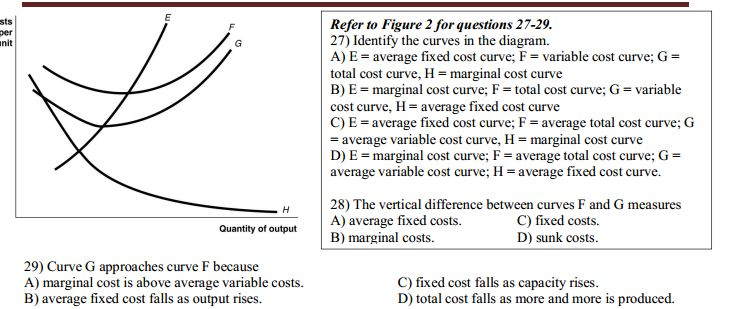
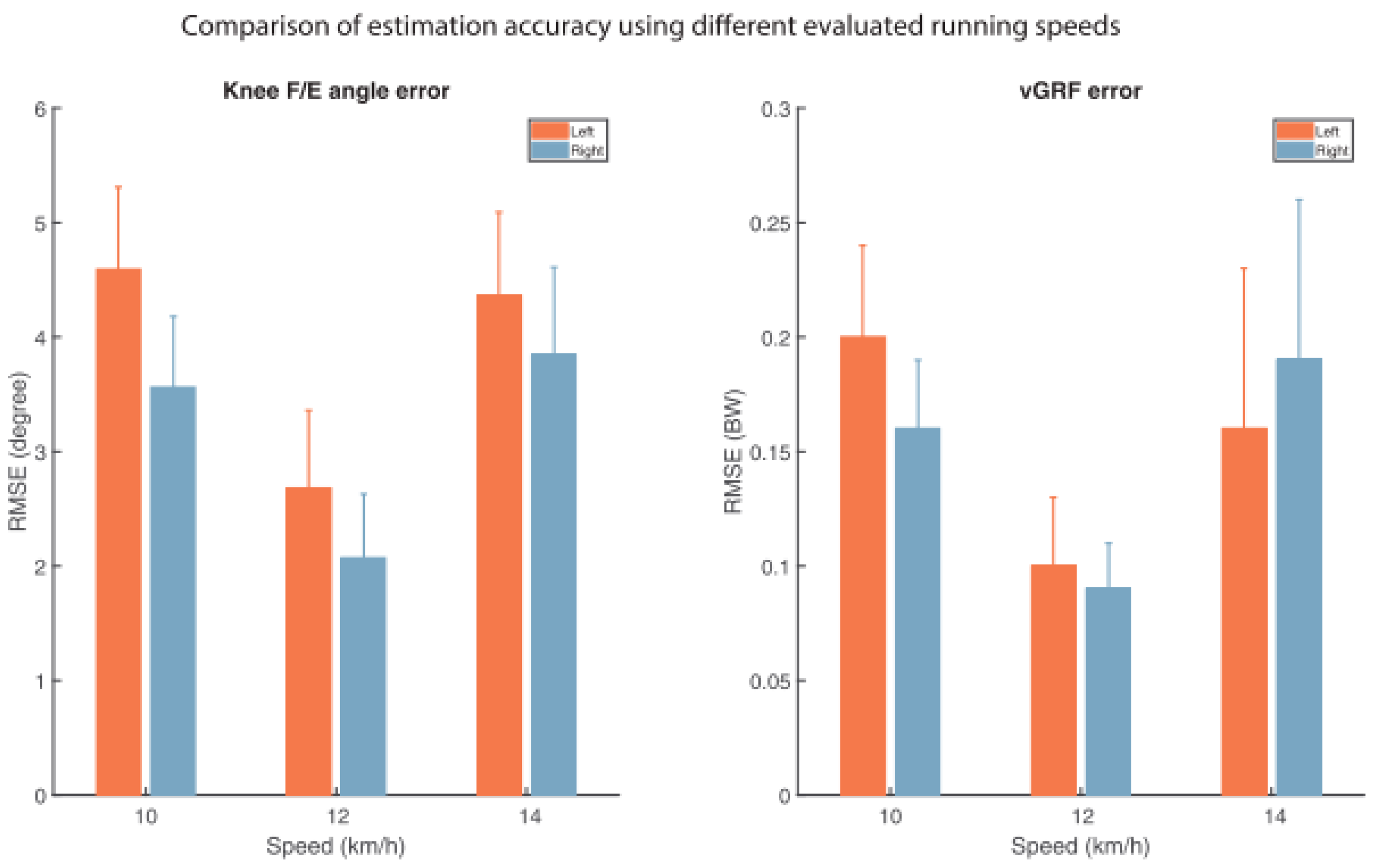
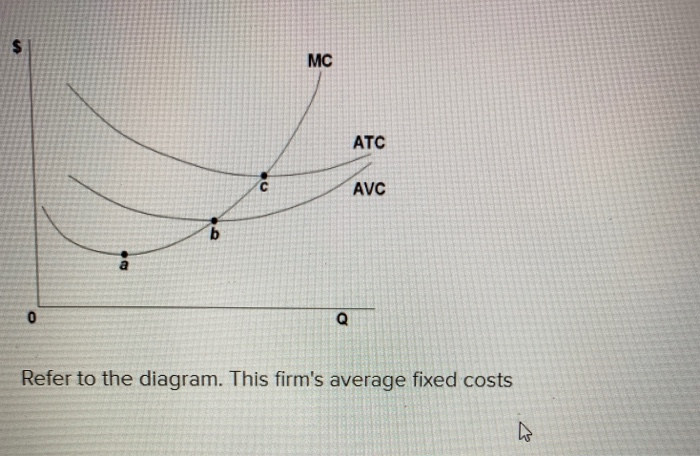
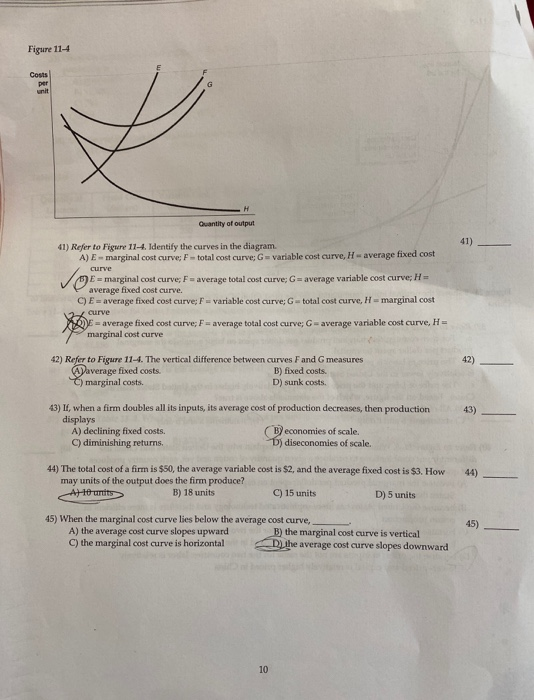
45 refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures
Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing - IPCC Myhre, G., D. Shindell, F.-M. Bréon, W. Collins, J. Fuglestvedt, J. Huang, ... and differences between models and observations persist, resulting in.82 pages › firm › top-3-theoriesTop 3 Theories of Firm (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion The slope of the TR curve measures MR and the slope of the TC curve measures MC. At points A and B, two curves have the same slope. Thus at OQ*, MR = MC. This can be verified by passing two tangents — one through A and the other through B and ensuring that they are parallel.
