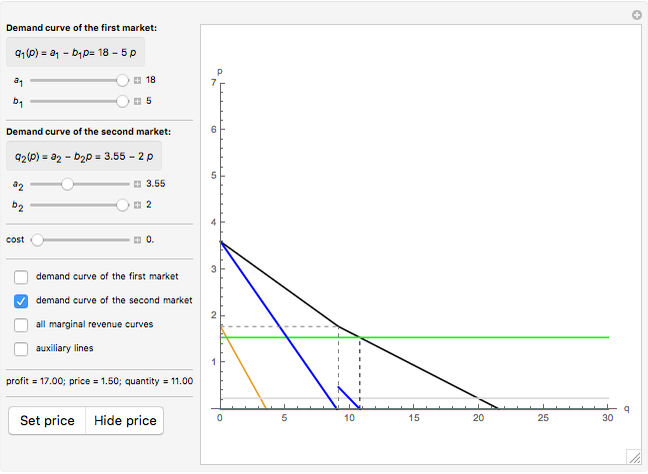
45 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output
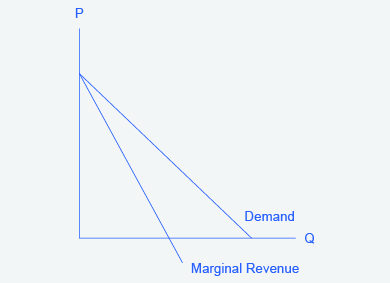
A nondiscriminating monopolist cannot maximize profits by producing where demand is: (a) above marginal cost. (b) price inelastic. (c) above marginal revenue. (d). price elastic. (e) greater than average fixed costs. 224. Price Elasticity of Demand and Total Revenue. Level: AS, A Level. Board: AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB. The relationship between elasticity of demand and a firm's total revenue is an important one.
Monopoly profit maximization dead weight loss price ceiling - 8.2 Fixing Monopoly Weight loss Because the monopolist is the only firm in the market, its demand curve is the same as the market demand curve, which is, unlike that for a perfectly competitive firm, downward-sloping.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output
The marginal cost of production is the cost of producing one additional unit. For instance, say the total cost of producing 100 units of a good is $200. The total cost of producing 101 units is ... (TCO 2) Total revenue falls as the price of a good is raised, if the demand for the good is (TCO 2) You are the sales manager for a software company and have been informed that the price elasticity of demand for your most popular software is less than 1. To increase total revenues, you should: Output Price ($) Marginal Revenue Average Cost $ Marginal Cost $ Tomos $16 13 10 7 $10 6 5 7 Loco v au WNO 16 14.5 13 11.5 1 1 answer please do not copy and paste the answer I need unique answer please thank you.
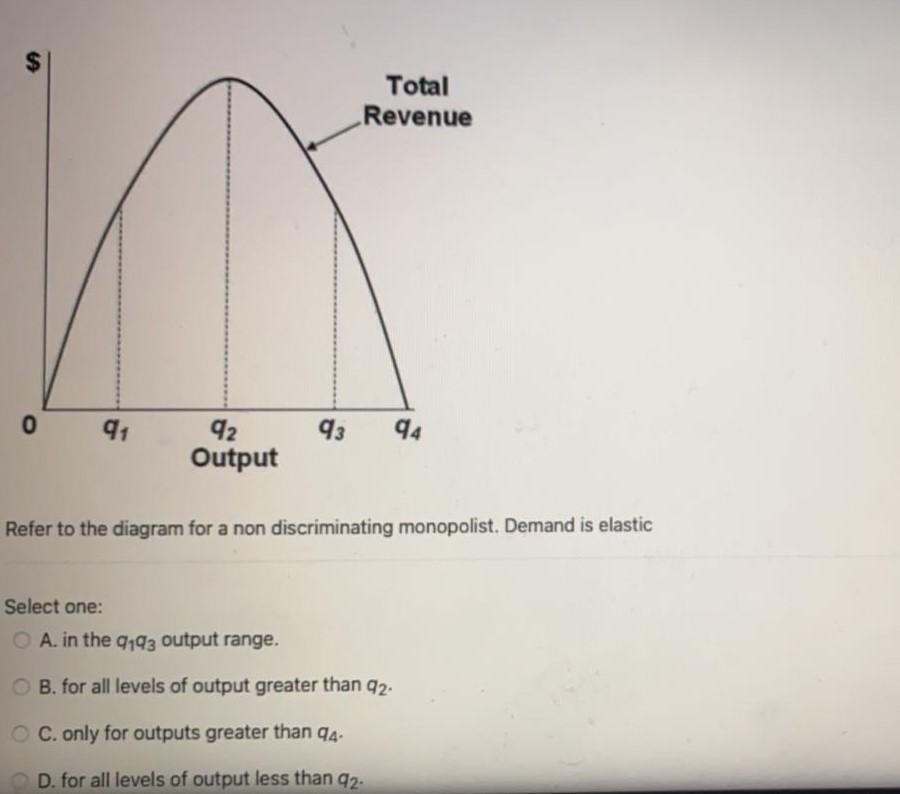
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output. d. Find the competitive price and quantity (as if the above marginal cost curve represents the market supply curve. (3 marks) e. Plot a graph on which you illustrate the monopoly's profit maximizing quantity and price, the competitive profit maximizing quantity and price and deadweight loss due to monopoly. (9 marks) f. Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Production and Costs Class 11 Economics MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. For a pure monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price be cause: C. when a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. 3. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Demand is elastic: C. for all levels of output less than q 2. 4. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its ...
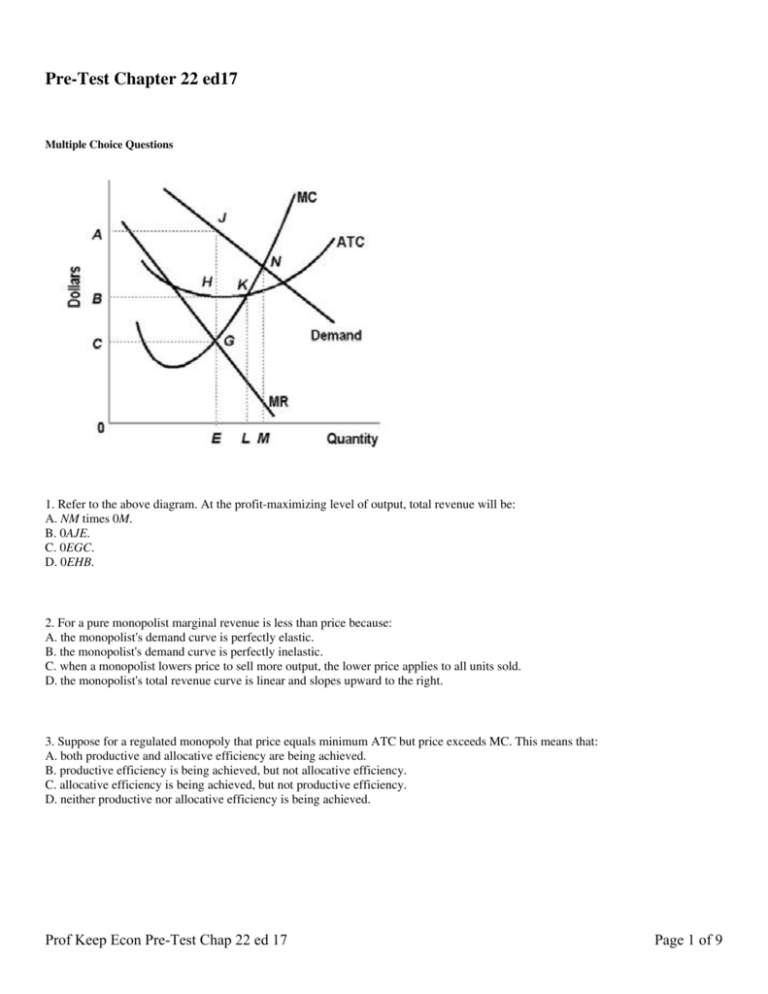
Business Game: Monopolist App for iPhone - Free Download ... 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ. B) an economic profit of ACGJ. C) a loss of GH per unit. D) a loss of JH per unit. 10. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will ... 16. If the marginal cost of producing this good rises by $3 at every output level, then the new equilibrium price will be _____. a) There is insufficient information to calculate the new equilibrium price b) $3. c) $8. d) $10. 17. Consider the supply and demand diagram drawn below. What does the equilibrium price equal in this market? a) $8. b ... TOPIC 4: POPULATION AND DEVELOPMENT ~ GEOGRAPHY FORM 6 $45, her marginal revenue is: $-55. $55. $1,100. $-1,100. The table below shows the marginal revenue and costs for a monopolist. Demand, Costs, and Revenues Price (dollars) Quantity Demanded Marginal Revenue (dollars) Marginal Cost (dollars) Average Total Cost (dollars) $130 200 $110 $25 $139.00 120 300 90 32 103.30 110
