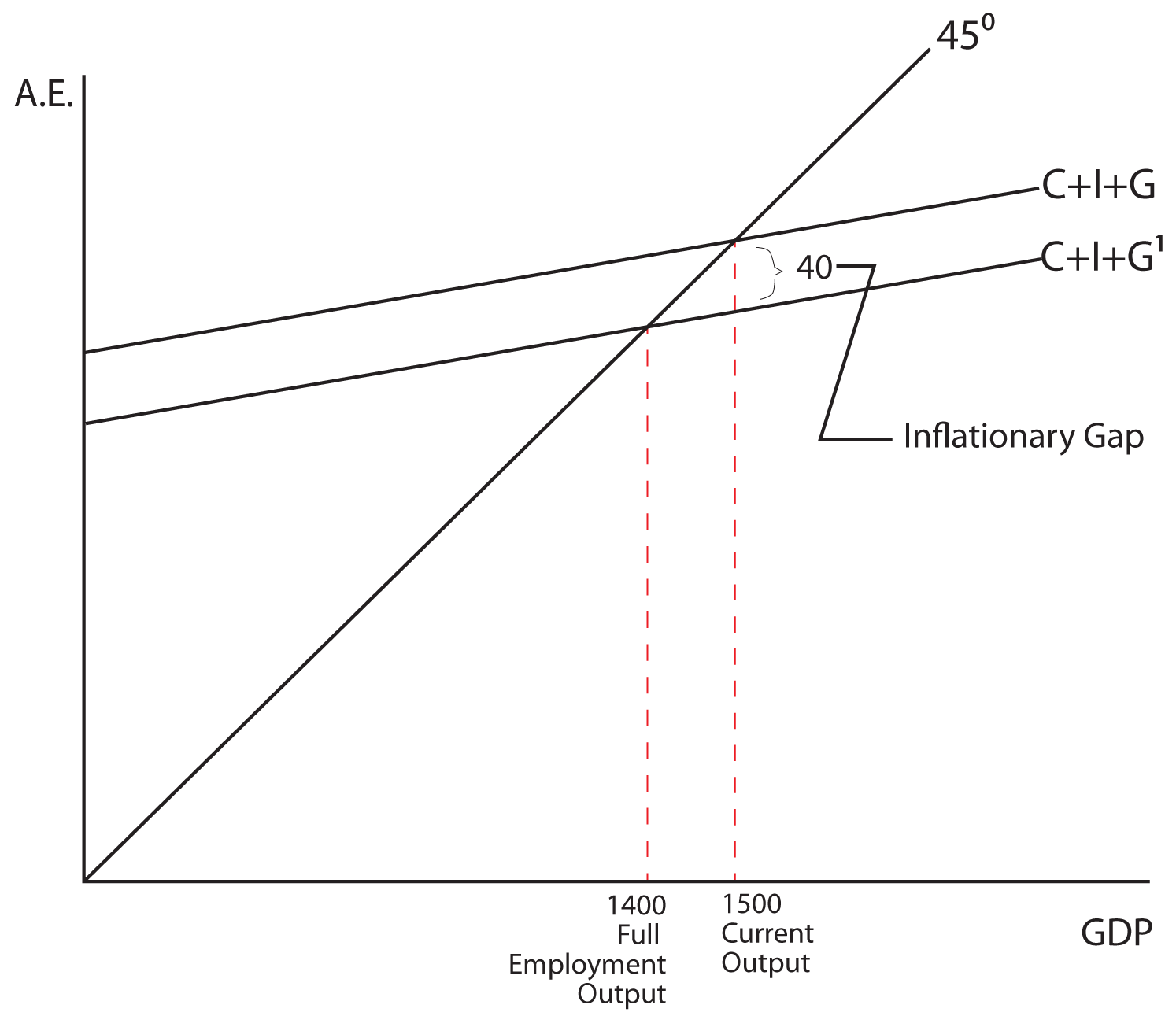
41 refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is
The expenditure-output, or Keynesian cross ... - Khan Academy The expenditure-output, or Keynesian cross, model. Use a diagram to analyze the relationship between aggregate expenditure and economic output in the Keynesian model. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. CHAPTER 8 MACRO TEST Flashcards - Quizlet If a $500 billion increase in investment spending increases income by $500 billion in the first round of the multiplier process and by $450 in the second round, income will eventually increase by: ... The multiplier in this economy is: a. 2. b. 4. c. 5. d. 10. C. ... Refer to the above diagram. At disposable income level D, the average ...
