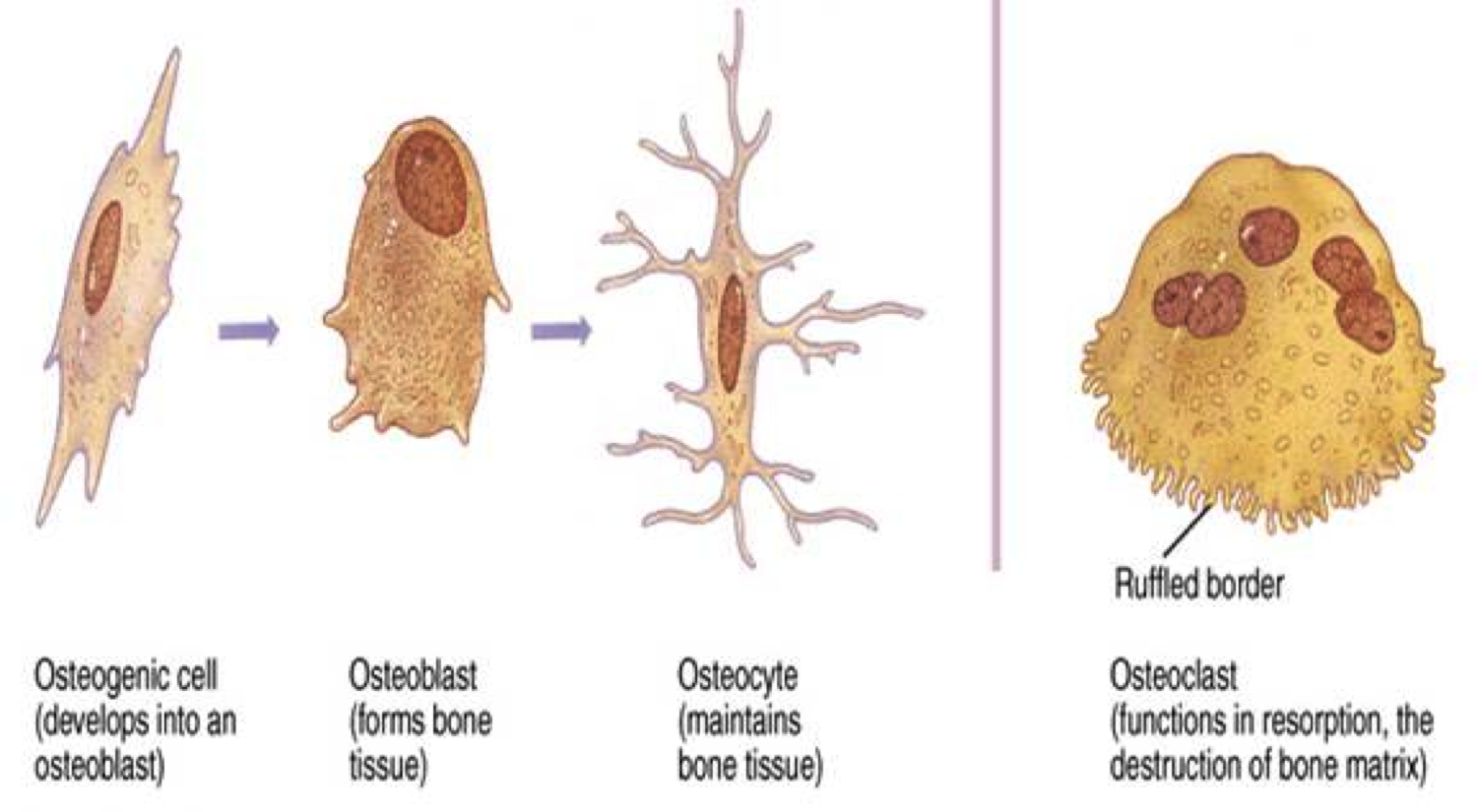
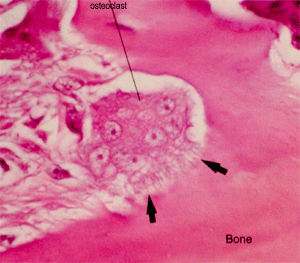
41 which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast?
Osteoclast precursors are cells of hematopoietic origin [141] that differentiate into osteoclasts in response to different transcription factors such as NF-kB and NFATc1 (Nuclear Factor of ... Free access to latest which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast news. Echemi provides a lot of different insights into which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast. Page 2
Further cellular studies show an increase of osteoclast (OC) differentiation in cocultures of bone marrow macrophages/monocytes (BMMs) and OBs after treatment with the conditioned medium (CM) from ...
Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast?
Apr 12, 2019 · Osteoblasts are made from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) along with muscle cells (myocytes) and fat cells (adipocytes). Osteoblasts work together in the form of clusters and perform their function of building up the bone. Once the cluster of osteoblasts finishes its work, the shape of osteoblasts gets flattened. Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? D. Which hormone is the MOST important for Ca2+ regulation? ... estrogen; osteoclast activity. If collagen is removed from bone, what happens to the bone? Choose the best answer. The bone becomes stiff and brittle. Related questions. There are three types of bone cells present in human body: 1. Osteoblast 2. Osteocyte 3. Osteoclast. Bone Cell # 1. Osteoblast: This is concerned with bone formation and is found in the growing surface where the bony matrix is deposited. This cell is strongly basophilic and cuboidal or pyramidal in shape and its nucleus is large with a ...
Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast?. 17-02-2017 · In the alimentary and respiratory systems (and likely in other mucosae), the surface of an epithelial cell located above its junctional complexes and exposed to the lumen is called the apical domain, whereas the surface below junctional complexes on the sides and base make up the basolateral domain (Fig. 4-10). 24-01-2022 · 36. Fu YT, et al. Porous gelatin/tricalcium phosphate/genipin composites containing lumbrokinase for bone repair. Bone. 2015 Sep;78:15-22. 37. Fu YT, et al. Earthworm (Pheretima aspergillum) extract stimulates osteoblast activity and inhibits osteoclast differentiation. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Nov 11;14:440. 38. ... to remove bacteria and damaged cells. 4) Osteoclasts migrate in to remove dead bone matrix. ... Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? What type of bone cell starts forming the bone matrix? Image: B. D. Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? Image: D.
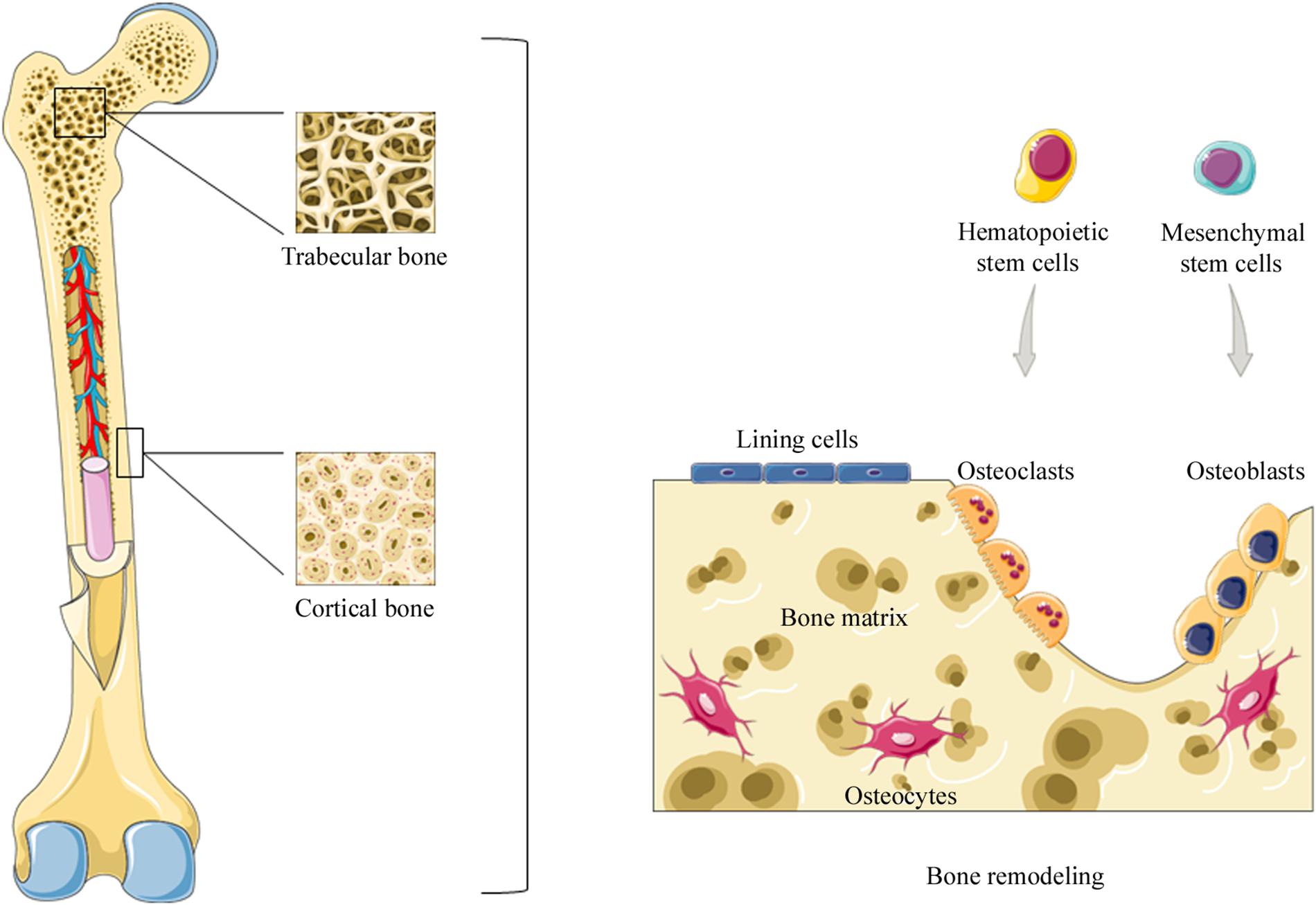
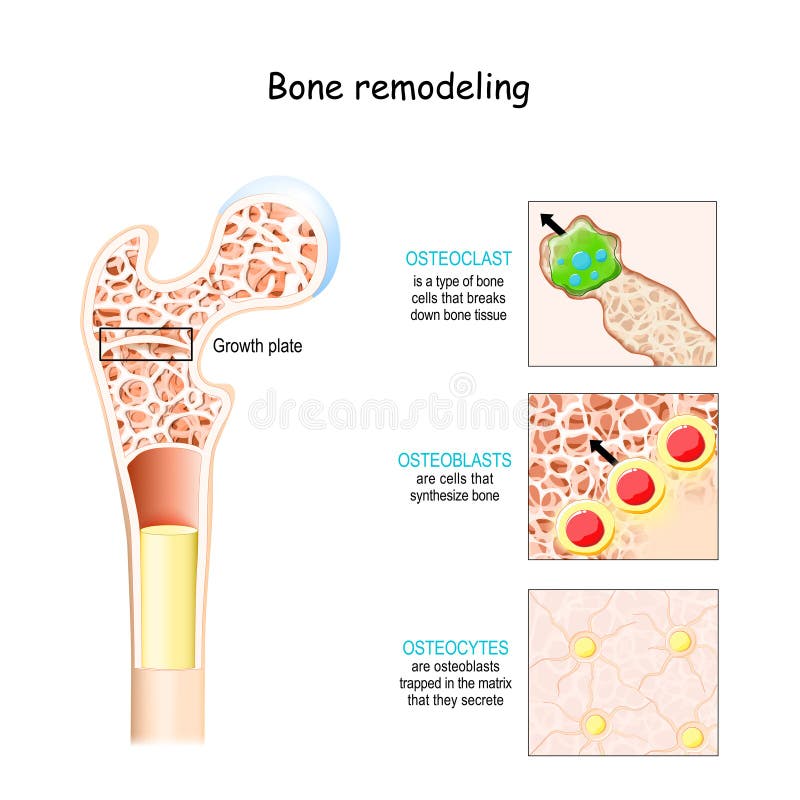
Bone cell origins. This diagram summarizes the origins and fates of the bone cells. Mesenchymal refers to cells which were deep within the embryo during early development; some of them remain in the bone marrow but do not form blood cells. The hematopoietic cells form the liquid part of the bone marrow, and some of them circulate with the blood. Being a derivative of LNCaP with its ability to metastasize to bone, LNCaP C4-2B is a PCa cell line that can induce bone lesions with mixed osteoblastic and osteolytic function. 23,24 PC3 is a ... osteoclasts and osteoblasts will be working on the same tunnel simultaneously. - it involves bone ... Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? Osteoclasts are bone-resorbing cells that play important roles in bone remodeling and metabolism 13.
