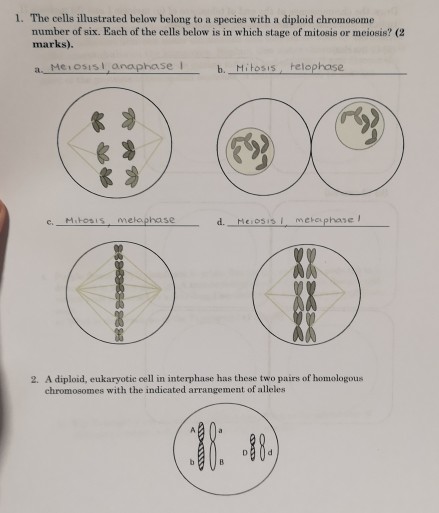
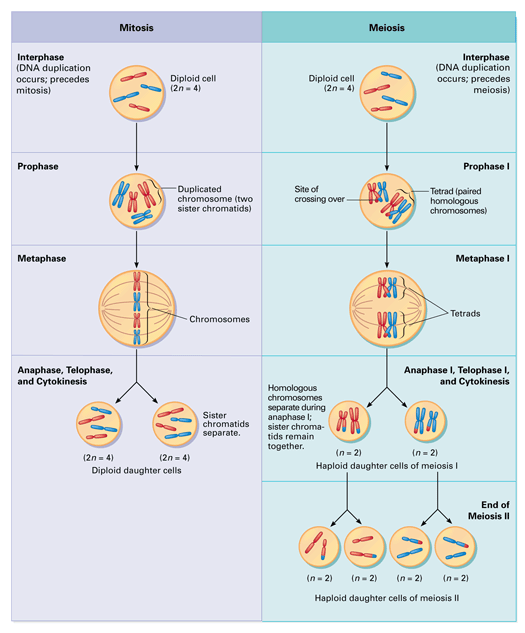
44 diagram the arrangement of the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis
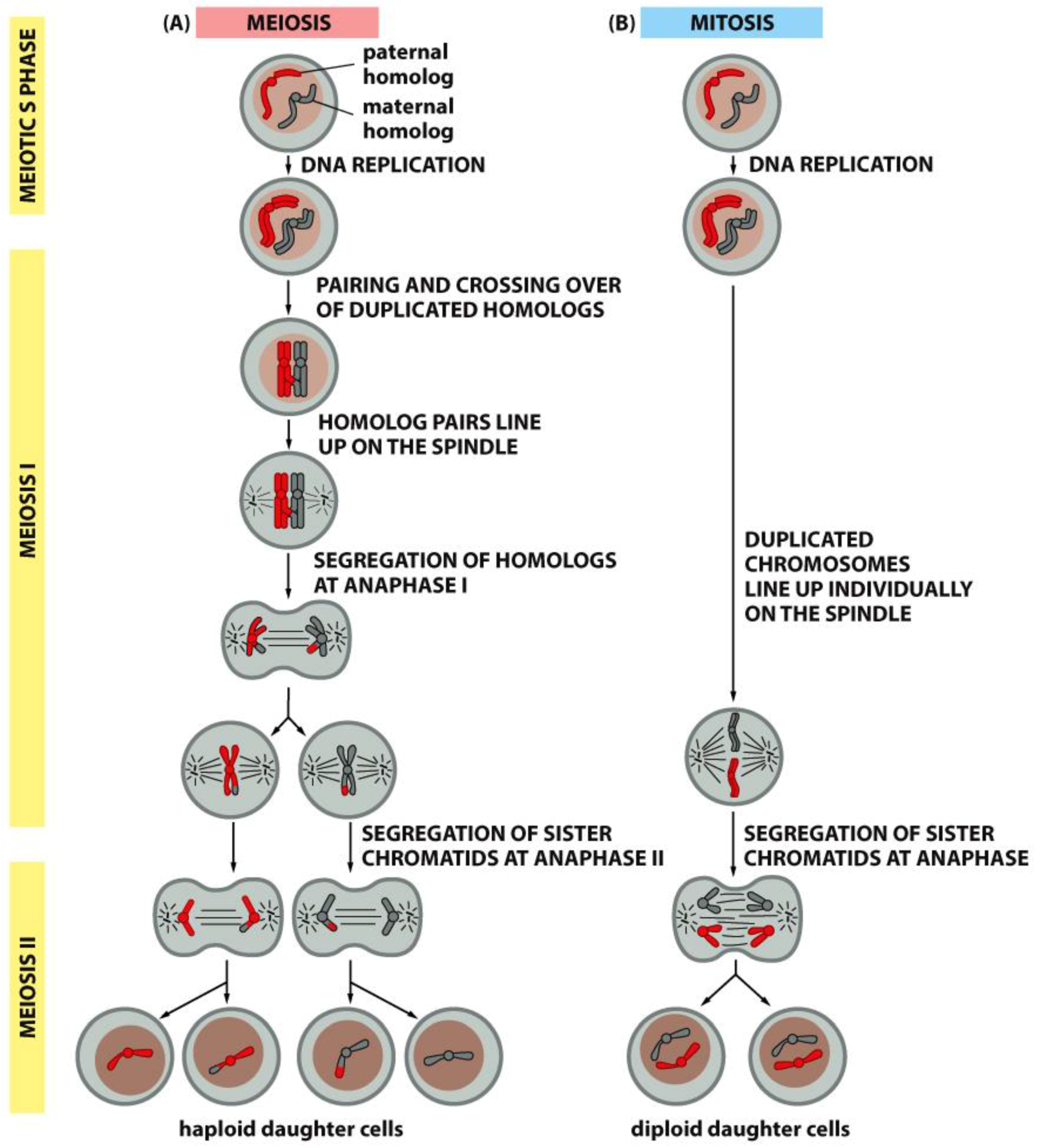
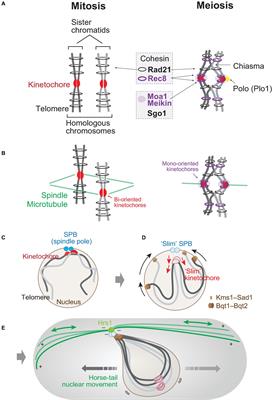
Although meiosis is different from mitosis in many ways, one of the most essential characteristics in meiosis could be pairing of homologous chromosomes. Meiosis might have first evolved from mitosis through the acquisition of homolog pairing as an additional step ( Wilkins and Holliday, 2009 ).
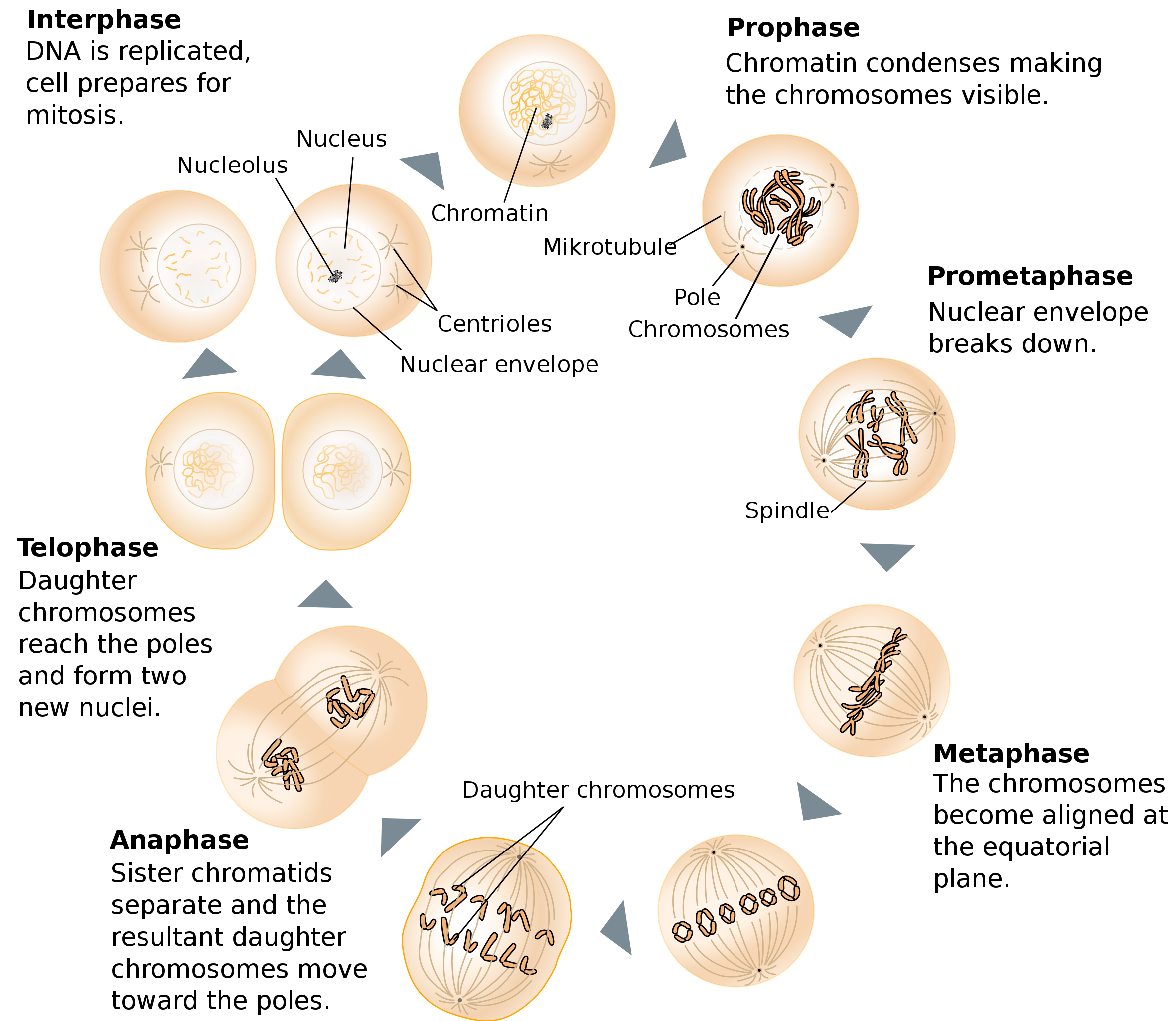