for all levels of output less than q 2. 4. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: B. q 2. Cassie's Quilts alters, reconstructs and restores heirloom quilts. Cassie has just spent $800 purchasing, cleaning and reconstructing an antique quilt… Price-output behavior 25-78 4. Efficiency aspects 79-88 5. Oligopoly: definition; characteristics 89-112 ... more difficult than under pure competition but not nearly as difficult as under pure monopoly. C) more difficult than under pure monopoly. D) blocked. Ans: 4. Monopolistic competition resembles pure competition because: ... 35 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output ... the context of the financial problems experienced by developing countries and emerging economies , this refer s to th…
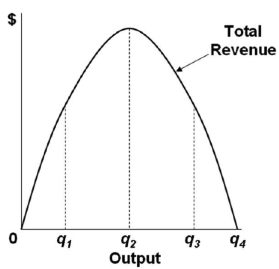
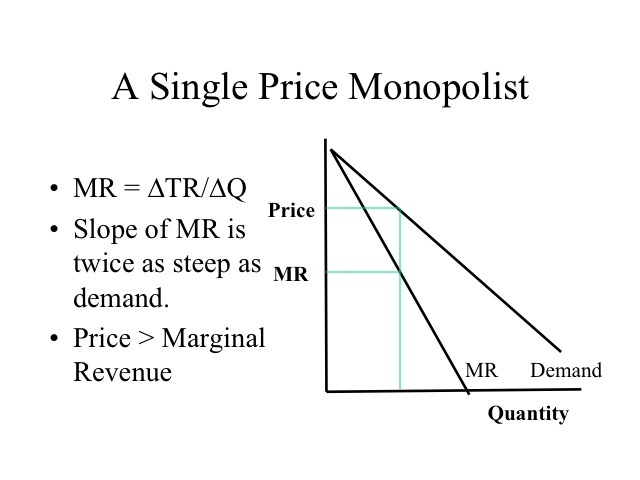
The level of output that maximizes a monopoly's profit is calculated by equating its marginal cost to its marginal revenue. Key Takeaways A monopolistic market is where one firm produces one product.
The Profit Maximization Rule states that if a firm chooses to maximize its profits, it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost (MC) is equal to Marginal Revenue (MR) and the Marginal Cost curve is rising. In other words, it must produce at a level where MC = MR. Profit Maximization Formula. The profit maximization rule formula is. MC = MR ...
Marginal cost refers to the additional cost to produce each additional unit. For example, it may cost $10 to make 10 cups of Coffee. To make another would cost $0.80. Therefore, that is the marginal cost - the additional cost to produce one extra unit of output. Marginal cost comes from the cost of production.
To understand how to calculate total cost, you will need to know two terms: Fixed cost: A cost that is constant and already set in stone, such as the cost of leasing a warehouse or the cost of renting an apartment. Variable cost: The opposite of fixed cost: A cost that changes based on how many goods the company produces or how much of a service or additional services a person uses.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. ... C. for all levels of output less than q 2. ... Marginal revenue will be zero at output: B. q 2. Rating: 5 · 1 review
18. If elasticity of demand is -2, marginal cost is 4, and average cost is 6, a profit maximizing markup price is. A. 4. B. 6. C. 8. D. 10. E. 12. 19. A chemical company can produce Q units of a chemical H, with marginal costs of MC = 9 + Q, and can distribute the chemical at marketing marginal costs of MC = 1.
25. (TCO 3) At an output of 20,000 units per year, a firm's variable costs are $80,000 and its average fixed costs are $3. The total costs per year for the firm are: 26. (TCO 3) If the price of a fixed factor of production increases by 50 percent, what effect would this have on the marginal-cost schedule facing a firm? ECON 312 Midterm Exam 2. 1.
Economists marginal utility to estimate how much of a good or service customers want to buy. When more of the same unit is consumed and total utility rises, positive marginal utility occurs. When the opposite occurs, the product experiences negative marginal utility. The third common type of marginal utility is known as zero marginal utility.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q1. B. q2. Correct C. q3. D. q4. Why is it B?
Marginal revenue will be zero at output A. q1.B.q2.C. q3.D. q4. 45. Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-seeking monopolist ...