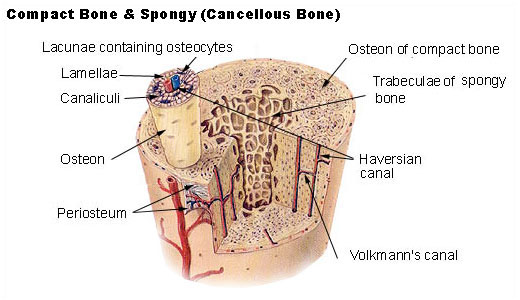
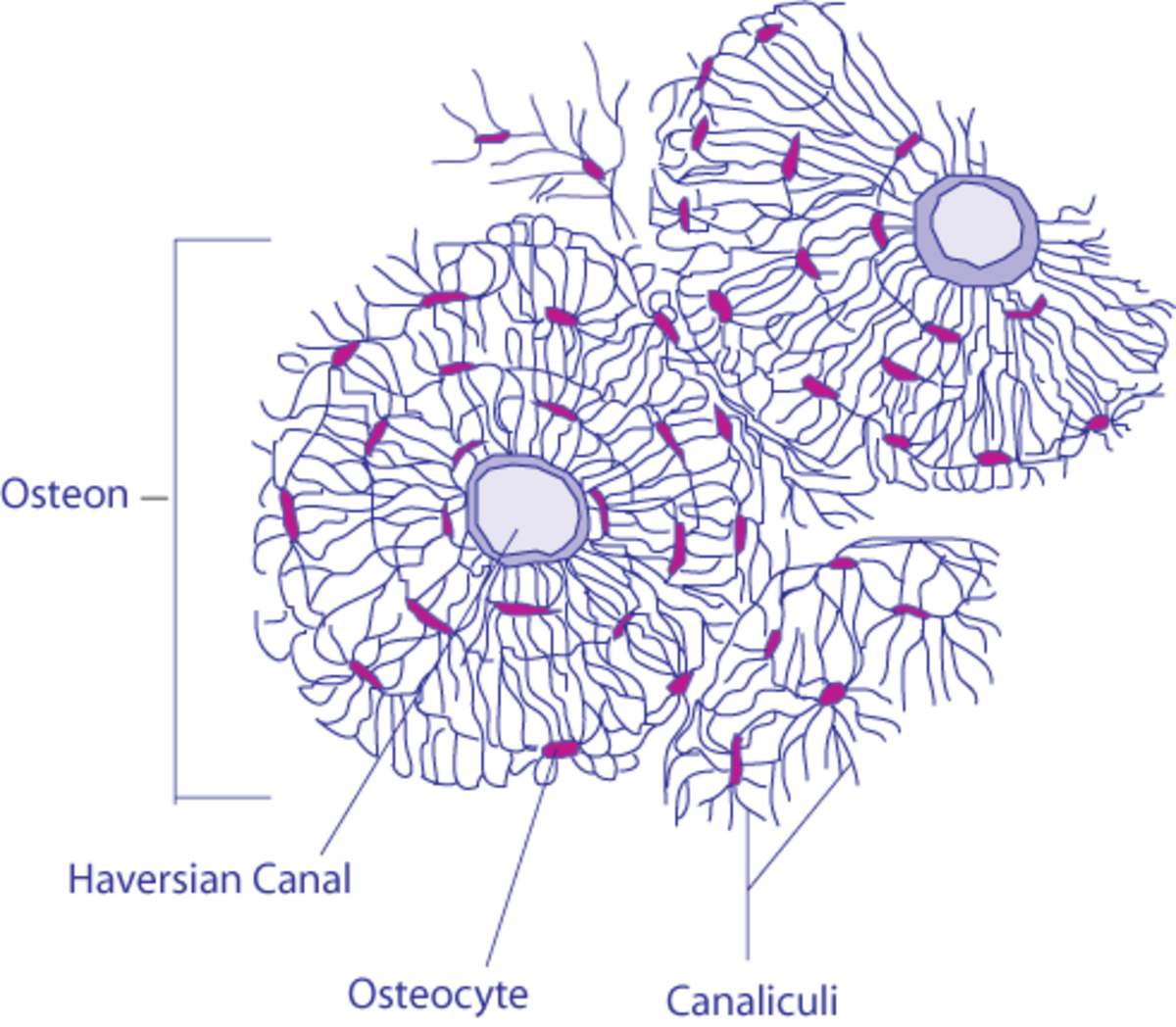
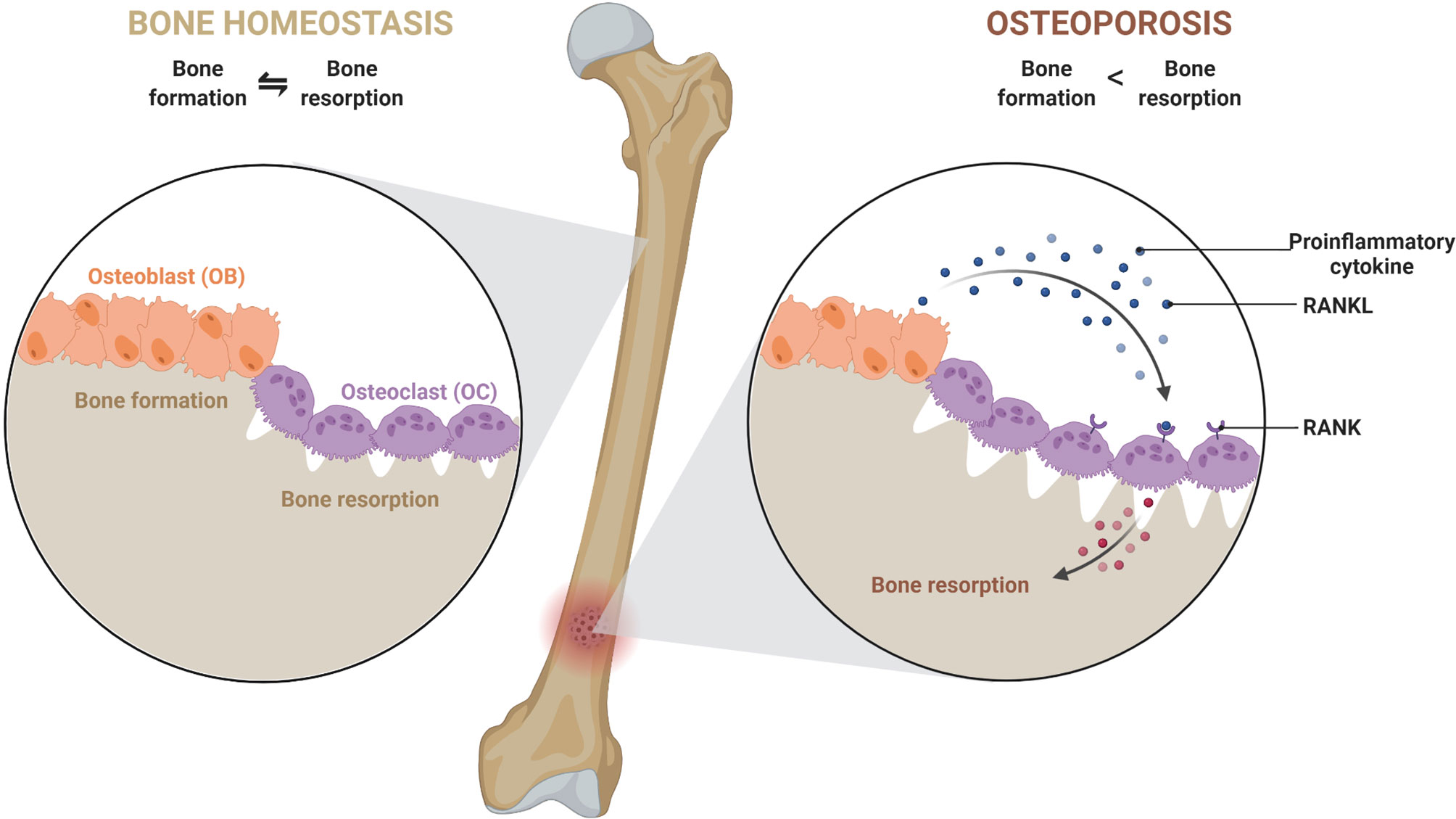
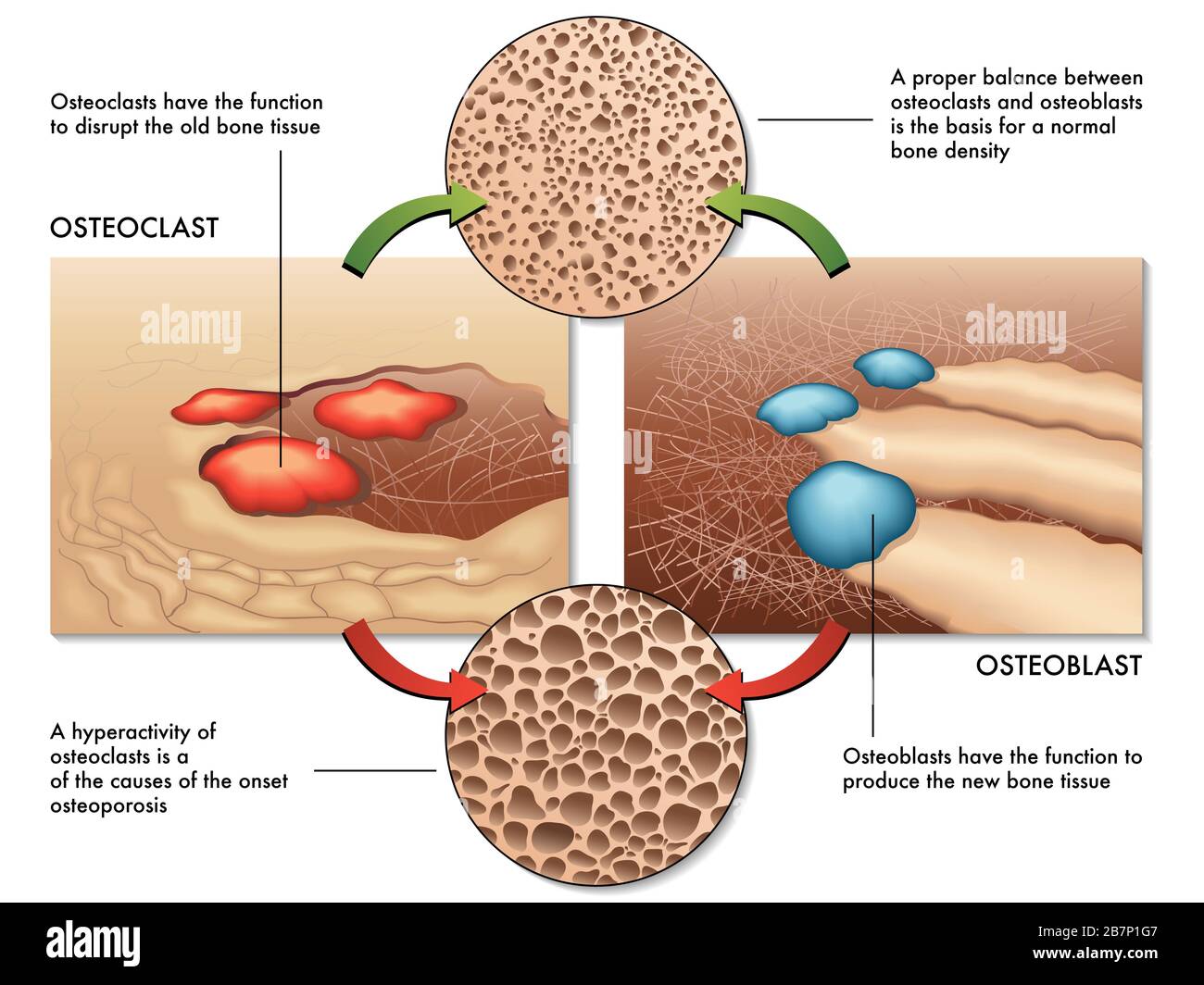
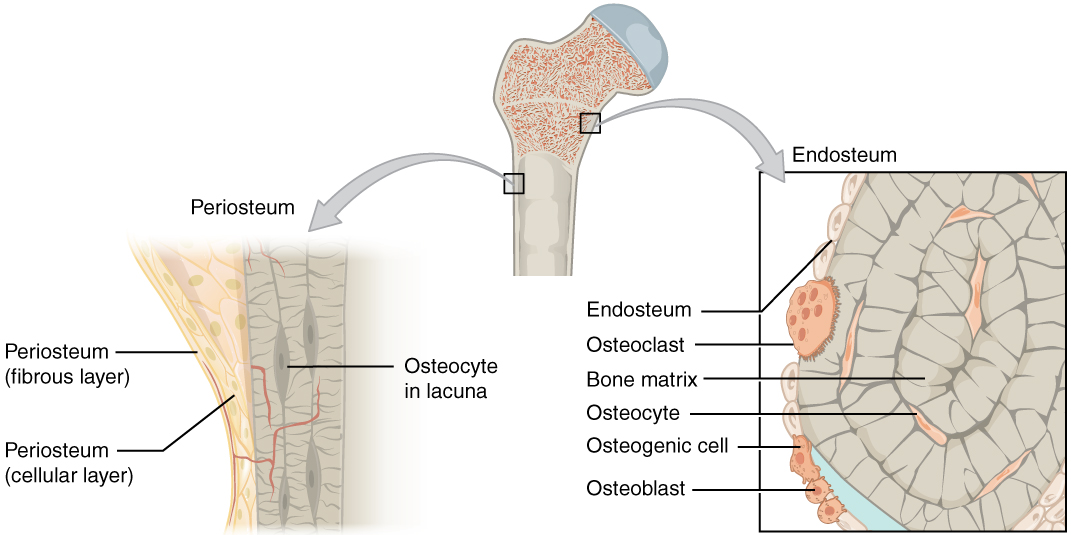
Osteoporosis is a condition of excessive bone loss caused by an imbalance between osteoblast and osteoclast activity, and occurs primarily in women. Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts [1, 2]. Bone exerts important functions in the body, such as locomotion, support and protection of soft tissues, calcium and phosphate