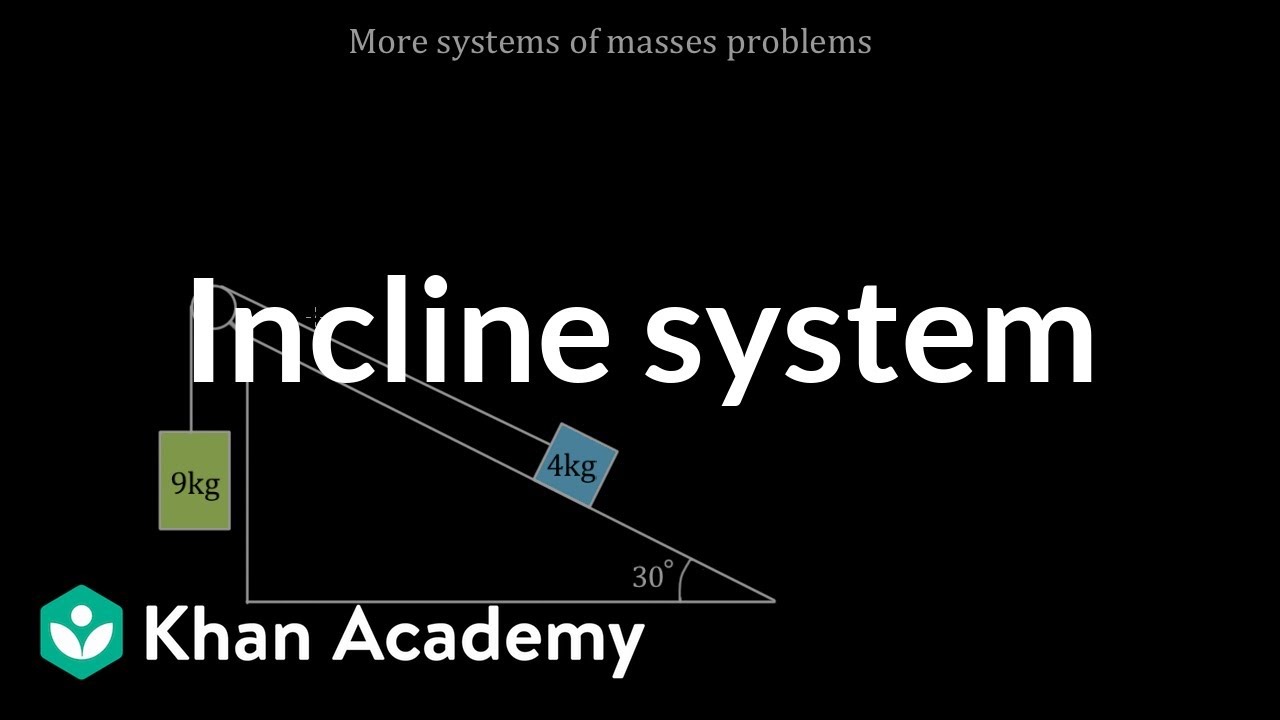
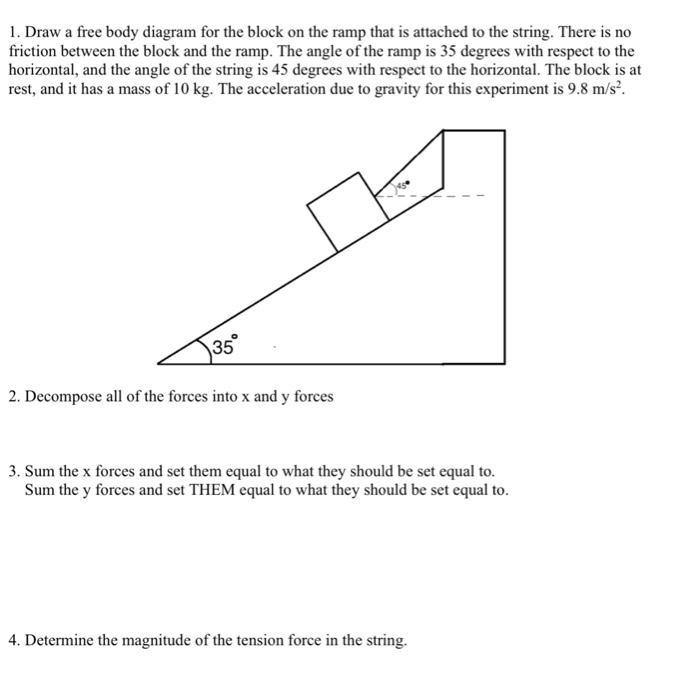
45 free body diagram block on ramp
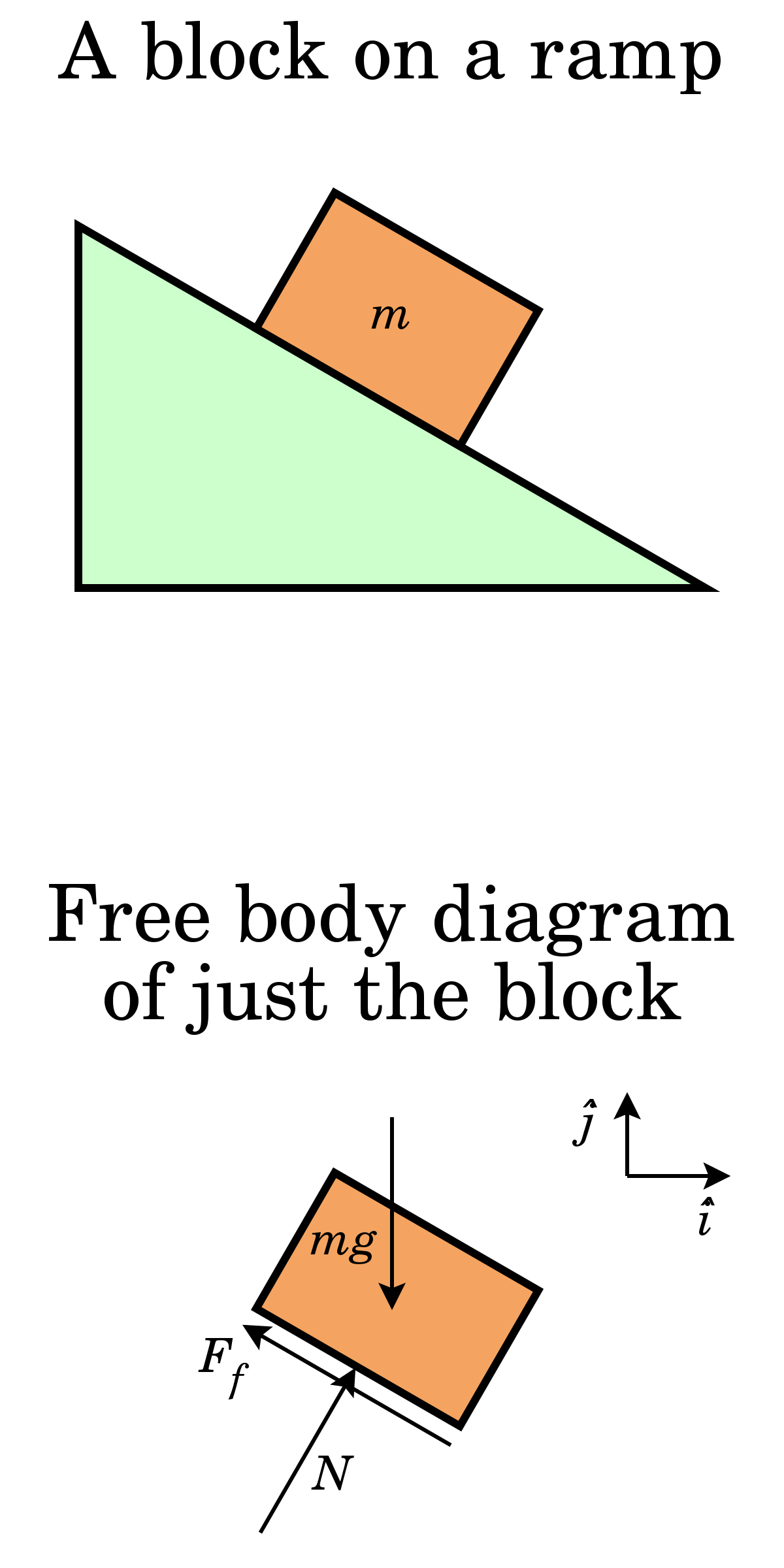
Force Body Diagrams of object sliding down ramp The cart would have a normal and fiction force from the ramp, a normal and friction force from the chocolate, and gravity. The chocolate would have the normal and friction force from the cart (equal and opposite to the cart's from the chocolate as per newtons third law) and gravity. This is true in general for multiple bodies, as long as they ... PDF Motion of a Block on an Inclined Plane Aim: Pre-Lab ... 2. The normal force: The block is sitting on the incline. So the block exerts a force on the surface of the incline. So from Newton's Third Law (action-reaction), the incline exerts a force back on the block. This force, called the 'Normal force', acts on the block so it must be included in the free body diagram of the block.
Block on ramp: Free-Body Diagram - GeoGebra Free body diagram of a block on a ramp, without friction. Drag the point at the top of the ramp to change the ramp angle. Note how the green angles always track one another.

Free body diagram block on ramp
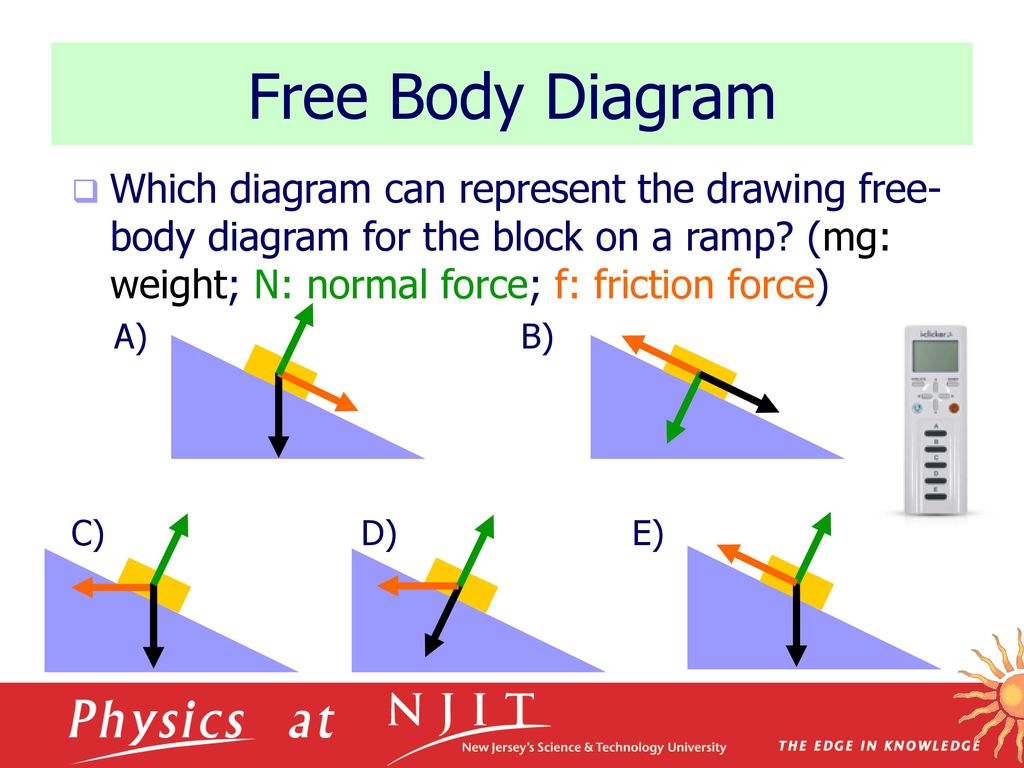