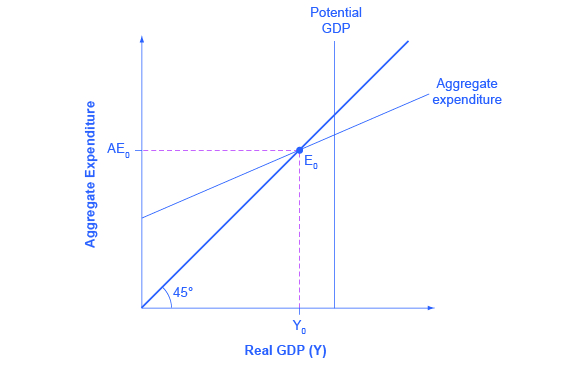
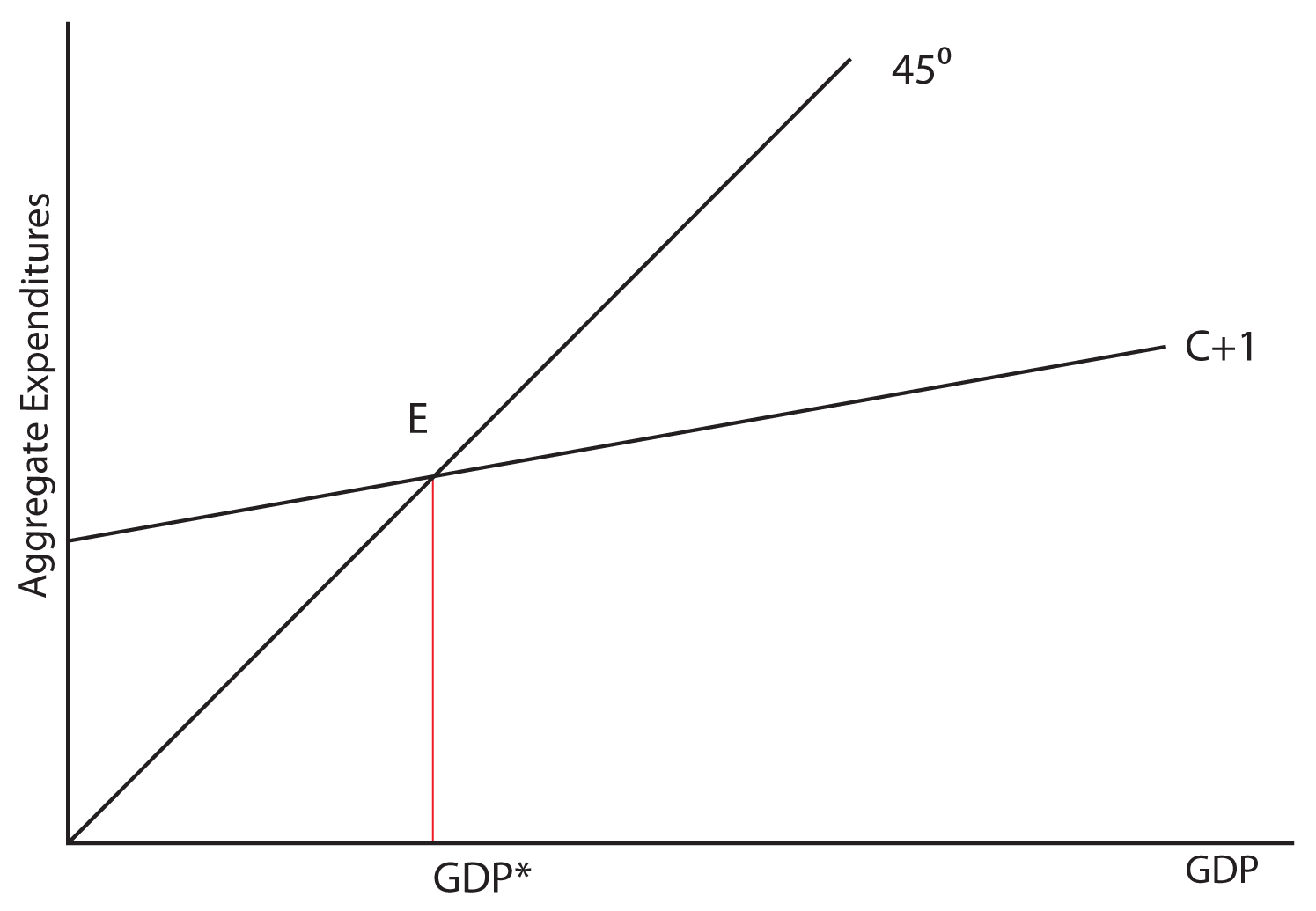
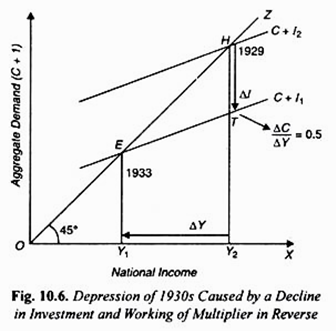
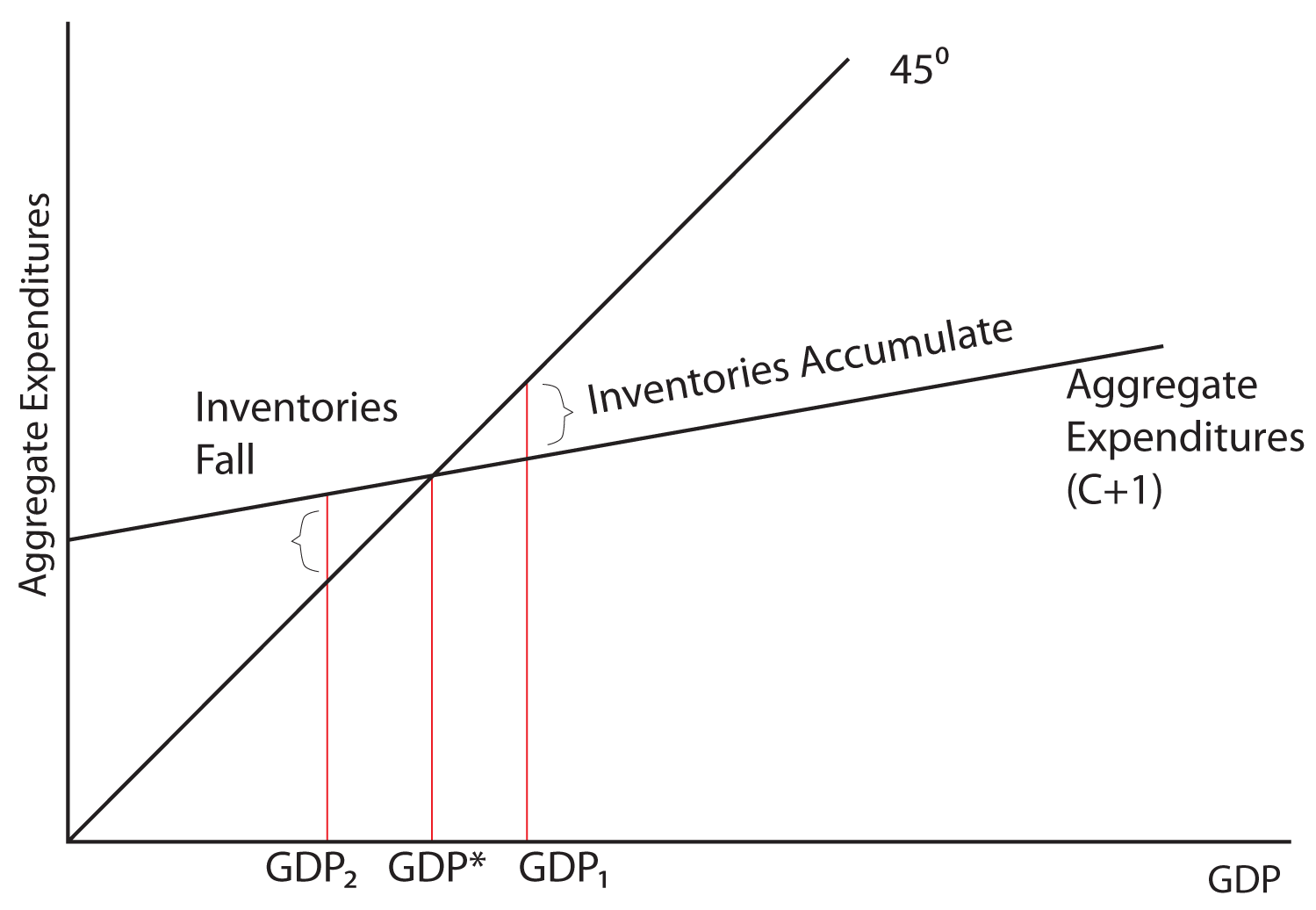
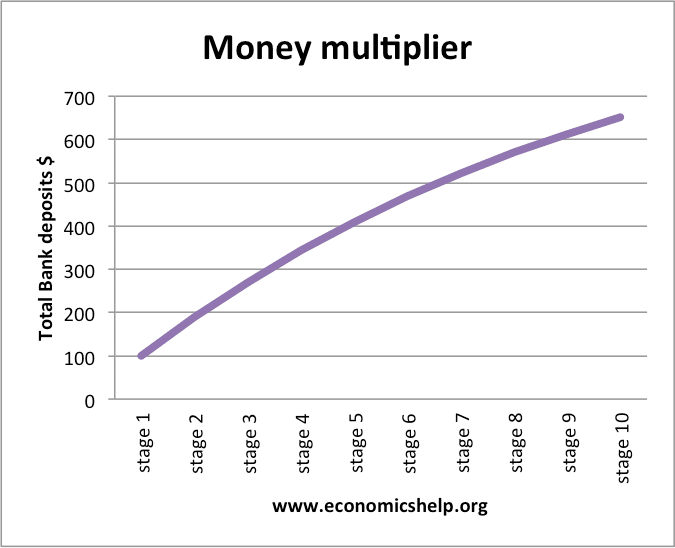
Keynes' Theory of Investment Multiplier (With Diagram) Diagrammatic Representation of Multiplier: Th e level of national income is determined by the equilibrium between aggregate demand and aggregate supply. In other words, the level of national income is fixed at the level where C + I curve intersects the 45° income curve. With such a diagram we can explain the multiplier.

Refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is
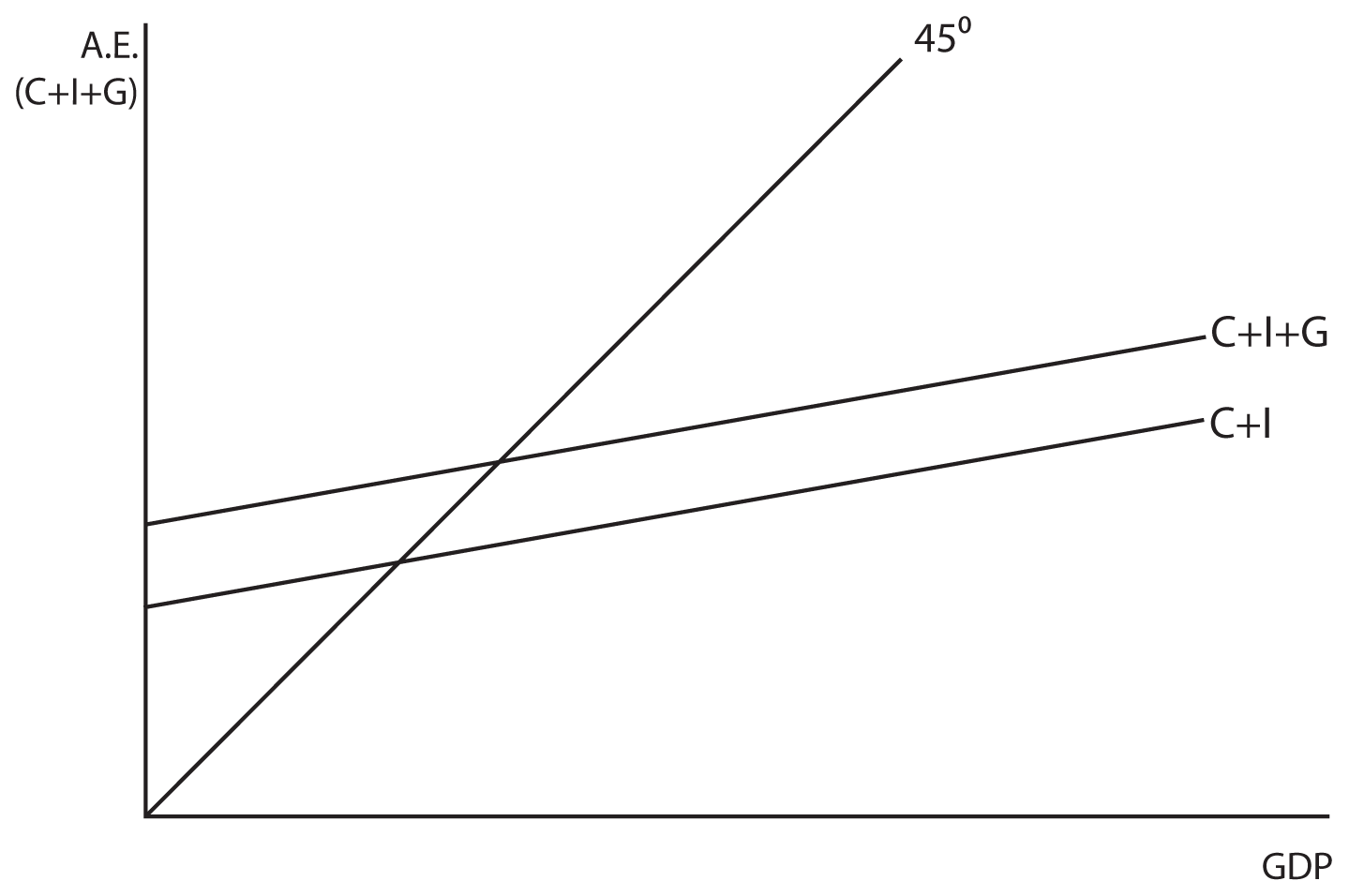
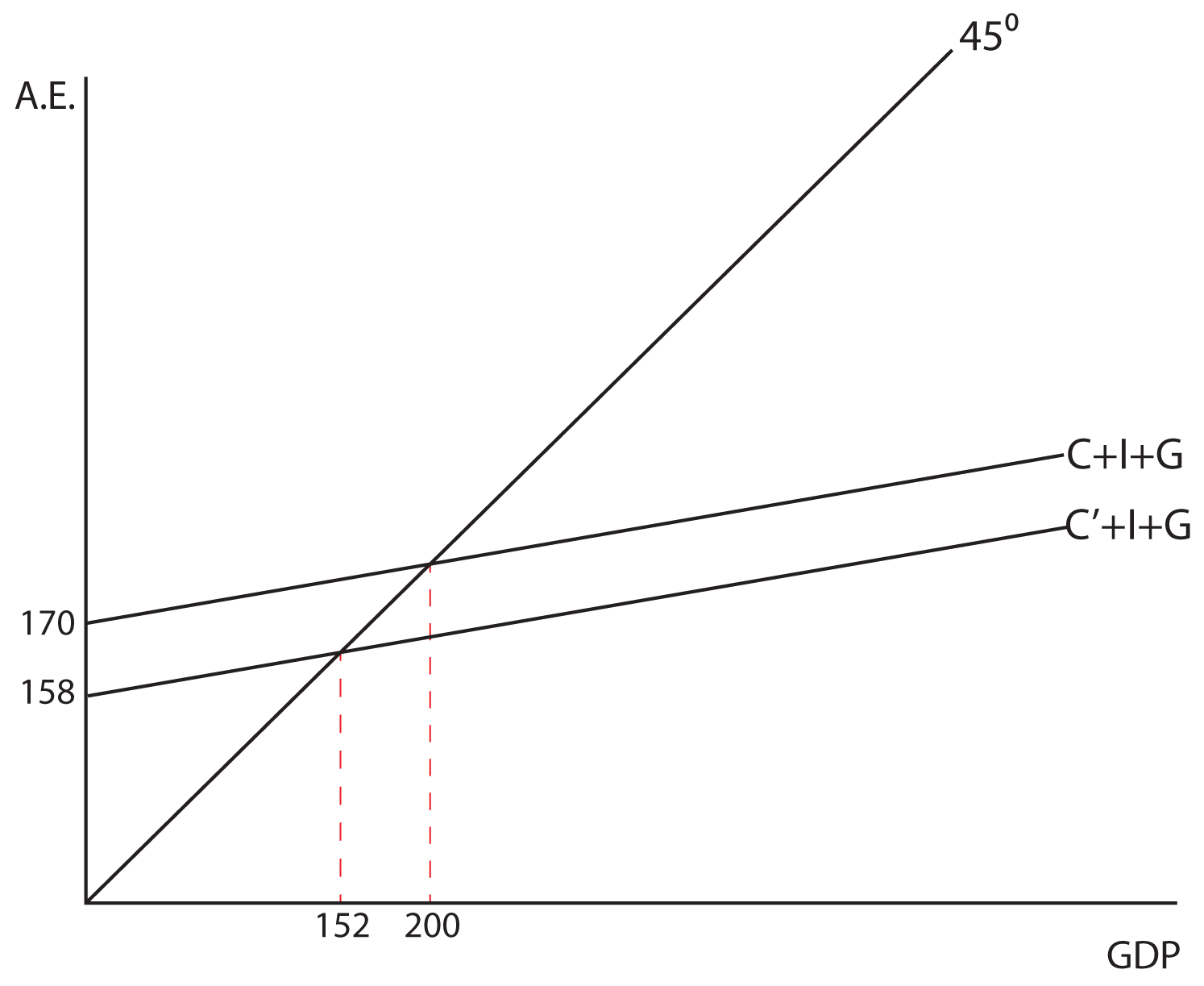
Lecture 6 Flashcards by Cassidy Porco - Brainscape The simple multiplier without government and foreign trade in this economy is _____ and the simple multiplier with government and foreign trade in this economy is _____. A) 1.67; 1.33 B) 2.5; 2.5 C) 2.5; 1.33 D) 2.5; 4 E) 1.67; 4 D | The Expenditure-Output Model - OpenStax With a higher multiplier, government policies to raise or reduce aggregate expenditures will have a larger effect. Thus, a low multiplier means a more stable economy, but also weaker government macroeconomic policy, while a high multiplier means a more volatile economy, but also an economy in which government macroeconomic policy is more powerful. Refer to the given diagram. The marginal propensity to save is Scenario 34-2. The following facts apply to a small, imaginary economy. • Consumption spending is $6,720 when income is $8,000. • Consumption spending is $7,040 when income is $8,500. -Refer to Scenario 34-2. Compare and contrast the controlling account Accounts Payable to the accounts payable subsidiary ledger.
Refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is. REVIEW: The Economic Functions of Government Refer to the above diagrams for two separate product markets. Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q0 and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S1 in diagram (a) and from S to S2 in diagram (b). The shift of the supply curve from S to S2 in diagram (b) might be caused by a per unit: The Multiplier - Short Question Answers - tutor2u The formula for the multiplier in a closed economy with no government is 1/marginal propensity to save or 1/(1-marginal propensity to consume) We can infer from the information that the value of the multiplier = 5. Therefore the marginal propensity to save must be 0.2. Because MPS + MPC always equals 1. Then the MPC = 1-0.2 = 0.8 PDF ECO 212 Macroeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 7. Refer to the above diagram. The simple multiplier for this economy is: A. 1.0 B. 1.5 C. 2.0 D. 2.5 Refer to the diagram, in which Qf is the full-employment ... Refer to the graph, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The interest rate and the level of investment spending in the economy are at point C on the investment demand curve.
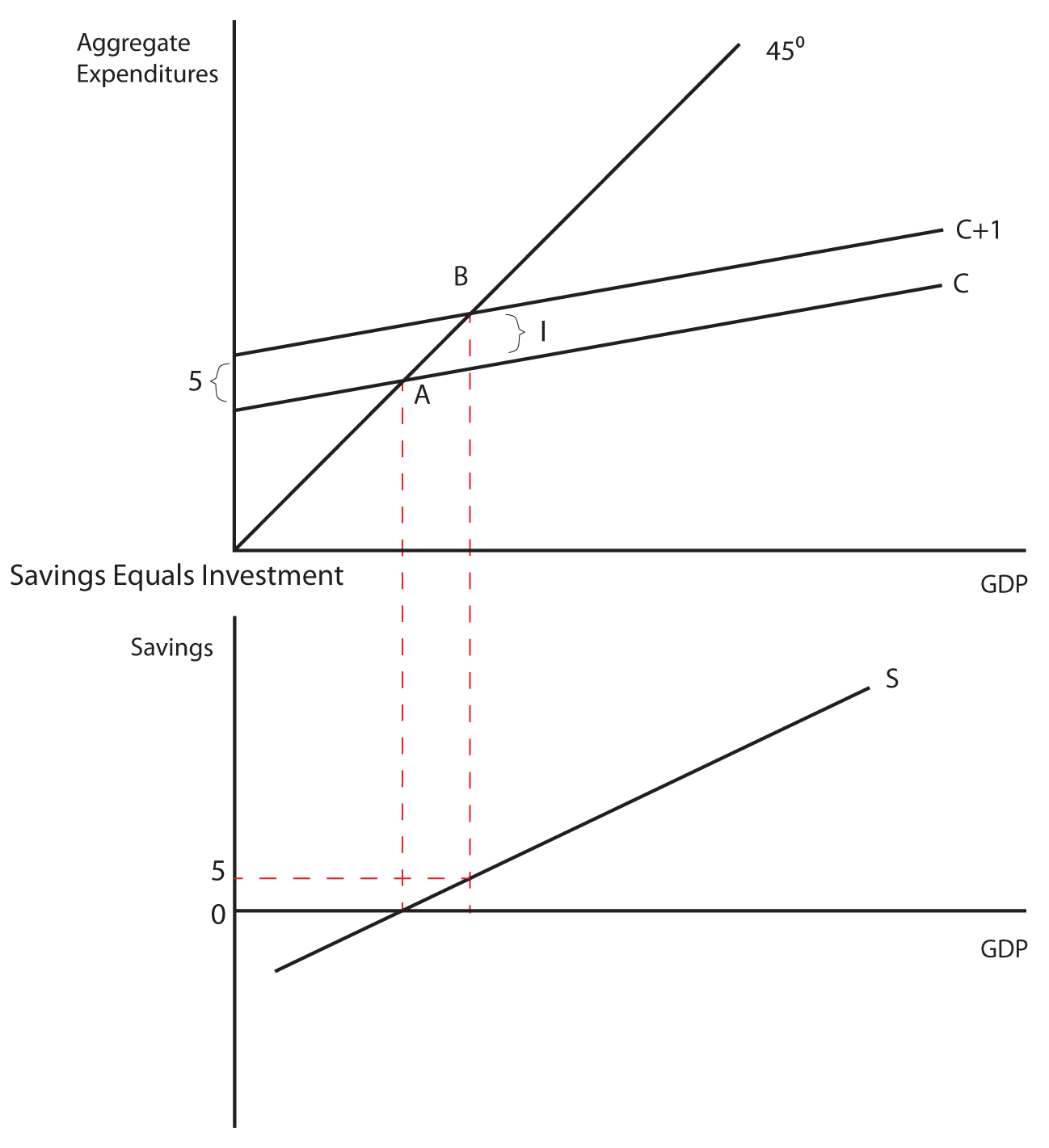
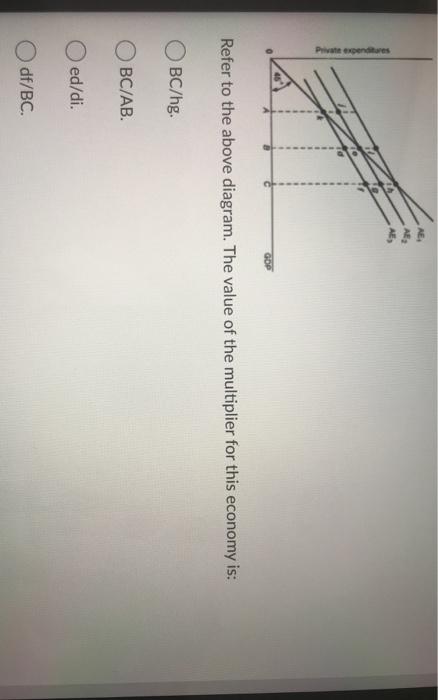
The Keynesian multiplier The multiplier refers to a change in an injection into the Circular Flow of Income (either investment (I), government expenditure (G) or exports (X)), will lead to a proportionately larger change (or multiplied change) in the level of national income i.e. the eventual change in national income will be greater than the initial injection of spending. Econ chapter 11 Flashcards - Quizlet The multiplier in this economy is: shift the C + Ig + Xn line downward by an amount equal to T × MPC. In an aggregate expenditures diagram, a lump-sum tax (T) will: Solved Consumption ο Consumption Ο (3 ot24:39 15 Ο Η F Ε ... Consumption ο Consumption Ο (3 ot24:39 15 Ο Η F Ε Income