43 aerobic cellular respiration diagram
Aerobic Respiration, Part 2: Oxidation of Pyruvate and The Citric Acid Cycle. Aerobic Respiration, Part 3: Oxidative Phosphorylation . Metabolism without Oxygen: Fermentation. Metabolism of molecules other than glucose. Anaerobic Cellular Respiration in Prokaryotes. Photosynthesis. Putting photosynthesis into context. The structure of the chloroplast. Light and Pigments. The Light …
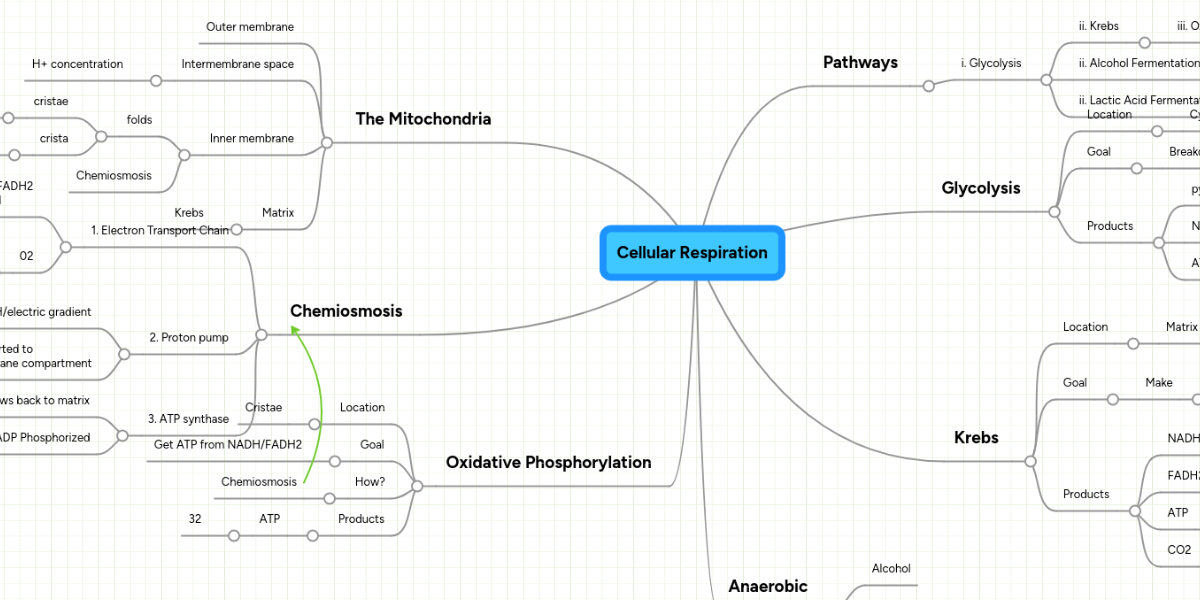
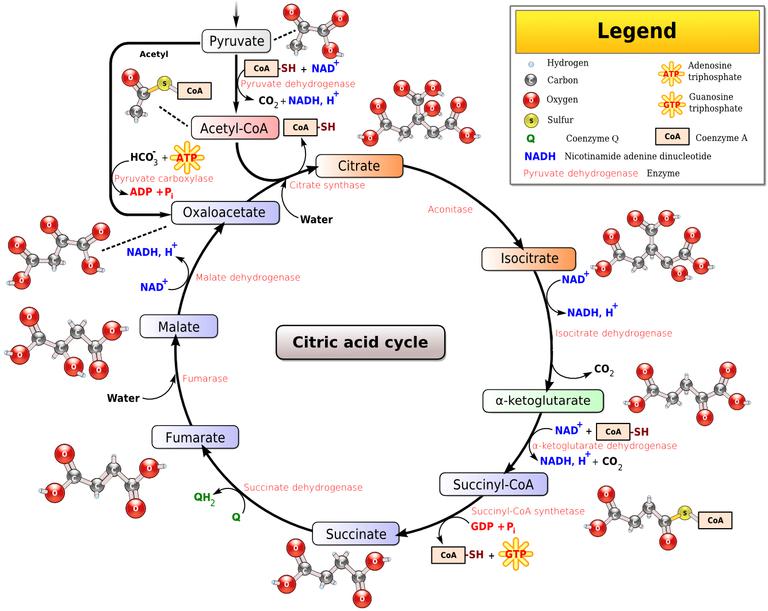
