45 fe2+ orbital diagram
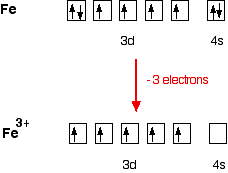
Answer (1 of 12): The configuration of neutral Fe atom is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁶ 4s² where 4s electrons are the most energetic ones, therefore they are the first ones to be removed when atom is ionized. Thus, configuration of Fe⁺ cation is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁶ 4s¹ and of Fe²⁺ cation is... Orbital Splitting and Electron Spin The position of the metal in the periodic table Second and third transition series form low-spin more easily than metals form the first transition series-The greater overlap between the larger 4d and 5d orbitals and the ligand orbitals-A decreased pairing energy due to the larger volume available for electrons
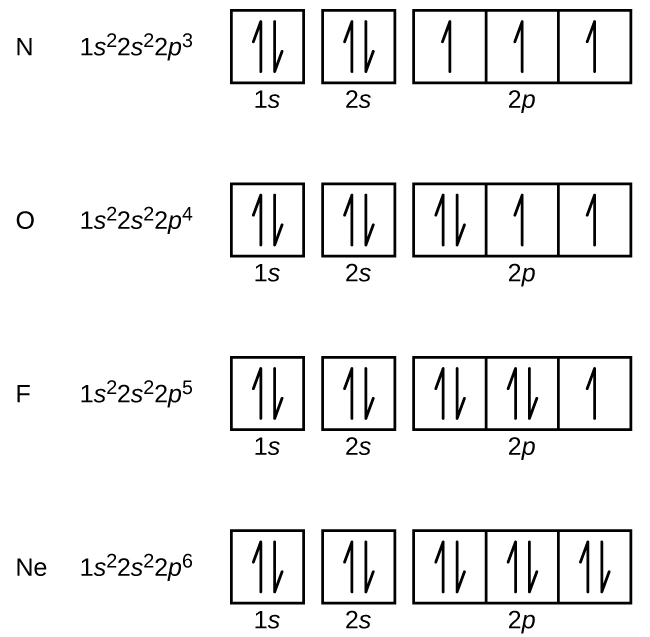
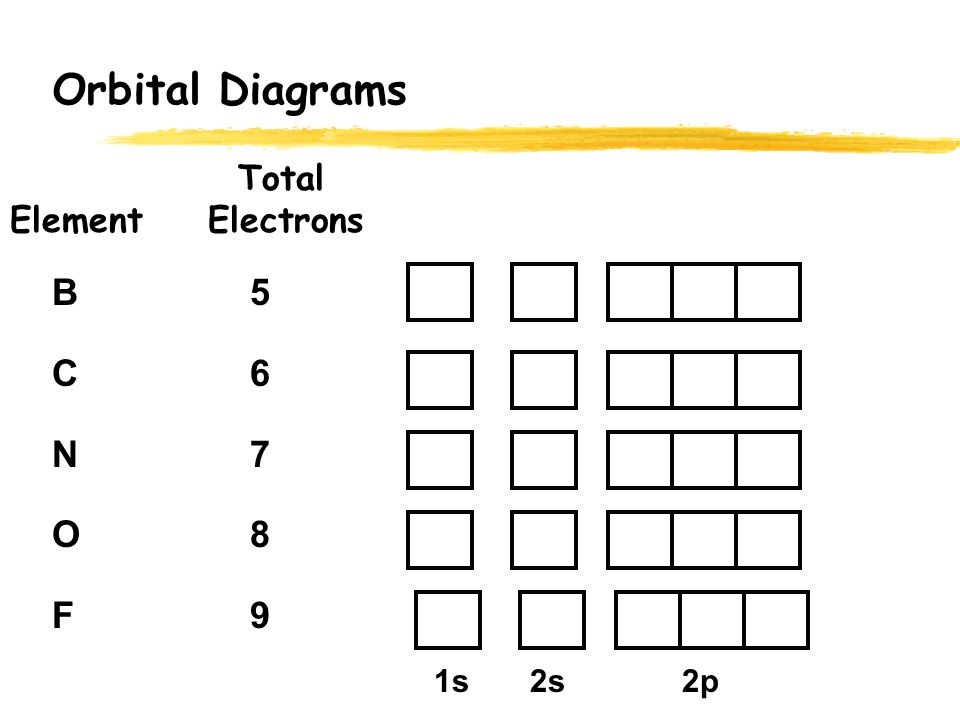
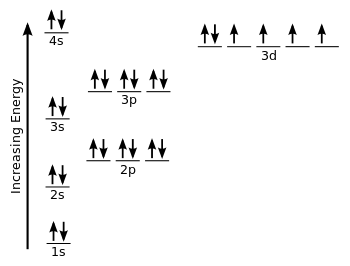
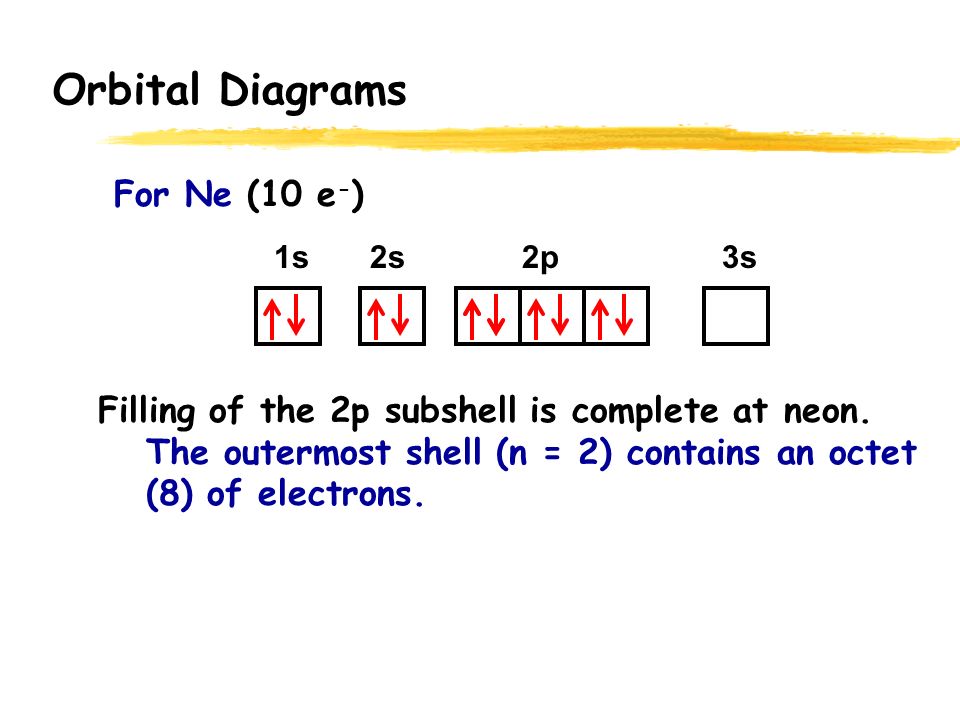
Orbital Diagram 1s ↿⇂ 2s ↿⇂ 2p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 3s ↿⇂ 3p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 3d ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 4s ↿⇂ 4p ↿⇂ ↿⇂ ↿⇂ 4d ↿ ↿ 4f 5s ↿⇂ 5p 5d 5f: ... Fe2+ is easy to oxidize to Fe3+ because ions with an odd charge are most stable for atoms with an even atomic number.
Fe2+ orbital diagram
This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. What is the correct orbital diagram for Fe2+? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Previous question Next question. By Hund's rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s2 2s2 2p2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c. Experimentally, it is found that the ground state of a neutral carbon atom does indeed contain two unpaired electrons. Which of the following has maximum number of unpaired electrons fe3+ Fe2+ Co2+ Co3 ... Sep 03, 2021 · The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. How many d electrons are there in fe2+? The number of d-electrons retained in Fe2+ (At. number of Fe=26) ions is 6 or 4?? 6 d-electrons are retained in Fe2 +.