eBook Refer to the given diagram. The economy is dissaving Multiple Choice Ο in the amount CD. Ο at all income levels greater than E. Ο at Income level H. Ο at Income level E (8 01:24:30 Domestic Output or Income (GDPEDI) $240 250 260 270 280 290 300 310 320 Consumption $244 250 256 262 268 ... Macroeconomics Unit 2 Exam Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram. The value of the multiplier for this economy is a. ed/di. b. df/BC. c. BC/hg. d. BC/AB
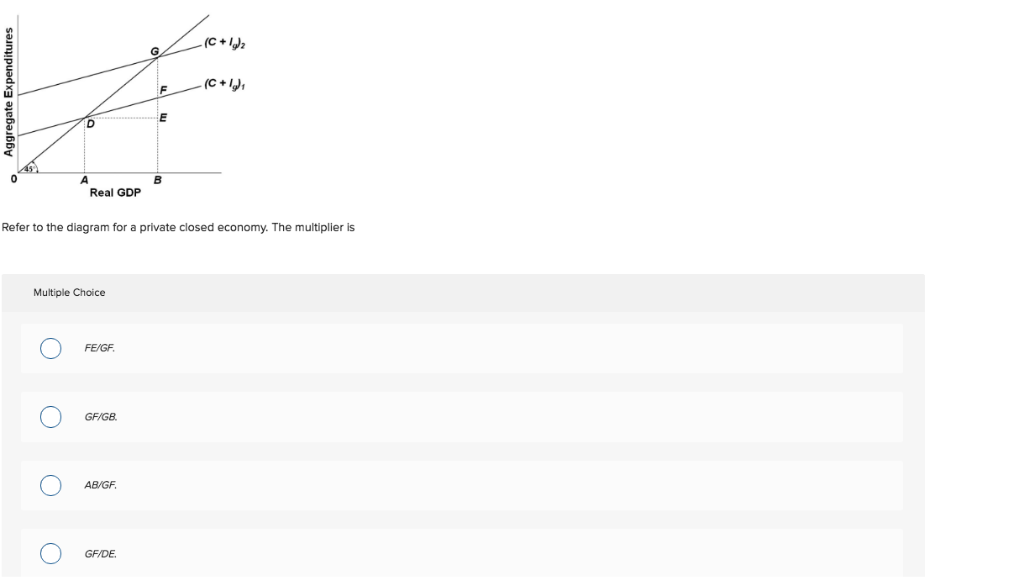
PurpleCutie2013's Blog 120. Refer to the above diagram. The multiplier in this economy is: A) 0E/0A. B) BD/FG. C) FG/BD. D) BD/AD. Answer: B . Type: G Topic: 3 E: 179-180 MA: 179-180 121. Refer to the above diagram. Solved Real GDP Refer to the diagram for a private closed ... Transcribed image text: Real GDP Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. The multiplier is Multiple Choice FE/GF GF/GB AB/GF GFIDE The multiplier is Multiple Choice FE/GF GF/GB AB/GF GFIDE Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) Definition, Formula ... The multiplier effect is driven by MPC. As people spend a higher percentage of their incomes, government investment in the economy becomes more effective - driven by the nations MPC. The marginal propensity to consume will usually fall between 0 and 1 as it refers to the percentage of income that is spent. mbch10quiz - paws.wcu.edu (Advanced analysis) Assume the consumption schedule for a private closed economy is C = 40 + 0.75Y , where C is consumption and Y is gross domestic product. The multiplier for this economy: The multiplier for this economy:
Unit 14 Unemployment and fiscal policy - The Economy - CORE Einstein The multiplier in an economy with a government and foreign trade. We can again use the fact that there is equilibrium in the goods market when output is equal to aggregate demand to find the multiplier (equilibrium is where the aggregate demand line crosses the 45-degree line in the multiplier diagram).
