42 in a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies.
The arrows above entities indicate all desirable dependencies in this table ie dependencies that are based on pk. In an diagram the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. This preview has intentionally blurred sections. A table that is in 1nf and includes no partial dependencies only is said to be in. Functional dependencies are used to describe further a relation schema R by specifying constraints on its attributes that must hold at all times. Certain FDs can be specified without referring to a specific relation, but as a property of those attributes given their commonly understood meaning.
Question 10 ( 5 points ) In a ( n ) _____ diagram , the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies . Question 10 options : Chen dependency functionality ER Question 11 ( 5 points ) A table that is in 2 NF and contains no transitive dependencies is said to be in _ ____.
In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies.
Jul 22, 2021 — In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. answer. dependency. 1 pts In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. Group of answer choices Chen dependency functionality ER Flag this Question Question 6 1 pts Dependencies based on only a part of a composite primary key are known as _____ dependencies. Step 3 -Dependency Diagram (1NF) • The connections above the entity show attributes dependent on the currently chosen Primary Key, the combination of PROJ_NUM and EMP_NUM. • The arrows below the dependency diagram indicate less desirable partial and transitive dependencies 15 CS275 Fall 2010 Resulting First Normal Form • First normal form ...
In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies.. In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. Crow Foot notation ERDs When designing a new database structure based on the business requirements of the end users, the database designer will construct a data model using a technique such as what? In a(n) ____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies: Chen, Functionality, Dependency, or ER Dependency A table that is in 1NF, includes no partial dependencies, but may include transitive dependencies is said to be in ____: BCNF, 2NF, 4NF, or 3NF 12 VMS/VSAM is an example of the _____. • hierarchical model • file system data model • XML data model • relational data model 13 A table where all attributes are dependent on the primary ... ... attributeDependencyIn a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies.ChendependencyfunctionalityERSurrogateIn a ...
21. _____ are important because they help to ensure data integrity. a. Attributes b. Entities c. Relationships d. Constraints 22. A (n) _____ exists when there are functional dependencies such that Y is functionally dependent on X, Z is functionally dependent on Y, and X is the primary key. Dependencies can be identified with the help of the dependency diagram. _F___ 12. Dependencies that are based on only a part of a composite primary key are called transitive dependencies. ... In a(n) ____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. a. Chen. c. functionality. b. dependency. d. ER. Sep 22, 2016 — In a(n) ____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. Answer. A) Chen. B) dependency. C) functionality. [Solved] In a(n)____ diagram,the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. A) Chen B) dependency C) functionality D) ER.Missing: _____ | Must include: _____
In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. In a dependency diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. s is a candidate key of R— this implies that X Y for any subset of attributes Y of R. If X is a candidate key of R, then X R. If X Y in R, this does not imply that Y X in R. A functional dependency is a property of the semantics or meaning of the attributes. Whenever the semantics of two sets of attributes in R indicate that a functional dependency should hold, we specify the The ER diagram represents the conceptual database as viewed by the end user. ... In a(n) ____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. anomalies. ... Dependencies that are based on only a part of a composite primary key are called transitive dependencies. In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. partial dependency A dependency based on only a part of a composite primary key is called a(n) _____.
In a(n) _____ diagram the arrows above the attributes indicate all the desirable dependencies a) Chen b) dependency c) functionality d) ER. answer. b) dependency. question
A(n) _____ database is used by an organization and supports many users across many ... In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all ...
In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. dependency From a system functionality point of view, _____ attribute values can be calculated when they are needed to write reports or invoices.
• Arrows point upward to parent • Line/arrow styles indicate if parent is a(n): • class: solid line, black arrow • abstract class: solid line, white arrow • interface: dashed line, white arrow • Often omit trivial / obvious generalization relationships, such as drawing the Object class as a parent Rectangle - x: int - y: int
Nov 25, 2018 · 2 posts · 1 authorIn a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. a. Chen b. dependency c. functionality d. ER.
In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. a. dependency; At the implementation level, the supertype and its subtype(s) depicted in a specialization hierarchy maintain a(n) _____ relationship. a. 1:
In a(n) ___ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. dependency A table that has all key attributes defined, has no repeating groups, and all its attributes are dependent on the primary key, is said to be in ___.
In a(n) ___ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. dependency A ________ group derives its name from the fact that a group of multiple entries of the same type can exist for any single key attribute occurrence.
Question 7 1 / 1 pts A ____ exists when there are functional dependencies such that Y is functionally dependent on X and Z is functionally dependent on Y, and X is the primary key. partial dependency repeating group atomic attribute transitive dependency. Question 8 1 / 1 pts In a (n) ____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all ...
