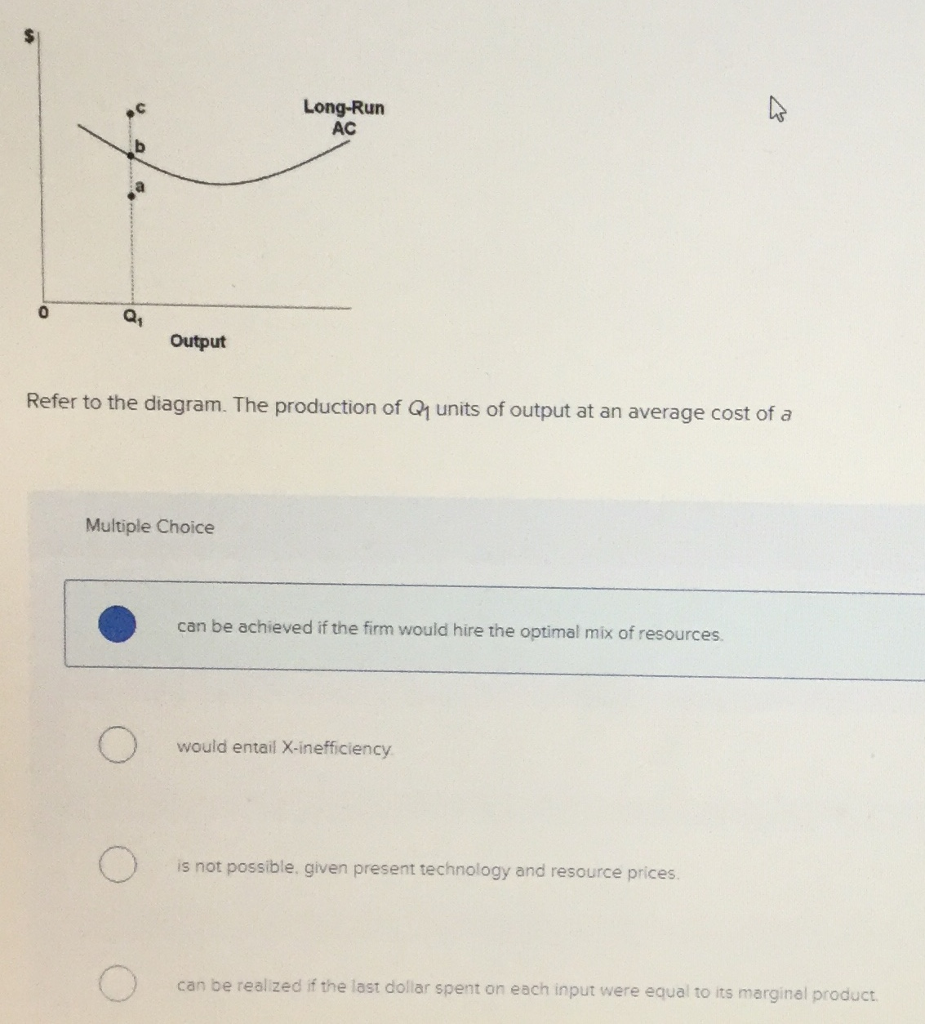
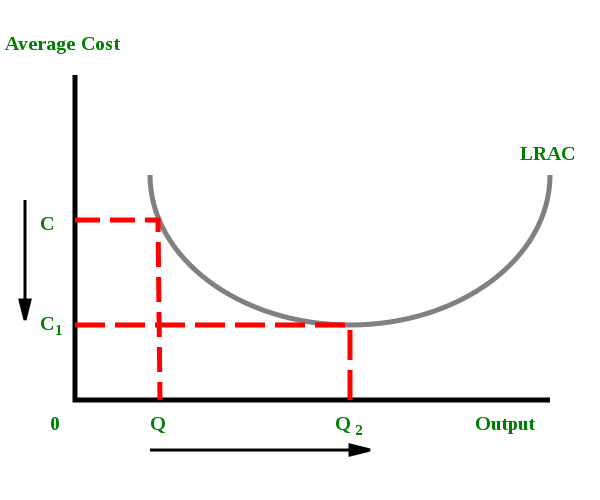
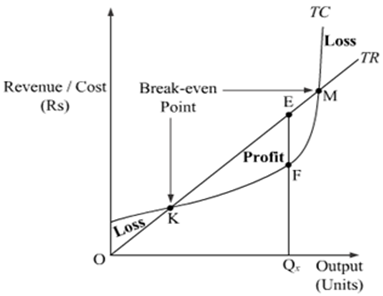
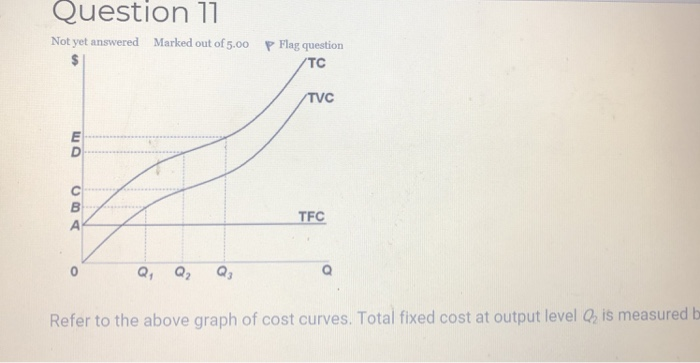
44 refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a
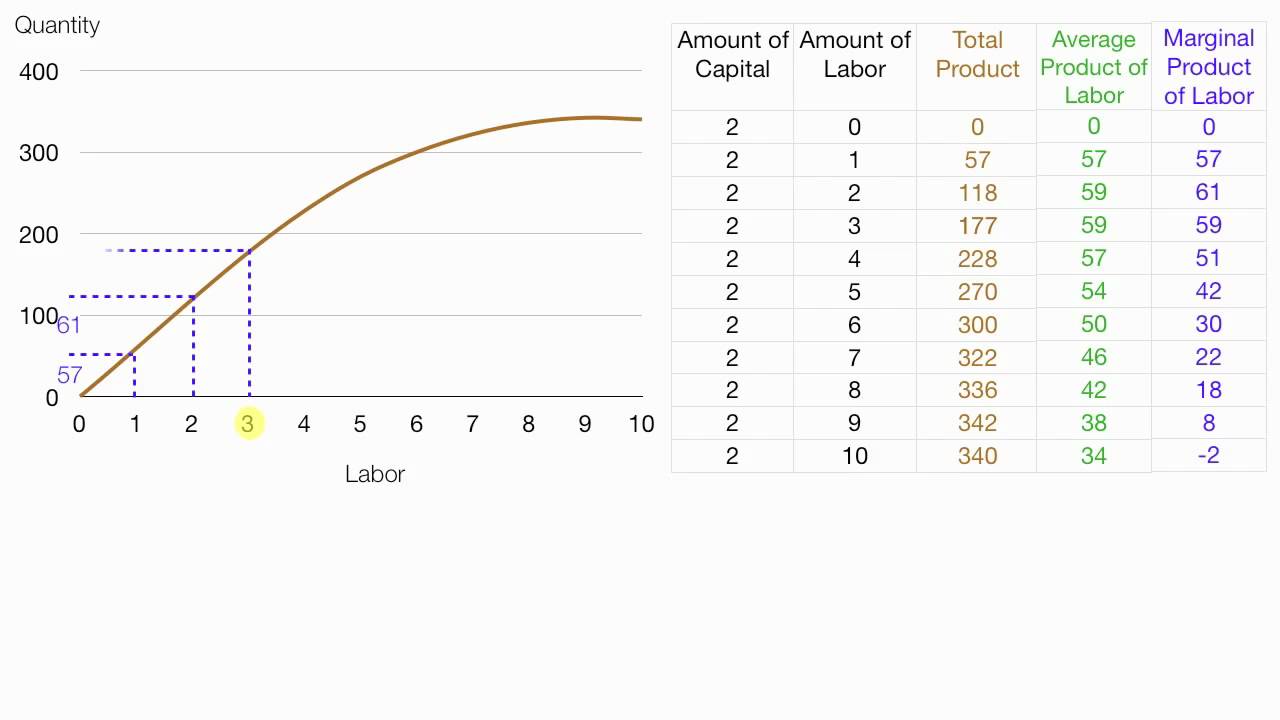
Because of this, oligopolistic firms take advantage of economies of scale thereby achieving great returns from their output. In other words, the product of an oligopolistic firm exhibits large economies of scale where the cost of producing each unit, that is average cost (AC) declines as the output increases. Average variable cost. Average total cost. Marginal cost ... Refer to Scenario 13-5. ... b. it should produce Q1 units of output. d. it should shut down ...
Assume a computer firm's marginal costs of production are constant at $1,000 per ... The firm should choose a very large output because average total cost ...5 pages
Refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a
firm may or may not be maximizing profits. Refer to the above diagram. The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of c: ... Refer to the above graph. Under purely competitive conditions in this labor market, the equilibrium wage rate will be: a. W1 and Q1 workers will be hired b. W2 and Q2 workers will be hired c. W2 and Q1 workers will be hired dW3 and Q1 workers will be hired 8.5 / 10 average quality score from customers. What advantages do you get from our Achiever Papers' services? All our academic papers are written from scratch. All our clients are privileged to have all their academic papers written from scratch. These papers are also written according to your lecturer’s instructions and thus minimizing any ...
