40 antigen antibody reaction diagram
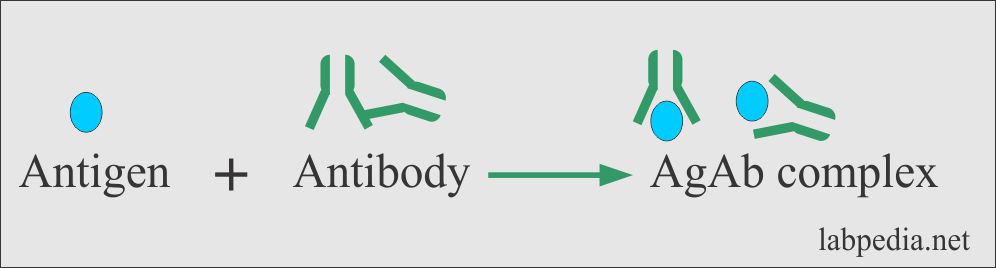
Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction.The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and ... Start studying Antigen-Antibody Reactions. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The mechanism of antigen-antibody reactions has been an attractive subject for experimentation and speculation ever since the early days of immunology. The precipitin reaction, because of its technical simplicity, has often been used for such studies without, however, any agreement as to the fundamental nature of the mechanism involved.

Antigen antibody reaction diagram
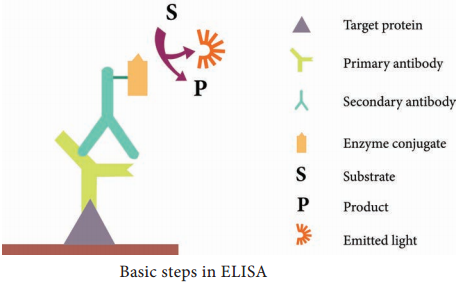
to detect antigen antibody reaction. It provides flexible and useful method for semi quantitating of either antigen or antibody concentration. The reaction occurs between insoluble (particulate)antigen and appropriate antibody. The reaction will results in forming aggregate or agglutinate. Ag= agglutinogen, Ab= agglutinin So that a networking reaction can expire, the particles contained in the samplefluid must have a binding place for at least two antibodies and can.1 page The reaction between the antibody and the virus inhibits (i.e., prevents) hemagglutination from occurring, which results in hemagglutination inhibition (as shown in Figure 2C). This is why the assay is called a "hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test." Hemagglutination (as depicted in Figure 2B) occurs when antibodies do not recognize and ...
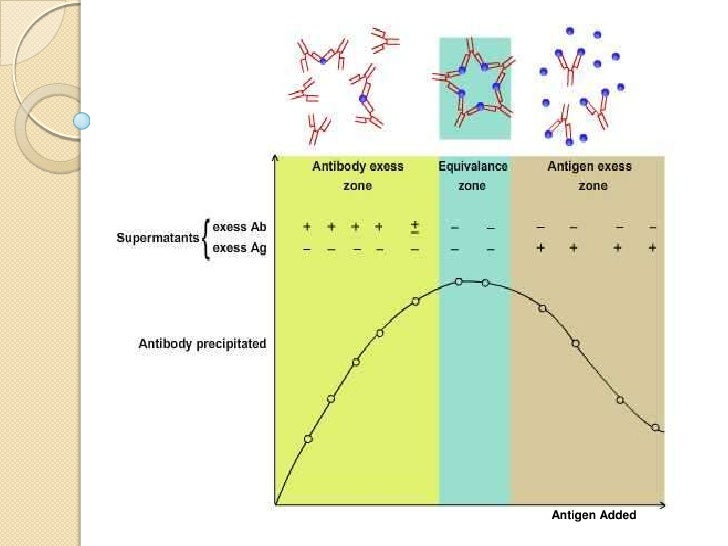
Antigen antibody reaction diagram. Antigen-antibody reactions occur in two stages; the first is rapid and the second takes time for the reaction to become demonstrable. • Centrifugation is the most widely used way to enhance antigen-antibody reactions. • Haemagglutination occurs when IgM antibodies react with their corresponding red cell antigens. • Antigen-antibody reactions (Fig. 8) are highly specific and both fit into each other like a lock and key. Because an antibody fits precisely with an antigen, an antibody that binds to one antigen cannot bind to another antigen. Antibody can inactivate the invading agent in one of the following ways: The interactions between antigens and antibodies are known as antigen-antibody reactions. The reactions are highly specific, and an antigen reacts only with antibodies produced by itself or with closely related antigens. Antibodies recognize molecular shapes (epitopes) on antigens. Generally, the better the fit of the epitope (in terms of ... In the antigen-capture format (Figure (Figure1A), 1A), the competition reaction occurs between the analyte (in sample) and a labelled analyte for the binding to a limited amount of anti-analyte antibody coated onto a solid support.