PDF Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 5 - New Jersey Institute of ... qSuppose a block with a mass of 2.50 kg is resting on a ramp. If the coefficient of static friction between the block and ramp is 0.350, what maximum angle can the ramp make with the horizontal before the block starts to slip down? Block on a Ramp | Math & Physics Problems Wikia | Fandom Problem. Figure 1. Free-body diagram of the block on a ramp. The free-body diagram (Figure 1) illustrates a block of mass that is stationary on a ramp (inclined plane). The angle of inclination is , and the coefficient of static friction is .. Part 1: Identify the forces in the free-body diagram. Part 2: Determine the formula for calculating the largest angle in which the block will remain ... 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton's third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance →A 21 A → 21 is the action force of block 2 on block 1. →A 12 A → 12 is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws. Example
Free body diagram block on ramp. Problem: Block pushed up a frictionless ramp | Phyley In this case we have a block moving up a ramp, so for our convenience, we will use tilted coordinate axes, with the x axis in the direction of motion (uphill). After drawing the coordinate axes on the free-body diagram of the block, we proceed to find the components of the individual forces acting on the block: Coefficient of Friction | Formula, Units & Examples - Video ... Sep 28, 2021 · Block A has a mass of 45 kg, and block B has a mass of 9 kg. The coefficients of friction between all surfaces of contact are mu_s = 0.20 and mu_k = 0.15. 1) If P = 0, determine the acceleration of b Solved Draw Free Body Diagrams (FBD) for the following ... Draw Free Body Diagrams (FBD) for the following systems: a. Block on a ramp b. Masses on a pulley c. Forces on a block d. Forces on connected objects with friction e. Forces on the plane attached with a string Expert Answer 100% (1 rating) Previous question Next question File:Free body diagram2.svg - Wikipedia Date: 26 May 2014, 15:54:31: Source: Own work: Author: Krishnavedala: SVG development The source code of this SVG is This vector image was created with a text editor. This SVG file uses embedded text that can be easily translated using a text editor.
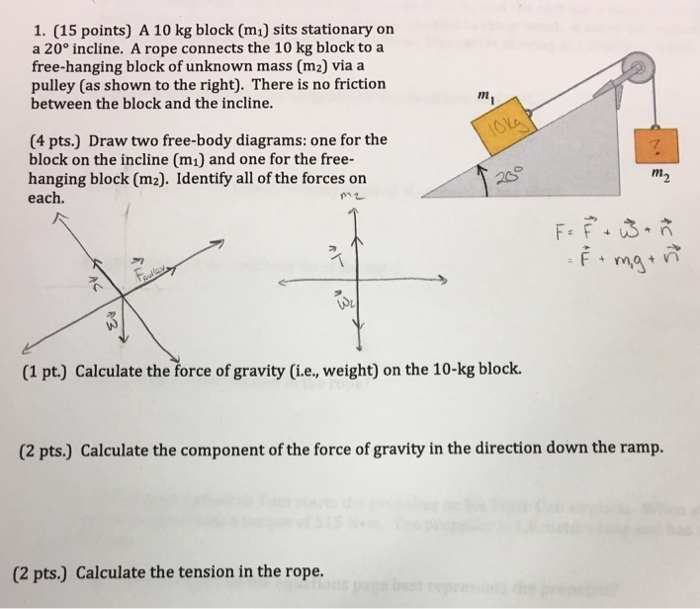
Ramp: Forces and Motion - Force | Position | Velocity - PhET Explore forces and motion as you push household objects up and down a ramp. Lower and raise the ramp to see how the angle of inclination affects the parallel forces. Graphs show forces, energy and work. 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams | University Physics Volume 1 Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton's third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance →A 21 A → 21 is the action force of block 2 on block 1. →A 12 A → 12 is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws. Example Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - University Physics Volume 1 Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton's third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance →A 21 A → 21 is the action force of block 2 on block 1. →A 12 A → 12 is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws. Free Body Diagrams on friction less surface - Physics Forums A 270-g block on the ramp is attached to a 75.0-g block using a pulley, as shown in the figure below. (a) Draw two free-body diagrams, one for the 270-g block and the other for the 75.0-g block. (b) Find the tension in the string and the magnitude of the acceleration of the 270-g block. (c) The 270-g block is released from rest.