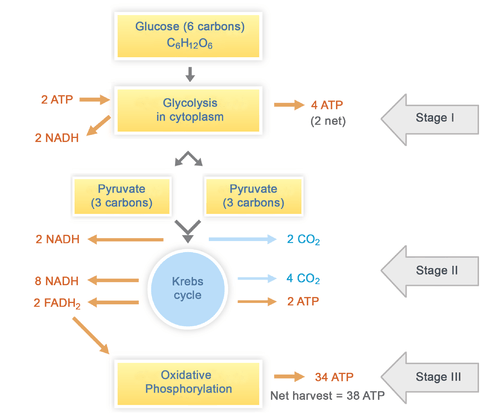
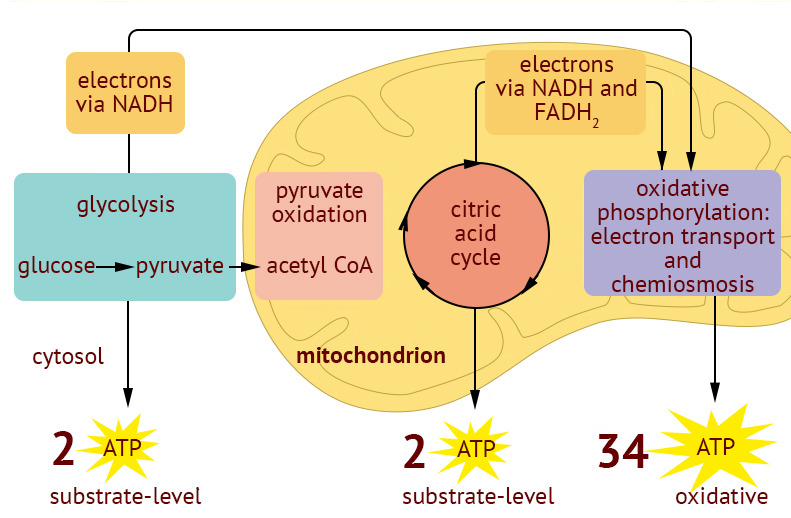
14.05.2019 · The Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic cycle, is the first step of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells. Its purpose is to collect high-energy electrons for use in the electron transport chain reactions. The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
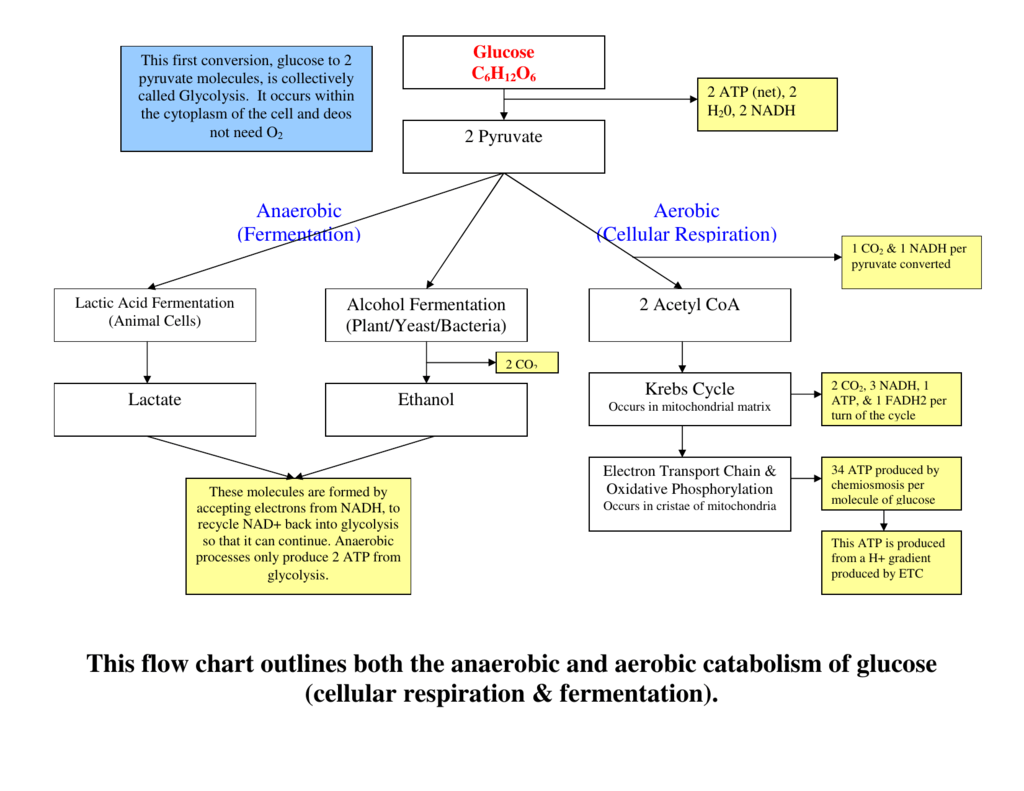
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration – an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration:
