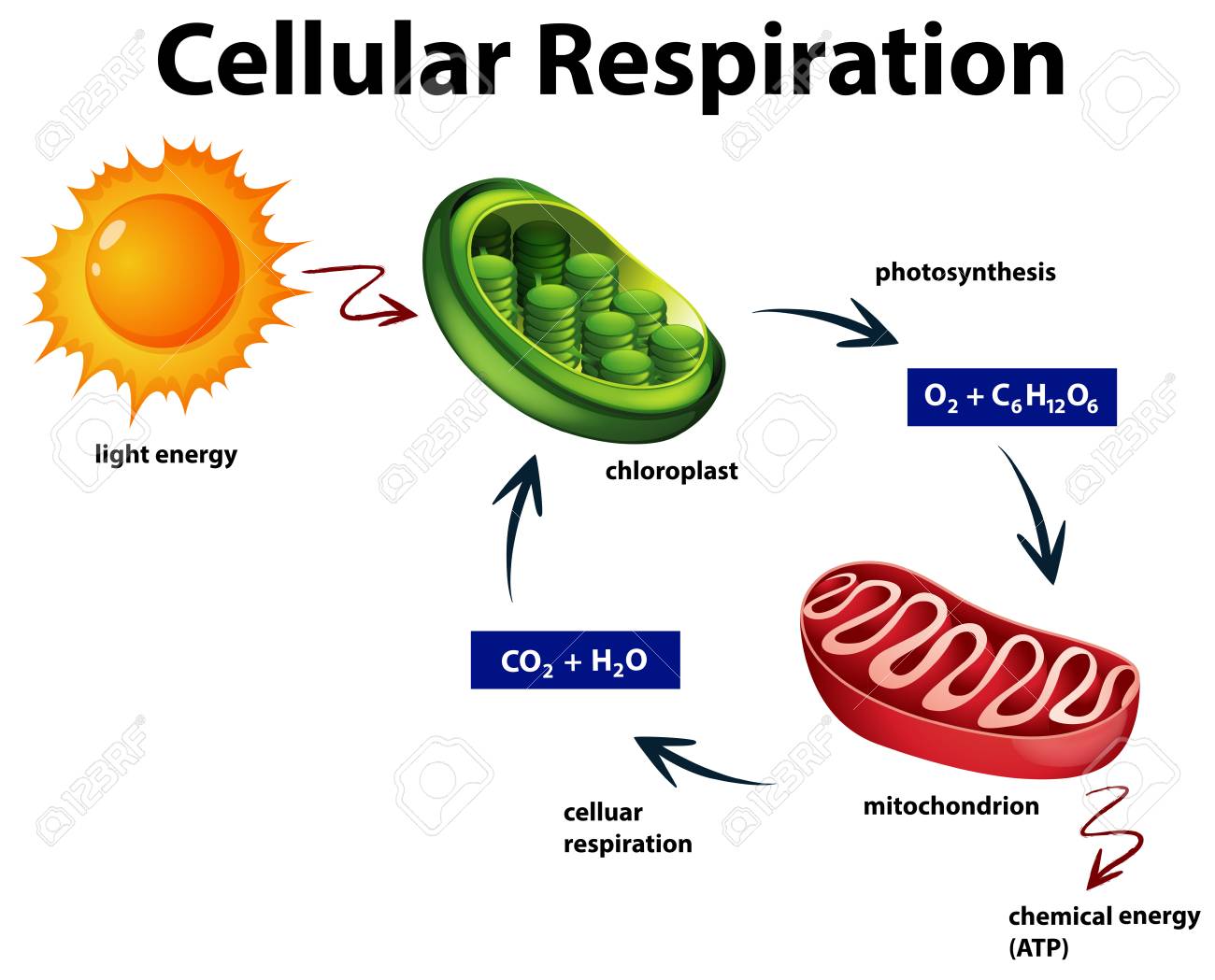
44 mitochondria diagram cellular respiration
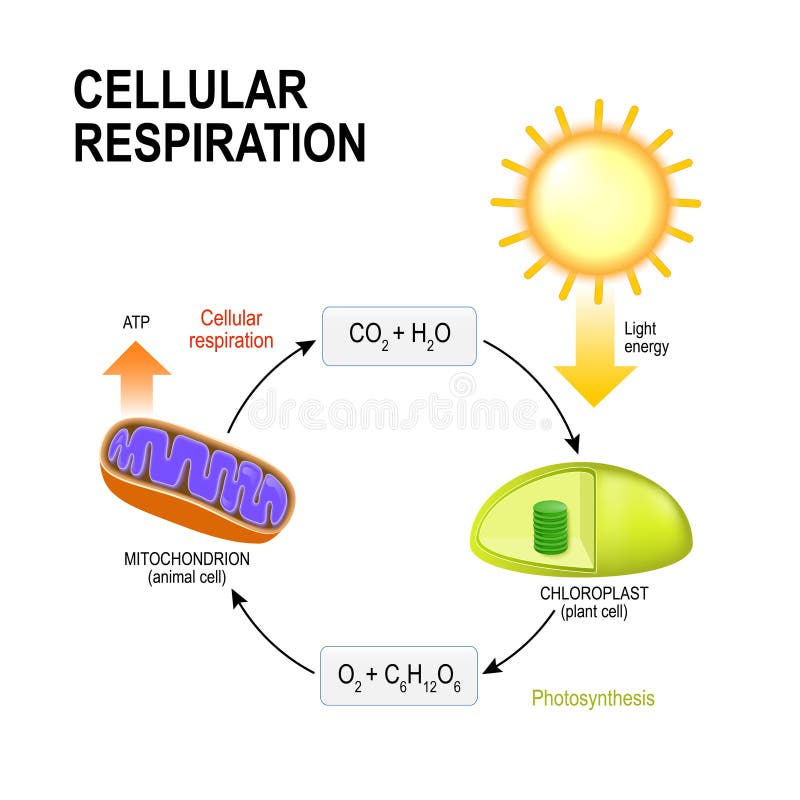
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration diagram worksheet. Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy. Pin On 5ºbb. Co2 h2o c6h12o6 h2o c6h12o6 co2 o2.
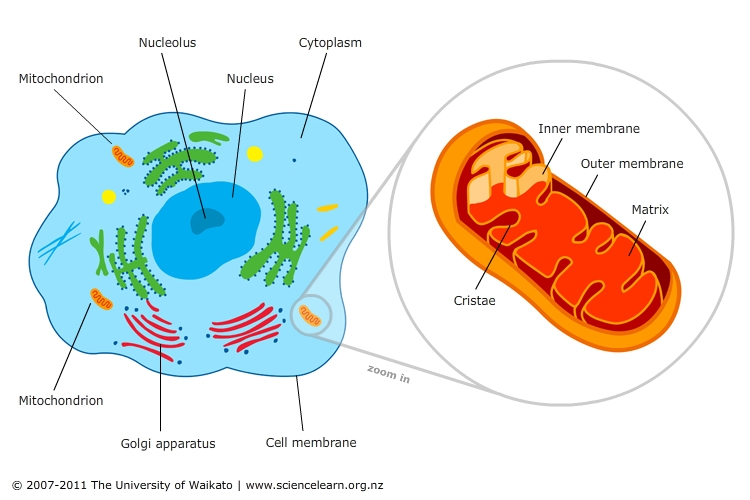
Many of the biochemical reactions involved in cellular respiration take place within the mitochondria. The term 'mitochondrion' is derived from the Greek words " mitos " and " chondrion " which means " thread " and " granules-like ", respectively. It was first described by a German pathologist named Richard Altmann in the year 1890.
