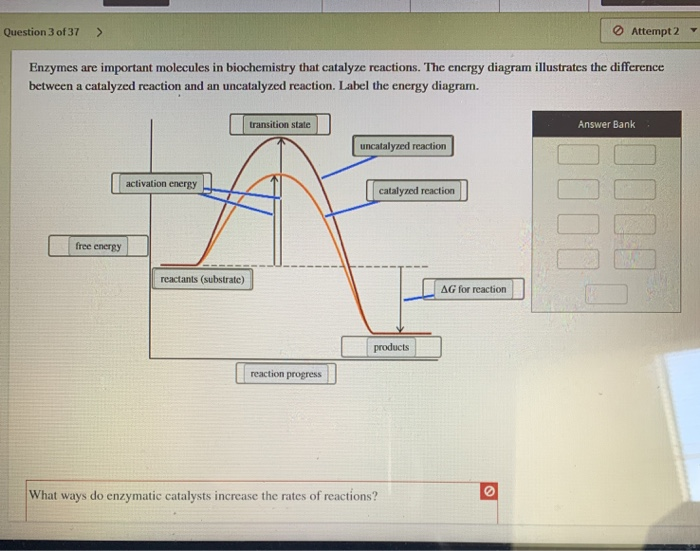
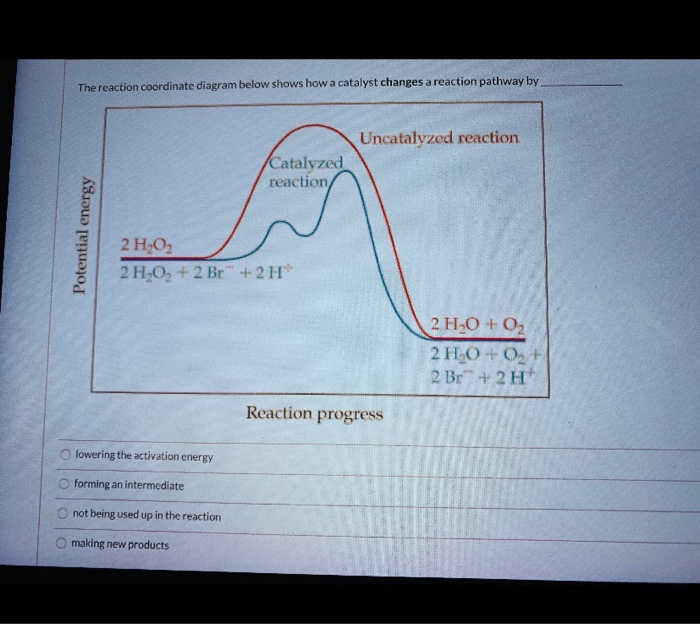
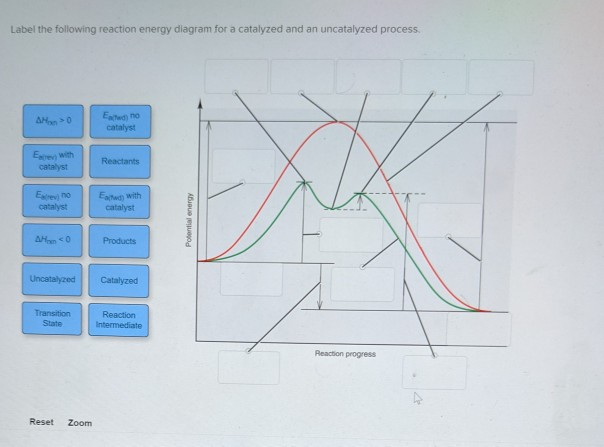
41 label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the reactant species to which the enzyme binds is called the substrate. The substrate is then converted into products by a series of steps. The lock-and-key model explains the steps involved in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Label the following diagram that illustrates the lock-and-key model of enzyme activity. Draw a reaction energy diagram for this reaction, postulate a transition state, and calculate Ea(rev). reverse reactions. A catalyzed reaction yields the products more quickly, but does not yield more product than the Reaction energy diagram of a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process.