Chromosomes arrange at the centre of the cell called the metaphase plate.I ANAPHASE Splitting of each chromosome at centromere into two sister chromatids. Two chromatids start moving towards opposite poles. TELOPHASE Telophase is the last stage of mitosis which involves
This can identified by the arrangement of chromosomes in the equatorial plane. ... Describe the events taking place in the various stages of karyokinesis of a cell undergoing mitosis. (Structure of Chromosomes Cell Cycle and Cell Division ICSE Class 10 Biology) Ans. a. Prophase ... Mitosis b. Meiosis.

Diagram the arrangement of the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis
In mitosis, the nuclear membrane is broken down, spindle fibres (microtubules) attach to the chromatids at the centromere and pull apart the chromatids. When the chromatids reach separate ends of the cells, the spindle fibres disintegrate and a nuclear membrane rebuilds around the chromosomes making two nuclei.
Modeling Meiosis Using Google Slides. Shannan Muskopf December 18, 2020. This activity was designed for remote learning during the 2020 Pandemic. Normal lessons on meiosis might have students label drawings, view animations, or even make models on their desks to show how homologous chromosomes pair and exchange DNA during crossing-over.
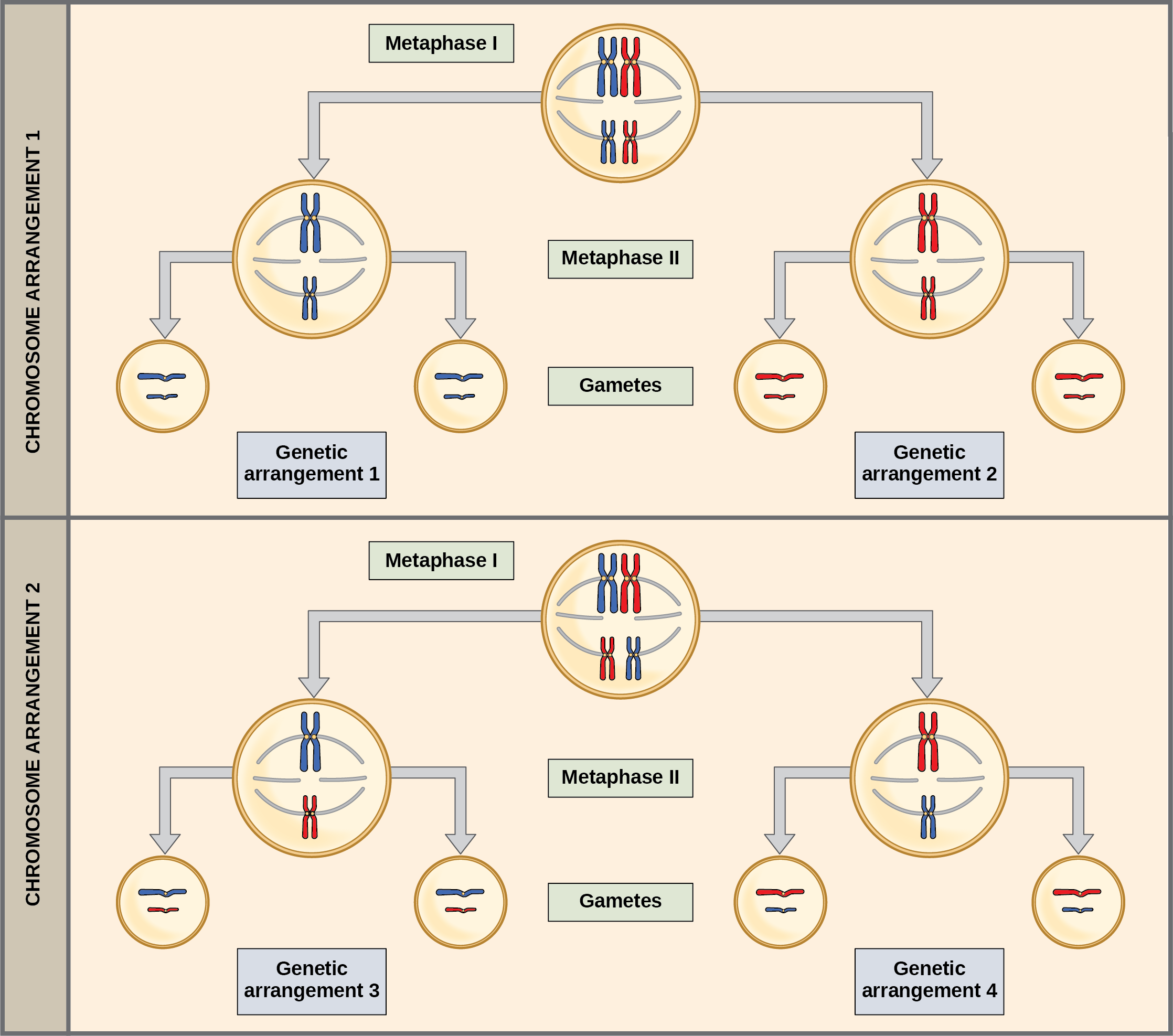
mitosis and meiosis, are involved in ... homologous pair of chromosomes line ... Objective 1, 4 Possible Metaphase I Arrangements: Metaphase I.6 pages
Diagram the arrangement of the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis.
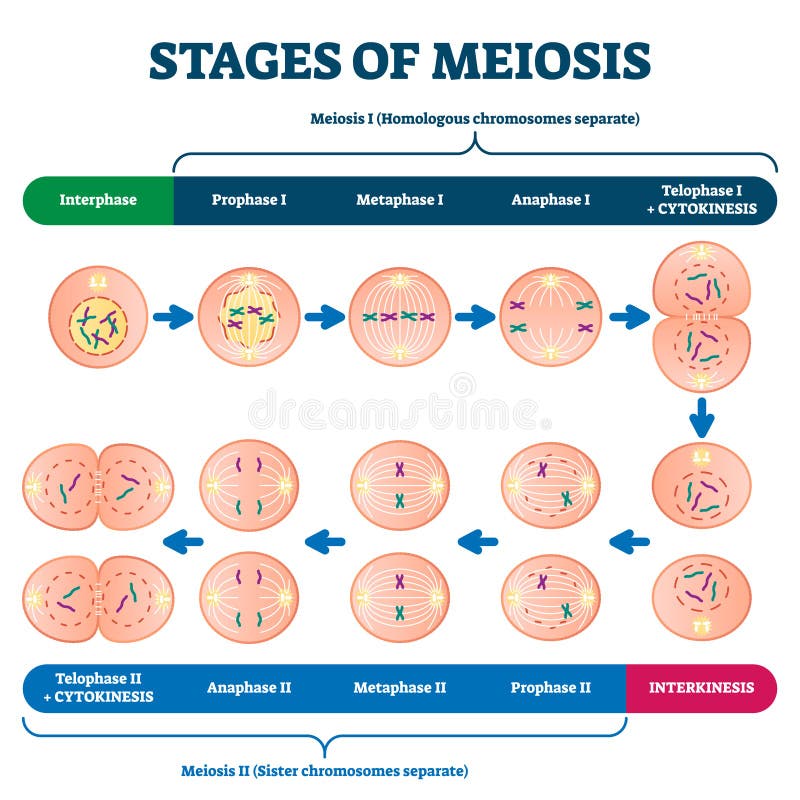
Meiosis has similar steps to mitosis but with two sets of divisions. The first division results in two cells that each have two sets of chromosomes, like in mitosis. The second division creates four cells that each contain one set of chromosomes, because the genetic information isn't copied a second time.