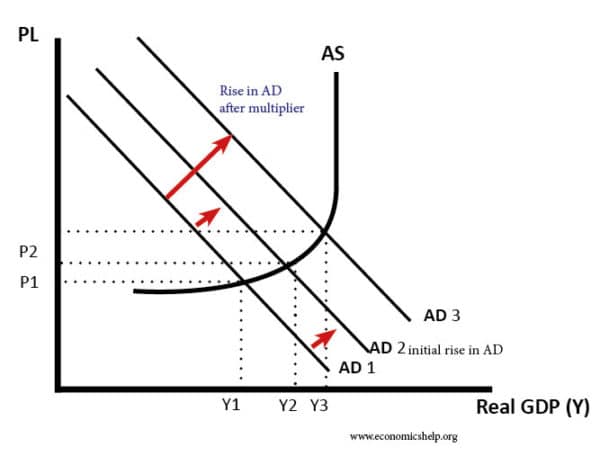
The Multiplier Effect Notes & Questions (A-Level, IB ... The Multiplier Effect Example & Explanation: If the UK government spends money in building a railroad (e.g. imagine the continuous spending on HS2 ), government spending (G) will rise, leading to an injection into the circular flow of income and a rise in aggregate demand (AD).
The multiplier - Economics Online The multiplier effect refers to the increase in final income arising from any new injection of spending. The size of the multiplier depends upon household's marginal decisions to spend, called the marginal propensity to consume (mpc), or to save, called the marginal propensity to save (mps).
Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy ... Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. The multiplier is: A. GF/DE B. GF/GB C. FE/GF D. AB/GF . . . . AACSB: Analytical Skills Bloom's: Application Learning Objective: 28-3 Topic: Equilibrium GDP in private closed economy 104.
Refer to the above diagram The multiplier in this economy ... Refer to the above diagram. If aggregate expenditures in this economy are (C + I g + X n 2), then the equilibrium levels of GDP and aggregate expenditures respectively will be: A) 0 A and 0 E. B) 0 B and 0 F. C) 0 A and AH. D) 0 D and DJ. Answer: D Type: G Topic: 3 E: 181 MA: 181 122. Refer to the above diagram.
Answered: 8. Refer to the diagrams. The… | bartleby Solution for 8. Refer to the diagrams. The multiplier associated with fiscal policy that increases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2 is less in graph b than in a…
PDF Humble Independent School District / Homepage Answer the next question(s) below on the basis of the following information for a private closed economy: Gross domestic product $100 200 300 400 500 Expected rate of return 25% 20 15 10 Amount of investment $0 20 40 60 80 Consumption $120 180 240 300 360 1. 2. 3. 4. Refer to the above information. The multiplier for this economy: A) is 2.5.
41 refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is ... Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. The multiplier is: Answer AB/GF. (Advanced analysis) Answer the question on the basis of the following information for a private closed economy. where S is saving, Ig is gross investment, i is the real interest rate, and Y is GDP. Refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is
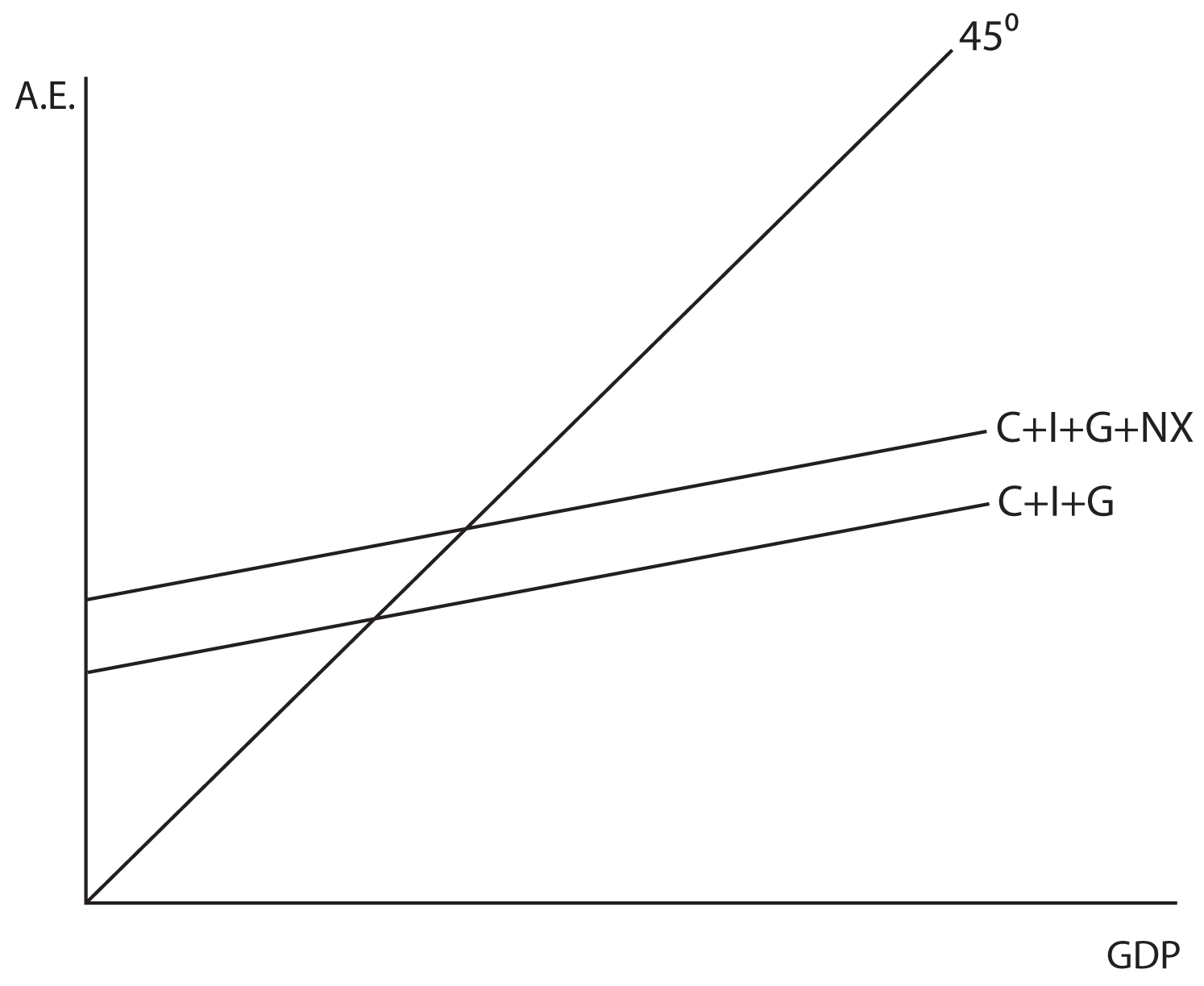
Foreign Trade Multiplier: Meaning, Working, Assumption ... Which is the equilibrium condition of national income in an open economy. The foreign trade multiplier coefficient (K f) is equal to . K f = ∆Y/∆X . And ∆X = ∆S + ∆M . It shows that an increase in exports by Rs. 1000 crores has raised national income through the foreign trade multiplier by Rs. 2000 crores, given the values of MPS and MPM.