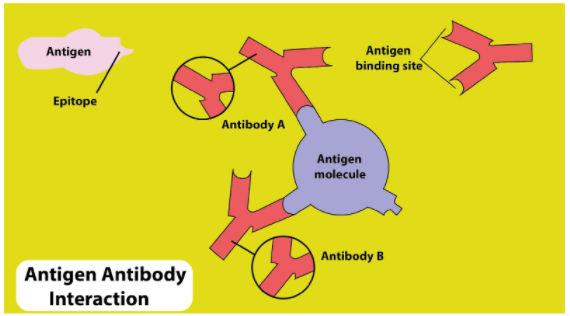
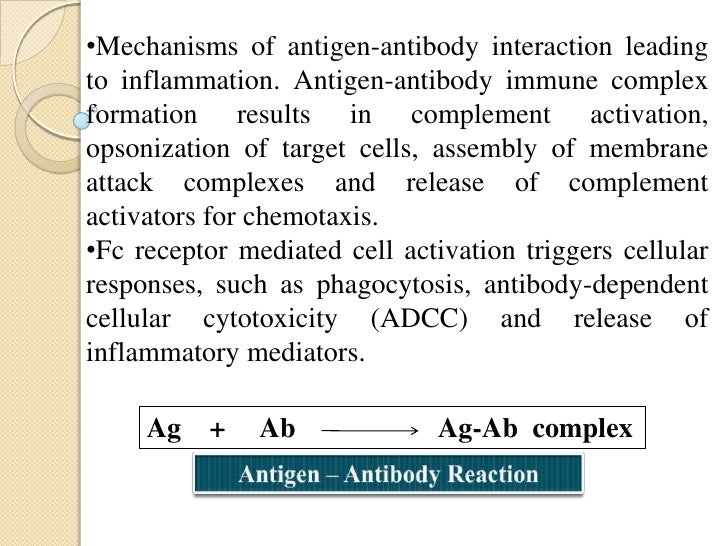
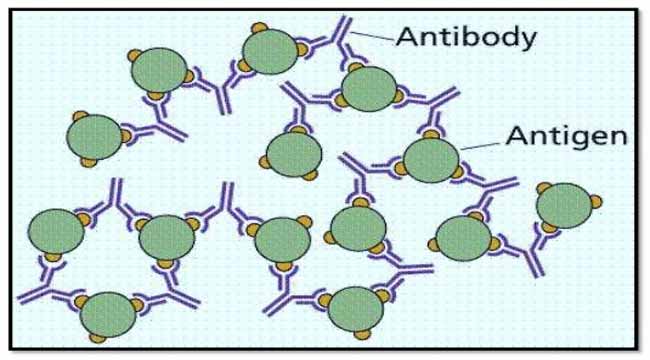
Types of antigen-- Antibody reactions in Antibody reactions in vivo 1. Agglutination 2. Precipitation 3. Complement fixation 4. Neutralization 5. Antibody dependant cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) 6. Immobilization 12/21/13 Prof. Md. Akram, MMC 22 If the patient's serum contains antibodies against streptococci, the test antigen will form complement sequence. This mixture is again incubated for about 30 minutes. At this point, no antigen-antibody reaction occurs. Stage 2: In stage 2, the complement fixed by antigen-antibody reaction is detected by an indication system. •In antigen - antibody reaction, the antibody attaches with the antigen. •The part of antigen which combines with antibody is called Epitope. •An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or 2. Precipitation and Flocculation Reaction: When an antibody binds to a soluble antigen, the antigen becomes insoluble and it may precipitate or float in the fluids. If Ag - Ab complex precipitates, it is referred as "precipitation reaction". Some times the Ag-Ab complex may float instead of precipitation; in that case the reaction is ...