storage, and harboring of bone marrow [3, 4]. : Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast?. The long bone has a shaft, with proximal and distal ends. A small opening, a small pit or depression, a small blank space, a gap or vacancy, or a hiatus. And placing the corresponding answer in the answer blank. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the ... Compact bone is the denser, stronger of the two types of bone tissue ( (Figure) ). It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones, where it provides support and protection. Diagram of Compact Bone. (a) This cross-sectional view of compact bone shows the basic structural unit, the osteon.
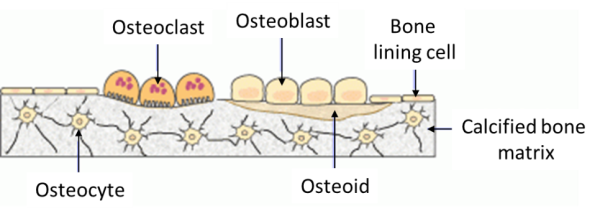
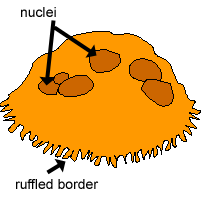
These cell names all start with "OSTEO" because that is the Greek word for bone. OSTEOCLASTS are large cells that dissolve the bone. They come from the bone marrow and are related to white blood cells. They are formed from two or more cells that fuse together, so the osteoclasts usually have more than one nucleus.