Fe2+ orbital diagram. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.electron configuration for Fe2+ - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITYMolecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia Electron Configuration for Fe, Fe2+, and Fe3+ (Iron and Iron Ions) In writing the electron configuration for Iron the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Iron go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. Jan 27, 2022 · Atomic Orbital Diagram for Iron(Fe) Iron ion(Fe 2+,Fe 3+) electron configuration. Ground state electron configuration of iron(Fe) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6 4s 2.The electron configuration shows that the last shell of iron has two electrons and the d-orbital has a total of six electrons. In this work, spin-unrestricted molecular orbital calculations on (FeMnO10) clusters are used to study the nature of magnetic exchange and electron delocalization (charge transfer) associated with Fe3+-Mn2+, Fe3+-Mn3+, and Fe2+-Mn3+ interactions in oxides and silicates. Molecular orbital (SCF-X-α-SW) theory of Fe 2+- Mn 3+, Fe 3+- Mn 2+, and ...
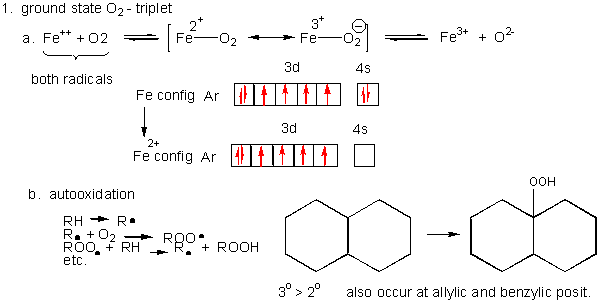
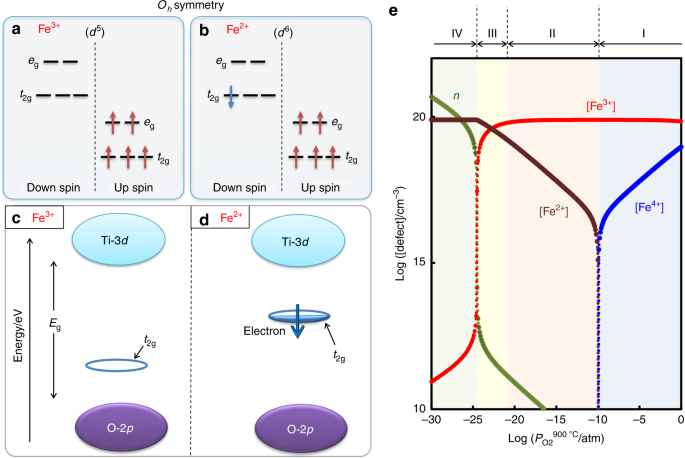
The Fe2* t^v) orbitals and the S2" v* orbitals are filled. Electron transfer can only occur from a v* orbital (HOMO) ofSj-, the bridging ligand, to a partially filled ti^ie) orbital (LUMO) ofFe3"^ from the aquo complex (Fig. 2). The Fe3* reduces to Fe24- (d6, tige} ion). Fig.2. Molecular orbital diagram for the Fe3*Mn2*O,o clus-ter in the (a) ferromagnetic and (b) antiferromagnetic configu-rations. Orbitals indicated with a dashed line are unoccupied. Note that the orbital energies correspond to "orbital electronega-tivities" (Slater, 1974). The energy differences between orbitals Nov 09, 2018 · The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. You're removing 2 electrons from it to generate the Fe2+ ion, which are removed from the 4s orbital first (this is always the case in transition chemistry - as far as. The electron configuration for Fe2+ will be 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d4 there is a special stabilty needed to balance the number of electrons in the 3d orbital. The relevant degrees of freedom are the spins S = 2 and the threefold orbital degeneracy of Fe2+ ions. W sites are integrated out by means of a fourth-order perturbative expansion. The magnetically and orbitally ordered ground states of the effective Hamiltonian are discussed as a function of the model parameters.