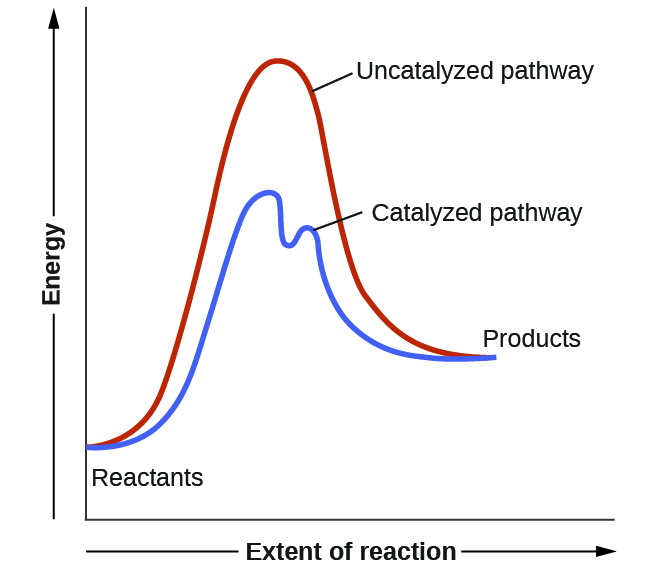
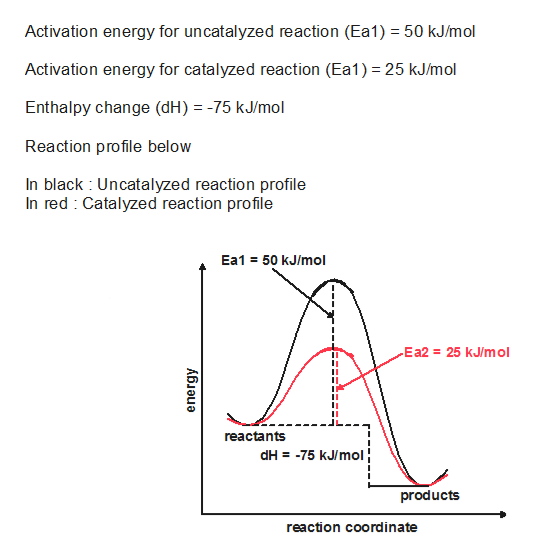
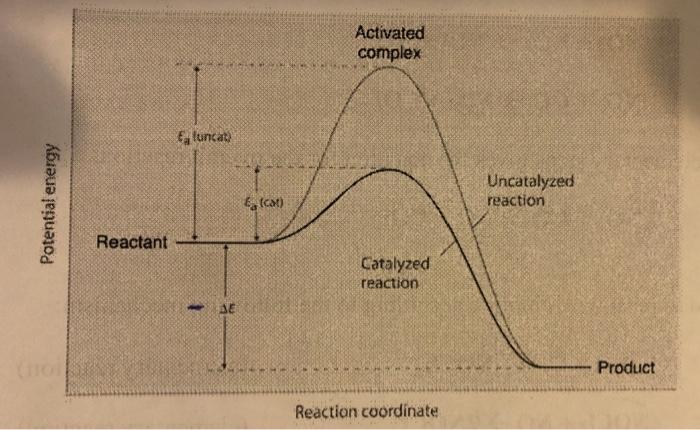
A catalyst speeds up the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy; in addition, the catalyst is regenerated in the process. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed hydrogenation of a simple hydrocarbon molecule...