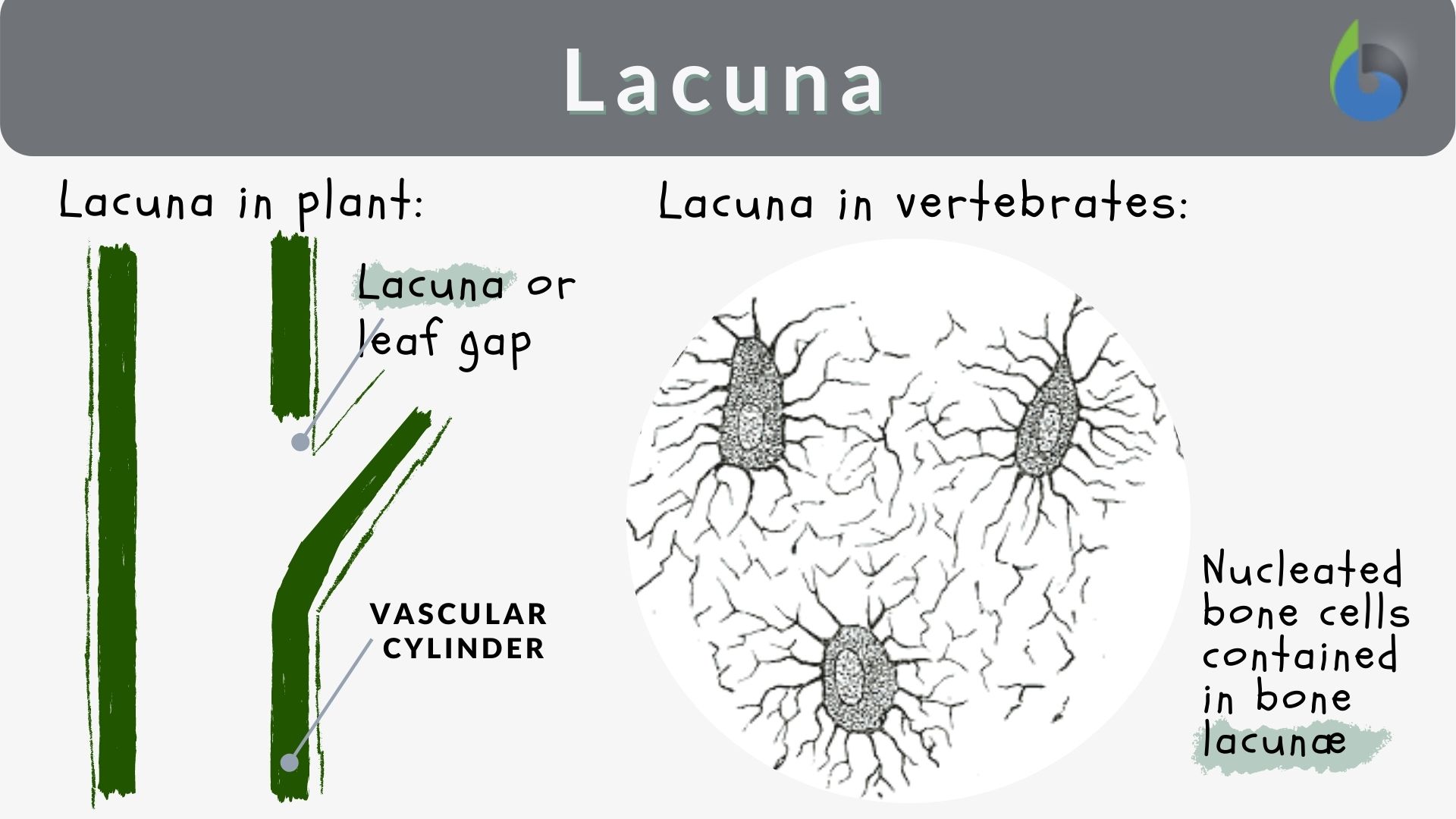
Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast. D. Which bone cell in the diagram below transport nutrients and waste trough tiny canals radiating from the lacunae. C. Which bone cell in the diagram is located in the inner layer of the periosteum, the endosteum, and perforating and Haversian canals ...
Osteoblasts are bone-forming cell, osteoclasts resorb or break down bone, and osteocytes are mature bone cells. An equilibrium between osteoblasts and ...
26-08-2021 · 2getrid 😢new zealand. Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) remains the gold standard for assessing glycaemic control and predicting the risk of development of long-term complications by providing an average glucose level, as measured over the previous 2–3 months.
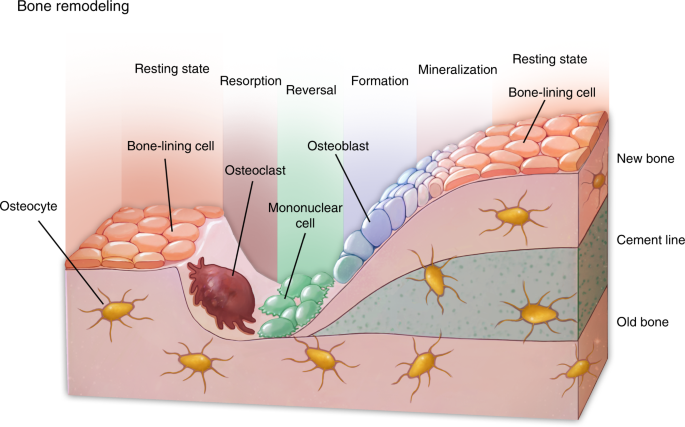
Bone tissue is continuously remodeled through the concerted actions of bone cells, which include bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts, whereas osteocytes act as mechanosensors and orchestrators of the bone remodeling process. This process is under the control of local (e.g., growth factors and cytokines) and systemic (e.g., calcitonin and estrogens) factors that all ...
