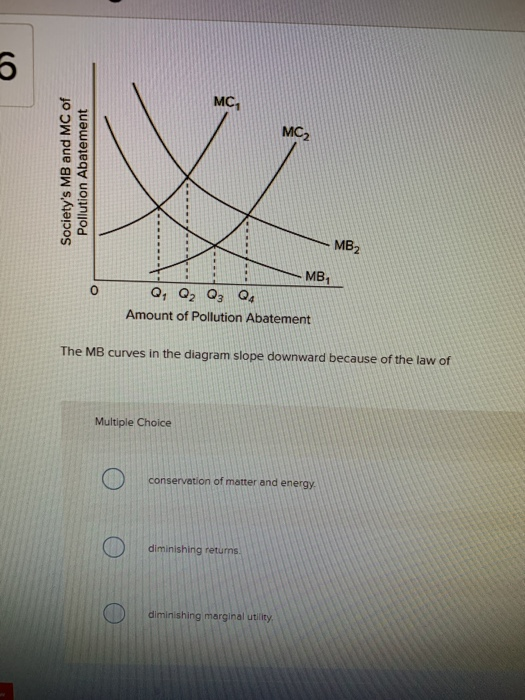
44 the mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of:
(a) See the graph. Over the 0 to 4 range of output, the TVC and TC curves slope upward at a decreasing rate because of increasing marginal returns. The slopes of the curves then increase at an increasing rate as diminishing marginal returns occur.' (b) See the graph. The MB curves in the above diagram slope downward because of the law of: diminishing marginal utility. (Consider This) Suppose that Susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place.
The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. When supply is represented visually on a graph with price on the y axis and quantity supplied on the x axis supply generally curves upward. This preview has intentionally blurred sections. Conservation of matter and energy. The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the ...

The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of:
Society's marginal cost of pollution abatement curve slopes upward because of the law of diminishing marginal utility. false What two conditions must hold for a competitive market to produce efficient outcomes? Supply curves must reflect all costs of production, and demand curves must reflect consumers' full willingness to pay. Producer surplus: The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: A) demand. B) conservation of matter and energy. C) diminishing marginal utility. D) diminishing returns. Correct Answer:Explore answers and other related questions. MC is the slope of the SRVC curve. A change in fixed cost would be reflected by a change in the vertical distance between the SRTC and SRVC curve. Any such change would have no effect on the shape of the SRVC curve and therefore its slope MC at any point. The changing law of marginal cost is similar to the changing law of average cost.
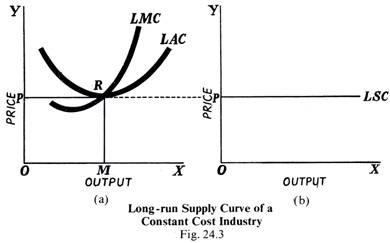
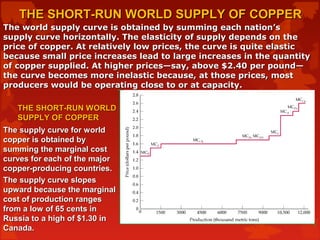
The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of:. Therefore, the curve MC remains above the curve AC. (iii) Law of Constant Returns or Constant Costs: According to the law of constant returns when a firm employs more and more factors, output increases at a constant rate. Therefore, the average cost curve as well as marginal cost curve remains parallel to horizontal axis. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: The MB curves in the diagram slope downward because of the law of. The MB curves in the diagram slope downward because of the law of. A) conservation of matter and energy. B) diminishing returns. C) diminishing marginal utility. D) increasing cost. Supply curves are traditionally represented as upward-sloping because of the law of diminishing marginal returns. This need not be the case, however, as described below. Special cases of a supply curve As described above, the general form of a supply curve is upward sloping. There are cases, however, when supply curves do not slope upwards. Along this curve: d P d Q = d d Q ( C ( Q) Q) − k Q 2. Thus d P / d Q is the difference of two terms, the first of which is the slope of the AC curve; we showed in Leibniz 7.3.1 (using the quotient rule) that this is ( MC − AC) / Q. Also, we know from the equation of the isoprofit curve that k / Q = P − AC. The marginal cost to society of reducing pollution rises with increases in pollution abatement because of the law of: diminishing returns. The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of: diminishing returns. Suppose that Susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place. Economists would expect: The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. A)demand. B)conservation of matter and energy. C)diminishing marginal utility. D)diminishing returns. Correct Answer: Explore answers and other related questions. 10+ million students use Quizplus to study and prepare for their homework, quizzes and exams through 20m+ questions in 300k quizzes. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of diminishing returns 2. Assume that a government is considering a new social program and may choose to include in this program one of four progressively larger projects. The marginal cost and the marginal benefits of each of the four projects are given in the table below. As you produce more, it gets more expensive, because of the upward slope of the supply curve. Let's say we are producing at Q = Q 1, with a marginal cost of MC 1. Given an equilibrium price P*, then Profit at Q = Q 1 = P* - MC 1. Now, we produce at Q = Q 2 (> Q 1), which means MC 2 > MC 1. Profit at Q = Q 2 = P* - MC 2, which is smaller than ... The classical depiction of a marginal cost curve initially slopes downwards because this reflects a degree of economies of scale. Then there is a