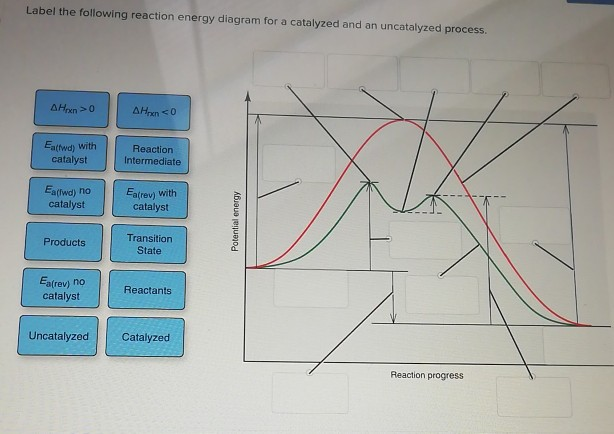
Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
The first energy-generating steps in glycolysis begin when glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate undergoes an energetically favorable reaction in which it is simultaneously oxidized and phosphorylated by the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, with the accompanying conversion of NAD+ to NADH. The activation energy is higher for a noncatalyzed reaction (a) than for the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme (b). Both reactions proceed through one Figure 5.8 An energy diagram for a typical, enzyme-catalyzed biological reaction (blue curve) versus an uncatalyzed laboratory reaction (red... Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. We offer assignment help in more than 80 courses. We are also able to handle any complex paper in any course as we have employed professional writers who are specialized in different fields of study. From their experience, they are able to work on the most difficult assignments. The following are some of the course we offer assignment help in ... 400 ( KD ) 300 200 Progress of the reaction Which of. Solved by Expert Tutors. Subscribe to unlock. 28. Figure 16.23 - Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed (green) and uncatalyzed (red) process. 40. Sample Problem 16.2 Determining Reaction Order from Rate Laws PROBLEM: For each of the following reactions, determine the reaction order with respect to each reactant and the... Cold fusion is a hypothesized type of nuclear reaction that would occur at, or near, room temperature.It would contrast starkly with the "hot" fusion that is known to take place naturally within stars and artificially in hydrogen bombs and prototype fusion reactors under immense pressure and at temperatures of millions of degrees, and be distinguished from muon …
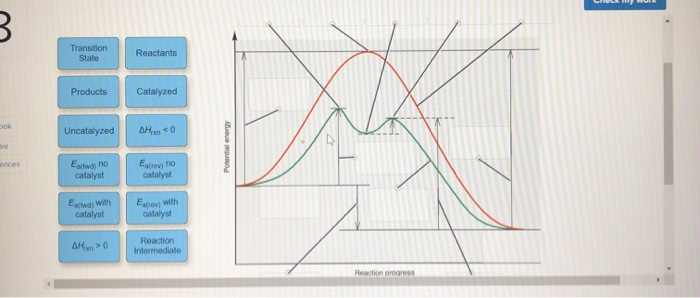
› Get more: Catalyzed reaction exampleShow All. Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction. The equation for the uncatalyzed reaction is. 2 H 2 O 2 (l) 2 H 2 O (l) + O 2 (g) Sketch a possible graph for this reaction, first without a catalyst and then with a catalyst. acid catalyzed... Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows. This problem has been solved. B the s where v0 vmax. The mechanism may be different for a catalyzed reaction reaction vs Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Draw and label a reaction coordinate diagram for an uncatalyzed reaction s p and the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme e. Chapter 13 Rates Of Reaction. Solvent Effects In Acid Catalyzed Dehydration Of The Diels Alder. What Is The Activation Energy For A Reverse Reaction... ...Products Catalyzed Ea(fwd) no catalyst Uncatalyzed AHxn 0 Reaction Intermediate Reaction progress AHrxn > 0 Ea(rev) stb catalyst. H rxn <0 because in this potential energy diagram energy of the product is less thant that of reactants. Which means there is a decrease in total enthalpy of the...
Need patience. Remain calm. Just fly the plane 🛫 Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Precious metals such as platinum and palladium can greatly increase the Consider the following energy diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. How many transition states are involved? Lower the free energy of activation to a value below that of the uncatalyzed reaction. A reaction intermediate b e a step 2 c reacta... A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. The two reaction diagrams below represent the same reaction: one without a catalyst and one with a catalyst.
We always make sure that writers follow all your instructions precisely. You can choose your academic level: high school, college/university, master's or pHD, and we will assign you a writer who can satisfactorily meet your professor's expectations.