Diagram the arrangement of the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis as they would appear in the phases noted here, where the diploid (2n) chromosomes number ...
A circular diagram of arrows pointing in a clockwise direction shows the cell ... During mitosis, chromosomes become attached to the structure known as the ...
Homologous Chromosomes in Mitosis. Although the general purpose of homologous chromosomes is the same in somatic and sex cells, their role and activity in mitosis is slightly different than in meiosis. Furthermore, errors that may affect these chromosomal pairs will also have different effects between these two forms of cell division.
Fig: Cell Cycle. What is Mitosis? Mitosis is a type of nuclear division that results in two daughter cells, each having a nucleus containing the same number and types of chromosomes found in the mother cell.Mitosis ensures that all the cells of an individual are genetically identical to each other.. Mitosis is also known as equational division because the chromosome number in the parent cell ...
Meiosis II and Gamete Maturation. At the completion of meiosis I there are two cells, each with one, replicated copy of each chromosome (1N). Because the number of chromosomes per cell has decreased (2->1), meiosis I is called a reductional cell division.In the second part of meiosis the chromosomes will once again be brought to the middle of the cell, but this time it is the sister chromatids ...
1 answerThe pairing of homologous chromosome occurs during zygotene phase of prophase I of meiosis. Metaphase is marked by the movement of chromosomes to the ...
Meiosis. 3. In what phase of mitosis do chromosomes split into sister chromatids?- Anaphase. 4. Which type of stem cell is . Biology . It is the unit 7 lesson 3 inputs and outputs of mitosis quick check Skin cells (1 point ) have terminally differentiated become quiescent quickly. become senescent quickly. continually replicate. Biology
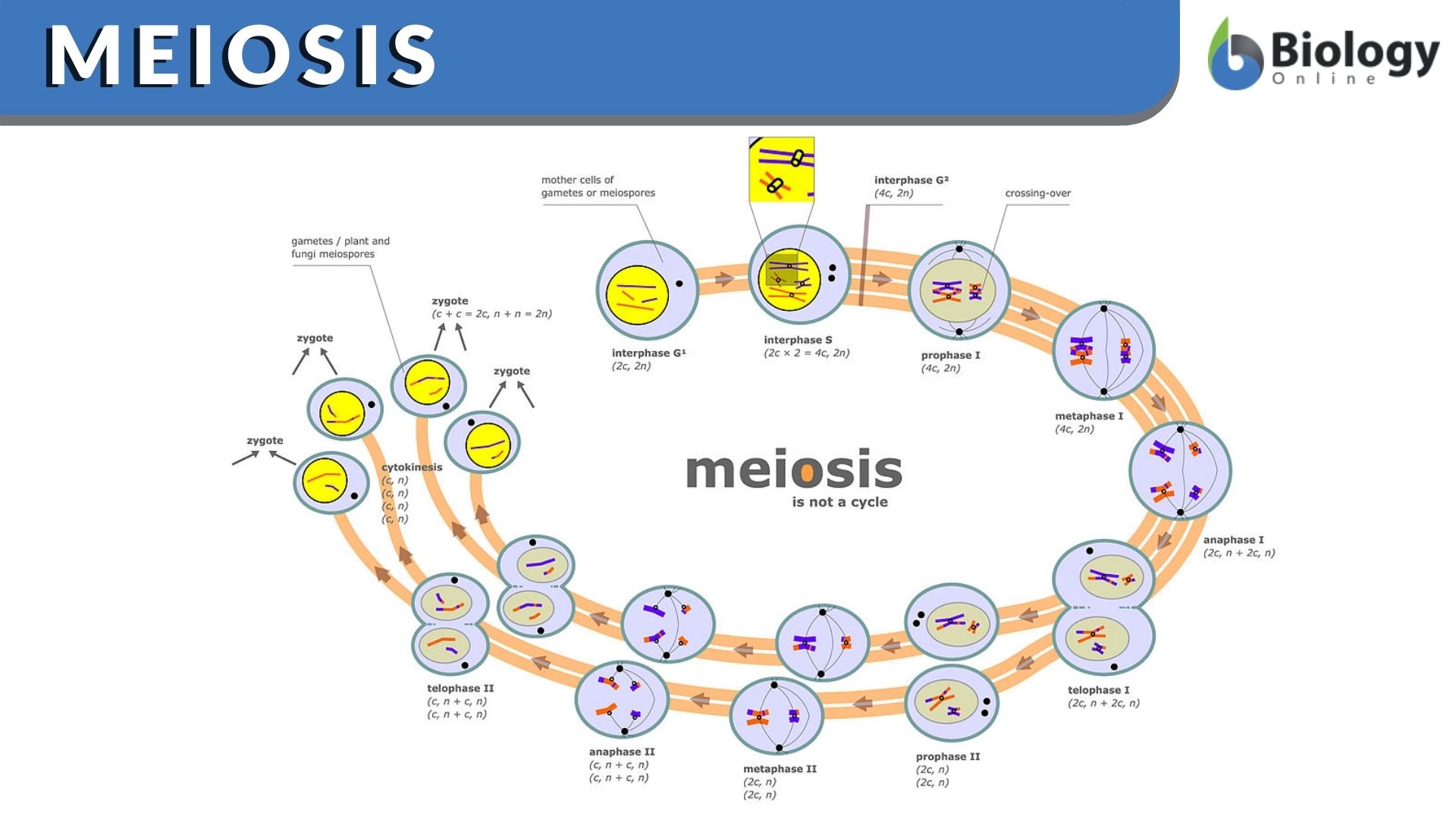
Meiosis is a cell division process that describes the division of germ cells, which comprises two nucleus fissions. The nucleus's two fissions, meiosis 1 and meiosis 2, produce four sex cells known as gametes. The number of chromosomes in each sex cell is half that of the parent cell. This kind of cell division happens during reproduction, when ...
The replicated chromosomes are attached to a 'mitotic apparatus' that aligns ... chromatids (or sister chromatids) held together by a structure known as the ...8 pages