Aerobic cellular respiration diagram
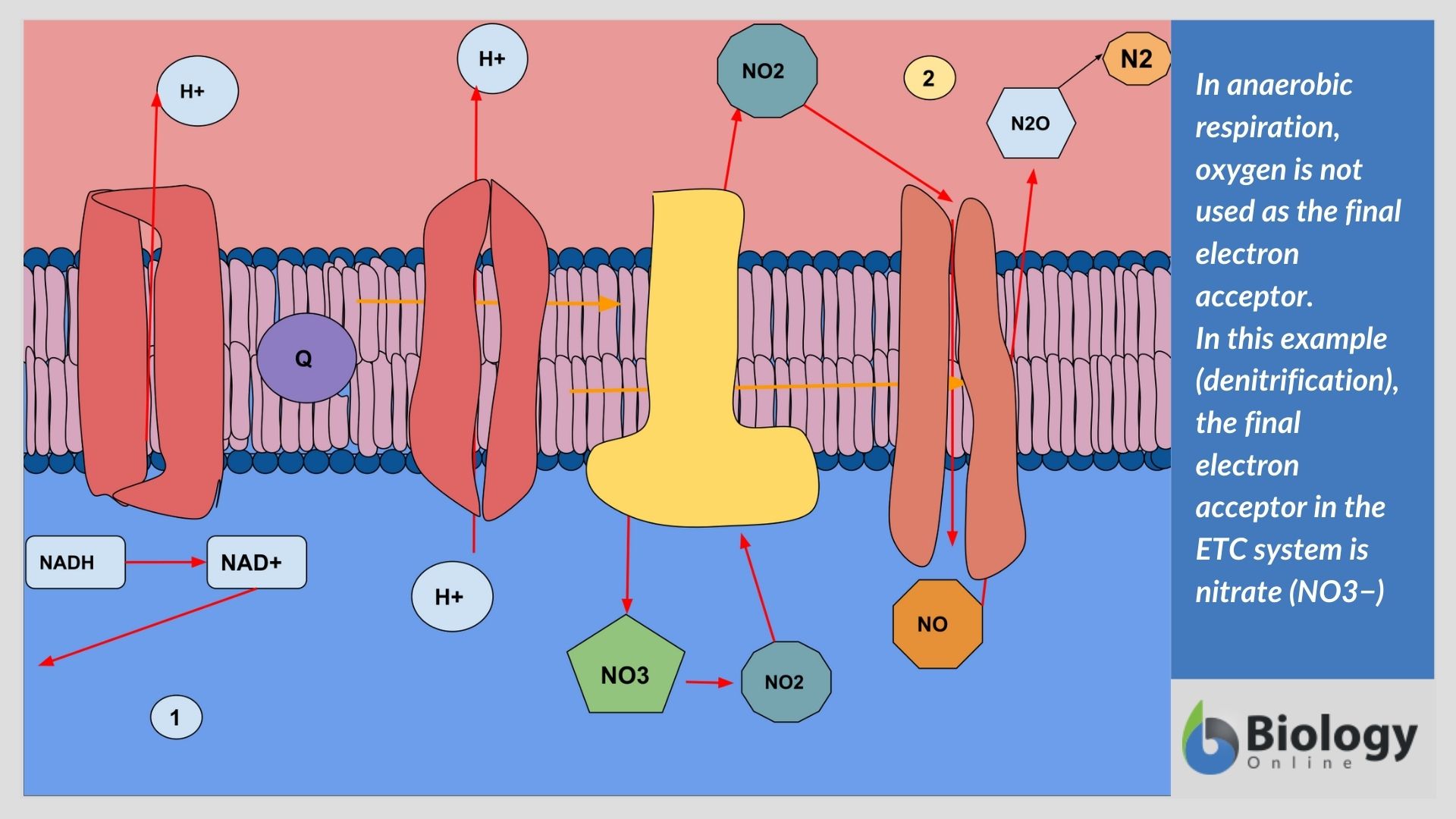
20.09.2021 · Anaerobic respiration is the process of creating energy without the presence of oxygen. Sometimes the body cannot supply the muscles with the oxygen it needs to create energy, for example during intense exercise. Without the process of anaerobic respiration, there would be no energy supplied to muscles in these times of high demand.This article will consider the process of anaerobic ...