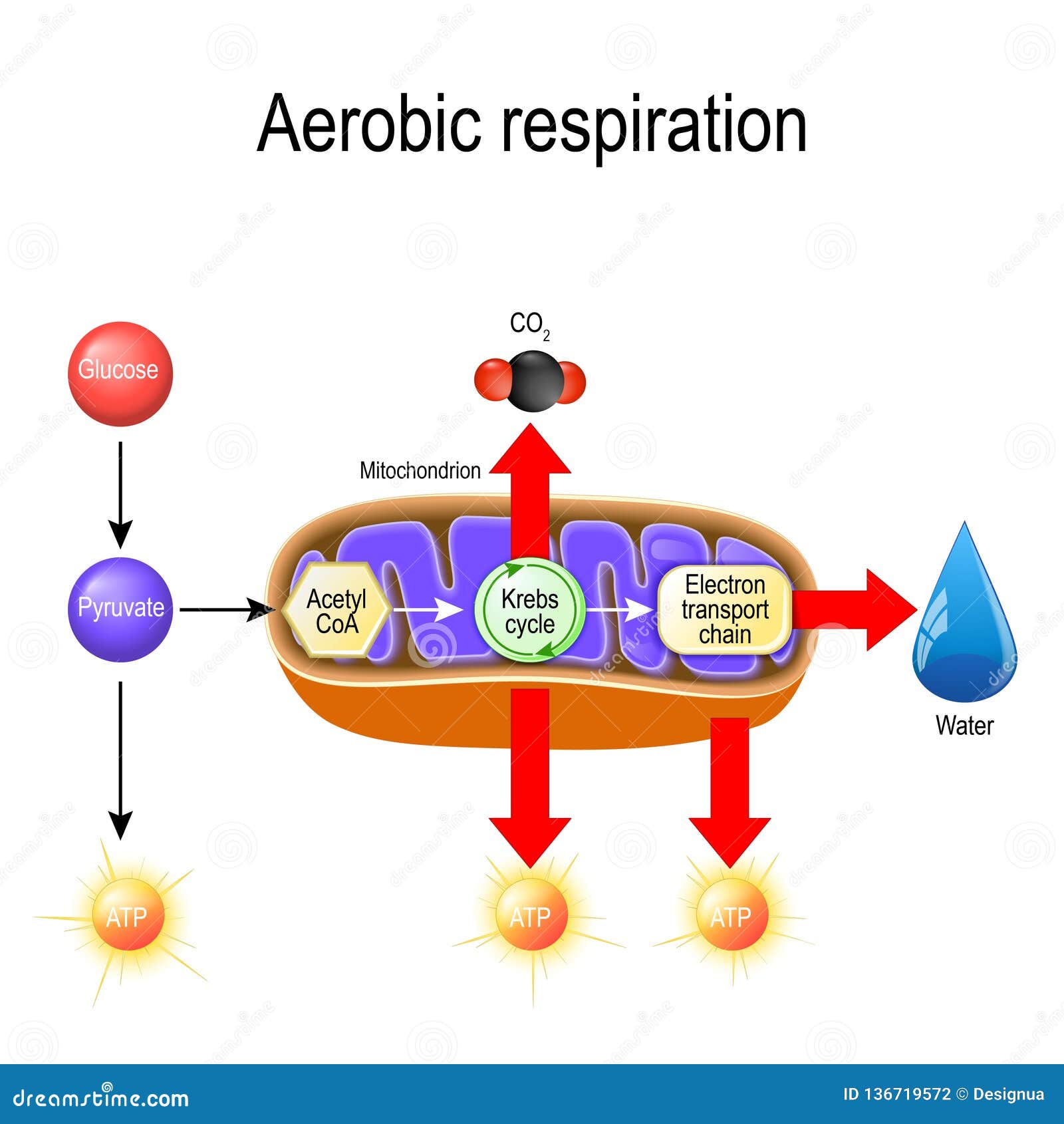
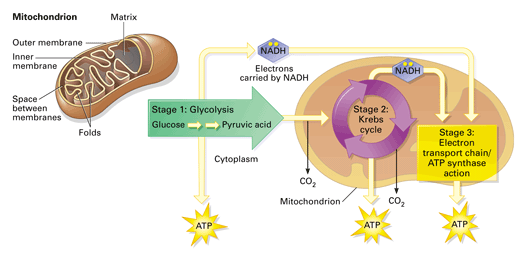
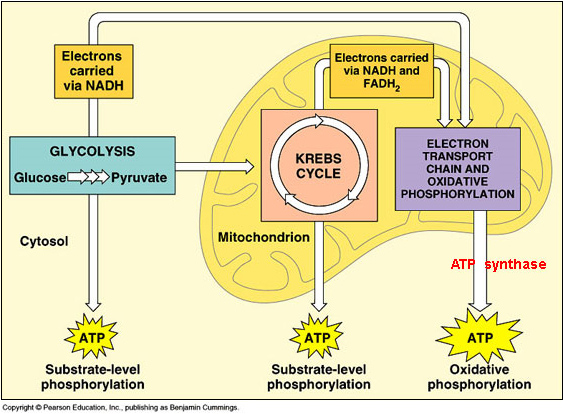
Mitochondria diagram. aerobic respiration equation. C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy. What is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)? An energy carrier molecule utilized by all cells. What are the 3 stages of cellular respiration? glycolysis, krebs cycle, oxidative phosphorylation. What is glycolysis? Glucose is broken down to form pyruvic acid in ...

