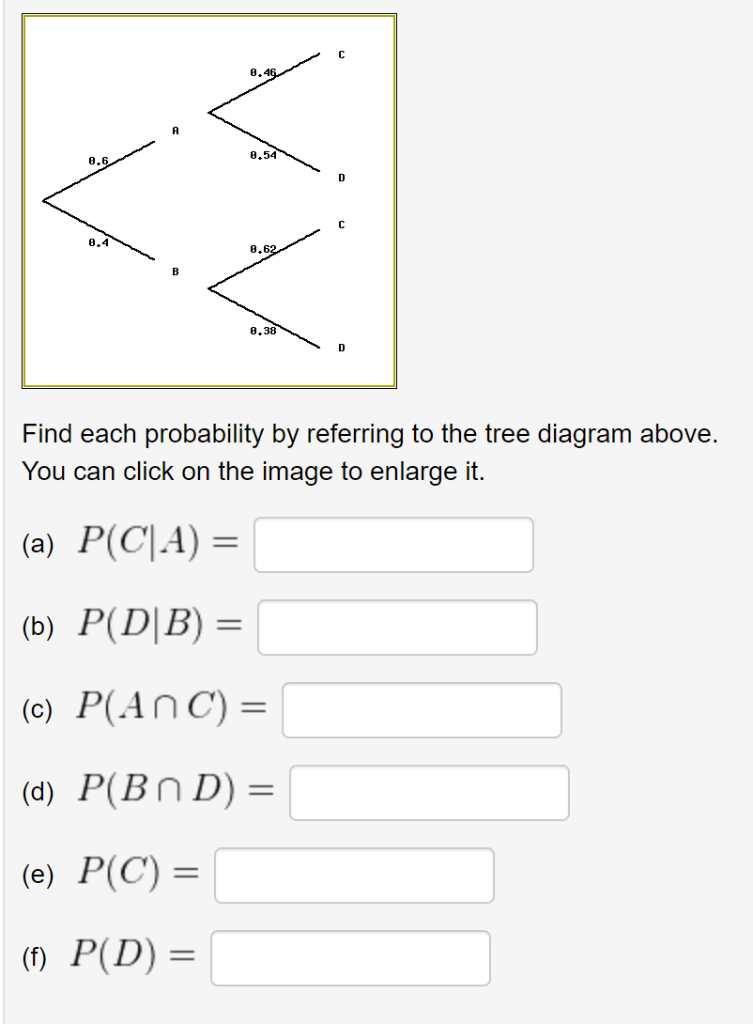
44 find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above.
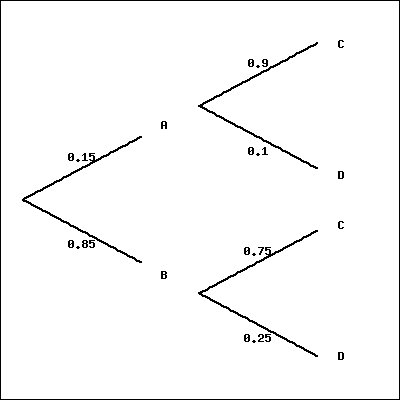
10.4 Tree diagrams | Probability | Siyavula The outcomes that lead to at least one 5 in four rolls of the die are marked on the tree diagram above. Summing the probabilities along all the branches gives. ( 1 6) + ( 5 6 × 1 6) + ( 5 6 × 5 6 × 1 6) + ( 5 6 × 5 6 × 5 6 × 1 6) = 671 1296. You flip one coin 4 times. [Solved] In" (6 points) Find each probability by ... the probability of B is 3/5 which can be written as P r (B) = 5 3 Now, on the second column of tree diagram, this is a conditional probability, given that A occur, the probability of having C is 3/4. We can write this as P r (C ∣ A) = 4 3 given that A occur, the probability of having D is 1/4. We can write this as P r (D ∣ A) = 4 1 given that B occur, the probability of having C is 5/8. We can write this as P r (C ∣ B) = 8 5
Finding Probability Using a Tree Diagram - onlinemath4all Find the number of possible outcomes for getting 2 heads. From the above tree diagram, let us list out the outcomes in which we have two heads. { HHT, HTH, THH } So, the number of possible outcomes in which have two heads = 3. Step 4 : Find the probability of getting 2 heads. Probability = 3/8
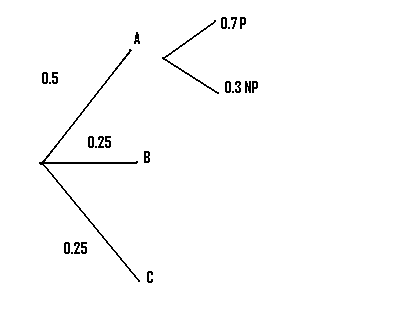
Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above.