PDF Horizontal Curves reverse curves. In the case of stream crossings or bluffs, it is a matter of not starting a curve until a certain point is reached. In the case of reverse curves, the total tangent distance between PI's must be shared by two curves and not overlap. Some road standards may call for a minimum tangent between curves. In any
Refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures
Chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical difference between curve F and G measures average fixed costs The marginal product of labor is defined as the additional output that results when one more worker is hired, holding all other resources constant If the marginal cost curve is below the average variable cost curve, then Appendix B: Indifference Curves - Principles of Economics Appendix B: Indifference Curves Economists use a vocabulary of maximizing utility to describe people's preferences. In Consumer Choices, the level of utility that a person receives is described in numerical terms. This appendix presents an alternative approach to describing personal preferences, called indifference curves, which avoids any need for using numbers to measure utility. Micro J Baker Chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizlet The vertical difference between curves F and G measures average fixed costs. If average total cost is $50 and average fixed cost is $15 when output is 20 units, then the firm's total variable cost at that level of output is $700 If, when a firm doubles all its inputs, its average cost of production decreases, then production displays
Refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures. Skew-T Parameters and Indices - National Weather Service They run horizontally from left to right and are labeled on the left side of the diagram. Pressure is given in increments of 100 mb and ranges from 1050 to 100 mb. Notice the spacing between isobars increases in the vertical (thus the name Log P). 11.3 The Expenditure-Output (or Keynesian Cross ... - OpenStax The second conceptual line on the Keynesian cross diagram is the 45-degree line, which starts at the origin and reaches up and to the right. A line that stretches up at a 45-degree angle represents the set of points (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3) and so on, where the measurement on the vertical axis is equal to the measurement on the horizontal axis. Environmental Economics, Econ 4545 Label area between MAC1 and MAC2 to the right of e1 as a. Label area below MAC2 to the right of e1 as b. Label area bounded by the charge line, MAC2, and e1 line as d. Label area bounded by MAC2, e1 line, and e2 line as c. Label area bounded by the charge line, e2 line, and the two axes as f. Compliance cost with MAC1 technology = (a+b+c+d+f) 42 refer to figure 11-5. identify the curves in the diagram. Identify the curves in the diagram. ... Refer to Figure 11-5. The vertical difference between curves F and G measures. average fixed costs. 1. If average total cost is $50 and average fixed cost is $15 when output is 20 units, then the firm's total variable cost at that level of output is. ... Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the ...
Solved Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical - Chegg Question: Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical difference between curves F and G measures marginal costs. average fixed costs. sunk costs. fixed costs. This problem has been solved! See the answer Why? Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (3 ratings) Since F curve denote ATC and G c … View the full answer 5.5 Contour Lines and Intervals | NWCG 5.5 Contour Lines and Intervals. A contour line is a line drawn on a topographic map to indicate ground elevation or depression. A contour interval is the vertical distance or difference in elevation between contour lines. Index contours are bold or thicker lines that appear at every fifth contour line. If the numbers associated with specific ... 1 Surveying Besavilla [vnd1513g6gnx] cD Compute the difference in elevation betWeen B and C, considering the effect of fheeartl1s curvature and refraction. @) CQmpute the difference in elevatiori between Aand C. @ Gompute the elevation ofB. A transit is sef up at point Bwhich is between Aand B. The Yertical angle obsef\led towards Ais known to be . 20' and thai of C is +12'. textbook-of-engineering-drawing.pdf - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
16 RefertoFigure10 4 Identifythecurvesinthediagram A E ... Identify the curves in the diagram. ... The vertical difference between curves F and G measures A) average fixed costs. B) marginal costs. C) fixed costs. D) sunk costs. 18) Refer to Figure 10-4. Curve G ... A Basic Introduction to Rheology - Technology Networks To measure shear viscosity using a single head (stress controlled) rotational ... Figure 3 - Typical flow curves for shear thinning fluids with a zero shear ...20 pages Chapter 1 Surveying - USDA (210-VI-EFH, October 2008) 1-vii Part 650 Engineering Field Handbook Chapter 1 Surveying Tables Table 1-1 Accuracy standards for horizontal and vertical control 1-3 Table 1-2 List of common abbreviations used 1-12 Table 1-3 Calculations for the angles and sides in figure 1-7 1-19 Table 1-4 Relationships between azimuths and bearings 1-25 PDF Chapter 15 Construction Survey Procedures (Refer to Chapter 9,"Total Station System"). 15-02.5 Modified Conventional Method There are times when it is advantageous to use the Data Controller with a Roading-type slope staking module to set out slope stakes. Input roadway design templates, horizontal and vertical alignments, and superelevation rate data in the Data Controller before ...