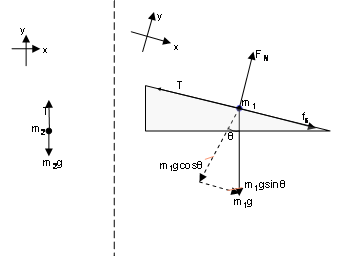
Solved 1. A block is at rest on a ramp. Draw a free-body ... 1. A block is at rest on a ramp. Draw a free-body diagram of the block in the space below. Label each force that you have included in your free-body diagram to indicate (1) the type of force, (2) the object on which the force is exerted, and (3) the object exerting the force Ramp Block 2. Answered: (a) Draw the free body diagrams for the… | bartleby (a) Draw the free body diagrams for the two blocks pictured below. There is friction on the ramp. 40° (b) Draw free body diagrams for the two situations involving a block of ice being pulled and pushed with an equal force and angle. 25° (c) Is the normal force up on the block of ice from the floor equal in the two situations in (b)? Free body diagram for a non-fixed (movable) ramp, with a ... I'm having trouble figuring out how this free body diagram would look. The question involves a block at rest on a ramp, which is in turn at rest on a table. All objects are made of the same material, with the same coefficients of friction. Below is what I've got so far, but it doesn't seem correct. 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - University Physics Volume 1 Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton's third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance is the action force of block 2 on block 1. is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws. Example Block on the Table (Coupled Blocks)
How to Make a Free Body Diagram - Saint Mary's Physics Demos In this demonstration, a wood block is pulled up an inclined plane by masses hanging from a pulley attached to the ramp. See Figure 1 for a diagram of the demo set up. Figure 1: Detailed Free-Body Diagram. Free body diagrams show all of the forces acting on each individual mass in a system.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
What is a Free-Body Diagram and How to Draw it (with ... What is a free-body diagram? A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body ...
7.3 Work-Energy Theorem - University Physics Volume 1 - OpenStax Draw a free-body diagram for each force on the object. Determine whether or not each force does work over the displacement in the diagram. Be sure to keep any positive or negative signs in the work done. Add up the total amount of work done by each force. Set this total work equal to the change in kinetic energy and solve for any unknown parameter.
Free body diagram with angled forces: worked example ... Include the force of friction acting on this block and include the normal force of the wall acting on the block as well. Pause the video and try to have a go at it. So before I even start to draw the free body diagram, let's break down this force into its vertical and horizontal components. So the first thing, let me do its vertical component.