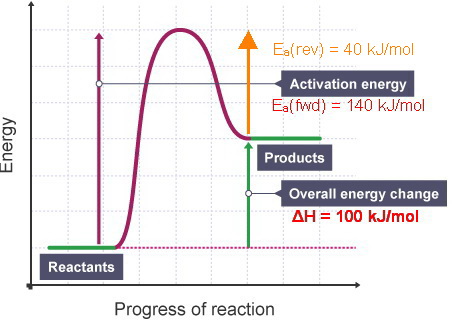
In a chemical reaction, the minimum energy necessary for reaching the activated complex and proceeding Figure 14.14 Potential Energy Diagram of the Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions that Convert The following reaction between methane, CH4 (the primary component of natural gas)
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
44 Reaction energy diagram of a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Generic graph indicates the effect of a catalyst in an hypothetical exothermic 47 Determining Molecularity and Rate Laws for Elementary Steps PROBLEM: The following two reactions are proposed as elementary steps in the...
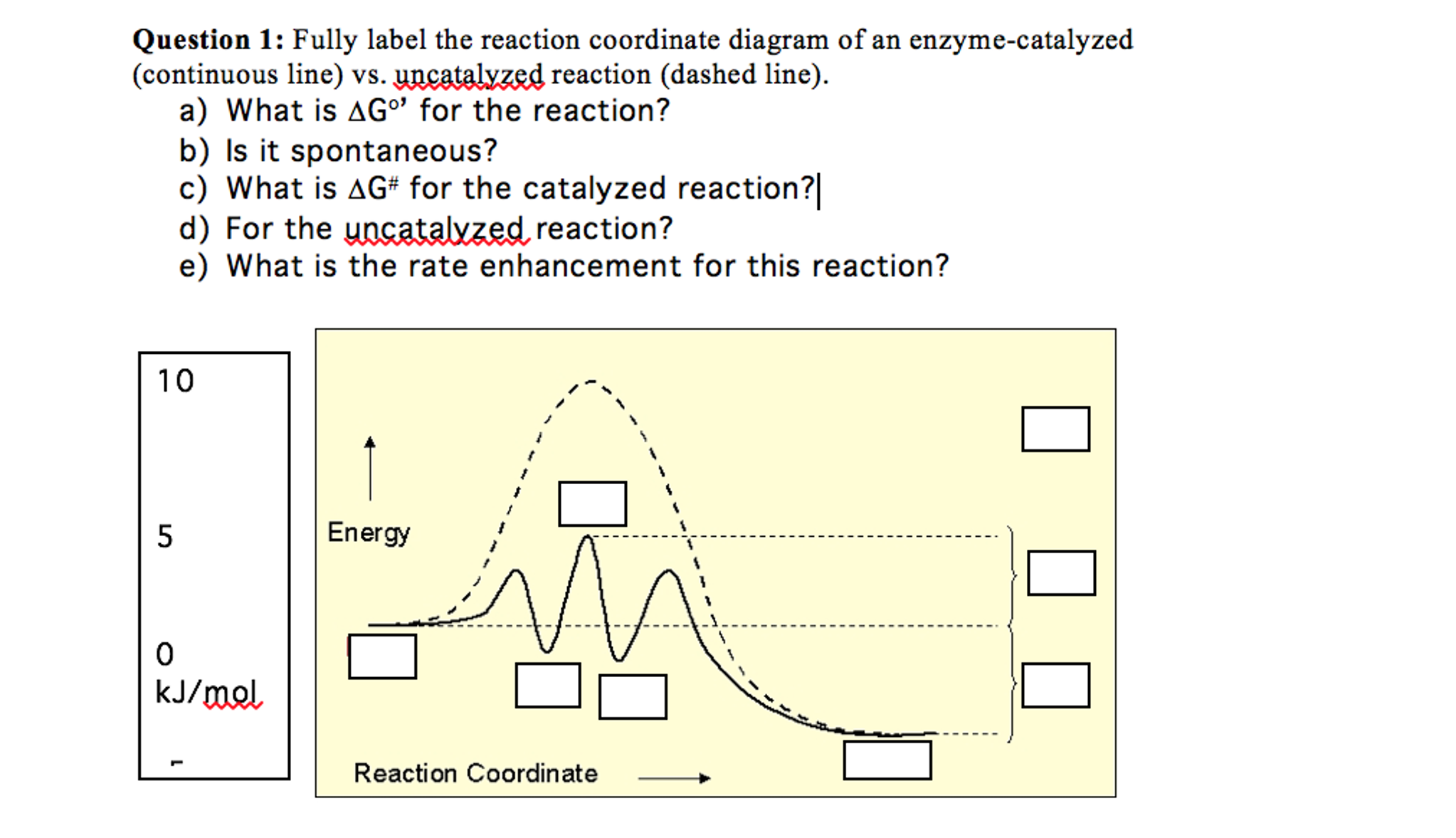
Energy reaction progress which curve represents the catalyzed reaction. O blue top o green bottom transition state reactants products note that a transition state One point is earned for an uncatalyzed reaction curve that must show that e a 0 and δh 0. The vertical y axis is energy. Answer to label this...