08.09.2020 · Respiration in Organisms Class 7 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type. Question 1. Where does cellular respiration take place? Answer: Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms. Question 2. What is aerobic respiration? Answer: The process of breakdown of glucose with the use of oxygen is called aerobic respiration.
... (2 kinds—Aerobic and Anaerobic). •Cellular respiration is the process by which the energy of ... Diagram. Glucose. Glycolysis. Electron. Transport Chain.17 pages
Aerobic cellular respiration diagram.
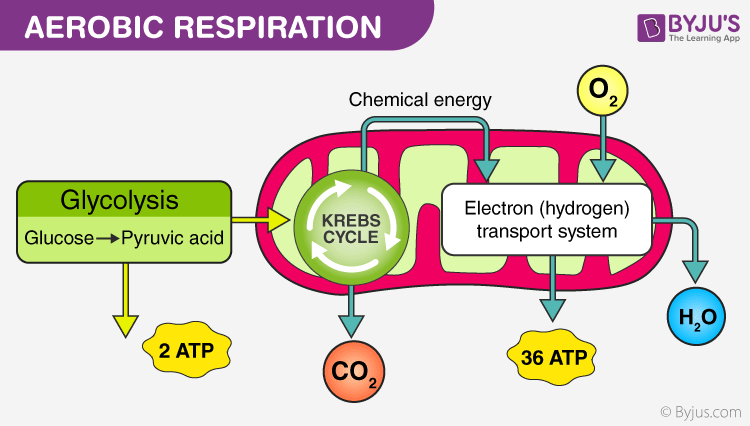
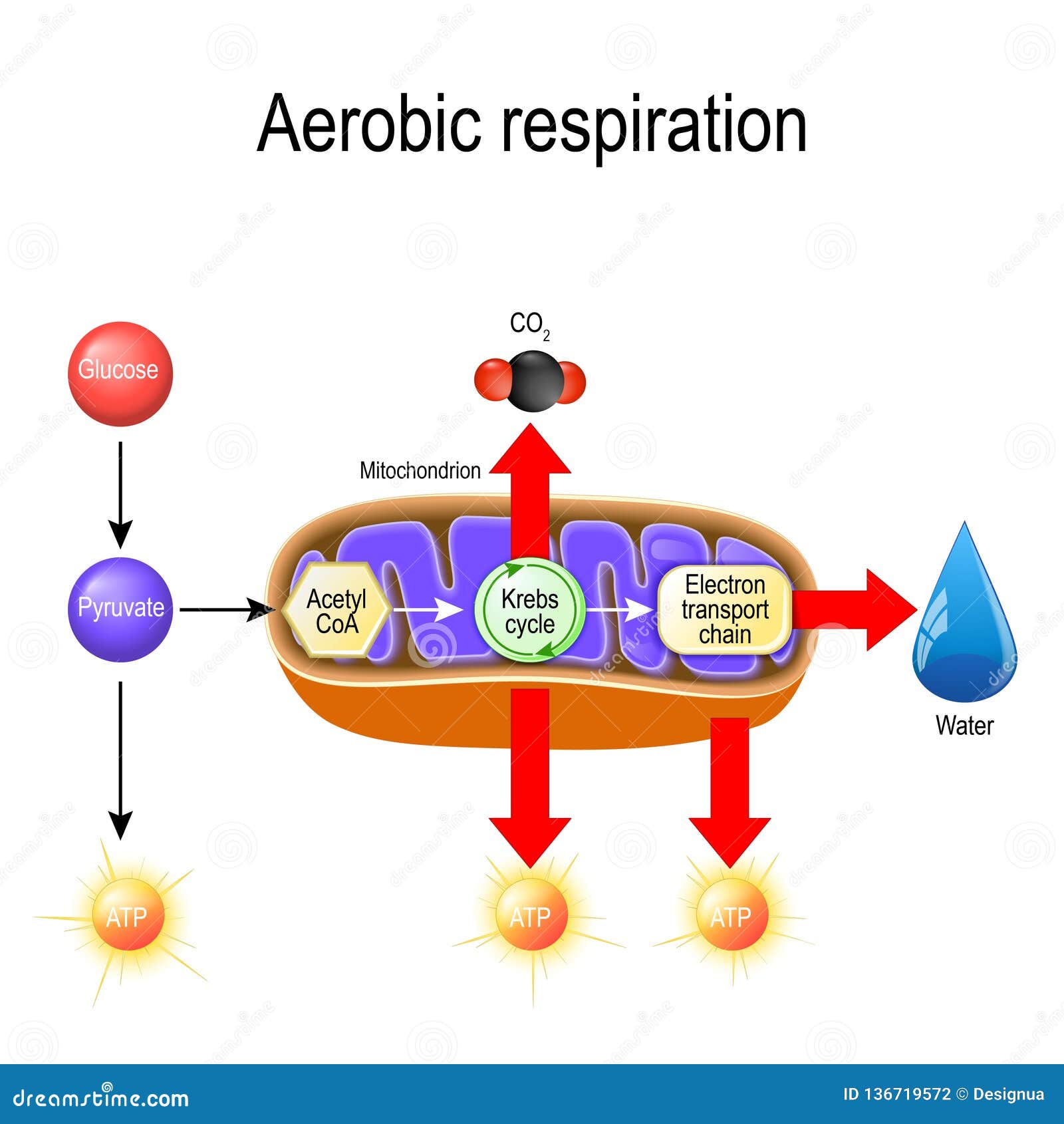