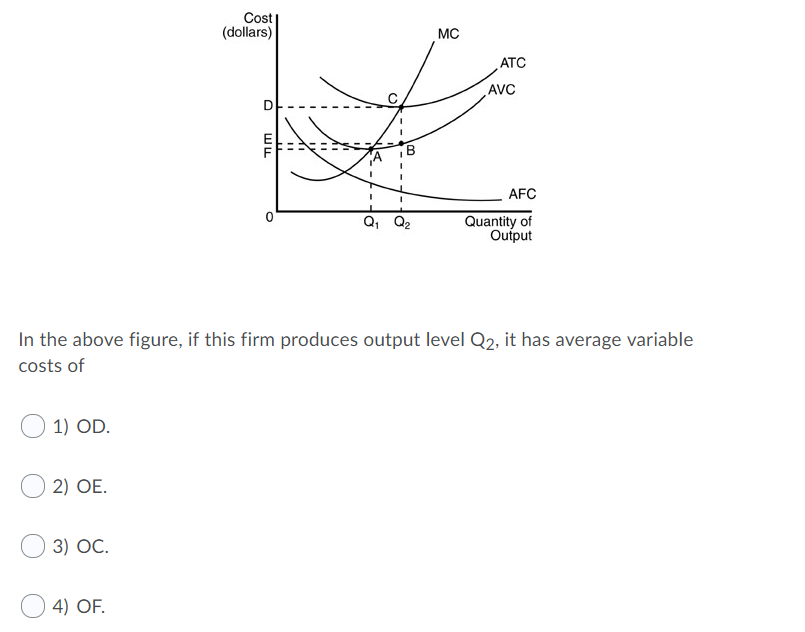
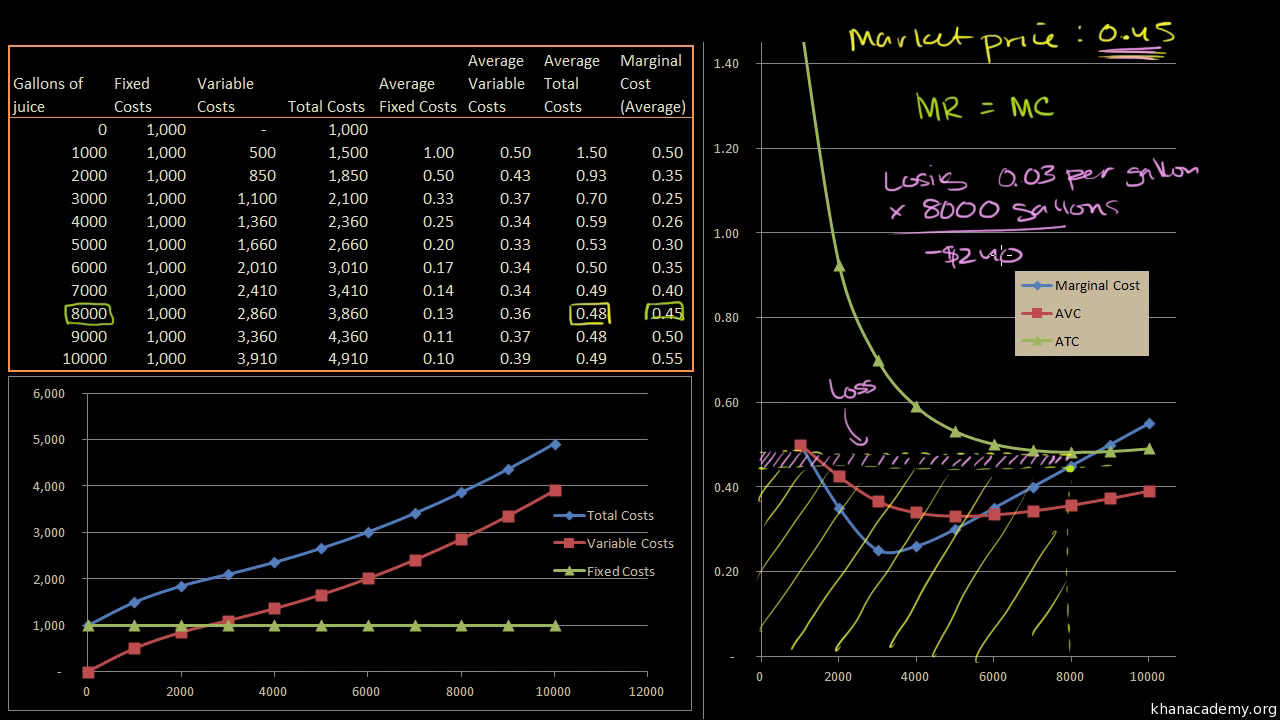
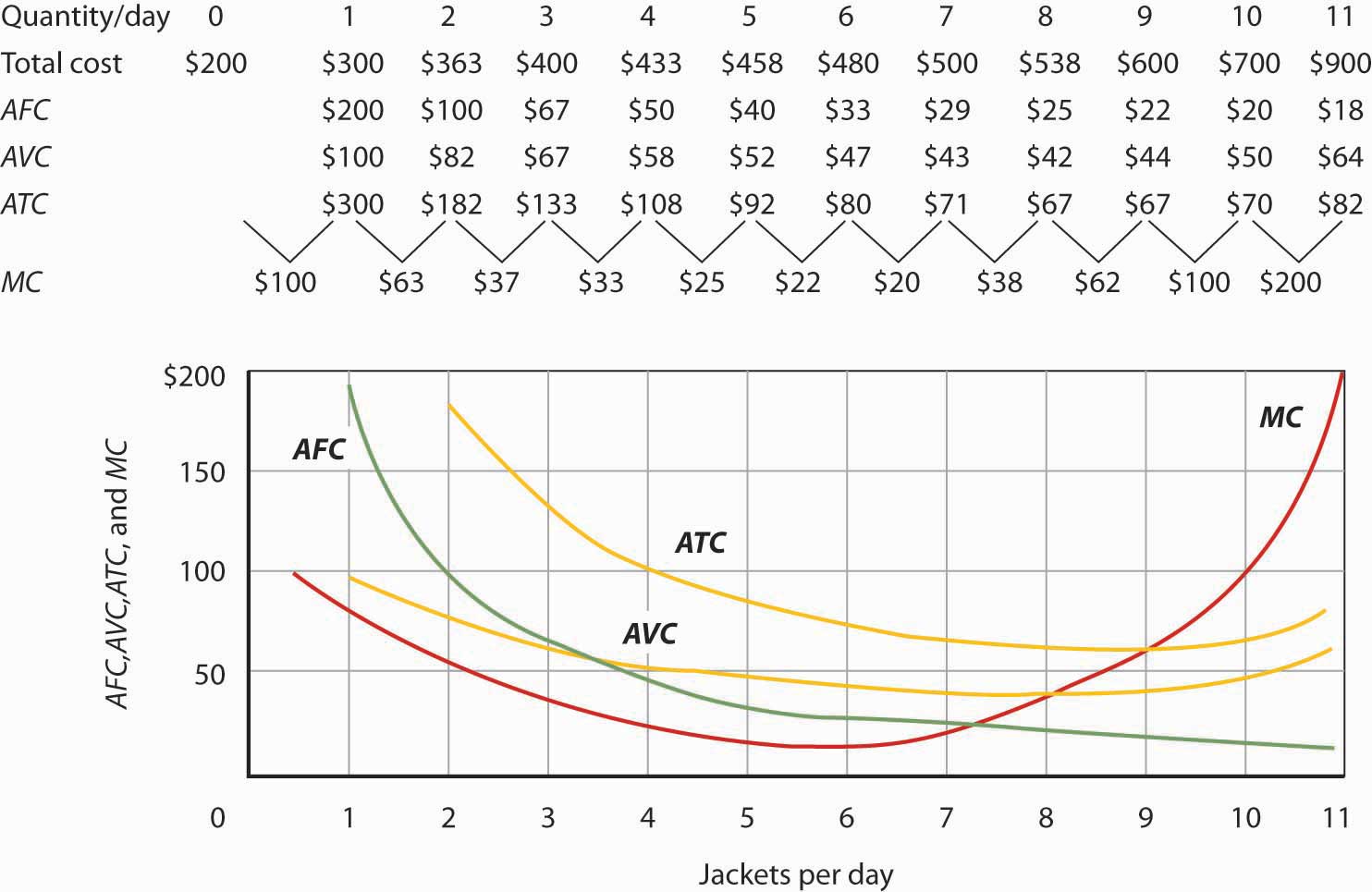
Refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a. Step 11) Let's calculate the average waiting time for above example. Wait time P4= 0-0=0 P1= 3-2=1 P2= 9-5=4 P5= 11-4=7 P3= 15-1=14 Average Waiting Time= 0+1+4+7+14/5 = 26/5 = 5.2 Preemptive SJF. In Preemptive SJF Scheduling, jobs are put into the ready queue as they come. A process with shortest burst time begins execution. In producing the 7,000 staplers, it incurred variable costs of $28,000 and a total cost of $45,000. Refer to Scenario 13-5. In producing the 7,000 staplers, the firm's average total cost was. $6.43. Refer to Table 13-9. What is average variable cost when output is 50 units? $4.80. ... The three average total cost curves on the diagram ... 8.5 / 10 average quality score from customers. What advantages do you get from our Achiever Papers' services? All our academic papers are written from scratch. All our clients are privileged to have all their academic papers written from scratch. These papers are also written according to your lecturer’s instructions and thus minimizing any ... The CPI frequently is called a cost-of-living index, but it differs in