Factors affecting measurement of antigen-antibody reactions. The only way that one knows that an antigen-antibody reaction has occurred is to have some means of directly or indirectly detecting the complexes formed between the antigen and antibody. The ease with which one can detect antigen-antibody reactions will depend on a number of factors. Antigen-Antibody Reactions To bridge the gap between basic immunology and antibody detection methods (Module 3), we will now briefly review the nature of antigen-antibody reactions. The antigen-antibody reactions that are used most in blood banking are known as hemagglutination, i.e., they cause the agglutination of red cells. Immune reactions against parasites. Antireceptor antibodies: IgG antibody is directed against receptors in target cells, resulting in complement-mediated destruction of the receptors. In the diagram above, antibody is directed against acetylcholine receptors at the motor end plate of a muscle, blocking the receptors and diminishing the muscular ... I. Basic Antigen-Antibody Testing A. Basic Red Cell-Antibody Interactions 1. Agglutination a. Clumping of red cells due to antibody coating b. Main reaction we look for in Blood Banking c. Two stages: 1) Coating of cells ("sensitization") a) Affected by antibody specificity, electrostatic RBC charge, temperature, amounts of antigen and antibody
Antigen-antibody reaction. Baumgarten, Alexander Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. A reaction that occurs when an antigen combines with a corresponding antibody to produce an immune complex. A substance that induces the immune system to form a corresponding antibody is called an ...
Binding Site of Antigen - Antibody Reaction: • In antigen - antibody reaction, the antibody attaches with the antigen. • The part of antigen which combines with antibody is called Epitope. • An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B ...
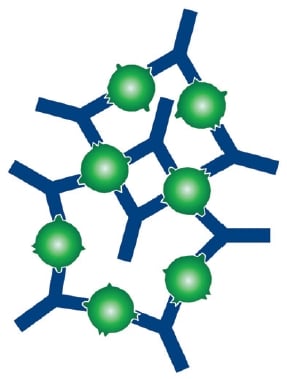
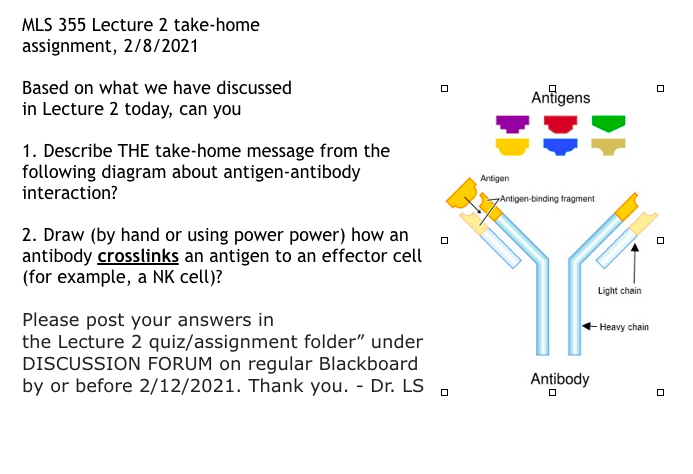
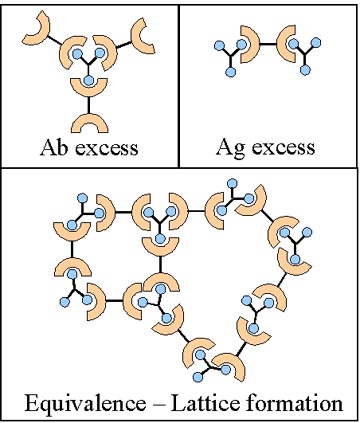
Precipitin reactions The interaction of antibody with antigen in solution may cause formation of an insoluble lattice that will precipitate out of solution. This precipitate will only form if: - the antibody is bivalent or polyvalent - the antibody or antibody mixture can bind to at least two different sites on the
The reaction between the antibody and the virus inhibits (i.e., prevents) hemagglutination from occurring, which results in hemagglutination inhibition (as shown in Figure 2C). This is why the assay is called a "hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test." Hemagglutination (as depicted in Figure 2B) occurs when antibodies do not recognize and ...
So that a networking reaction can expire, the particles contained in the samplefluid must have a binding place for at least two antibodies and can.1 page
to detect antigen antibody reaction. It provides flexible and useful method for semi quantitating of either antigen or antibody concentration. The reaction occurs between insoluble (particulate)antigen and appropriate antibody. The reaction will results in forming aggregate or agglutinate. Ag= agglutinogen, Ab= agglutinin






















0 Response to "40 antigen antibody reaction diagram"
Post a Comment