Mitochondria diagram cellular respiration
Mitochondria is a semi-autonomous cell organelle present in almost all the eukaryotic animal cells except for a few, like RBCs. Mitochondria are known as the Powerhouse of the cell because it is responsible for generating energy currency in the form of ATP which is later utilized by the cell for performing various functions.
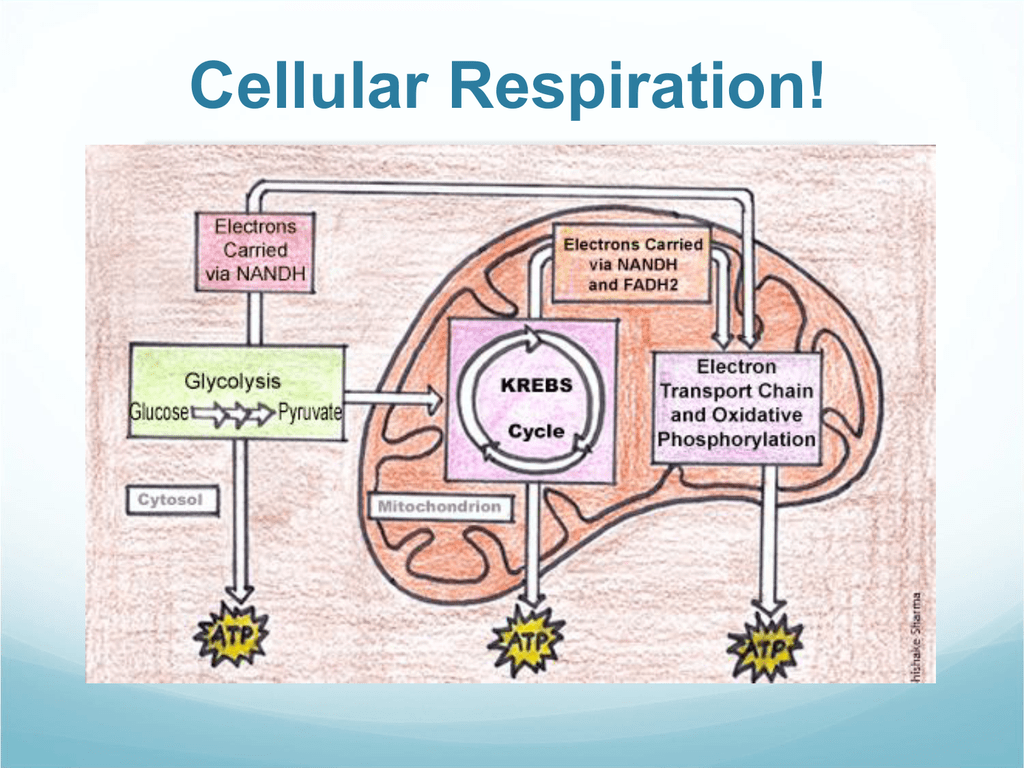
1. Cellular respiration happens in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria. In previous tutorials in this module, we used this diagram to set cellular respiration in its cellular context. Now let's increase the level of detail. Number "1" represents the cell's exterior.
a. cytoplasm b. mitochondria c. chloroplast 9. Which process produces the largest amount of ATP? a. fermentation b. Krebs Cycle c. ETC 10. The oxygen required by cellular respiration is reduced and becomes part of which molecule? a. ATP b. CO 2 c. H 2 0
Mitochondria diagram cellular respiration.
Prolonged exercise increases the mitochondrial mass in muscle cells. The scientist, GH Hogeboom was provided a piece of experimental evidence for the first time that mitochondria play a central role in cellular respiration. References: The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition.Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000.
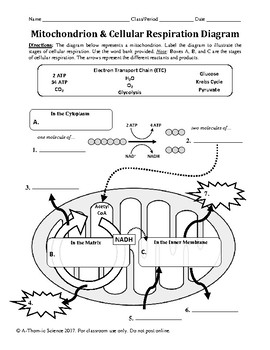
Mitochondrion & Cellular Respiration Diagram Worksheet Two worksheets are included. The first is a simple worksheet that has students label the main parts of a mitochondrion. The second worksheet has students identify the main reactants and products of cellular respiration as they relate to the mitochondrion.
