of SPC or magnificent 7 of SPC (statistical process control). 2k factorial design is a part of design of experiments. 2.
The Pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem-solving tool. asked Aug 11, 2019 in Computer Science & Information Technology by wdean409 Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
3. Pareto Chart:-A Pareto Chart is a combination of a bar graph and a line graph. Pareto Diagram is a tool that arranges items in the order of the magnitude of their contribution, thereby identifying a few items exerting maximum influence. Pareto Charts are useful to find the defects to prioritize in order to observe the greatest overall ...
enterprise. The problem solving tools used in SPC, called the "management seven" [1], are traditional management tools, namely check sheets, histogram, Pareto chart, cause and effect diagram, scatter diagram and control chart. These tools are very popular and are commonly called the 7 QC tools. Their
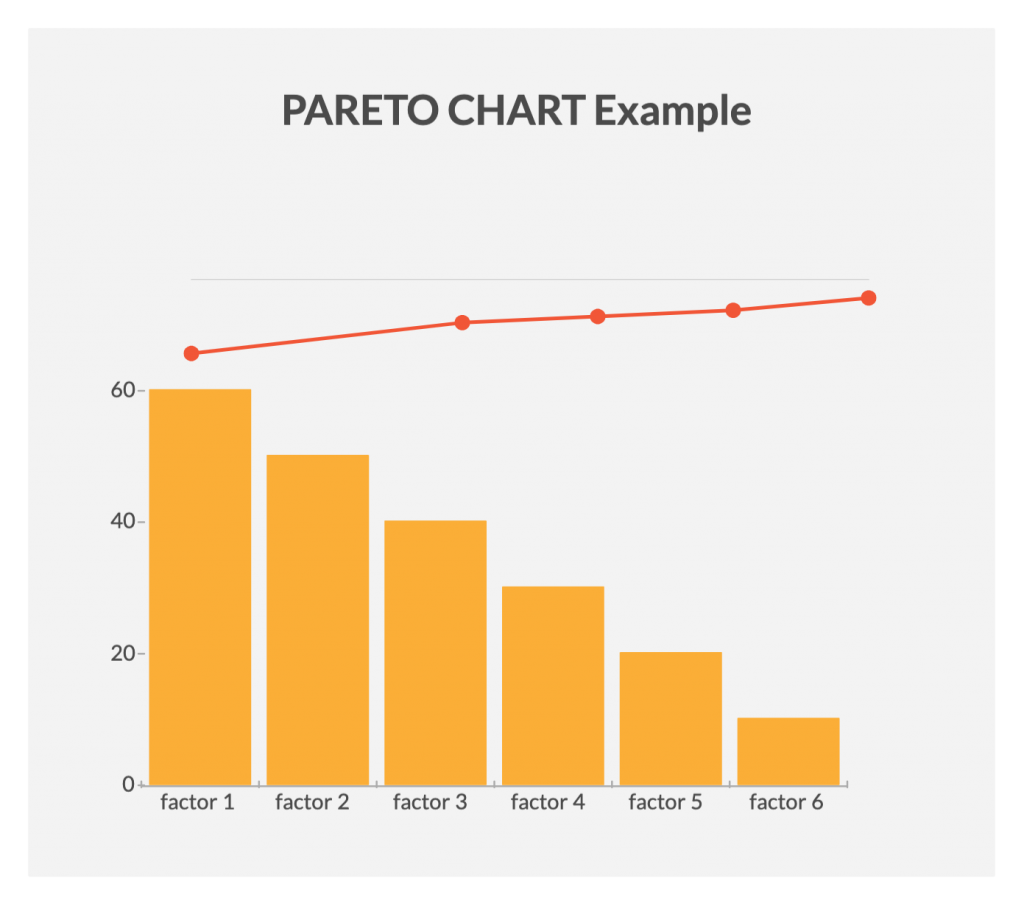
Because the Pareto chart is, essentially, a plain old bar graph. A Pareto chart, in its simplest form, is a bar chart that arranges the bars from largest to smallest, from left to right. The bigger bars on the left are more important than the smaller bars on the right. Like a lot of bar charts.
The 1st one is a Pareto Chart. Since this chart sorts data in frequency order of occurrences, you can see the most important factor at a glance. Cause and Effect Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram) Next one is a Cause and Effect Diagram. From the diagram shape, it’s also called a Fish bone Diagram.
The Pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem-solving tool. False In a preliminary investigation report, the findings section includes a summary of a project request and a specific recommendation. False The letters SWOT stand for spending, weeks, overtures, and time. False
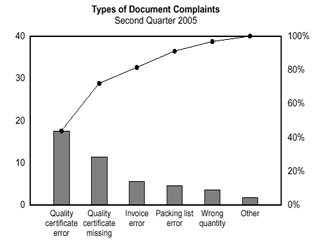
A Pareto chart is a histogram or bar chart combined with a line graph that groups the frequency or cost of different problems to show their relative significance. The bars show frequency in descending order, while the line shows cumulative percentage or total as you move from left to right.