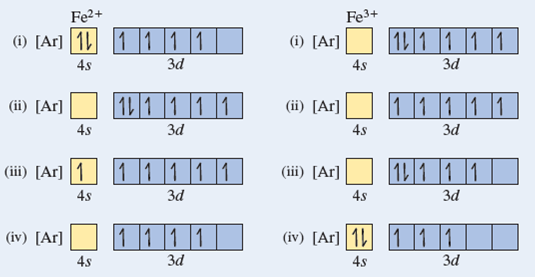
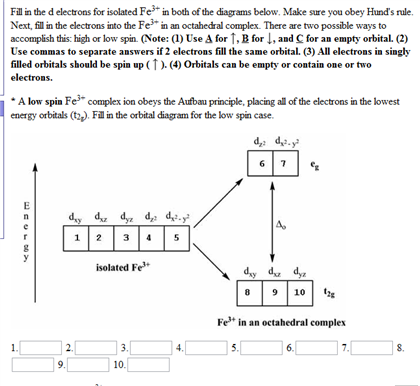
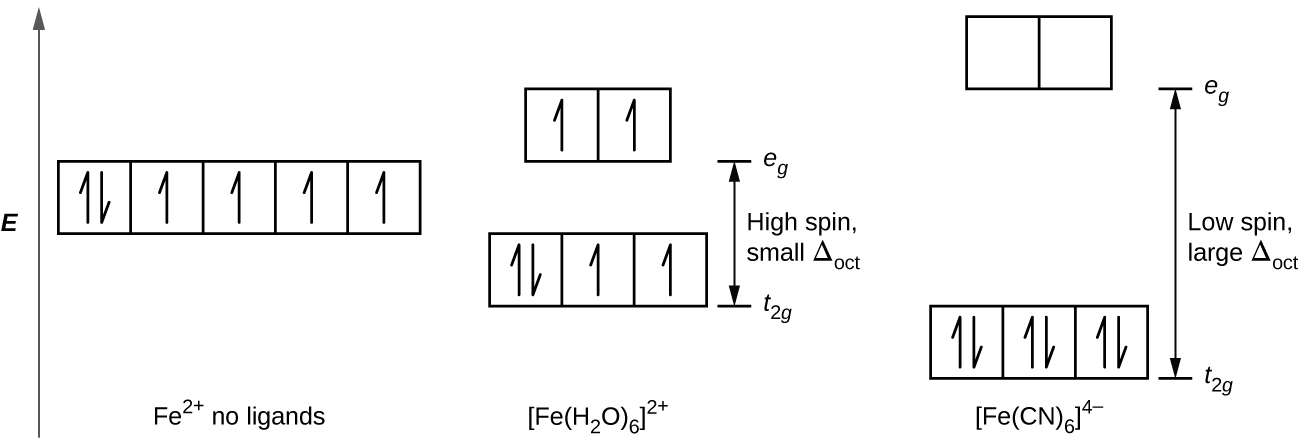
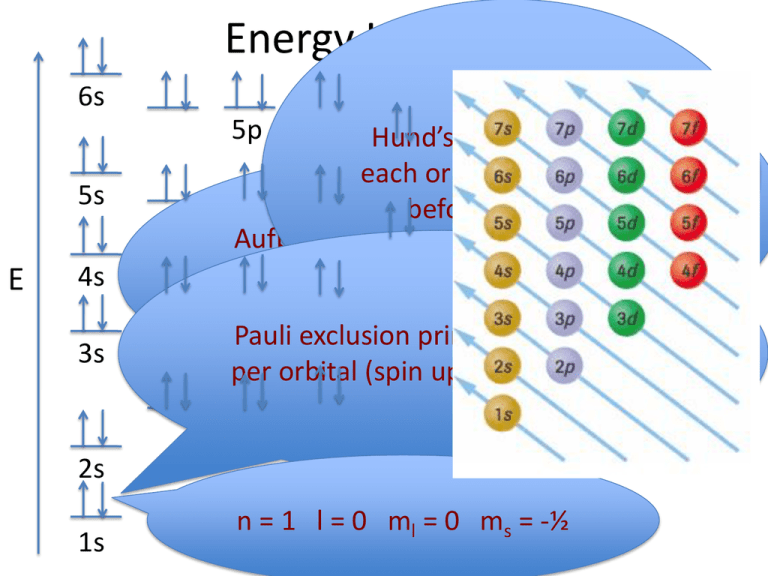
electrons into the same orbital •Πeis a stabilizing energy for electron exchange associated with two degenerate electrons having parallel spin total 3 e 0 c eg* t2g d4HS eg* t2g d8 eg* t2g d6LS total 7 e 3 c total 6 e 3 c LFSE 3 0.4 O 10.6 O 0.6 O LFSE 6 0.4 O 20.6 O What is the correct orbital diagram for fe2+? Starts here3:18Electron Configuration of Fe2+ and Fe3+ - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clip60 second suggested clipNumber you're going to remove 4s electrons before you remove 3d electrons because 4 is bigger than 3MoreNumber you're going to remove 4s electrons before ... For example, iron (1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6 4s 2) forms the ion Fe2+ (1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6) by the loss of the 4s electron and the ion Fe3+ (1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 5) by the loss of the 4s electron and one of the 3d electrons. Although the d orbitals of the transition elements are—according to the Aufbau principle—the ... Feb 08, 2014 · What is the orbital diagram for FE? Electrons & Oxidation. Oxidation States. +3,2. Electrons Per Shell. 2 8 14 2. Electron Configuration. [Ar] 4s2 3d6. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6.