Anaphase of Meiosis. Meiosis ' anaphase is made up of two successive cell divisions, known as anaphase I and anaphase II. Since there is no DNA replication at this stage of meiosis, the diploid cell with two alleles for each gene is reduced to a haploid cell with a single allele for each gene. Anaphase I entails separating the chromosomes ...
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate and go to different daughter cells. This diagram shows just the nuclei of the cells. Notice the exchange of genetic material that occurs prior to the first cell division. Phases of Meiosis Meiosis I begins after DNA replicates during interphase of the cell cycle.
During mitosis, genome folds creating chromosomes. Each chromosome contains of four "arms" that are attached at the centromere. The two long arms are identical, and the two short arms are identical as well. It can happen that the centromere is located at the end of the chromosome, in that case there is no short arm.
Plant Cell Metaphase Diagram.Part one of this series looked at the cycles within cycles that make up the existence of a cell. During metaphase in mitosis and meiosis, the chromosomes condense and they become visible and distinguishable during alignment at the center of the dividing cell, to form a metaphase plate at the center of the cell.
However in meiosis I, the sister chromatids stay together which is different from what happens in mitosis and meiosis II. Telophase I and cytokinesis. The chromosomes complete their move to the opposite end of the cell. Hence at each end of the cell, a full set of chromosomes gather together and a membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes.
Answer (c) Coloured bodies. Question 3: The number of chromosomes in a certain type of cell division is halved.This kind of cell division occurs in (a) only testis (b) only ovary (c) both ovary and testis (d) all body cells. Answer (c) both ovary and testis. Question 4: In which one of the following options the two stages of mitosis have been given in correct sequence?
In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is packaged with proteins in the nucleus, and varies in structure and appearance at different parts of the cell cycle. Chromosomes ...
Mitosis given first: 1. one division, two division in meiosis 2. Daughter cells genetically identical, daughter cells genetically different in meiosis 3. Two cells produced, usually four cells produced in meiosis 4. Diploid to diploid/ haploid to haploid, diploid to haploid in meiosis 5. Separation of chromosomes only in meiosis 6.