In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. a. Chen b. dependency c. functionality d. ER. b. dependency. 33. Dependencies based on only a part of a composite primary key are known as _____ dependencies. a. primary b. partial
12 Chapter 8 Relational Database Design 8.8 Consider the algorithm in Figure 8.18 to compute a+.Show that this algorithm is more efficient than the one presented in Figure 8.8 (Sec-tion 8.4.2) and that it computes a+ correctly. Answer: The algorithm is correct because: • If Ais added to result then there is a proof that a → A.To see this,
The arrows above the attributes indicate all. The arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies, i.e., dependencies that are based on the full primary key (PROJ_NUM + EMP_NUM). The arrows below indicate the undesirable dependencies - 'transitive' and 'partial'. 6 2NF Definition A table is in 2NF if: It is in 1NF and ...
____ 38. In a(n) ____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. a. c. Chen functionality b. dependency d. ER ____ 39. A table that is in 1NF and includes no partial dependencies only is said to be in ____. a. c. BCNF 3NF b
In a(n)diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. a. Chen b. dependency c· functionality d. ER 6. If a table has multiple candidate keys and one of those candidate keys is a composite key, the table can have based on this composite candidate key, even when the primary key chosen is a single attribute. a.
Match the following terms with their descriptions:I.NormalizationII.First normal formIII.Second normal formIV.Third normal formV.Normal formsA.No transitive dependencies existB.Process of efficiently organizing dataC.Table contains no repeating groups or columnsD.The rules to optimize and fix potential repetition issues in a databaseE.All non-key fields are functionally dependent on the entire ...
• arrows point upward to parent • line/arrow styles indicate whether parent is a(n): -class: solid line, black arrow -abstract class: solid line, white arrow -interface: dashed line, white arrow • often omit trivial / obvious generalization relationships, such as drawing the Object class as a parent
Step 3 -Dependency Diagram (1NF) • The connections above the entity show attributes dependent on the currently chosen Primary Key, the combination of PROJ_NUM and EMP_NUM. • The arrows below the dependency diagram indicate less desirable partial and transitive dependencies 15 CS275 Fall 2010 Resulting First Normal Form • First normal form ...
1 pts In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. Group of answer choices Chen dependency functionality ER Flag this Question Question 6 1 pts Dependencies based on only a part of a composite primary key are known as _____ dependencies.
Jul 22, 2021 — In a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies. answer. dependency.













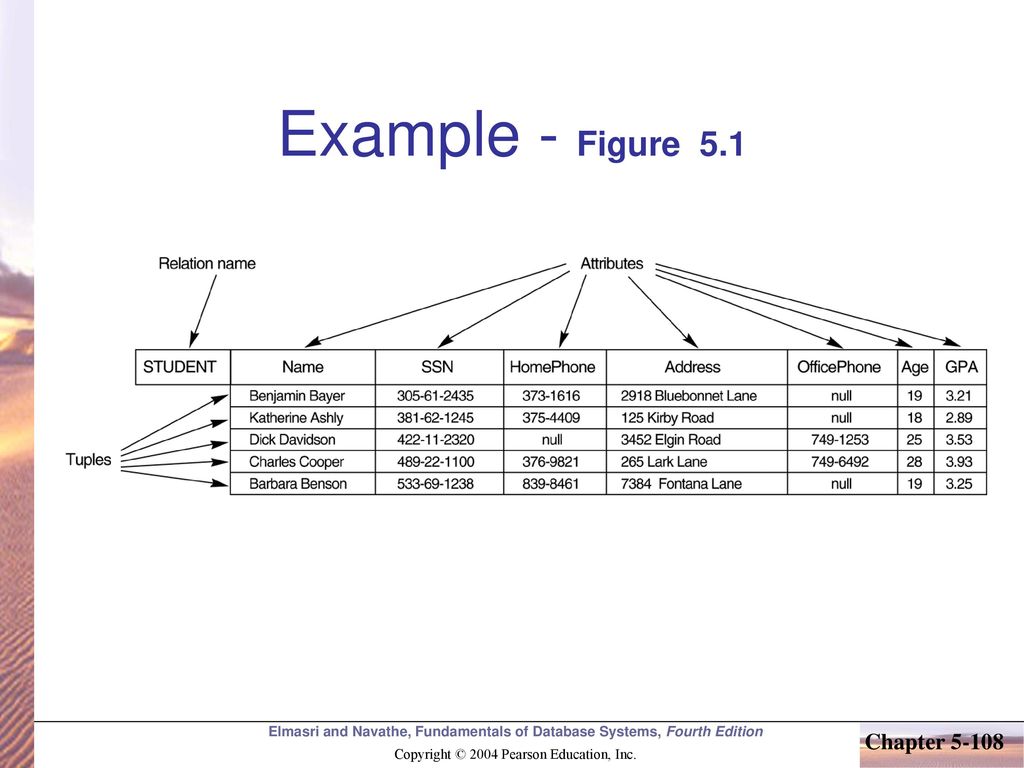







0 Response to "42 in a(n) _____ diagram, the arrows above the attributes indicate all desirable dependencies."
Post a Comment