important ways from a complete cost-of-living measure. We use a cost-of-living framework in making practical decisions about questions that arise in constructing the CPI. A cost-of-living index is a conceptual measurement goal, however, and not a straightforward alternative ...
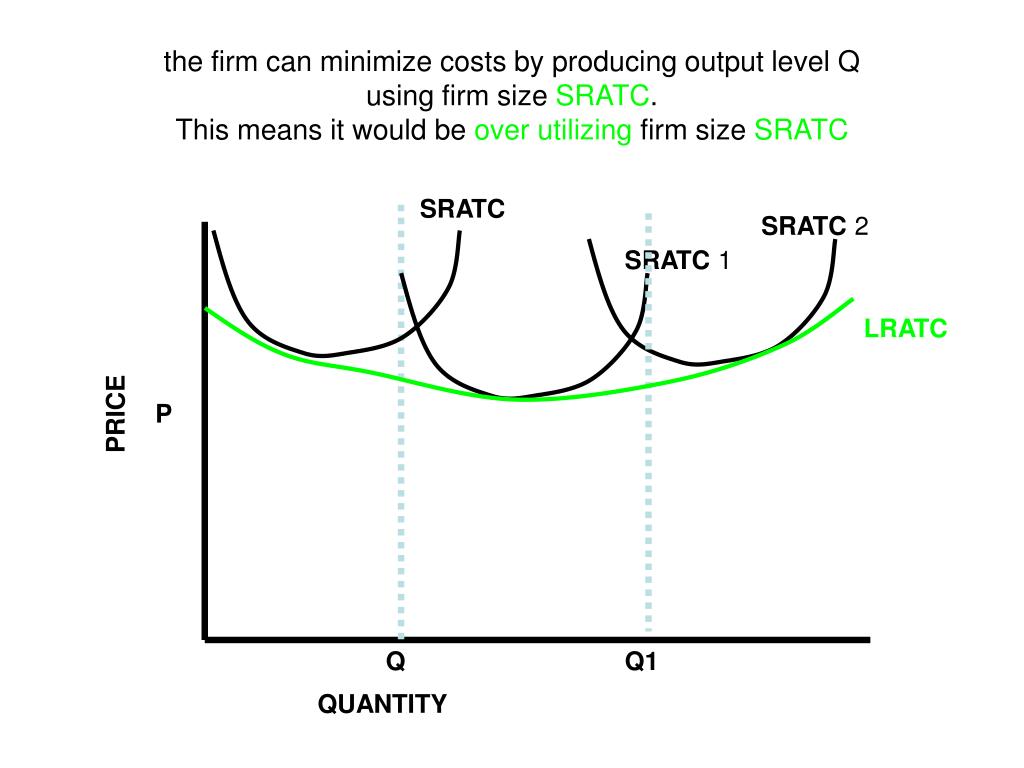
The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of a is not possible, given present technology and resource prices. Suppose a technological improvement increases the productivity of a firm's capital and, simultaneously, its workers' union negotiates a wage increase. Gross profit (how much revenue the company retains after deducting the production cost of goods sold) Costs (to figure out ways to lower them) A comparison of projected vs. actual revenue. A comparison of expenses vs. budget. Debt vs. equity ratio. Day sales outstanding (DSO) (the average number of days it takes to receive payment after a sale) The five marked quantities show where each short-run average total cost (ATC) curve is tangent to the long-run average total cost (LRATC) curve; for example, Q1 shows where the ATC1 curve is tangent to the LRATC curve. The orange point represents the firm's current output level in the short run (Q2). The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of a, which lies below the long-run actual cost curve: is not possible, given present technology and resource prices. Recommended textbook explanations