6.3. Probability Using Tree Diagrams and Combinations ... Two apples are chosen from a basket containing five red and three yellow apples. Draw a tree diagram and find the following probabilities: a. P (both red) b. P (both yellow) 2. Three marbles are drawn from a jar containing five red, four white, and three blue marbles. Find the following probabilities using combinations: a. P (all three red) b. P (none white) 3. pm4py.fit.fraunhofer.de › documentationPM4Py - Process Mining for Python PM4Py is a process mining package for Python. PM4Py implements the latest, most useful, and extensively tested methods of process mining. The practical handling makes the introduction to the world of process mining very pleasant. Tree diagrams and conditional probability - Khan Academy Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted. Conditional probability tree diagram example.
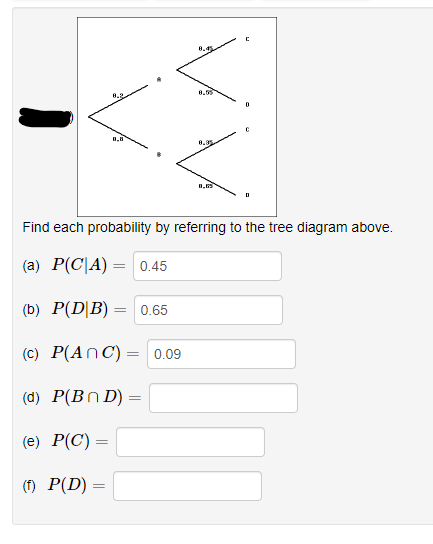
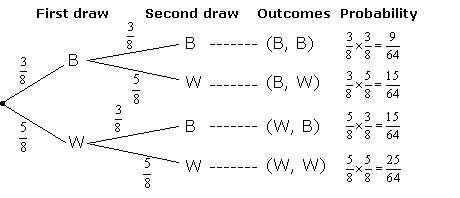
Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above.. Tree Diagram in Probability Theory with Example - BYJUS Draw the probability tree diagram for two draws. Solution: Given: No. of black balls = 3. No. of white balls = 5. Total Number of balls = 8. So, the probability of getting black balls = 3/8. The probability of getting white balls = 5/8. Therefore, the tree diagram for two draws of balls with possible outcomes and probability is given as below. Solved Find each probability by referring to the tree ... Statistics and Probability questions and answers Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) 𝑃(𝐶|𝐴)= (b) 𝑃(𝐷|𝐵)= (c) 𝑃(𝐴∩𝐶)= (d) 𝑃(𝐵∩𝐷)= (e) 𝑃(𝐶)= (f) 𝑃(𝐷)= online.stat.psu.edu › stat505 › bookLesson 14: Cluster Analysis - STAT ONLINE This contains the information required by the tree procedure to draw the tree diagram. In the tree procedure, we chose to investigate 6 clusters with ncluster=6. A new SAS dataset called clust2 is output with the id numbers of each site and the cluster that site belongs stored in a new variable called cluster. Answered: Find each probability by referring to… | bartleby Solution for Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) P(C\A) = 0.45 (b) P(D\B) = 0.65 (c) P(AnC) = 0.09 (d) P(Bn D) = (e) P(C) = (1)… Answered: Find each probability by referring to… | bartleby
› mathworks › ME-Curriculum6th Grade Mathematics - Important Vocabulary Words ... Probability In an experiment in which each outcome is equally likely, the probability P(A) of an event A is m/n where m is the number of outcomes in the subset A and n is the total number of outcomes in the sample space S. Proper Fraction A fraction whose value is greater than 0 and less than 1. Proportion EOF › topics › computer-scienceHierarchical Cluster Analysis - an overview | ScienceDirect ... The goal of hierarchical cluster analysis is to build a tree diagram where the cards that were viewed as most similar by the participants in the study are placed on branches that are close together. For