The electron configuration for Fe2+ is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6The electron configuration for Fe3+ is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5Ask me questions: http://www.chem...
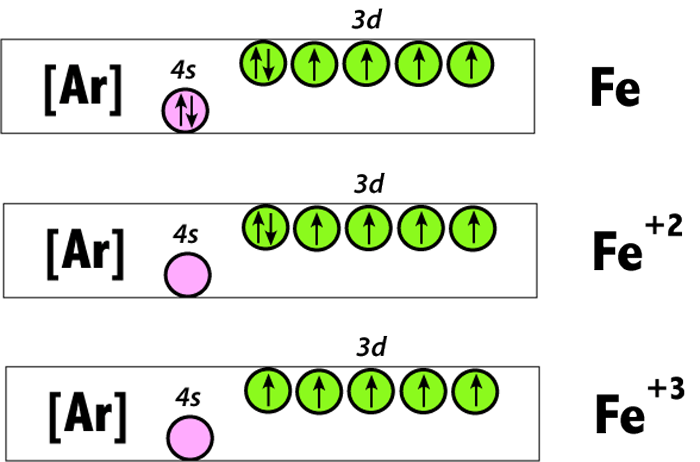
Hello! So the electron configuration for Fe is [Ar] 3d^6 4s^2. Fe^2+ means that 2 electrons are taken away. You start removing e- from the outermost shell. The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. So removing 2 electrons would leave you with the electron configuration of [Ar] 3d^6. Hope this helps! Top DAllaf Posts: 20
Atomic Orbital Diagram for Iron(Fe) Iron ion(Fe 2+,Fe 3+) electron configuration. Ground state electron configuration of iron(Fe) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6 4s 2. The electron configuration shows that the last shell of iron has two electrons and the d-orbital has a total of six electrons. In this case, the valence electrons of iron are eight. There are two types of iron ions.
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...
