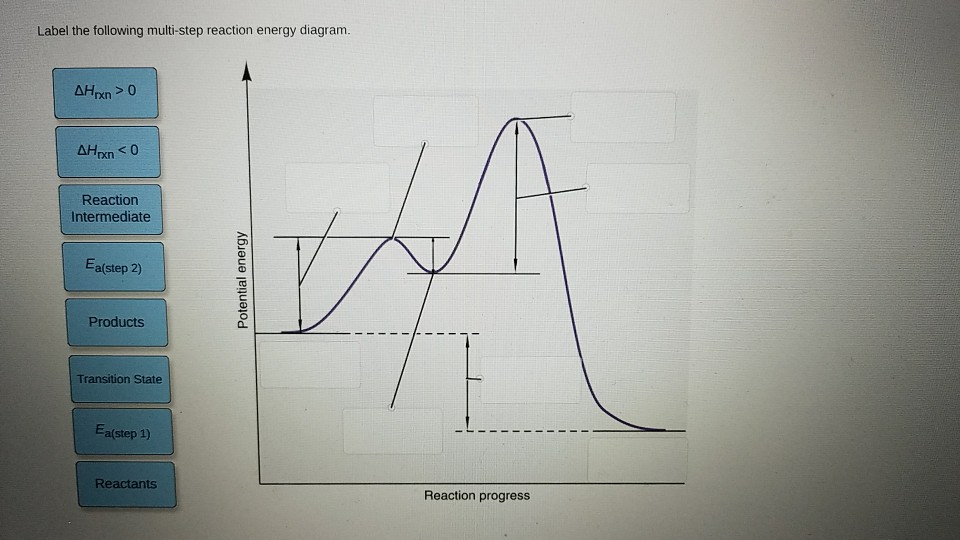
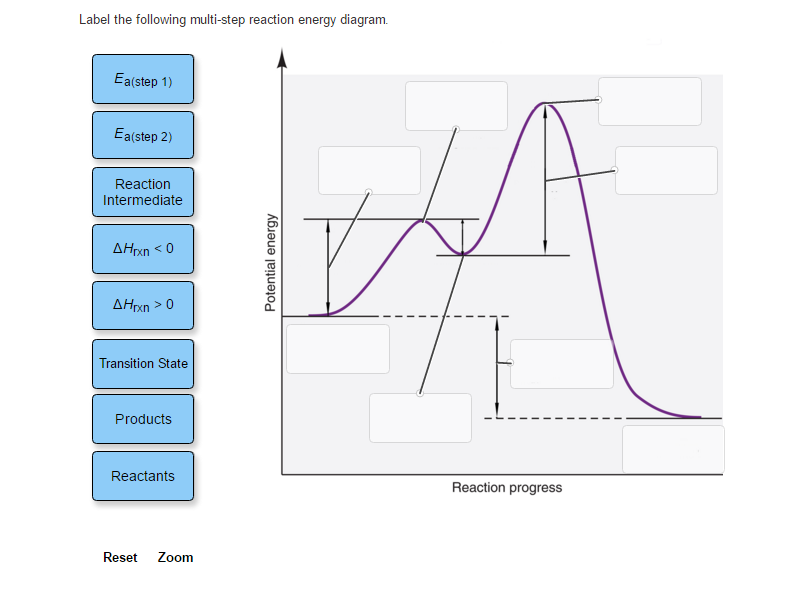
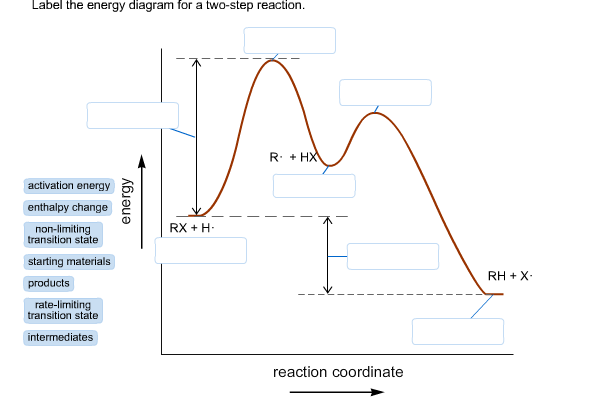
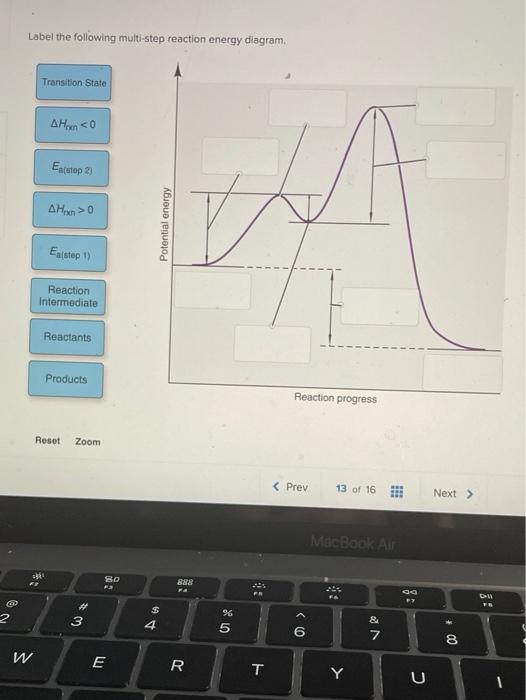
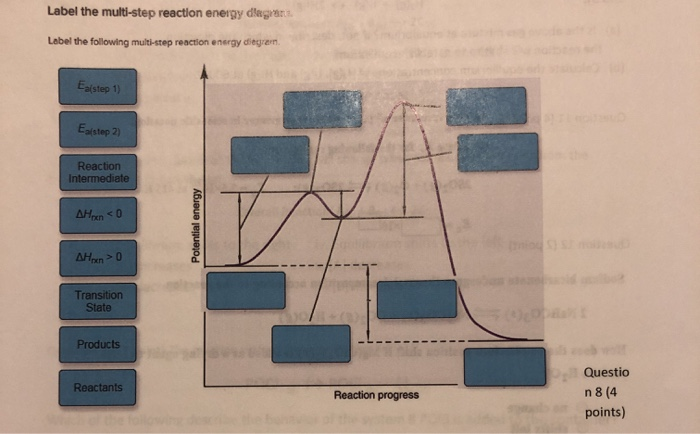
44 label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.