• a catalyst accelerates a reaction without being consumed. • the rate of catalysis is given by the turnover • catalysis accelerates a reaction by stabilising a TS relative to the ground state - free energy of • catalyst forms a covalent intermediate that reacts faster than uncatalysed reaction
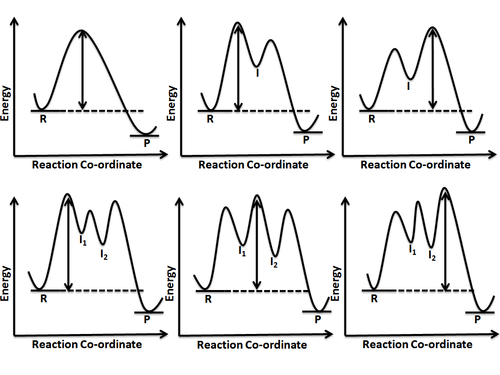
question 100 deals with being able to draw a reaction. Coordinate diagram simply from information that is provided. It asks you to draw on eggs. Problem 67 Easy Difficulty. OBJECTIVE. Draw energy-level diagrams for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. A catalyst decreases the...
Consider the following reaction. The aqueous solution with the highest ph is. Enzyme Body Used Water Process Life Plants Ch...
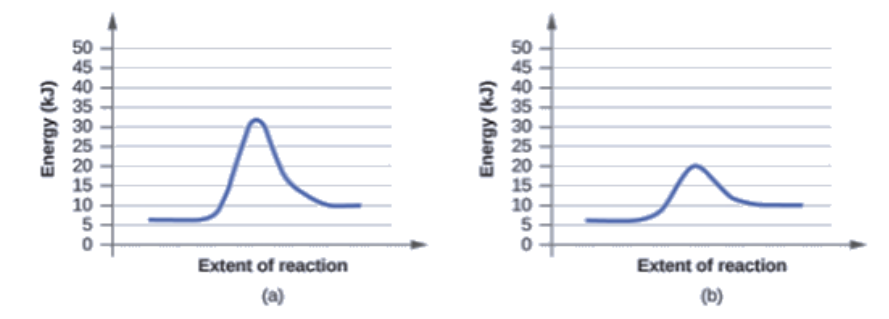
Catalysts are substances that increase the reaction rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. This graph compares potential energy diagrams for a single-step reaction in the presence and absence of a catalyst.