#2: "Mitosis: Splitting Up Is Hard To Do" by Crash Course If you're a bit exhausted from reading dense material and need someone else to put the stages of mitosis into more accessible terms, head over to YouTube and watch Crash Course's 10 minute video on mitosis, called "Mitosis: Splitting Up Is Hard to Do.". The nice thing about this video is that, while being a bit more thorough ...
(e) Draw a duplicated chromosome and label its parts. Answer 9 (a) It is a plant cell because centrioles are not shown in the diagram. (b) Prophase (c) Metaphase. Chromosomes arrange themselves on the metaphase or equatorial plate. (d) Difference between mitosis and meiosis based on the chromosome number in daughter cells:
Telophase in mitosis: Summary. Telophase is the final phase of mitosis. The processes involved here are a reverse of what happened in anaphase and metaphase, whereby a new nuclear membrane is formed, the unfolding of the chromosomes into chromatins, the cell nucleoli reappears and the cell starts to enlarge, again.
Mitosis. Meiosis. If a cell has 15 pairs of chromosomes (n = 15), ... diagram depicts the behavior of one homologous pair of chromosomes during mitosis.2 pages
Meiosis I. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated into two cells such that there is one chromosome (consisting of two chromatids) per chromosome pair in each daughter cell, i.e. two chromosomes total. Prophase I. Prior to prophase, chromosomes replicate to form sister chromatids.There are initially four chromatids (c) and two chromosomes (n) for each of the 23 chromosome pairs (4c ...
The difference between is metaphase in mitosis has 'pairs of chromosomes', while metaphase in meiosis have 'spindle fibers'. They are the same because metaphase 2 is found in meiosis 2. The metaphase 2 in mitosis, chromosomes are arranged on the metaphase plate and are attached to the completed spindle. What is the process of metaphase 1?
Meiosis begins with a parent cell that is diploid, meaning it has two copies of each chromosome. What is mitosis with diagram? Mitosis Diagram showing the different stages of mitosis. Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei with an equal amount of genetic material in both the daughter nuclei.
Biology 102/103 Lab 5: Meiosis INSTRUCTIONS: On your own and without assistance, complete this Lab 5Answer Sheet electronically and submit it via the Assignments Folder by the date listed intheCourse Schedule (under Syllabus). To conduct your laboratory exercises, use the Laboratory Manual located under Course Content. Read the introduction and the directions for each exercise/experiment […]
Mitosis,Mieosis Meiosis,Mitosis Metosis,Meiosis. The Structure responsible for initiating the cell division in animal cell. Chromosomes Centrioles Nucleotides Aster. Process by which gametes are produced? Mitosis Meiosis Cell Cycle Reproduction. The stage when chromosomes arrange at the equator ? Telophase Anaphase Metaphase Prophase. The stage ...
Mitosis definition. Mitosis is the process of cell division in which one cell gives rise to two genetically identical daughter cells, resulting in cell duplication and reproduction. The number of chromosomes is preserved in both the daughter cells. Mitosis is a short period of chromosome condensation, segregation, and cytoplasmic division.
Five basic differences between mitosis and meiosis. One cell produce two daughter cells in mitosis whereas four daughter cells in meiosis. Meiosis is reduction division which means the diploid cells (2n) divide into haploid cells (n), whereas in mitosis the progeny cells remain diploid.The genetic recombination takes place at chiasmata from crossing over of the paired chromosomes in prophase I ...
Meiosis is a little longer process than mitosis because it involves the separation of chromosomes in two rounds. Because prophase is divided into two phases, prophase I and prophase II, the procedure takes longer. Prophase I is a lengthy process that entails the pairing of homologous chromosomes and the exchange of genetic data.
7)When a body cell divides through the process of mitosis, the chromosomes in the daughter cells *. 10 points. are formed when chromosomes from the parent cell cross over. are identical to the chromosomes of the parent cell. represent only the healthiest chromosomes from the parent cell. represent only half of the chromosomes in the parent cell.
20 Nov 2018 — Mitosis and meiosis are two kinds of cell division that are ... Cytokinesis, Chromosomes have returned to their interphase structure.



























0 Response to "44 diagram the arrangement of the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis"
Post a Comment