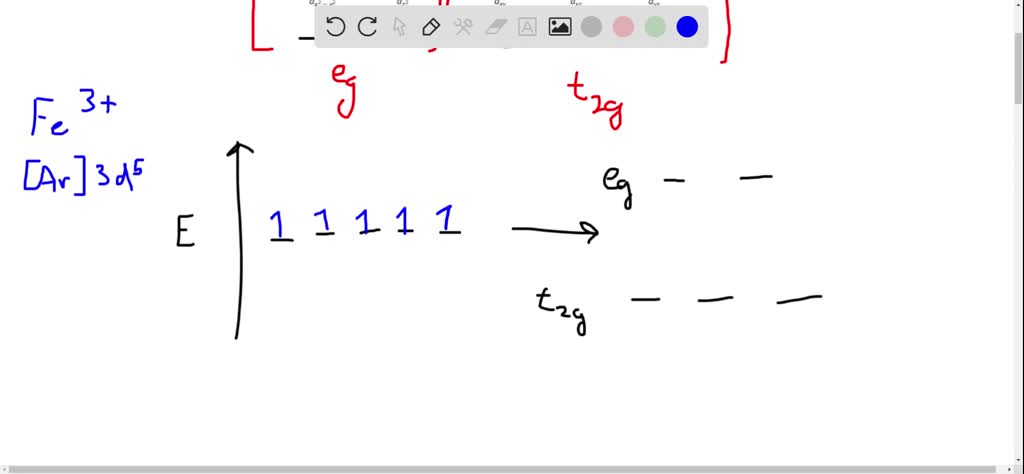
Transition Fe3+ ions and draw the orbital box diagrams for both ions. Using this. There for 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 is the electronic configration for Fe3+. half of electrons (there must be one electron in each orbital, and d has 5 orbitals). That's for filling up orbitals for ground state atoms.
The 3d_(xy) orbital of "Fe" does not match up with any of "O" atom's atomic orbital symmetries, so it is nonbonding. The 4s and 3d_(x^2 - y^2) are mostly nonbonding, because the 2p_z orbital has already been used, and no other orbitals on "O" that are of that symmetry are available to pair up with these orbitals on "Fe".
Paramagnetic. Iron metal has 2 lone electrons. Iron (II) Usually, paramagnetic. However because there are an even number of electrons in Fe 2+, it is possible that all of the electrons could end up paired in certain situations (see explanation below). Iron (III) Paramagnetic (1 lone electron). Salt. Diamagnetic.
This orbital is formed from Fe 3d and CO π* orbitals, and one can see that it corresponds to the $\mathrm{2e''}$ orbitals in the MO diagram provided by NotEvans. The article then goes on to provide a qualitative MO diagram for the complex, using Hoffmann's earlier approach 2 which invokes the isolobal analogy.
Draw an orbital diagram for the Zn2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ ions in the presence of solvent molecules. Use up and down arrows to represent the spin of electrons. Only two electrons can occupy a single box. Fill the lower three boxes before filling the upper two and make sure to follow Hund's rule as you fill the orbitals with electrons.
ASK AN EXPERT. Science Chemistry Q&A Library What is the electron configuration and orbital diagram of: (a) Na+ (b) P3- (c) Al2+ (d) Fe2+ (e) Sm3+.
Sep 03, 2021 · The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. How many d electrons are there in fe2+? The number of d-electrons retained in Fe2+ (At. number of Fe=26) ions is 6 or 4?? 6 d-electrons are retained in Fe2 +.
By Hund's rule, the electron configuration of carbon, which is 1s2 2s2 2p2, is understood to correspond to the orbital diagram shown in c. Experimentally, it is found that the ground state of a neutral carbon atom does indeed contain two unpaired electrons. Which of the following has maximum number of unpaired electrons fe3+ Fe2+ Co2+ Co3 ...
This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. What is the correct orbital diagram for Fe2+? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Previous question Next question.