range in which it shows diminishing returns to scale (sloping upwards). If it slopes downwards over the full range, there's no equilibrium market structure with more than one producer. Both supply and demand can be represented visually as curves on a graph - supply slopes upward, while demand slopes downward. The supply curve shows the lowest price at which a business will sell a product or service, and can be the difference between a successful business and a struggling one. Law of Demand The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of: diminishing returns. The MB curves in the above diagram slope downward because of the law of: diminishing marginal utility. (Consider This) Suppose that Susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place. Economists would expect: The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: The mb curves in the diagram slope downward because of the law of; The mb curves in the diagram slope downward because of the law of: Which of the following is the reason supply curves typically slope upward? The practice of plowing fields along the curves of a slope is called ... The average total cost curve is upward-sloping. B) ... There are diseconomies of scale. In Figure 8.1, diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market. ... A law established by the government to protect new industries. B) We see that the short-run supply curve SRC of the industry rises upwards, because the short-run marginal curve SMC rises upwards. Long-run Supply Curve: The long-run is supposed to be a period sufficiently long to allow changes to be made both in the size of the plant and in the number of firms in the industry. Answer (1 of 2): First of all before answering this question u should know total utility curve is not always upward sloping. The curve is only upward sloping until marginal utility turns 0.once marginal utility becomes negative the curve is downward sloping Now your question why total utility cu... Best answer MC curve is U-shaped. As output increases, MC curve slopes downward (up to OQ units), reaches the minimum (at point A) and then starts sloping upward beyond OQ level of output. (See Fig.) The U-shape of MC curve is because of the law of variable proportions. The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: The practice of plowing fields along the curves of a slope is called contour plowing. The