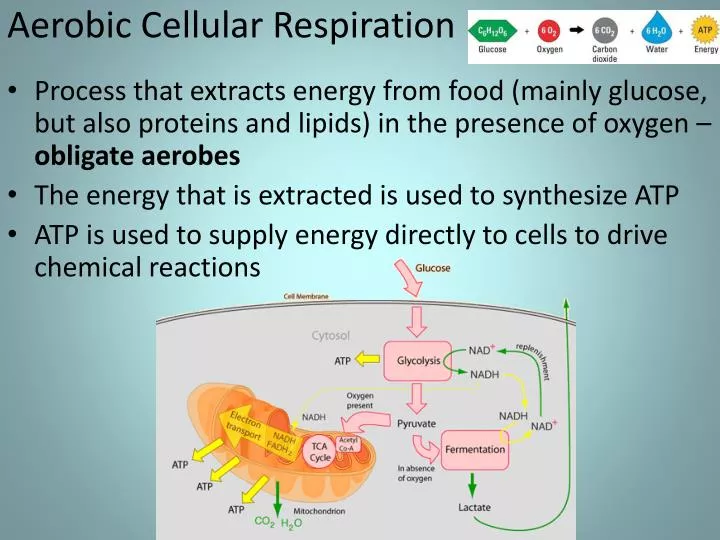
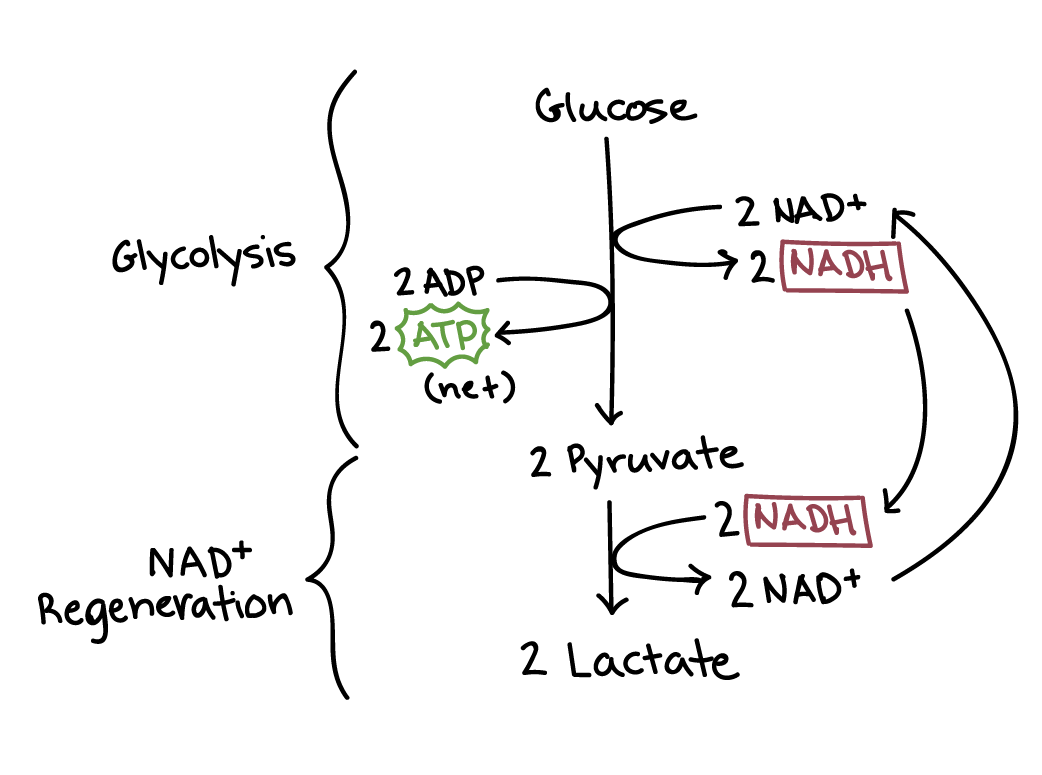
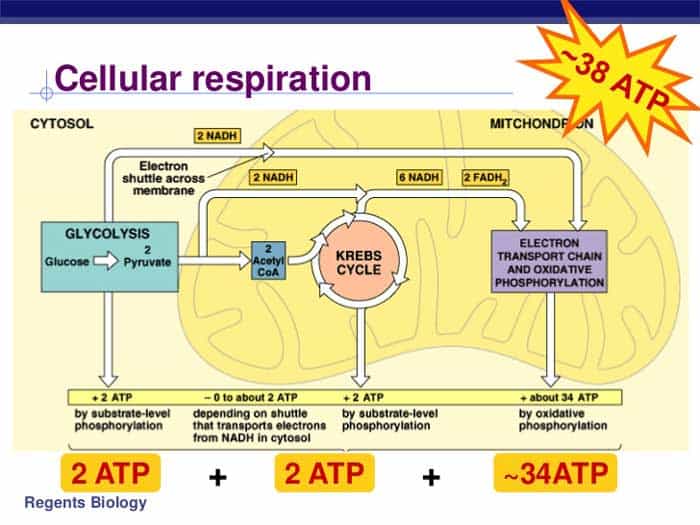
Examine the diagram below that shows these three stages. Notice that ATP is generated in each stage. Aerobic Cellular Respiration Aerobic cellular respiration occurs when the two pyruvic acid molecules from glycolysis are modified and diffuse into the mitochondria where the next two processes occur. Aerobic implies that the process requires oxygen.
Overview of Cellular Respiration Complete the diagram using Figure 7-13 p146 Fig. Students first color the diagram cut out the reactant and product flaps and glue the flaps next to the corresponding arrows. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process while the other two pathways are aerobic.
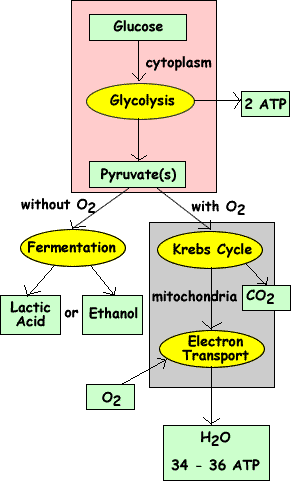
Thus, the total ATP yield in the cellular respiration process is 36 or 38 ATP molecules. Hope this article on simple cellular respiration diagram has helped you understand the process well. The process of cellular respiration is a very complex reaction that involves many enzymes, coenzyme, and molecules.
Start studying AEROBIC CELLULAR RESPIRATION (DIAGRAM). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, ...