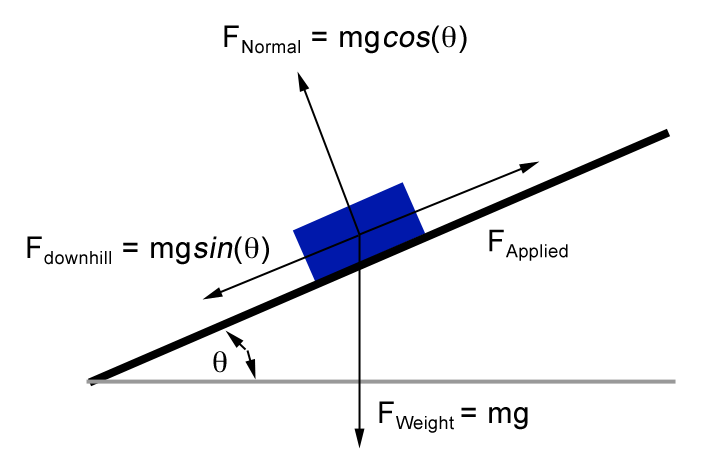
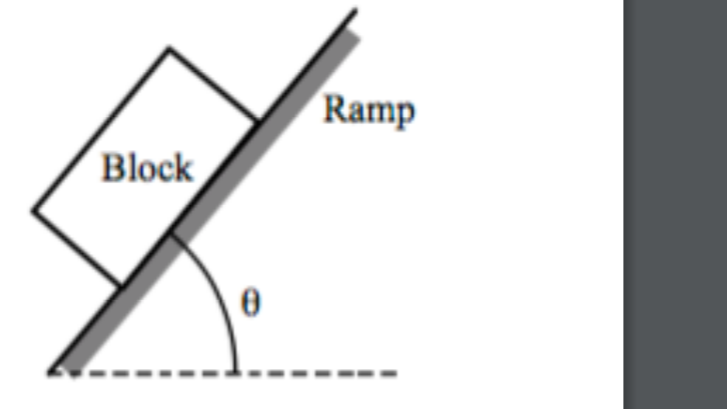
Free body diagram - Wikipedia Free body diagram From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Block on a ramp and corresponding free body diagram of the block. A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it.
PDF Explain the concept of free body diagram Diagram showing applied forces and moments on a physical body Block on a ramp and corresponding free body diagram of the block. A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it.
3 Ways to Calculate Acceleration - wikiHow Jun 14, 2021 · Solution: This problem uses tricky language to try and catch you. Draw a diagram and you'll see the forces are 150 newtons right, 200 newtons right, and 10 newtons left. If "right" is the positive direction, the net force is 150 + 200 - 10 = 340 newtons. Acceleration = F / m = 340 newtons / 400 kg = 0.85 m/s 2.
Free Body Diagrams - Tension, Friction, Inclined Planes ... This physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acceleration. It explains when to uses...
Free Body Diagrams, Tutorials with Examples and Explanations The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn.
Free Body Diagram - What is FBD and How to draw an FBD ... In a free body diagram (FBD), all the forces acting on a body are shown with their magnitudes and direction. The purpose of the FBD is to ensure that we consider all the forces acting on the body properly without missing out on any. If there is more than one body in the problem, each body requires an FBD.
Wikizero - Free body diagram Block on a ramp and corresponding free body diagram of the block. A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it.
Free Body Diagram - 941 Words | Cram Move the ramp to an angle of zero (horizontal) and draw a free body diagram of the cabinet here: On a horizontal plane, the normal force is _Perpendicular_______ to the weight. The cabinet has a mass of 100kg. It therefore has a normal force of __-100______ N and a friction force (on the horizontal plane) of _2.22N_ μ = 0.30.
6.8: Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics LibreTexts We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws. Example 6.8. 3: Block on the Table (Coupled Blocks) A block rests on the table, as shown. A light rope is attached to it and runs over a pulley. The other end of the rope is attached to a second block. The two blocks are said to be coupled.