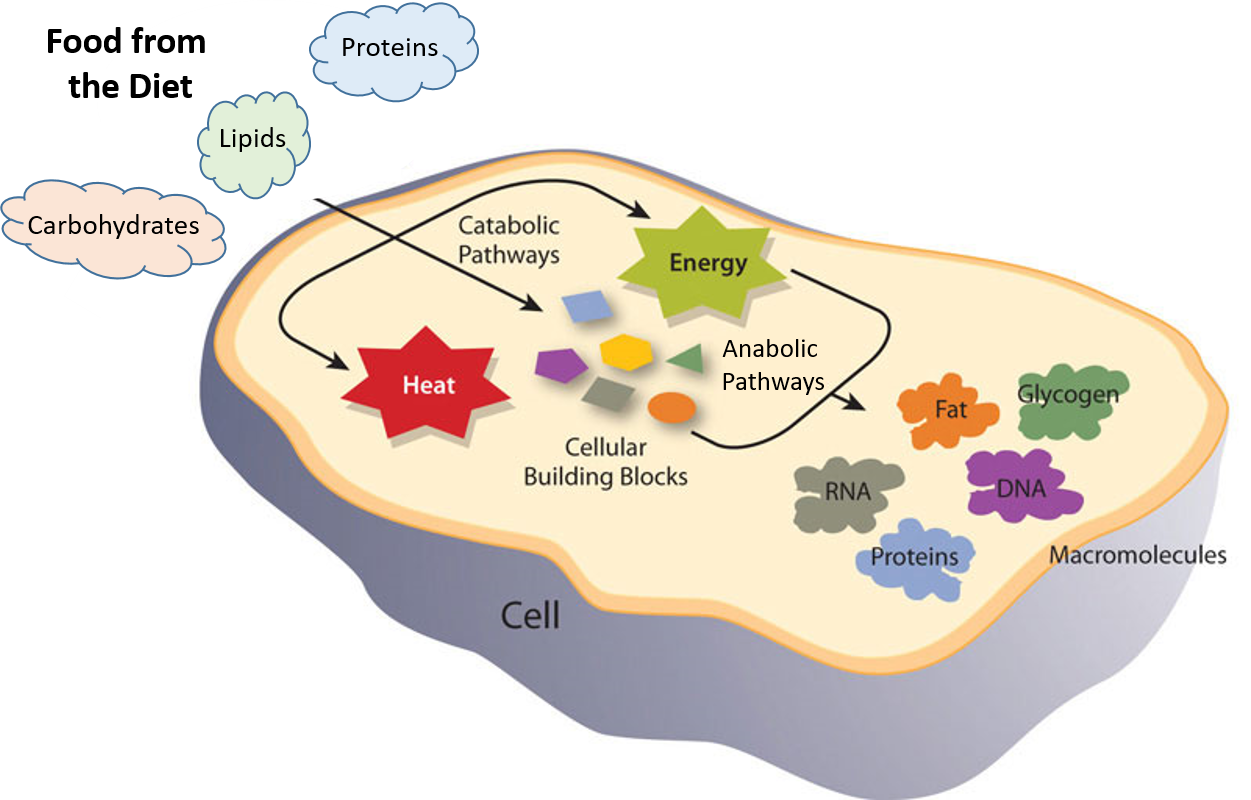
Energy Generation in Mitochondria and Chloroplasts 455 Cells Obtain Most of Their Energy by a Membrane-based Mechanism 456 Chemiosmotic Coupling Is an Ancient Process, Preserved in Present-Day Cells 457 MITOCHONDRIA AND OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION 459 Mitochondria Are Dynamic in Structure, Location, and Number 459 A Mitochondrion Contains …
Analyzing the potential energy diagram of a regular/uncatalyzed and a catalyzed (adding a catalyst) reaction. Remember that the ... Definition of a catalyst; accelerated reactions that are not catalyzed. Catalyzed versus uncatalyzed mechanisms.
[herman.pontzer@duke.edu](mailto:herman.pontzer@duke.edu) \-> Email! [https://twitter.com/HermanPontzer/status/1453058319619264514](https://twitter.com/HermanPontzer/status/1453058319619264514)
Jan 10, 2022 · Protein‒polymer interactions are fundamental to biomaterial design, yet few techniques can elucidate these interactions at the atomic scale. Herein we introduce Direct Saturation COmpensated (DISCO) transfer NMR, a saturation transfer-based technique refined specifically for macromolecular systems. Using DISCO, we probe mucin‒polymer interactions …
Catalysed reactions lower the activation energy - the hump that needs to be overcome for the reaction to proceed. So: relatively speaking, an uncatalysed reaction will have a high hump or peak; a catalysed reaction will have a lower hump.