The Pareto Chart is a series of bars whose heights reflect the frequency or impact of problems. On the Chart, bars are arranged in descending order of height from left to right, which means the categories represented by the tall bars on the left are relatively more frequent than those on the right. 3. 5 Whys
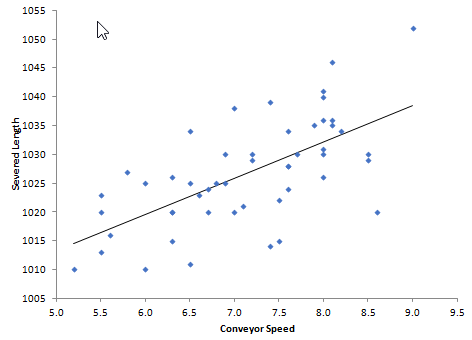
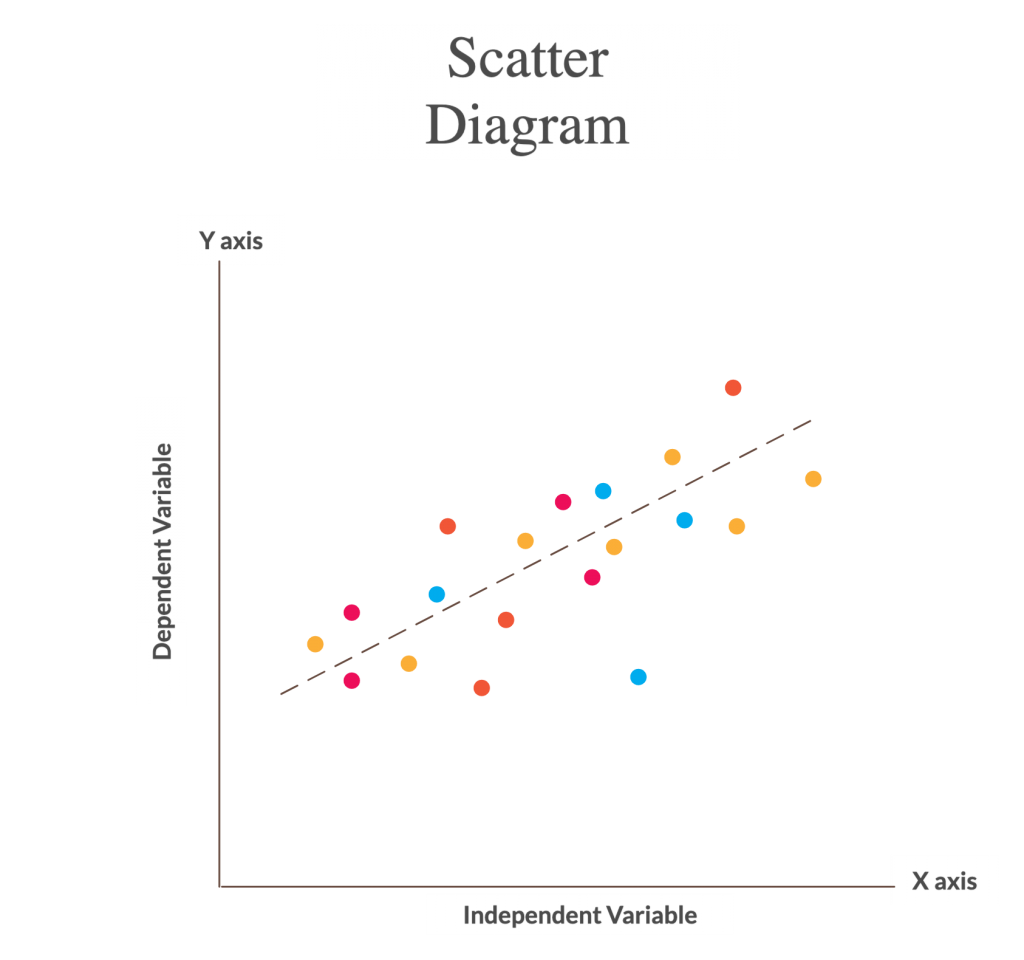
The scatter diagram (scatter charts, scatter plots, scattergrams, scatter graphs) is a chart that helps you identify how two variables are related. The scatter diagram shows the values of the two variables plotted along the two axes of the graph. The pattern of the resulting points will reveal the correlation. Uses
Fishbone Diagram (Click on the template to edit it online) . Here's how to use the cause and effect analysis to solve business problems.You can also refer to our guide on fishbone diagrams to learn how to use the tool in more detail.. Pareto Chart . Pareto chart is a combination of a bar chart and a line graph. While the length of the bars represent the frequency or cost of faults, they are ...