5 Nov 2021 — For the cellular respiration diagram, see the next section below. ... Below are examples of aerobic respiration and anaerobic cellular ...Cellular Respiration Overview · Steps of Cellular Respiration
Photorespiration (also known as the oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle, or C 2 photosynthesis) refers to a process in plant metabolism where the enzyme RuBisCO oxygenates RuBP, wasting some of the energy produced by photosynthesis.The desired reaction is the addition of carbon dioxide to RuBP (carboxylation), a key step in the Calvin–Benson cycle, but approximately 25% of reactions by ...
7 Dec 2021 — Aerobic Respiration; Photosynthesis Equation; Cellular Respiration ... As shown in the above diagram, glycolysis takes place in the cytosol.
05.07.2021 · Aerobic vs Anaerobic Respiration- Definition, 11 Differences, Examples Categories Biochemistry Tags Glycolysis , Glycolysis Diagram , Glycolysis Steps Post navigation Phylum Annelida- characteristics, classification, examples
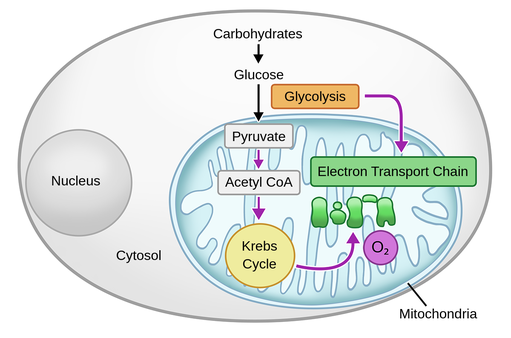
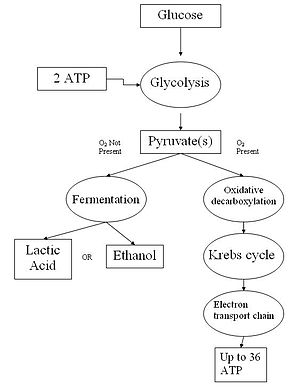
Types of Cellular Respiration Aerobic Respiration. Aerobic respiration is the burning or oxidation of glucose in the presence of oxygen to release energy (ATP). The whole process of aerobic respiration takes place in three steps: glycolysis, Krebs’ cycle, and electron transport system. Sites of respiration are cytoplasm and mitochondria. Glycolysis: Glycolysis is the lysis or splitting of ...
Aerobic respiration — Aerobic metabolism is up to 15 times more efficient than anaerobic metabolism (which yields 2 molecules ATP per 1 molecule glucose) ...
29 Feb 2012 — Identify advantages of aerobic and anaerobic respiration. ... This is clear from the diagram in Figure below. The products of photosynthesis ...
Cellular or Aerobic (in air) Respirationis a series of chemical reactions in the mitochondrion where molecules of glucose are broken down to make CO 2 water, and ATP. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 →6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + glucose oxygen carbon dioxide water 38ATP What’s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Where does cellular respiration occur?
The aerobic respiration diagram given below represents the entire process of aerobic respiration. The different cycles involved in aerobic respiration such as glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain are clearly mentioned in the diagram. Steps of Aerobic Respiration
PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobe’s decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support.
Cellular respiration has 4 distinct processes, which drive the creation of atp. The process of this conversion is known as aerobic respiration and it is the reason why humans need to. While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration.
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds.Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe.
Cellular respiration (both aerobic and anaerobic) utilizes highly reduced species such as NADH and FADH2 to establish an electrochemical gradient (often a proton gradient) across a membrane, resulting in an electrical potential or ion concentration difference across the membrane. The reduced species are oxidized by a series of respiratory integral membrane proteins with sequentially increasing ...
Answer (1 of 3): All plants and animals are obligate aerobes Most fungi are obligate aerobes, some are facultative, few are anaerobes. Most protista are obligate aerobes, some are facltative, few are anaerobes. Many bacteria are aerobes, many are anaerobes. Many archae are anerobes, some are ...
Cellular respiration 2 Aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration (red arrows) is the main means by which both plants and animals utilize energy in the form of organic compounds that was previously created through photosynthesis (green arrow). Aerobic respiration requires oxygen in order to generate energy (ATP). Although carbohydrates, fats, and ...
























0 Response to "43 aerobic cellular respiration diagram"
Post a Comment