Chapter 8 Micro Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical difference between curves F and G measures As the size of the firm increases it becomes more difficult to coordinate the operations of its manufacturing plants.
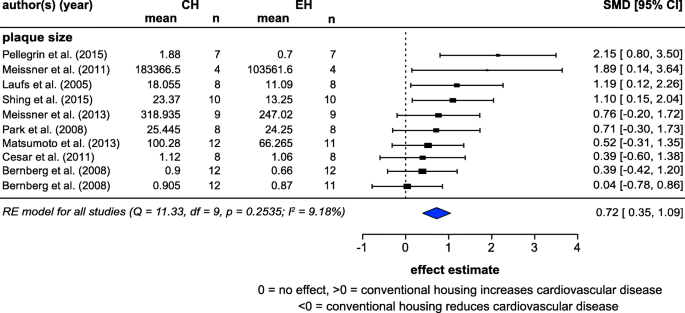
(PDF) The Early Origins and Development of the Scatterplot is shown as a bar graph using the right vertical scale, also with a range of 0-100. ... ally difficult to judge the difference between two curves. ... or between such measures in parents and ...
5.1 Externalities - Principles of Microeconomics Consider our diagram of a negative externality again. Let's pick an arbitrary value that is less than Q 1 (our optimal market equilibrium). Consider Q 2.. Figure 5.1b. If we were to calculate market surplus, we would find that market surplus is lower at Q 2 than at Q 1 by triangle e.. The market surplus at Q 2 is equal to area a+b. [(a+b+c) - (c)].
PDF Chapter 11 Geometrics - Washington State Department of ... P.C.C. Point of compound curvature - Point common to two curves in the same direction with different radii P.R.C. Point of reverse curve - Point common to two curves in opposite directions and with the same or different radii L Total length of any circular curve measured along its arc Lc Length between any two points on a circular curve
Indifference Curves - Overview, Diminishing Marginal ... Indifference curves assume a convex shape. As illustrated above in the indifference curve map, the curve gets flatter as you move down the curve to the right. It illustrates that all individuals experience diminishing marginal utility, where additional consumption of another good will generate a lesser amount of utility than the prior.
ECON 8 FINAL Flashcards - Quizlet 29. Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. A.E = average fixed cost curve, F = variable cost curve, G = total cost curve, H = marginal cost curve B. E = average fixed cost curve, F = average total cost curve, G = average variable cost curve, H = marginal cost curve
A Complete Guide to Line Charts | Tutorial by Chartio As time progresses from left to right, points connect the daily exchange rates. We can read from the general slope of the line and its vertical positions that the rate improved from about 0.75 to 0.78 between March and early April, then fell gradually to about 0.765 in late May and June. When you should use a line chart
› the-economy › bookUnit 3 Scarcity, work, and choice – The Economy - CORE Draw a diagram with free time on the horizontal axis and weekly pay on the vertical axis, and plot the combination of hours and the wage corresponding to your job offer, calling it A. Assume you need about 10 hours a day for sleeping and eating, so you may want to draw the horizontal axis with 70 hours at the origin.
PDF Course Objectives Chapter 4 4. Stability assumed vertical center of gravity, using the Cross Curves of Stability. 7. Correct a GZ curve for a shift of the ship's vertical center of gravity and interpret the curve. Draw the appropriate sectional vector diagram and use this diagram to show the derivation of the sine correction. 8.
The vertical distance between the horizontal axis and any ... The vertical distance between the horizontal axis and any point on a pure competitor's demand curve measures: A) total revenue. B) total cost. C) product price, marginal revenue, and average revenue. D) the quantity demanded. Answer: C. C ) product price , marginal revenue , and average revenue . Type: A Topic: 2 E: 416 MI: 172 28.