_____ inhibits bone resorption and osteoclast activity and restore bone mass and density. asked Dec 12, 2016 in Health Professions by Katia. ... with osteoclast reabsorption of bone? asked Sep 26, 2016 in Anatomy & Physiology by Platini. anatomy-and-physiology; Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? asked Sep 25, 2015 in Anatomy ...
Bone tissue is removed above the tooth, but added below the tooth. We covered evidence for this when we discussed how permanent teeth fail to erupt in people with cleido-cranial dysostosis ← . There, a faulty matrix metalloproteinase enzyme lead to the inability to degrade ECM proteins, leaving permanent teeth trapped within their bony crypt.
Osteoclast-derived apoptotic bodies show extended biological effects of parental cell in promoting bone defect healing . Qinyu Ma 1, Mengmeng Liang 2, Nathachit Limjunyawong 3, Yang Dan 4, Junchao Xing 1, Jianmei Li 2, Jianzhong Xu 1 , Ce Dou 1,5 . 1. Department of Orthopedics, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing 400038, China. 2.
Briefly describe what is happening in each step of fracture repair shown in the diagram. The diagram illustrates repair of a bone fracture. In step one, there is formation of a fracture hematoma. In step two, a fibrocartilaginous callus is formed. In step three, a bony callus is formed.
05-10-2021 · Introduction. The main function of the bone marrow microenvironment is to provide signals that support and regulate the function of various cell types of the skeleton, including hematopoietic- and mesenchymal-lineage cells, to maintain homeostasis (Cao et al., 2020; Suchacki et al., 2020; Zhong et al., 2020).Proper bone homeostasis depends on the concerted …
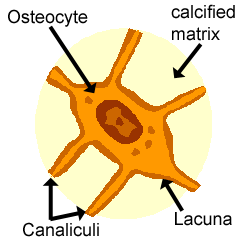
Sep 16, 2018 · An osteocyte, a star-shaped type of bone cell, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone tissue, and can live as long as the organism itself. The adult. Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts [1, 2]. Osteocyte: Osteocyte, a cell that lies within the substance of fully formed bone.
in the diagram, what bone is considered the strongest January 31, 2022 in nas' net worth $200 million ...
Electrospinning is a fiber production method that uses electric force to draw charged threads of polymer solutions or polymer melts up to fiber diameters in the order of some hundred nanometers. Electrospinning shares characteristics of both electrospraying and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers. The process does not require the use of coagulation chemistry …
Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? a) A b) B c) C d) D. c) C. Which bone cell in the diagram below is a mature bone cell that helps maintain bone tissue? a) A b) B c) C d) D. a) A. Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteogenic cell? a) A b) B c) C d) D. e) E. In the diagram, where is the central (Haversian) canal?
Pharmacological treatments such as G-CSF or stress conditions induce HSC mobilization, with osteoclast involvement. 107 Stress-induced osteoclasts produce proteolytic enzymes such as metalloproteinases, which cleave factors involved in the regulation of the HSC niche, thus inducing cell mobilization. 108,109 Bone mineralization matrix growth factors such as IGF, …
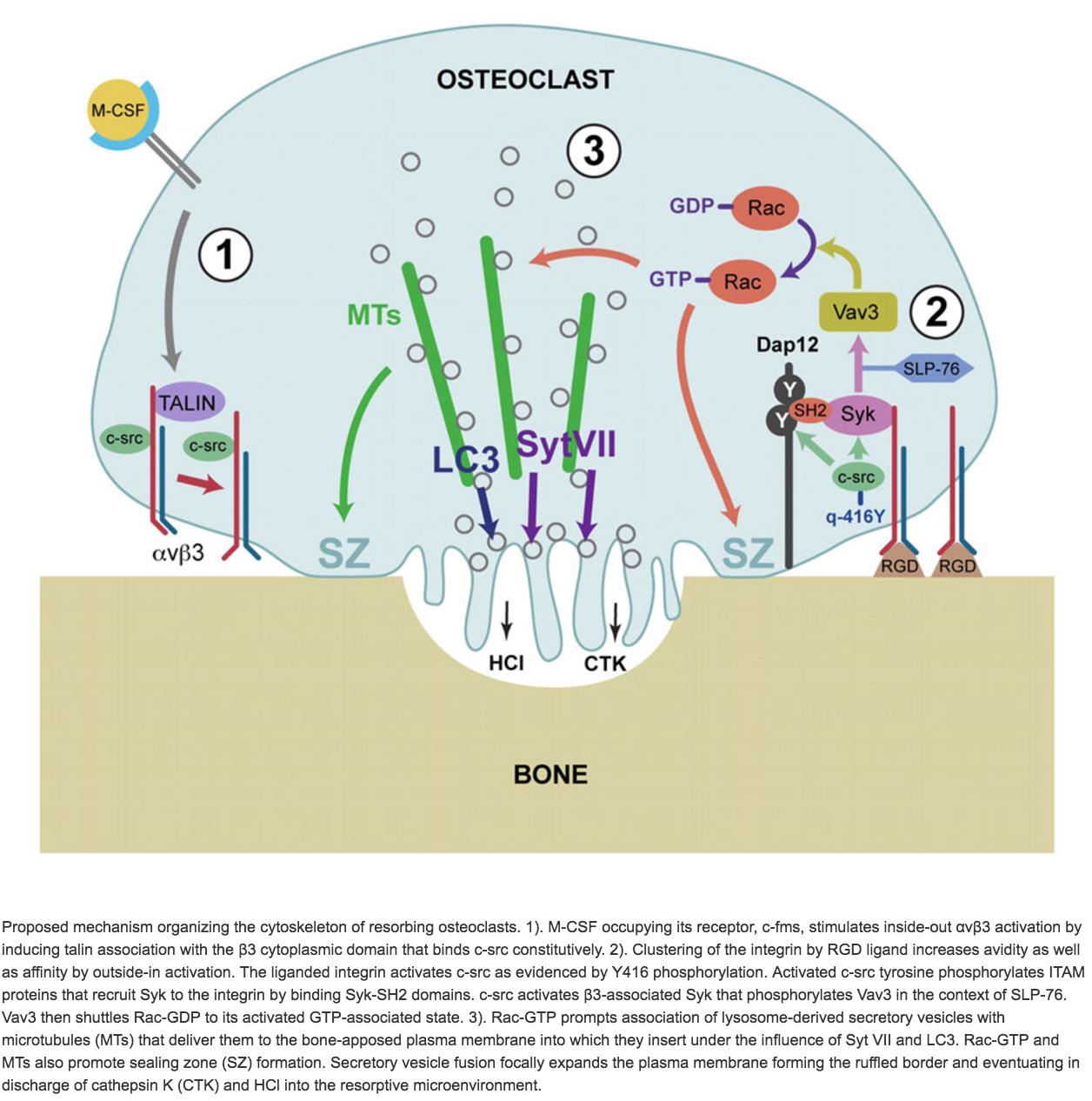
66781. Anatomical terms of microanatomy. An osteoclast (from Ancient Greek ὀστέον (osteon) 'bone', and κλαστός (clastos) 'broken') is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of ...
During bone resorption, an osteoclast attaches tightly to the endosteum or periosteum of the bone ... Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast?
Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? Money. If bone is analogous to a bank, calcium is analogous to _____. A .. ... Which bone cell in the diagram below transports nutrients and wastes through tiny canals radiating from the lacunae? .. 1,3,4.