Mitochondrion ultrastructure (interactive diagram) a mitochondrion has a double membrane; The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. This series of reactions produces 36 molecules of atp! Please update your bookmarks accordingly.
D. cellular respiration 9. ATP is a compound that is synthesized when A. chemical bonds between carbon atoms are formed during photosynthesis B. energy stored in chemical bonds is released during cellular respiration C. energy stored in nitrogen is released, forming amino acids D. digestive enzymes break amino acids into smaller parts 10.
Mitochondria play a pivotal role in cellular energy production through the mitochondria-housed pathways of citric acid cycle, fatty acid oxidation, respiration and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Mitochondria have an important anabolic role in cellular metabolism, as they are fundamental for the synthesis of several amino acids, nucleobases ...
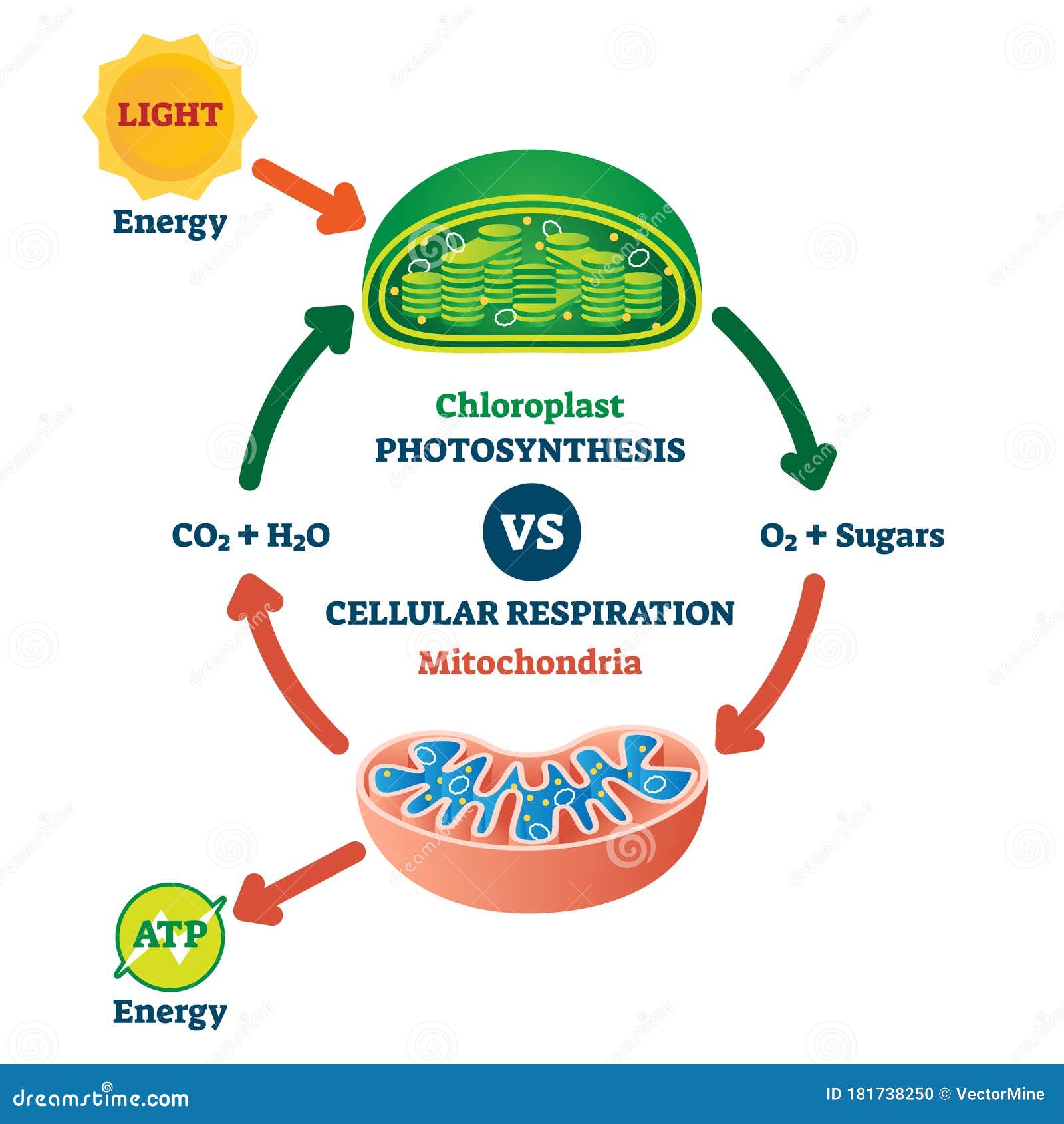
The flow of energy and materials during the production of ATP is shown in the diagram below. What kind of energy transformation occurs during the process of photosynthesis? ... mitochondria : respiration. respiration :: cell membrane: photosynthesis. ... Photosynthesis and cellular respiration both involve the use and release of gases. Which ...