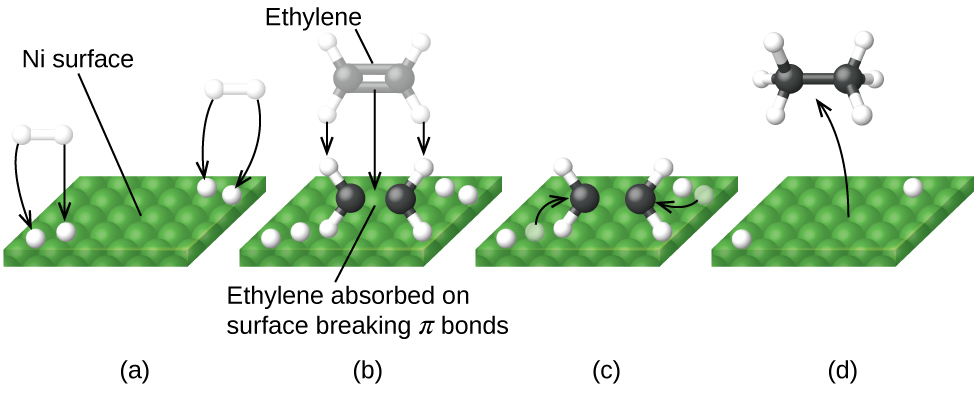
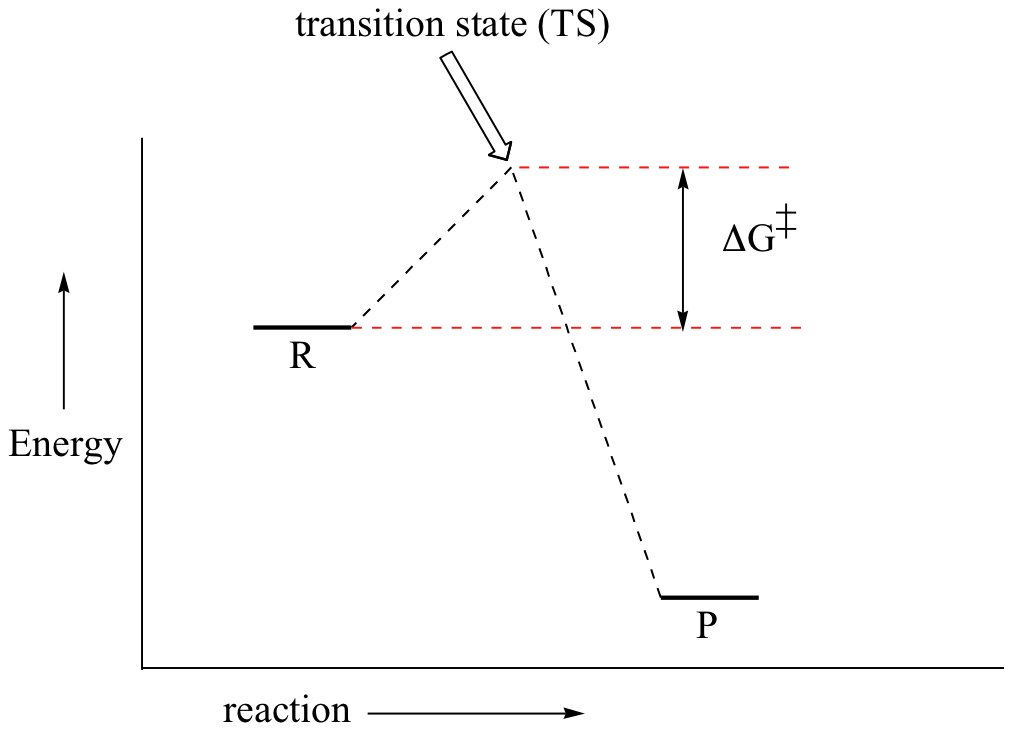
Draw a reaction energy diagram for this reaction, postulate a transition state, and calculate Ea(rev). Consider the relationships among the reactants, products Reaction energy diagram of a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process The metal-catalyzed hydrogenation of ethylene H2C CH2 (g) + H2 (g)...
Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows. Click card to see the definition. Enzymes are important molecules in biochemistry that catalyze reactions. Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference between a catalyzed reaction and an uncatalyzed reaction.
Category: Label Templates Show details. Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction This process is called catalysis. A catalyst is not consumed by the reaction and it may participate in Energy Diagrams for Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions. Models of Enzyme-Substrate...
Potential Energy Diagram: Labels and Meaning. 11:05. 1 192 просмотра • 29 мар. 2020 г. • Analyzing the potential energy diagram of a regular/uncatalyzed and a catalyzed (adding a catalyst) reaction.