practice of plowing fields along the curves of a slope is called; Which of the following is the reason supply curves typically slope upward? Write the equation of the line that passes through ... Why MC curve is U shaped in short run? The curve has a "u" shape because when marginal cost drops at the beginning of production, marginal returns increase. However, as more of an item is produced, eventually the law of diminishing returns sets in, leading to an increase of marginal cost. See further detail related to it here. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. A) demand. B) conservation of matter and energy. C) diminishing marginal utility. D) diminishing returns. Previous Refer to the diagram. Marginal Cost will keep increasing (have upward slope) because of the principle of diminishing marginal returns. The MC curve above the its intersection with AVC is the Supply Curve *because below minimum AVC, the firms stops production) Read More MC is the slope of the SRVC curve. A change in fixed cost would be reflected by a change in the vertical distance between the SRTC and SRVC curve. Any such change would have no effect on the shape of the SRVC curve and therefore its slope MC at any point. The changing law of marginal cost is similar to the changing law of average cost. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: A) demand. B) conservation of matter and energy. C) diminishing marginal utility. D) diminishing returns. Correct Answer:Explore answers and other related questions. Society's marginal cost of pollution abatement curve slopes upward because of the law of diminishing marginal utility. false What two conditions must hold for a competitive market to produce efficient outcomes? Supply curves must reflect all costs of production, and demand curves must reflect consumers' full willingness to pay. Producer surplus:




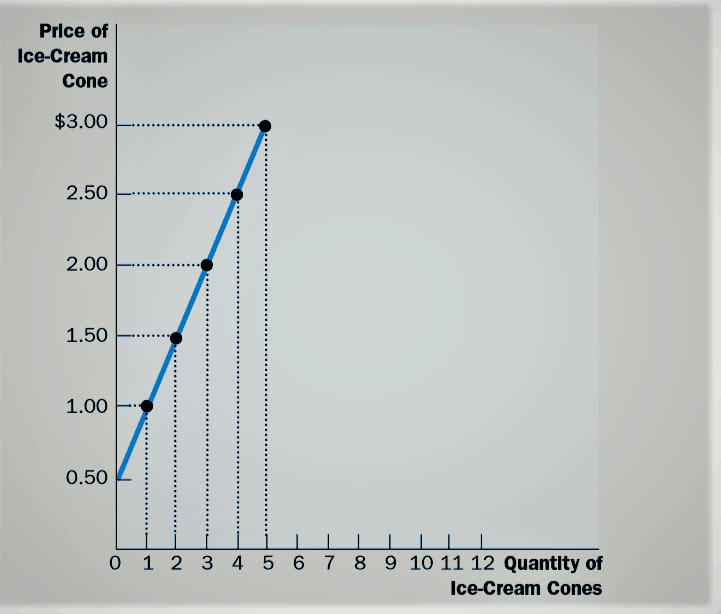

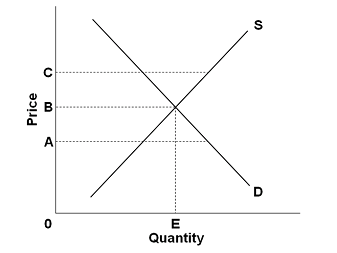
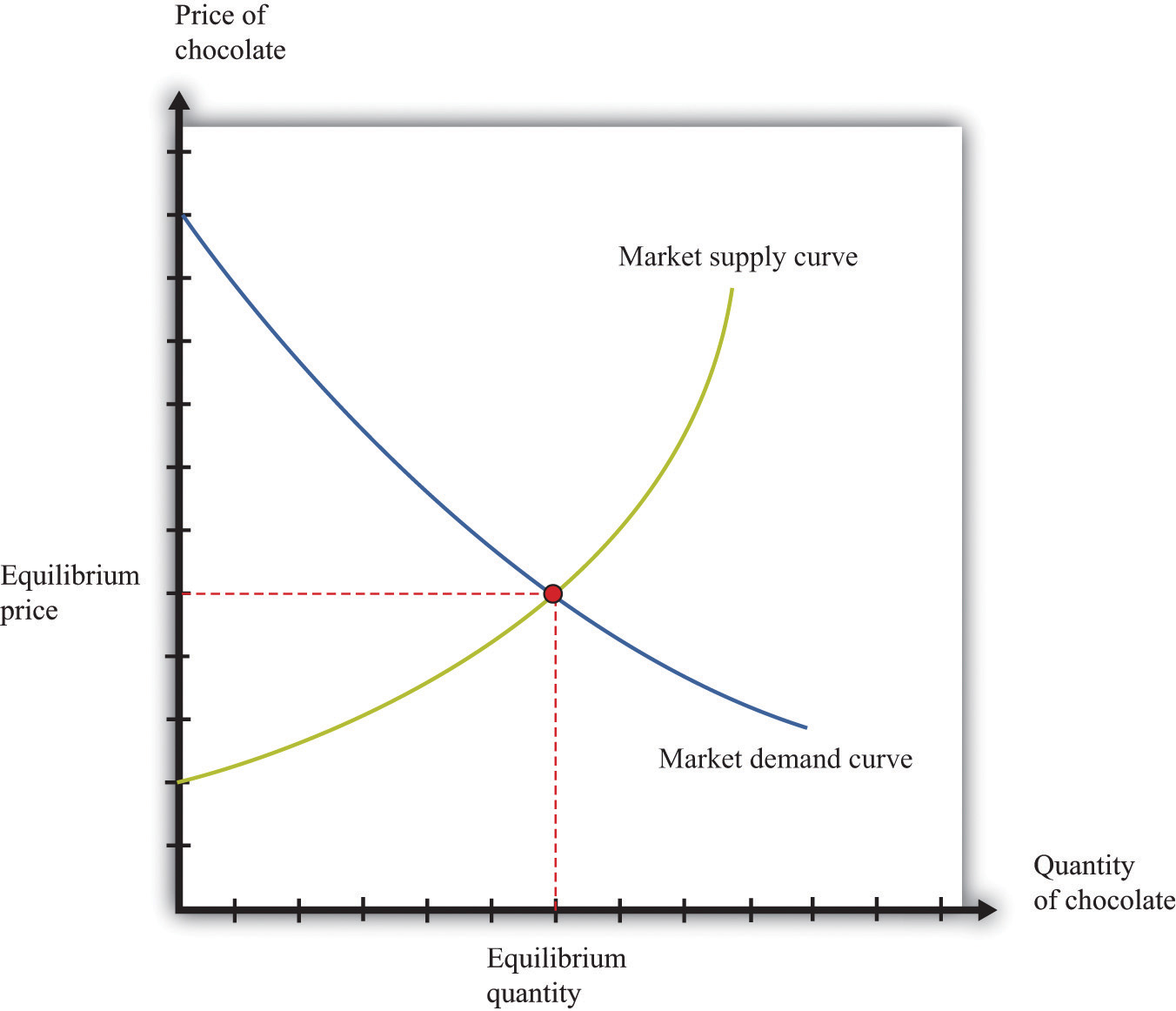




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Supplyrelationship-c0f71135bc884f4b8e5d063eed128b52.png)
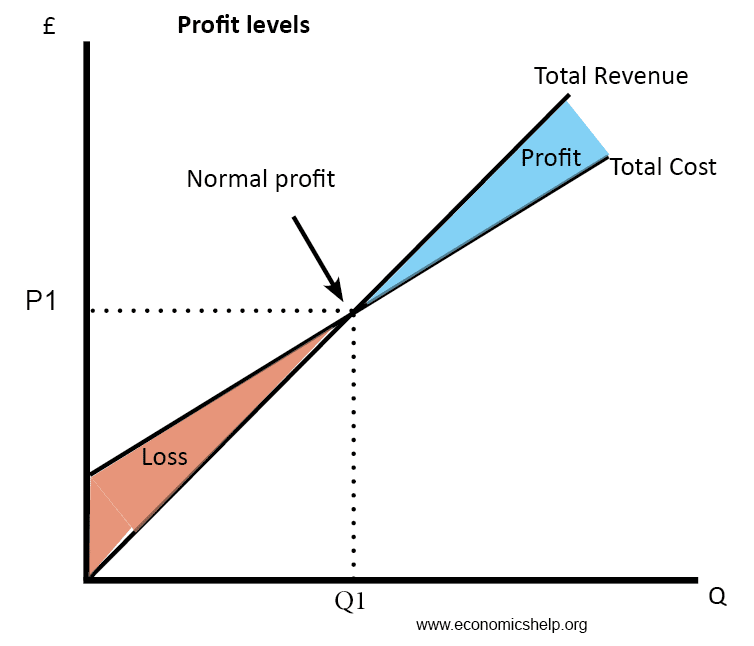
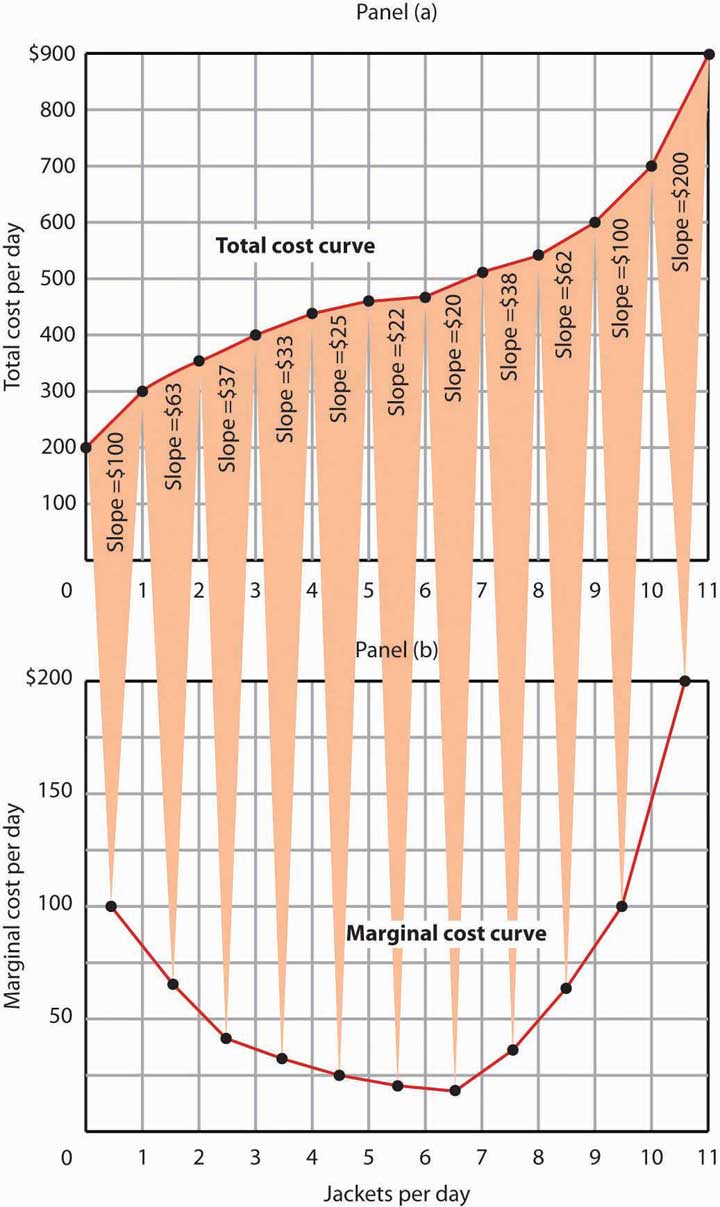
/dotdash_Final_Law_of_Diminishing_Marginal_Productivity_Oct_2020-01-d3c30a9c6ba442b9bccc7b99158251e3.jpg)










0 Response to "44 the mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of:"
Post a Comment