PDF Homework for Chapter 10 answers - University College London economy is .80? If the MPC is .67? Explain the difference between the simple and the complex multiplier. The multiplier effect is the magnified increase in equilibrium GDP that occurs when any component of aggregate expenditures changes. The greater the MPC (the smaller the MPS), the greater the multiplier. M=1/MPS MPS = 0, multiplier = infinity;
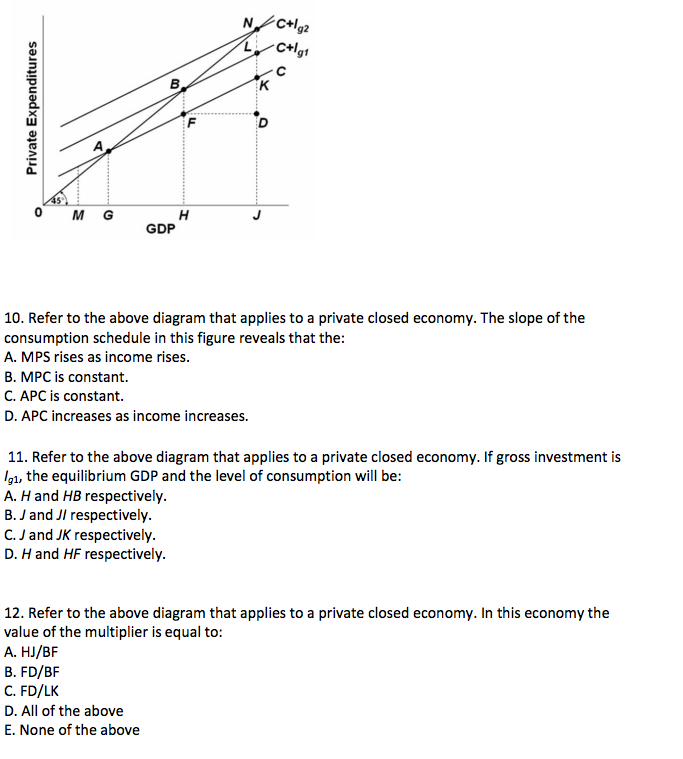
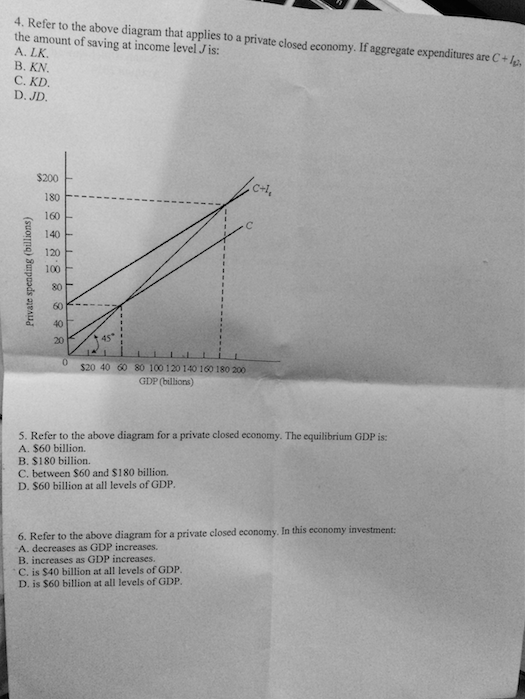
PDF Part A Multiple-Choice Questions [20 marks] 17. Refer to the above diagram which applies to a private closed economy. If gross investment is I g1, the equilibrium GDP and the level of consumption will be: A) H and HB respectively. B) J and JI respectively. C) J and JK respectively D) H and HF respectively. 18. Refer to the above diagram which applies to a private closed economy. If gross
Refer to the given diagram. The marginal propensity to save is Scenario 34-2. The following facts apply to a small, imaginary economy. • Consumption spending is $6,720 when income is $8,000. • Consumption spending is $7,040 when income is $8,500. -Refer to Scenario 34-2. Compare and contrast the controlling account Accounts Payable to the accounts payable subsidiary ledger.
D | The Expenditure-Output Model - OpenStax With a higher multiplier, government policies to raise or reduce aggregate expenditures will have a larger effect. Thus, a low multiplier means a more stable economy, but also weaker government macroeconomic policy, while a high multiplier means a more volatile economy, but also an economy in which government macroeconomic policy is more powerful.
Lecture 6 Flashcards by Cassidy Porco - Brainscape The simple multiplier without government and foreign trade in this economy is _____ and the simple multiplier with government and foreign trade in this economy is _____. A) 1.67; 1.33 B) 2.5; 2.5 C) 2.5; 1.33 D) 2.5; 4 E) 1.67; 4












/dotdash_Final_Economic_Growth_2020-01-a0ace0fdcf3142ae94494dcfd9986daa.jpg)


0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram. the multiplier in this economy is"
Post a Comment