An osteoclast is a cell that breaks down bone tissue, releasing calcium for use in the body. Learn how to define an osteoclast, then explore its morphology, function, and formation. Updated: 10/11 ...
The immune cells involved are macrophages, T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells, and osteo-related cells include osteoclasts and osteoblasts. The macrophage-osteoclast axis plays an essential role in osteoimmunity, regulating the balance of bone remodeling and bone resorption.
Here is a diagram I drew for my presentation on the paper "Sphingosine-1-phosphate mobilizes osteoclast precursors and regulates bone homeostasis" by Ishii et al., 2009. The femur above is just to illustrate where the diagram below takes place, that being where the blood vessel, marrow and bone interact. Below, you can see what this system…
Osteoclasts, multinucleated cells responsible for bone resorption, are derived from monocyte-macrophage lineage cells. Osteoblast lineage cells, whose mature form is responsible for bone formation, also regulate the differentiation of osteoclast precursors into osteoclasts.
Osteoclasts -are derived from osteoblasts and break down bone tissue. Osteogenic cells - ... Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast?
Hormonal control of bone remodeling is done mainly by the parathyroid glands, which produces parathyroid hormone. This stimulates osteoclasts, which well discuss below, to begin their work as bone resorbing cells, sending calcium into the bloodstream. Eventually, the blood-calcium level gets too high and triggers the PTH to stop.
04-01-2012 · 1.1. Bone Healing. Bone healing is one of the most complex cascades of events aiming to the repair of fractured bone without the formation of scar tissue [].In this physiological process, several cell types participate along with signal pathways and alternations in the biochemical profile of the local area.
Osteoclast production is regulated mainly by the thyroid gland. They are produced when more blood calcium is needed, and suppressed when there is no deficiency of calcium in the body. They are also vital in repairing mechanical breaks (fractures) to the bone. These cells form the cycle of bone remodeling, as illustrated in the diagram below:
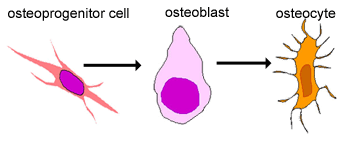
Bone Cells. Although bone cells compose less than 2% of the bone mass, they are crucial to the function of bones. Four types of cells are found within bone tissue: osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts (Figure 6.3.5). Figure 6.3.5 – Bone Cells: Four types of cells are found within bone tissue. Osteogenic cells are ...
Bone cells are sensitive to this hormone, too. Researchers have found that when this hormone attaches to "receptor" molecules on bone cells, osteoclast (bone destroying) activity goes down and osteoblast (bone creating) activity goes up.
There are three types of bone cells present in human body: 1. Osteoblast 2. Osteocyte 3. Osteoclast. Bone Cell # 1. Osteoblast: This is concerned with bone formation and is found in the growing surface where the bony matrix is deposited. This cell is strongly basophilic and cuboidal or pyramidal in shape and its nucleus is large with a ...
Which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast? D. Which hormone is the MOST important for Ca2+ regulation? ... estrogen; osteoclast activity. If collagen is removed from bone, what happens to the bone? Choose the best answer. The bone becomes stiff and brittle. Related questions.
Apr 12, 2019 · Osteoblasts are made from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) along with muscle cells (myocytes) and fat cells (adipocytes). Osteoblasts work together in the form of clusters and perform their function of building up the bone. Once the cluster of osteoblasts finishes its work, the shape of osteoblasts gets flattened.
























0 Response to "41 which bone cell in the diagram below is an osteoclast?"
Post a Comment