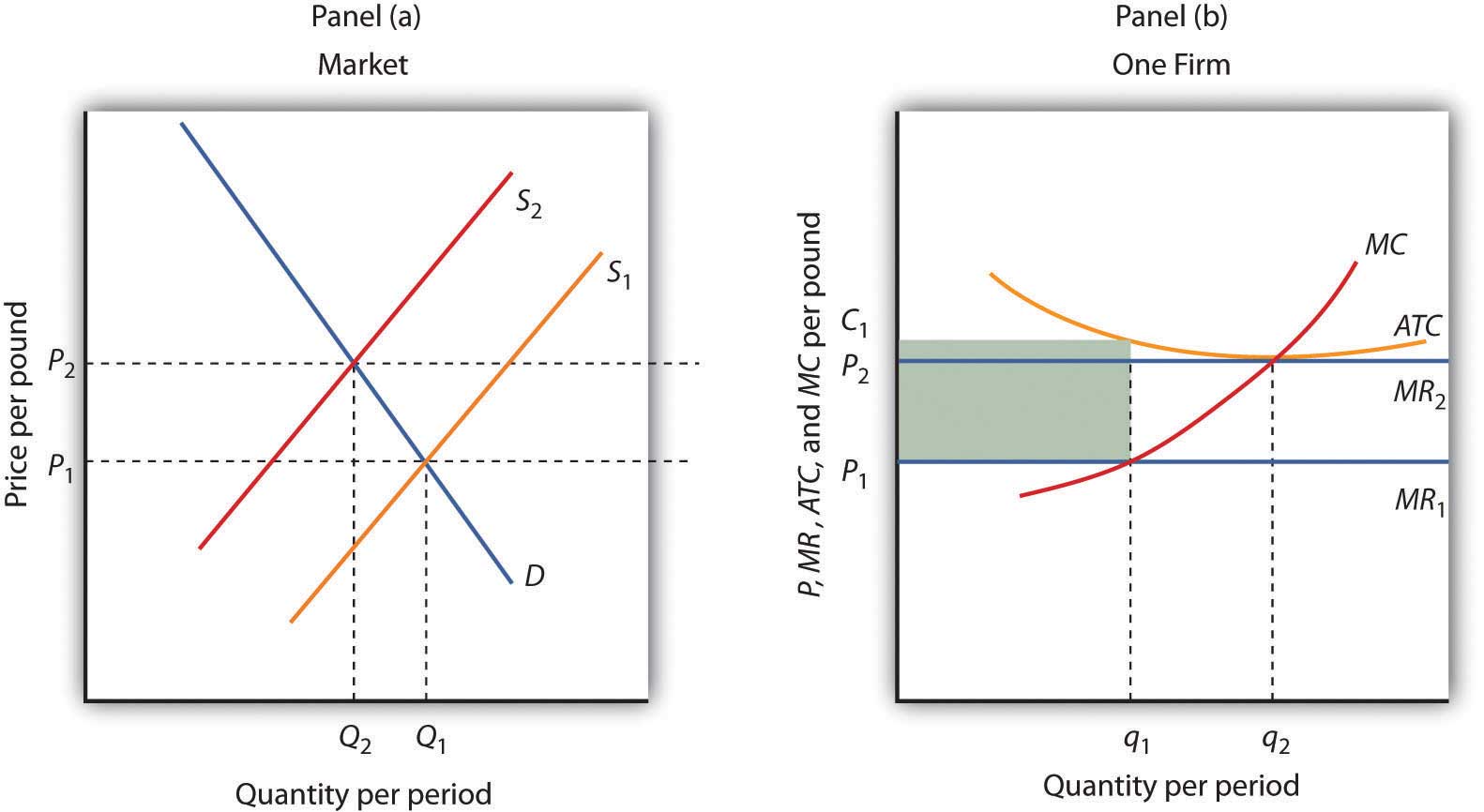
3.a. In process A, 1000 units of raw materials were introduced at the cost of Rs. 15,000. Direct wages amounted to Rs. 7,500 and manufacturing overheads to Rs. 5,000. 10% of the units trained are typically lost during manufacture, and these are sold @ Rs. 5 per unit. The actual output of the process was 940 units. Industry output is now 800 x q2. Now the price exceeds average total cost, so each firm is making a positive profit. Without restrictions on the market, this ... The EOQ formula is the square root of (2 x 1,000 pairs x $2 order cost) / ($5 holding cost) or 28.3 with rounding. The ideal order size to minimize costs and meet customer demand is slightly more ... Questions 6-7 refer to the graph below, which shows the cost curves for a profit-maximizing, ... (B) average total cost of producing Q1 units of output.13 pages
Deadweight Loss = .5 * ($2 - $1.50) * (7000 - 5000) Deadweight Loss = .5 * $.50 * 2000. Deadweight Loss = $500. Lesson Summary. Deadweight loss is defined as the loss to society that is caused by ...