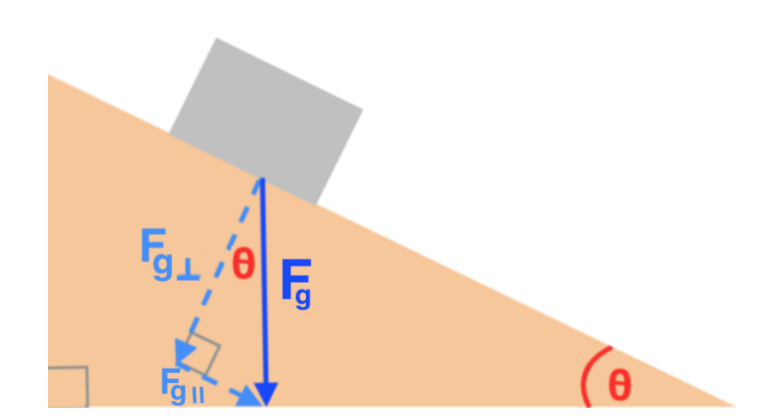
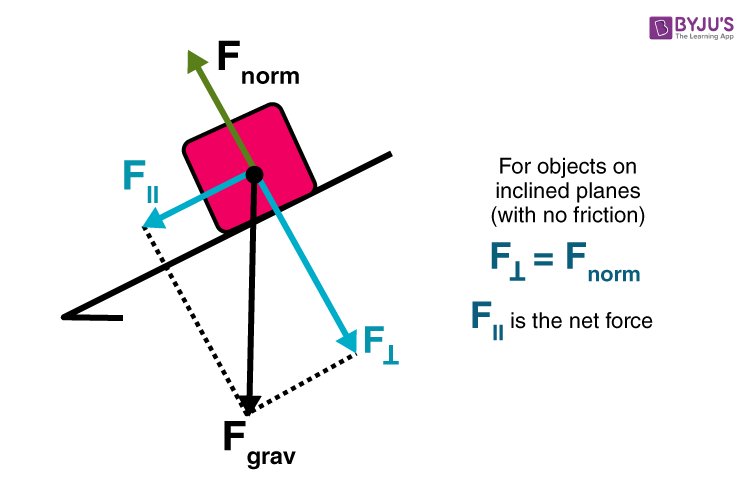
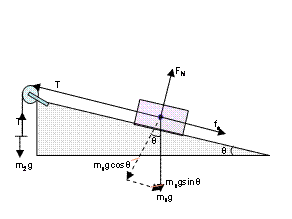
Ramps and Inclines - APlusPhysics Let's take the example of a box on a ramp inclined at an angle of Θ with respect to the horizontal. We can draw a basic free body diagram for this situation, with the force of gravity pulling the box straight down, the normal force perpendicular out of the ramp, and friction opposing motion (in this case pointing up the ramp).
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton's third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance →A 21 A → 21 is the action force of block 2 on block 1. →A 12 A → 12 is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton's Laws. Example
Block on a Ramp | Math & Physics Problems Wikia | Fandom Problem. Figure 1. Free-body diagram of the block on a ramp. The free-body diagram (Figure 1) illustrates a block of mass that is stationary on a ramp (inclined plane). The angle of inclination is , and the coefficient of static friction is .. Part 1: Identify the forces in the free-body diagram. Part 2: Determine the formula for calculating the largest angle in which the block will remain ...
PDF Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 5 - New Jersey Institute of ... qSuppose a block with a mass of 2.50 kg is resting on a ramp. If the coefficient of static friction between the block and ramp is 0.350, what maximum angle can the ramp make with the horizontal before the block starts to slip down?