Practice Problems Ch. 11 Technology, Production, and Costs ... The vertical difference between curves F and G measures. A) average fixed costs. B) marginal costs. C) fixed costs. D) sunk costs. 38. Refer to the figure.10 pages
IS-Curve: Subject Matter, Shifting, Slope and Position ... ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make an in-depth study of the IS-Curve:- 1. Subject Matter of the IS-Curve 2. Shifting of the IS Curve 3. The Slope and Position of the IS Curve. Subject Matter of the IS-Curve: The AS'-curve is concerned with interest-induced changes in aggregate demand. The investment function is of great importance to Keynesian […]
Contemporary Economic Analysis (Routledge Revivals): Papers ... David Currie, Will Peters · 2016 · Business & EconomicsThe vertical axis measures d, the ratio of public debt to income, ... the difference between WW and SS, at that r Curve DD may or may not be steeper than SS ...
PDF Unit 10 Practice Test Solutions - Turlock High AP CHEMISTRY The elements K and Cl react directly to form the compound KCI according to the equation above. Refer to the information above and the table below to answer the questions that follow. Process C12(g) 2 Cl(g) Cl(g) + e- CF(g) K+(g) + Cl-(g) KC1(s) (kJ/molrxn) -DI-I 34 (A) 87.4 kJ is released B 43.7kJ is released ( 43.7 kJ is absorbed
Inflationary and Deflationary Gap (With Diagram) In other words, because of full employment, output cannot increase to Y*. Thus at Y f level of full employment output, there occurs an inflationary gap to the extent of AB. The vertical distance between the aggregate demand and the 45° line at the full employment level of national income is termed the inflationary gap.
ECON 3630 Test 3 Flashcards - Quizlet The vertical difference between curves F and G measures average fixed costs. 1. If average total cost is $50 and average fixed cost is $15 when output is 20 units, then the firm's total variable cost at that level of output is $700 1. If production displays economies of scale, the long-run average cost curve is downward sloping.
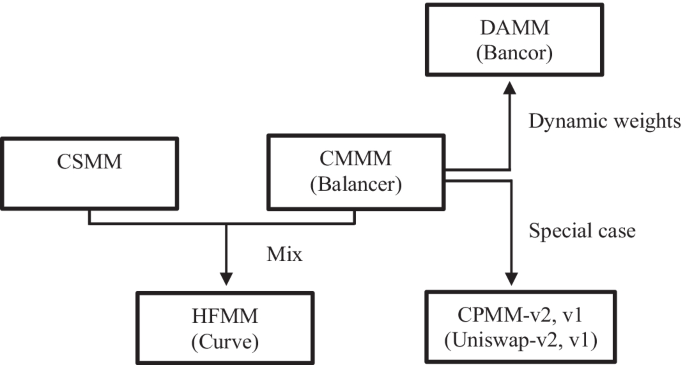
TikZ and pgf 13.12.1Referencing a Node in a Different Picture . ... features of TikZ or pgf, just of those that you are likely to use right away.405 pages
Micro J Baker Chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizlet The vertical difference between curves F and G measures average fixed costs. If average total cost is $50 and average fixed cost is $15 when output is 20 units, then the firm's total variable cost at that level of output is $700 If, when a firm doubles all its inputs, its average cost of production decreases, then production displays
Appendix B: Indifference Curves - Principles of Economics Appendix B: Indifference Curves Economists use a vocabulary of maximizing utility to describe people's preferences. In Consumer Choices, the level of utility that a person receives is described in numerical terms. This appendix presents an alternative approach to describing personal preferences, called indifference curves, which avoids any need for using numbers to measure utility.
Chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram to the right. The vertical difference between curve F and G measures average fixed costs The marginal product of labor is defined as the additional output that results when one more worker is hired, holding all other resources constant If the marginal cost curve is below the average variable cost curve, then













:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Skewness2-866dfeb82de440aea40aed9eb6e59e57.jpg)


0 Response to "45 refer to the diagram to the right. the vertical difference between curves f and g measures"
Post a Comment