example, Figure 9.4 shows the result of a hierarchical cluster analysis of the data in Table 9.8 . Probability Calculator Finding P as shown in the above diagram involves standardizing the two desired values to a z-score by subtracting the given mean and dividing by the standard deviation, as well as using a Z-table to find probabilities for Z. If, for example, it is desired to find the probability that a student at a university has a height between 60 inches and 72 inches tall given a mean of 68 inches tall with a standard deviation of 4 inches, 60 and 72 inches would be standardized as such:
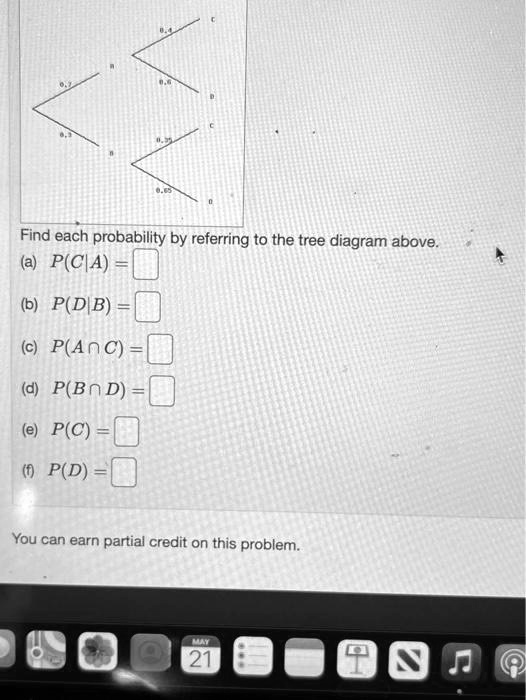
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Decision_tree_learningDecision tree learning - Wikipedia Each leaf of the tree is labeled with a class or a probability distribution over the classes, signifying that the data set has been classified by the tree into either a specific class, or into a particular probability distribution (which, if the decision tree is well-constructed, is skewed towards certain subsets of classes). › mathworks › ME-Curriculum7th Grade Mathematics - Texas State University Tree Diagram. A process used to find the prime factors on an integer. A method to organize the sample space of compound events. Triangle A plane figure with three straight edges and three angles. Triangle Sum Theorem The sum of the measures of the interior angles of any triangle is 180 degrees. Trichotomy Probability Tree Diagrams - mathsisfun.com 0.3 + 0.12 = 0.42 probability of being a Goalkeeper today (That is a 42% chance) Check. One final step: complete the calculations and make sure they add to 1: 0.3 + 0.3 + 0.12 + 0.28 = 1. Yes, it all adds up. You can see more uses of tree diagrams on Conditional Probability. Conclusion Answered: 0.2 Find each probability by referring… | bartleby Math Probability Q&A Library 0.2 Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) P(C|A) = (b) P(D|B) = (C) P(Αn C)- ( d) P(Βn D ). (e) P(C) = (1) P(D) =
Tree Diagrams | Mathematics Quiz - Quizizz Q. A bag contains 3 white balls, 4 green balls. 2 balls are drawn from the bag without replacement. Use a tree diagram to find the probability that the balls are white colors.
Probability Tree Diagrams (video lessons, examples and ... From the probability tree diagram, we get: P (second ball black) = P (B, B) or P (W, B) = P (B, B) + P (W, B) Example: Bag A contains 10 marbles of which 2 are red and 8 are black. Bag B contains 12 marbles of which 4 are red and 8 are black. A ball is drawn at random from each bag.
Tree Diagrams | Probability Quiz - Quizizz none of the above. Tags: Question 2 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . ... Two dice are rolled and it is recorded whether the result on each is odd or even. What is the probability that one is even and one is odd? answer choices . 1/2. 1/4. 3/4. 1/3. ... Use the tree diagram to find the probability of spinning the same number in succession when the ...