![Solved 5. [1pt] Four free-body diagrams of a block on a ramp ...](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media%2F466%2F46655d69-2a32-4f84-ac56-ed81d13d08f1%2FphprvNYHD.png)


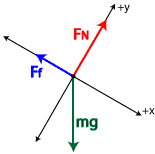







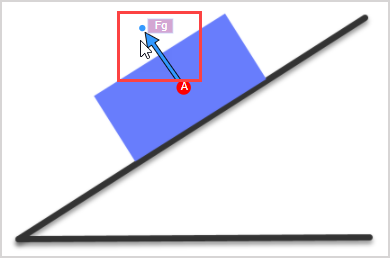








![Gr 11 Physics] Free Body diagram of a ramp : r/AskPhysics](https://external-preview.redd.it/jvOUyctCWu9d_r4DBRJCn0aI5uMZ-UlskKSAquuwkLM.jpg?width=640&crop=smart&auto=webp&s=4350c33cfaf04481cce0505a5e8e1954351d30d2)
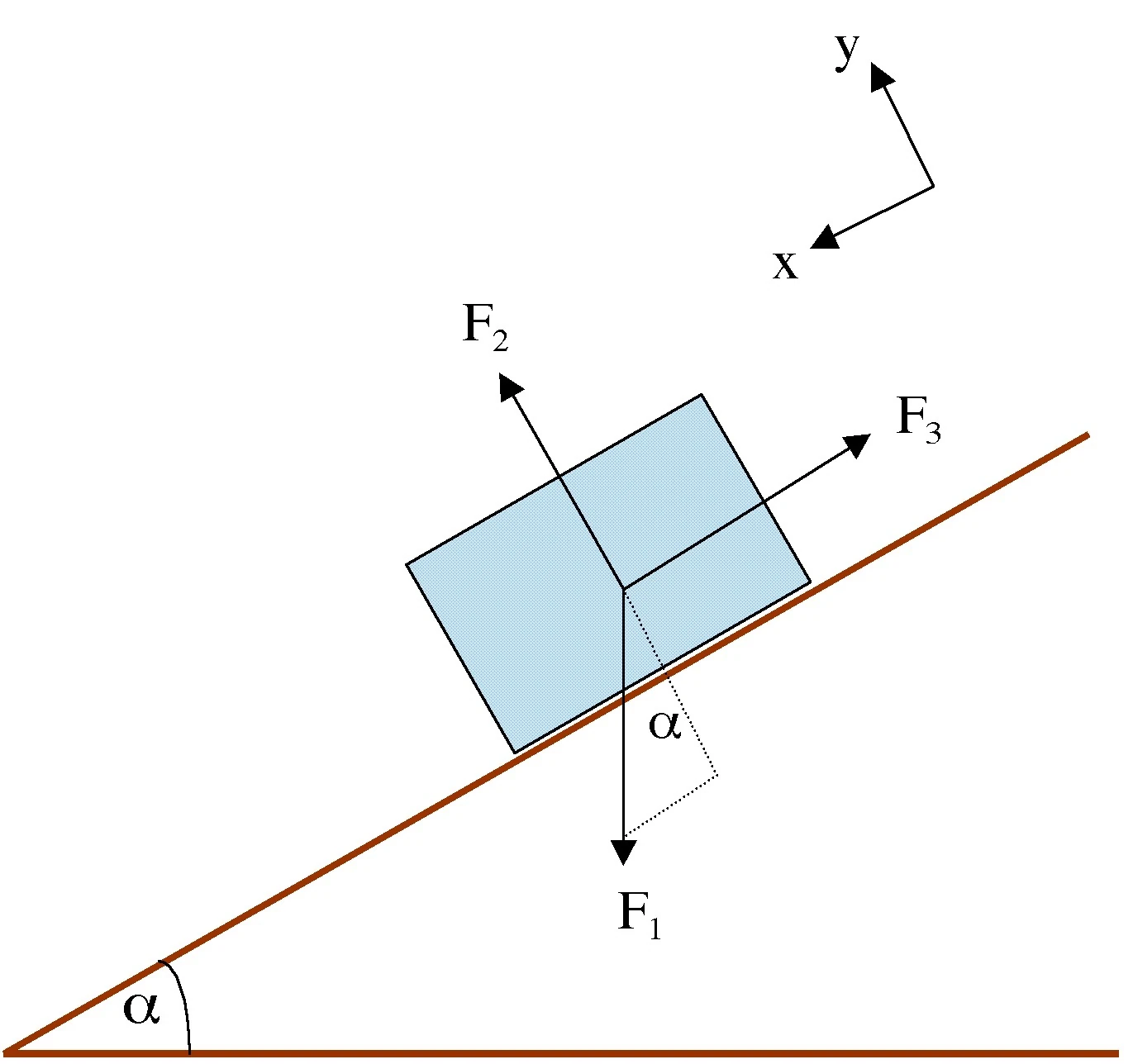

0 Response to "45 free body diagram block on ramp"
Post a Comment