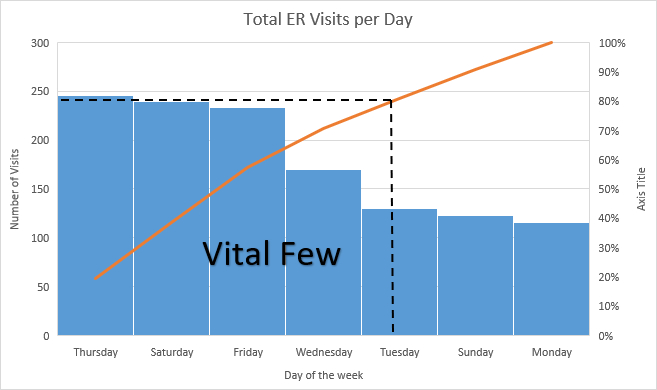
" Pareto Chart " also called as " Pareto Diagram ". Named after Italian Economist Wilfredo Pareto. 80 % of issues comes from 20% of the problems. Shows focus area to get most gains. Bar chart arranged in descending order of height. Bars on left side relatively important than those in right. Separates "Vital few" from "Trivial many".
Pareto charts cause and effect diagrams and design of. 16) Pareto charts, cause-and-effect diagrams and design of experiments are used in which step of the problem solving process for quality improvement? 16) ______ A) Problem analysis B) Data collection C) Monitoring solutions to see if they accomplish goals.
Nov 11, 2021 · Pareto Chart. A Pareto chart is a h is togram or bar chart combined with a line graph that groups the frequency or cost of different problem s to show the ir relative significance. Well-suited to traditional project management tools and techniques. ... The Pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem-solving tool.
Pareto analysis According to Pareto analysis,80 % of the problems are caused due to 20% of the causes. Hence if we focus on the vital few causes, the majority of the problem can be solved. It saves precious time in solving a problem. This is a universal philosophy and can be applied anywhere. Example:
The Pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem-solving tool. False True False (The XY chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem-solving tool) Which is an example of a discretionary project? Including annual updates to payroll and tax percentages Adding a report required by a new federal law
On the other hand, tools sometimes have statistical basis to support decision making or facilitate analysis of data. The best tools for this purpose is check sheet, Pareto chart, histogram, scatter diagram, run chart and statistical process control (SPC). The data collected by these tools can be used to measure the process.
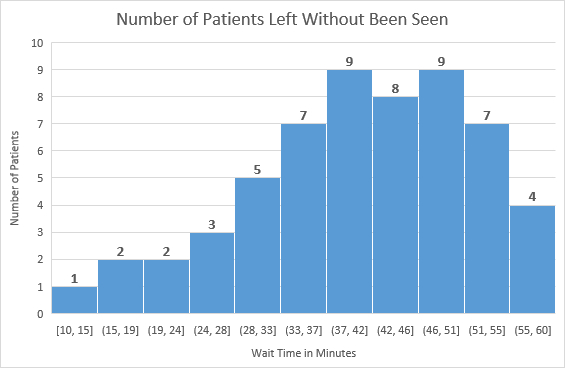
Pareto Diagrams The fourth tool introduced in the book is the Pareto diagram. A Pareto diagram is a bar chart that is used to help separate the ^vital few _ problems from the ^trivial many _ problems. It is a data-based approach to help decide what problem to work on first. An example of the Pareto diagram from the book is given in Figure 5.
This list is sometimes called the "seven quality control tools," the "seven basic tools" or the "seven old tools." 1. Cause-and-effect diagram (also called Ishikawa or fishbone chart): Identifies many possible causes for an effect or problem and sorts ideas into useful categories. 2.
Pareto Diagram . 2. Cause & Effect Diagram . 3. Histogram . 4. Control Charts . 5. Scatter Diagrams . 6. Graphs . 7. Check Sheets . 2 Pareto Diagram . Pareto Diagram is a tool that arranges items in the order of the magnitude of their contribution, thereby identifying a few items exerting maximum influence.
The very purpose of Pareto Chart is to highlight the most important factors that is the reason for major cause of problem or failure. Pareto chart is having bars graphs and line graphs where individual factors are represented by a bar graph in descending order of their impact and the cumulative total is shown by a line graph.





















0 Response to "39 the pareto chart, sometimes called a scatter diagram, is a problem solving tool."
Post a Comment