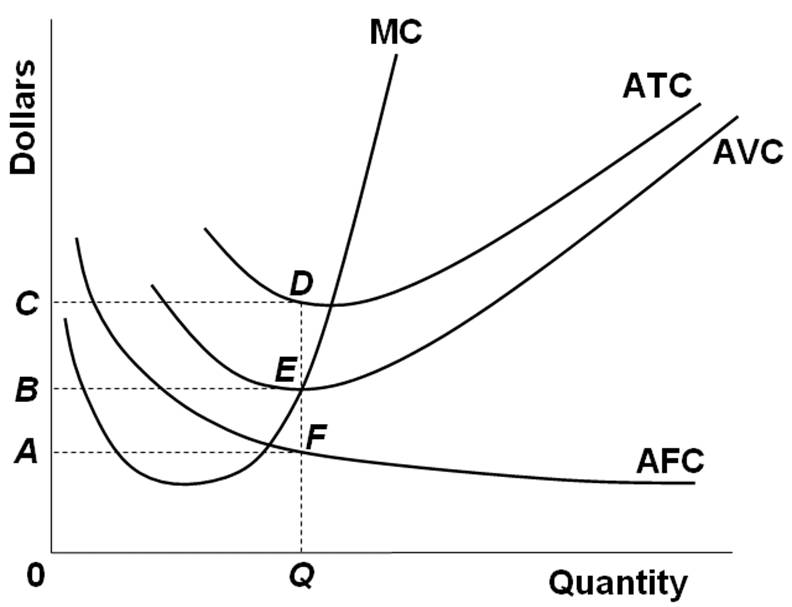
Of the $75 per unit, $55 goes for the costs of production, packaging, marketing, employee wages and benefits, and rent on a building. The economic profits of Harvey's firm in the first year were ...
If we decide to use a LEVEL production strategy to meet the average demand in the previous question, then the required quarterly output is a. 96,250 units b. 93,750 units c. 98,750 units d. 94,250 units
The output voltage of the device is linearly proportional to temperature (10 mV/°C) and has a DC offset of 500 mV. The offset allows reading negative temperatures without the need for a negative supply. The ideal output voltage of the LM50 or LM50-Q1 ranges from 100 mV to 1.75 V for a -40°C to 125°C temperature range. The LM50 and LM50-Q1 ...
Q2 Assume the ABC Inc. estimated a short-run average variable cost function for its product as: AVC = a + bQ + cQ2, using time-series data for 15 years where Q = number of units of output. The output obtained from the computer is below: DEPENDENT VARIABLE: AVC OBSERVATIONS: 15 R-SQUARE 0.4135 F-RATIO 4.230 P-VALUE ON F 0.040
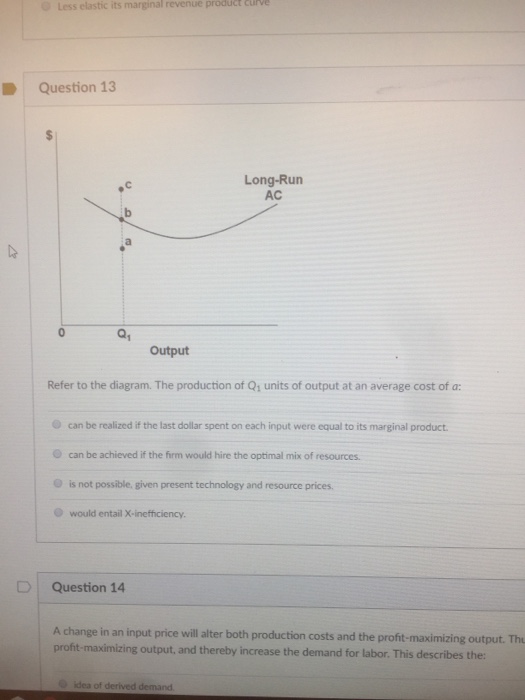
Economics questions and answers. Long-Run AC 0 Output Refer to the diagram. The production of units of output at an average cost of a Multiple Choice can be achieved if the firm would hire the optimal mix of resources. would entail X-inefficiency is not possible. given present technology and resource prices can be realized if the last dollar ...