Playing Hard To Get An Economic Rationale For Crowding Out Of Intrinsically Motivated Behavior Sciencedirect
Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist ... Solved: Below Is A Graph Of A Monopolist. ... Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output ... Monopolist for Android - APK Download ... Price & Marginal Revenue for a Monopolist Micro Visual 3.10; A pure monopolist. - Topnewsdesk
The Ultimate Quiz On Microeconomics Part II. . 1. 2. 3. If a monopolist sets her output such that marginal revenue, marginal cost and average total cost are equal, economic profit must be: Indeterminate from the given information. 4. A monopolist has equated marginal revenue to zero.
If a perfectly competitive firm sells its product at the market price of $14 per unit, _____. its average revenue is $14 and its marginal revenue is also $14. Refer to Exhibit 8.4, which shows the demand and the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm. The firm will earn zero economic profit ____. at a price of P2.
Output Price ($) Marginal Revenue Average Cost $ Marginal Cost $ Tomos $16 13 10 7 $10 6 5 7 Loco v au WNO 16 14.5 13 11.5 1 1 answer please do not copy and paste the answer I need unique answer please thank you.
(TCO 2) Total revenue falls as the price of a good is raised, if the demand for the good is (TCO 2) You are the sales manager for a software company and have been informed that the price elasticity of demand for your most popular software is less than 1. To increase total revenues, you should:

True Or False Refer To The Diagram For A Nondiscriminating Monopolist The Profit Maximizing Output For This Firm Is M Study Com
The marginal cost of production is the cost of producing one additional unit. For instance, say the total cost of producing 100 units of a good is $200. The total cost of producing 101 units is ...

Figure Monopolist Refer To The Figure Based On The Demand Curves For A Monopolist S Product In Homeworklib

Pure Monopoly Demand Revenue And Costs Price Determination Profit Maximization And Loss Minimization
(186).jpg)

















0 Response to "45 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. marginal revenue will be zero at output"
Post a Comment