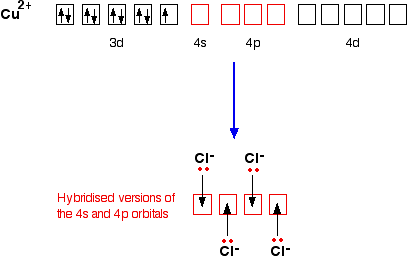



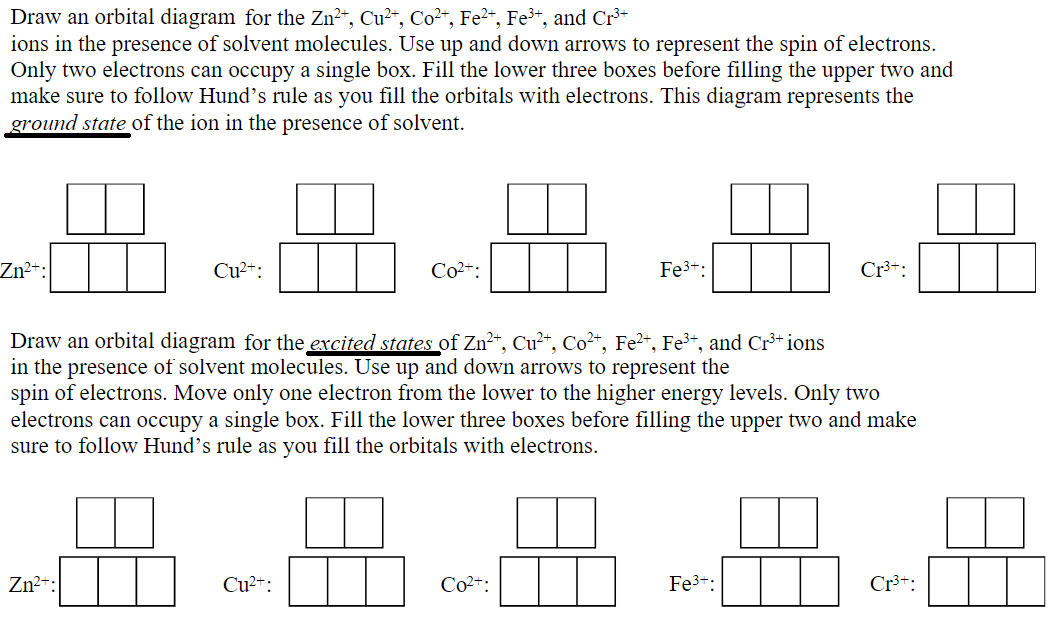
![PDF] Mixed Orbital Ground States of Fe2+ in Prussian Blues ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/6866326fea903c0c4e01beaaf74ab78cf1b82215/7-Figure5-1.png)
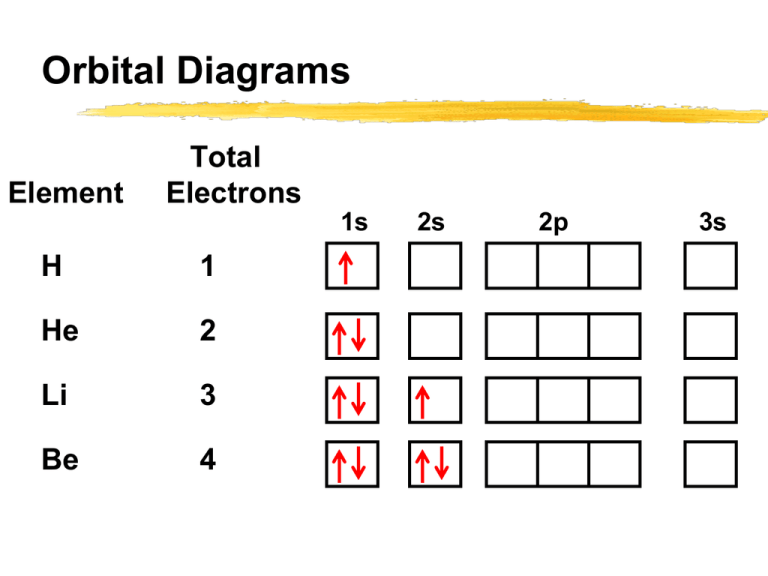
0 Response to "45 fe2+ orbital diagram"
Post a Comment