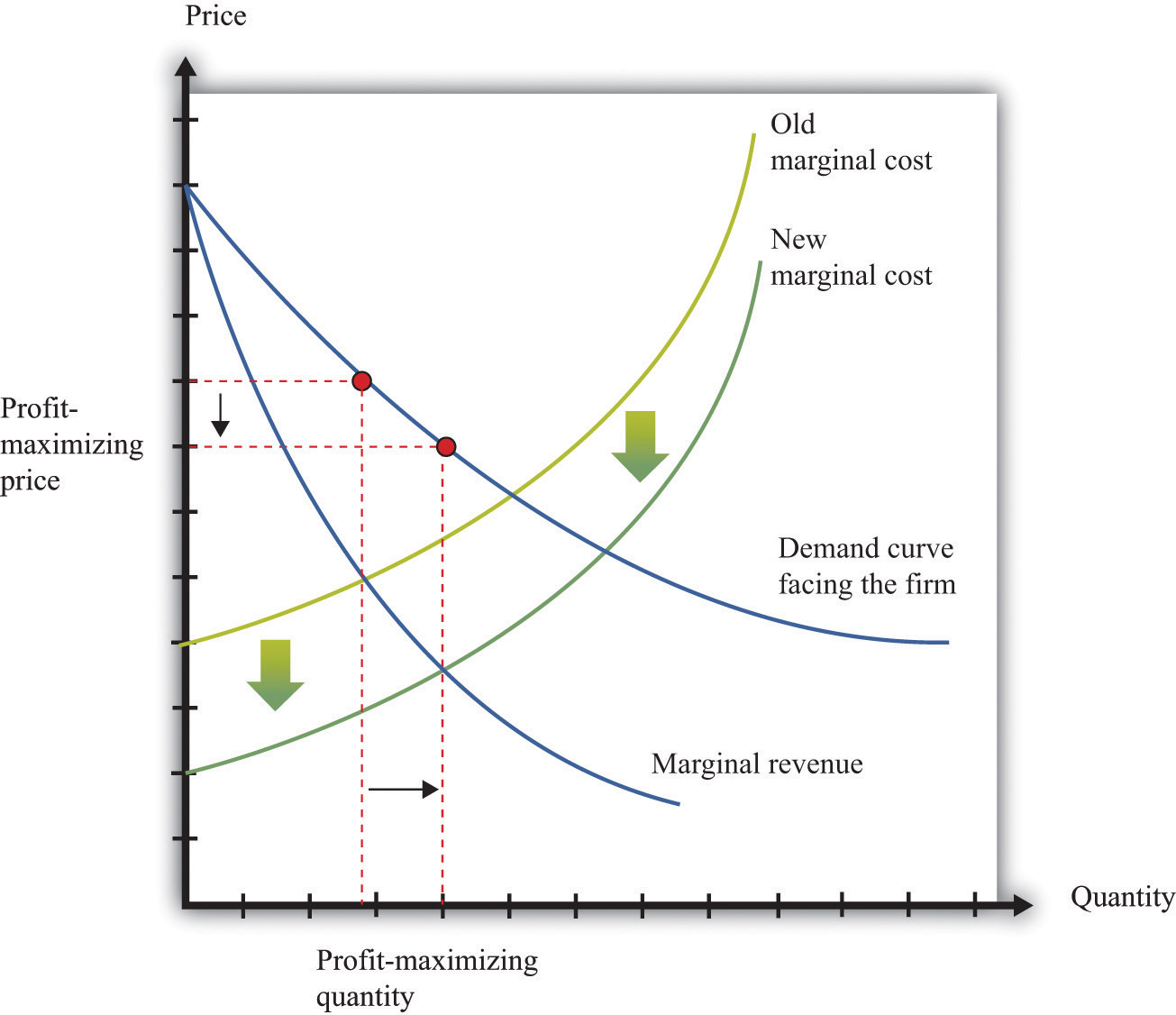
TR = 25Q - Q^2 T R = 25Q−Q2. The marginal cost (MC) function is: M C = 1 0 + 2 Q. MC = 10 + 2Q M C = 10+2Q. The marginal revenue (MR) is: M R = 3 0 − 2 Q. MR = 30 - 2Q M R = 30−2Q. The ...
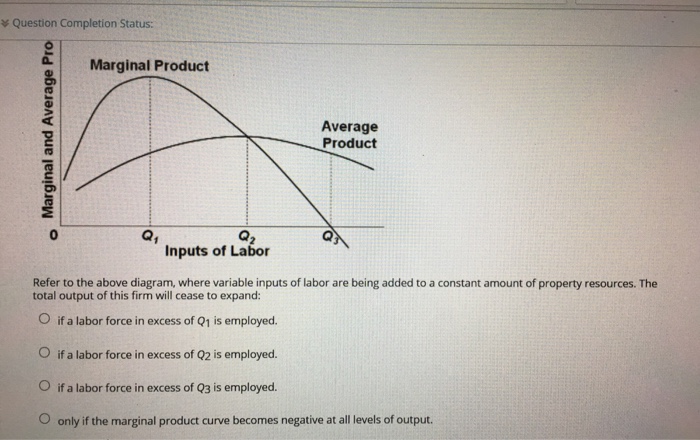
when marginal product lies above average product, average product is rising Suppose that a business incurred explicit costs of $1 million and implicit cost of $200,000 in a specific year. If the firm sold 4,000 units of its output at $300 per unit, its accounting profits were:
The unit price may be adjusted for marketing promotions. If any sales discounts or sales returns are anticipated, these items are also listed in the sales budget. It is extremely important to do the best possible job of forecasting, since the information in the sales budget is used by most of the other budgets (such as the production budget and ...
Productivity, in economics, measures output per unit of input, such as labor, capital, or any other resource. It is often calculated for the economy as a ratio of gross domestic product (GDP) to ...