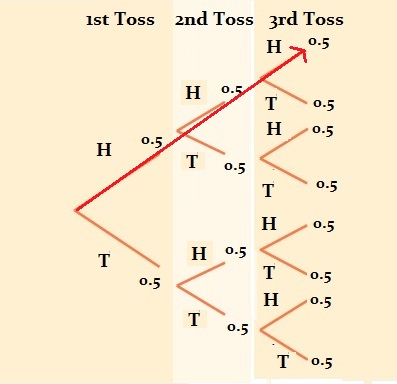
Coin & Dice Probability: Using A Tree Diagram (video ... a) Draw a tree diagram to show all the possible outcomes. b) Find the probability of getting: (i) Three tails. (ii) Exactly two heads. (iii) At least two heads. Solution: a) A tree diagram of all possible outcomes. b) The probability of getting: (i) Three tails. Let S be the sample space and A be the event of getting 3 tails. n(S) = 8; n(A) = 1 P(A) =
› 34463194Statistics and Probability for Engineering ... - Academia.edu Statistics and Probability for Engineering Applications With Microsoft ® Excel. Swampfire X. Download Download PDF. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package. This ...
Solved Find each probability by referring to the tree ... Math. Statistics and Probability. Statistics and Probability questions and answers. Find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above. (a) P (C|A) = (b) P (D|B) = (c) P (A intersection C) = (d) P (B intersection D) = (e) P (C) = (f) P (D) =.
Tree diagrams and conditional probability - Khan Academy Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted. Conditional probability tree diagram example.