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. It is involved in different cellular activities like respiration, differentiation, cell signalling, cell senescence, controlling the cell cycle, cell growth and other metabolic activities of the cell.
Start studying Respiration Diagram, Cellular Respiration.Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Detailed Diagram of Cellular Respiration Poster. A diagram of cellular respiration including glycolysis, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place ...
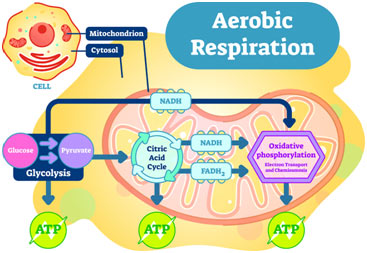
Cellular respiration is a multi-step process that converts the chemical energy in food into usable cellular energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is like the energy currency of...
Both plants and animals carry out the process of respiration, but only plants proceed to another process called 'photosynthesis'. The process of glycolysis begins in the cytoplasm of the cells and is completed in the mitochondria as you can see in the diagram given above. The simple sugar molecules are broken down to energy or ATP molecules.
Overview Cellular respiration is the process of using oxygen in the mitochondria to chemically break down organic molecules such as glucose. This releases the energy stored in the bonds of glucose. In this process, molecules of water and carbon dioxide are released as waste products. This series of reactions produces 36 molecules of ATP! You can draw…
Mitochondria and Cellular respiration - an example of a metabolic pathway It is difficult to describe mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) in terms of numbers and sizes because they are very dynamic organelles in living cells. Mitochondria continually fuse together, divide into smaller fragments
Glucose and other carbohydrates made by plants during photosynthesis are broken down by the process of aerobic cellular respiration(requires oxygen) in the mitochondria of the cell. This releases energy for the cell. ATP is the energy-carrying molecule produced by the mitochondria through a series of chemical reactions.
Glucose, a simple sugar, and other carbohydratesmade by plants during photosynthesis are broken down by the process of aerobic cellular respiration (requires oxygen) in the mitochondria of the cell. This releases energy (ATP)for the cell. The more active a cell (such as a muscle cell), the more mitochondria it will have.
Mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion) are often called the "powerhouses" or "energy factories" of a cell because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy-carrying molecule. The formation of ATP from the breakdown of glucose is known as cellular respiration.