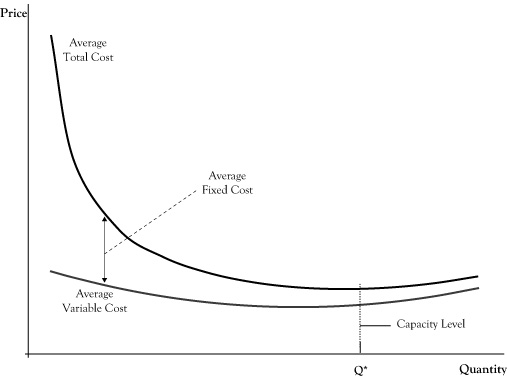
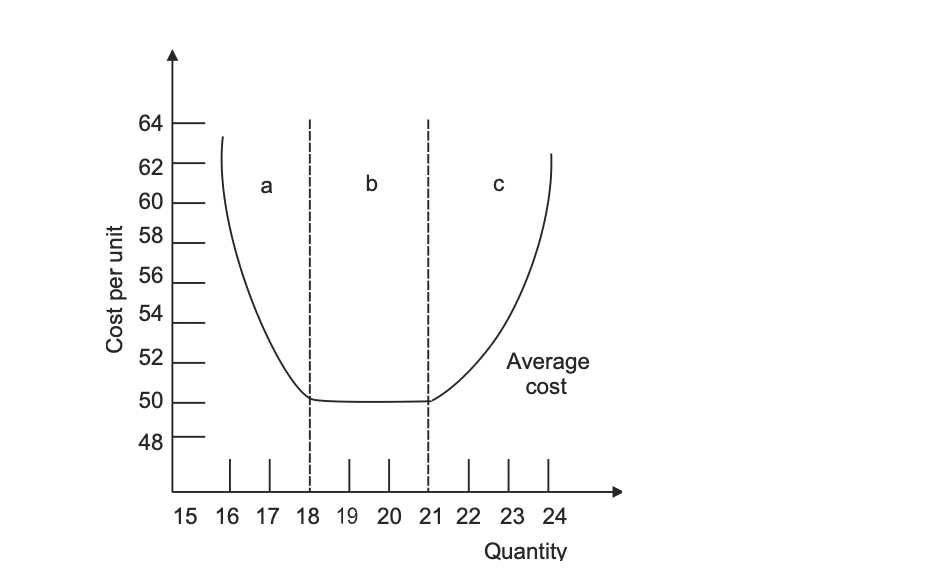
In economics charts, this has been illustrated with some flavor of a U-shaped curve, in which the average cost per unit falls and then rises. Costs rising as production volume grows is termed "dis ...
What is the average revenue the individual firm receives? ... b) Calculate the marginal cost of producing the first unit of output ... a. from Q1 to Qz.
Refer below for MCQ Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs with solutions. ... Marginal cost is the increase in total cost resulting from a unit increase in output. (e) Average total cost is total cost per unit of output. ... the long-run cost of producing a unit of output falls as the output increases (d) a firm's decision to hire ...
Refer to the diagram. The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of a Multiple Choice would entail X-inefficiency. can be achieved if the firm would hire the optimal mix of resources. can be realized if the last dollar spent on each input were equal to its marginal product. is not possible, given present technology and resource prices.
#14 Cost Per Lead. It is the average cost of generating a lead. Cost per lead = total cost/total leads #15 Cost Per Acquisition. It is the average cost of acquiring a customer or generating a conversion. Cost Per Acquisition = Total Cost/ Total acquisitions #16 Revenue Per Acquisition. It is the average revenue earned through an acquisition.
A firm is producing 20 units with an average total cost of $25 and ... Marginal cost is increasing for output greater than a certain quantity because of.
In sum, economies of scale refers to a situation where long run average cost decreases as the firm's output increases. One prominent example of economies of ...
Factors of production is an economic term that describes the inputs used in the production of goods or services to make an economic profit. These include any resource needed for the creation of a ...
At a specific point in production, the process starts to become less efficient. In other words, it starts to cost more to produce an additional unit of output. In economic jargon, diseconomies of scale occur when average unit costs start to increase. For example, the graph below illustrates that at a point Q1, average costs start to increase.
391. The total cost at 10 units of output is ₹ 55. The fixed cost is ₹ 5. The average variable cost at 10 units of output is-(a) ₹ 25 (b) ₹ 6 (c) ₹ 5 (d) ₹ 1. 392. The total cost of producing 5 units of a commodity is ? 20 and that of producing 4 units is? 15, what will be the marginal cost? (a) ₹ 2.5 (b) ₹ 5 (c) ₹ 7.5 (d ...
141. Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q1 at an average total cost of ATC1, then the firm is: A) producing the potentially profit-maximizing output, but is failing to minimize production costs. B) incurring X-inefficiency, but is realizing all existing economies of scale.
Refer to the diagram. If actual production and consumption occur at Q3, A) efficiency is achieved. ... At output level Q1, in this diagram, A) resources are ...
If the values of a and b are known, the demand for a commodity at any given price can be computed using the equation given above. For example, let us assume a = 50, b = 2.5, and P x = 10: Demand function is: D x = 50 - 2.5 (P x) Therefore, D x = 50 - 2.5 (10) or D x = 25 units. The demand schedule for the above function is given in Table.
SQL employee Database [115 Exercise with Solution] [An editor is available at the bottom of the page to write and execute the scripts.Structure of employee Database: 1. From the following table return complete information about the employees.
9) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q1 A) marginal cost is falling. B) average total cost is falling. C) average variable cost is less than average fixed cost. D) marginal cost is less than average total cost. E) all of the above 10) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q2 A) average fixed cost is increasing.
Economic growth is the increase in the value of an economy's goods and services over time. Real gross domestic product is the best way to measure economic growth, because it removes the effects of inflation. The government stimulates growth with expansive fiscal policy by spending more or cutting taxes.
8.5 / 10 average quality score from customers. What advantages do you get from our Achiever Papers' services? All our academic papers are written from scratch. All our clients are privileged to have all their academic papers written from scratch. These papers are also written according to your lecturer’s instructions and thus minimizing any ...
Refer to the above graph. Under purely competitive conditions in this labor market, the equilibrium wage rate will be: a. W1 and Q1 workers will be hired b. W2 and Q2 workers will be hired c. W2 and Q1 workers will be hired dW3 and Q1 workers will be hired
firm may or may not be maximizing profits. Refer to the above diagram. The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of c: ...



















0 Response to "44 refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a"
Post a Comment