pm4py.fit.fraunhofer.de › documentationPM4Py - Process Mining for Python PM4Py is a process mining package for Python. PM4Py implements the latest, most useful, and extensively tested methods of process mining. The practical handling makes the introduction to the world of process mining very pleasant.
6.3. Probability Using Tree Diagrams and Combinations ... Two apples are chosen from a basket containing five red and three yellow apples. Draw a tree diagram and find the following probabilities: a. P (both red) b. P (both yellow) 2. Three marbles are drawn from a jar containing five red, four white, and three blue marbles. Find the following probabilities using combinations: a. P (all three red) b. P (none white) 3.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TreeDiagram2-c209ffffddd14e989cd72e9c38e518f0.png)
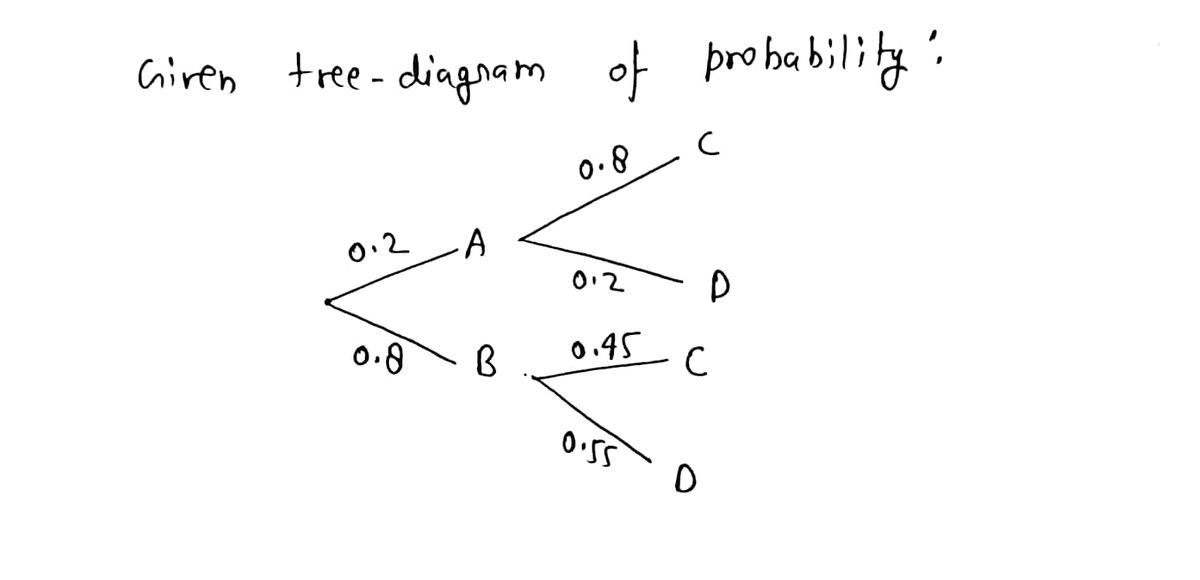

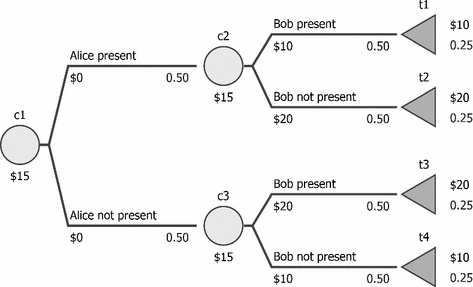




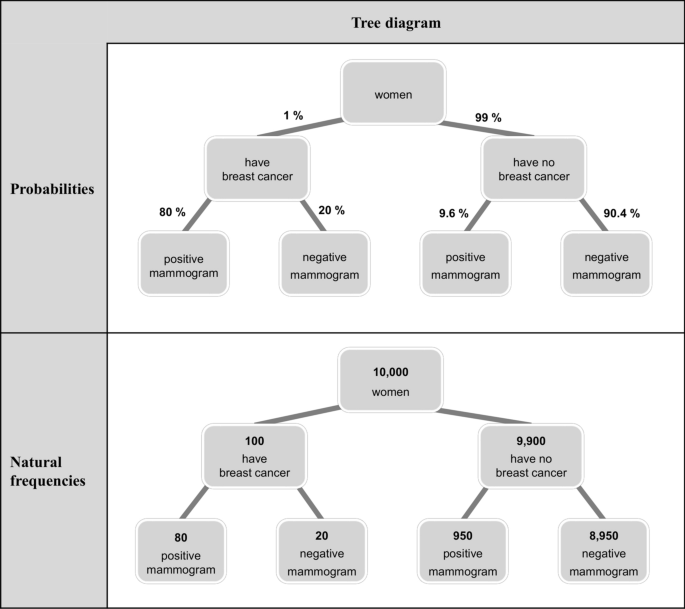








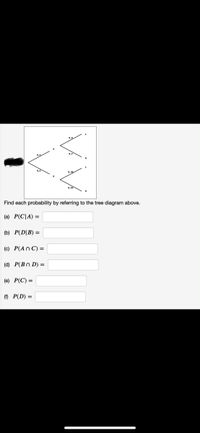


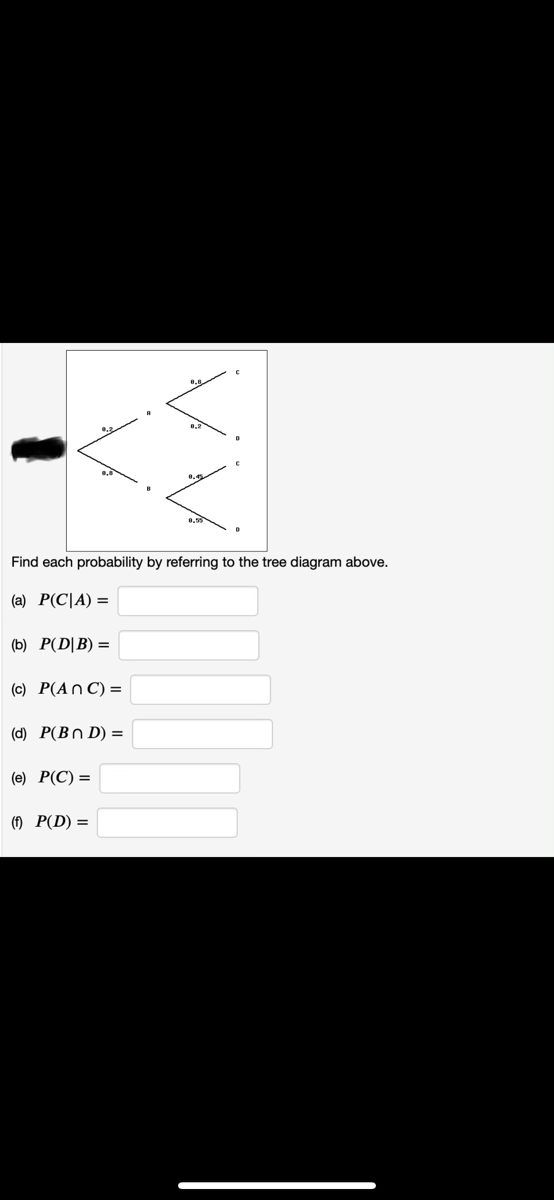





0 Response to "44 find each probability by referring to the tree diagram above."
Post a Comment