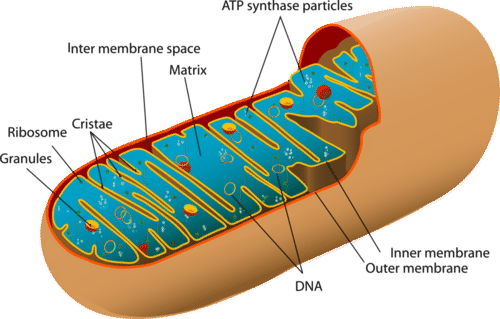
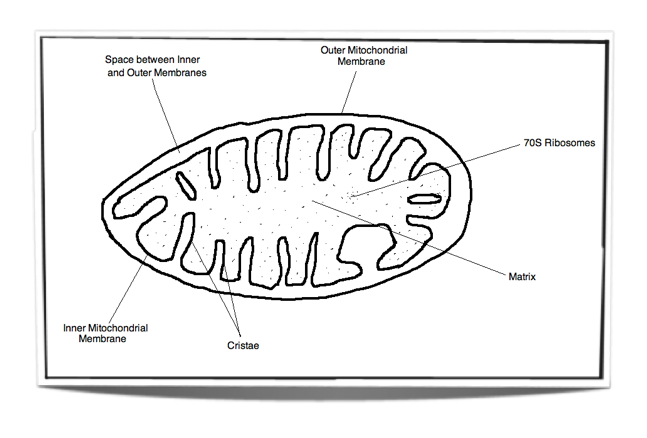
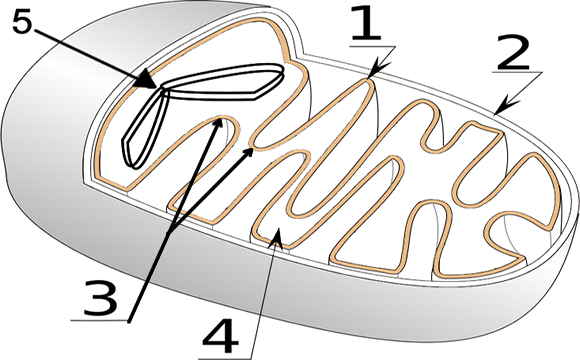
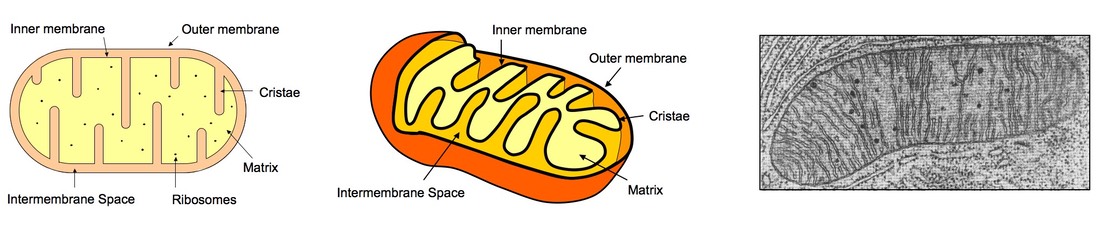
Mitochondria in plant cells and in animal cells all perform the same function of cellular respiration. They are known as the Powerhouse of the cell. Cellular respiration The inner membrane of the mitochondria is folded in the form of shelf-like inward projections called cristae and it covers the inner matrix space.
Name The Mitochondrion Class Date In plant and animal cells, the final stages of cellular respiration take place in mitochondria. A mitochondrion has two membranes. The inner membrane is folded up inside the outer membrane. The space between the inner and outer membranes is called the inter- membrane space.
When the glucose and oxygen reaches our cells, we have the materials we need to perform cellular respiration. This process starts in the cells' cytoplasmand is completed in the mitochondria- the cellular powerhouse.
The fluid of the mitochondria where the Kreb's cycle happens. 38 amount of ATP broken down from 1 sugar molecule during the 3 step process of cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration medical vector illustration diagram, respiration process scheme. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. mitochondria stock illustrations
Mitochondria are energy-producing organelles. The multi-layered process of converting food into energy is called cellular respiration. A pathway is a series of biochemical reactions. Cellular...
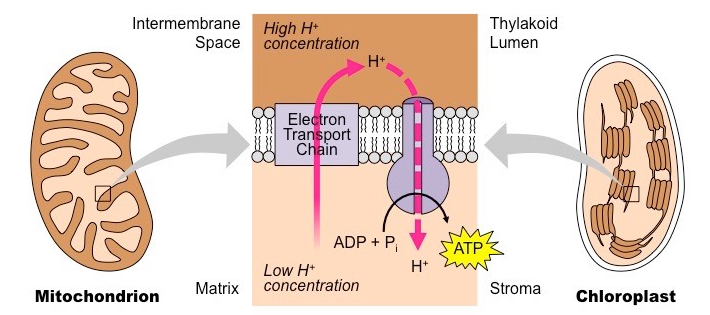
As a result, children inherit their mitochondria and their mitochondrial DNA from their mother. Through their ATP synthesis function in the matrix and through cellular respiration across the double membrane, mitochondria and the mitochondrial function are a key component of animal cells and help make life as it exists possible.
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...







/Cellular-Respiration-58e52b113df78c5162b38dca.jpg)














0 Response to "44 mitochondria diagram cellular respiration"
Post a Comment