Reaction Diagram for a Catalyzed and an Uncatalyzed Reaction. Notice that the only effect of the catalyst is the decrease in the energies of activation, Ea, for both the forward and reverse reactions. The presence of the catalyst has no impact on the free energies of the reactants or the products or...
A catalyst is a substance which speeds up a reaction, but is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction. When the reaction has finished, you would have exactly the same mass of catalyst as Nitration of benzene. concentrated sulphuric acid. Manufacture of ammonia by the Haber Process.
Thus, enzymes not only increase the rate of a chemical reaction, but also do so in a highly specific manner through specific interactions between the enzyme and the uncatalyzed reactant(s) for the reaction. catalyzed Activation energy Activation energy 0 Reactant DG Product Course of Reaction 36 MHR • Unit 1 Biochemistry
Transcribed image text: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Transition State Transition State Transition intermediate Reaction Intermediate Transition State Transition Uncatalyzed Transition State Reactants Products Catalyzed Ea(fwd)...
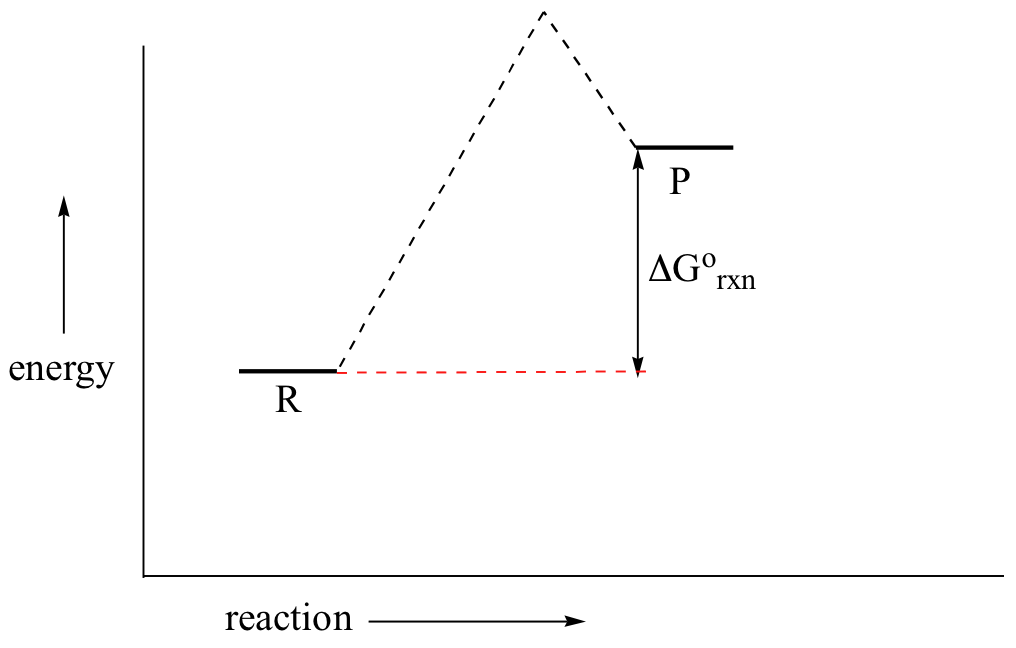
Reaction profiles for uncatalysed reactions and catalysed reactions are compared and explained. These revision notes on reaction profiles of chemical reactions, activation energies and effects of a Energy level diagram for an endothermic chemical reaction without showing the activation energy.
Question: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Sep 24, 2018 · diagrams for a catalyzed reaction (blue line) and its corresponding uncatalyzed reaction (red line). The Gibbs free energy difference of the products and reactants is...
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
The activation energy is higher for a noncatalyzed reaction (a) than for the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme (b). Both reactions proceed through one Figure 5.8 An energy diagram for a typical, enzyme-catalyzed biological reaction (blue curve) versus an uncatalyzed laboratory reaction (red...
The first energy-generating steps in glycolysis begin when glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate undergoes an energetically favorable reaction in which it is simultaneously oxidized and phosphorylated by the enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, with the accompanying conversion of NAD+ to NADH.












0 Response to "41 label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process"
Post a Comment