2) For the following reaction, the chlorination of methane, give the mechanism of the initiation and propagation steps(s), including arrow pushing in each mechanism. Initiation: Propagation: 3) For the following reaction coordinate (or energy diagram): ffÐ/uct5 energy a. b. d. ccadd/tltr Draw in x- and y-axes and label them.
2) Draw an energy diagram (using the ∆H° for each step to set appropriate energy levels) for the two propagation steps, and decide which step is more likely the rate-determining step? (label this step as rds) see the textbook for chlorination of methane and apply it to this case. energy reaction coordinate (progress) CH4 + Br2 CH3Br + HBr
step in a multistep reaction. EXAMPLE 5.1 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step exothermic reaction in which the second step is rate determining. STRATEGY A two-step reaction involves the formation of an intermedi-ate. In order for the reaction to be exothermic, the products must be lower in energy than the reactants. In order for the
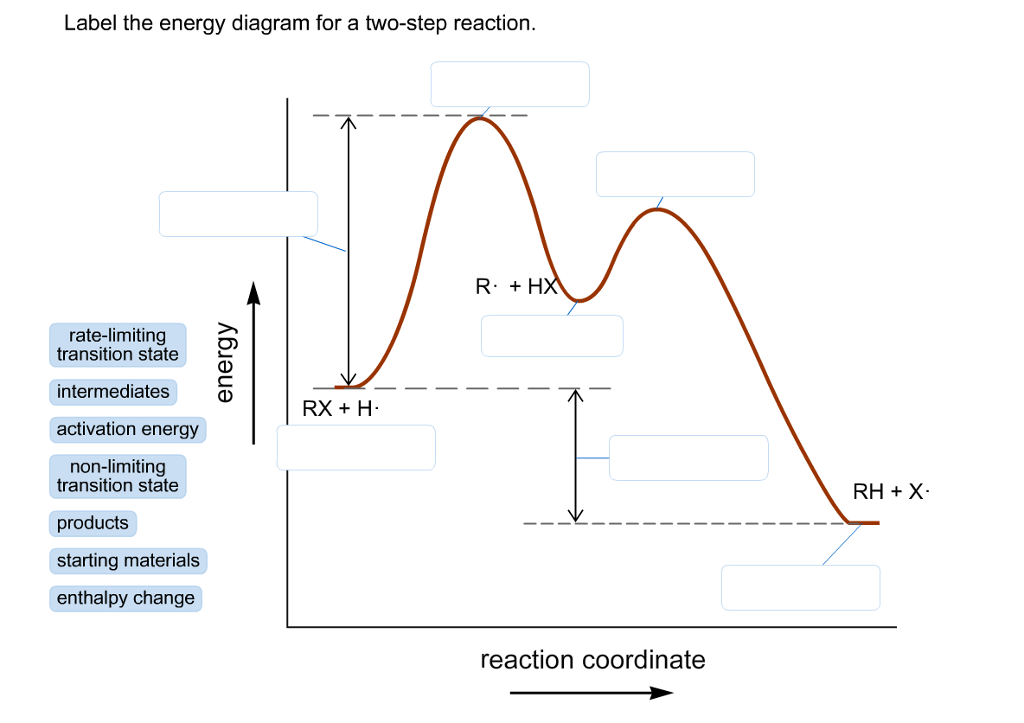
Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.
Feb 23, 2012 — Draw the potential energy diagram for the following multi-step reaction \begin{align*}(\triangle H < 0)\end{align*}. Properly label the ...
Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
Identify whether each of the statements applies to DNA, RNA, both RNA and DNA, or neither DNA nor RNA. ... Place an asterisk * next to 3' carbon atoms in the polynucleotide shown GTC Identify the key structural features of a DNA molecule. The backbone of DNA is made of a sugar and a phosphate molecule.
Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram..
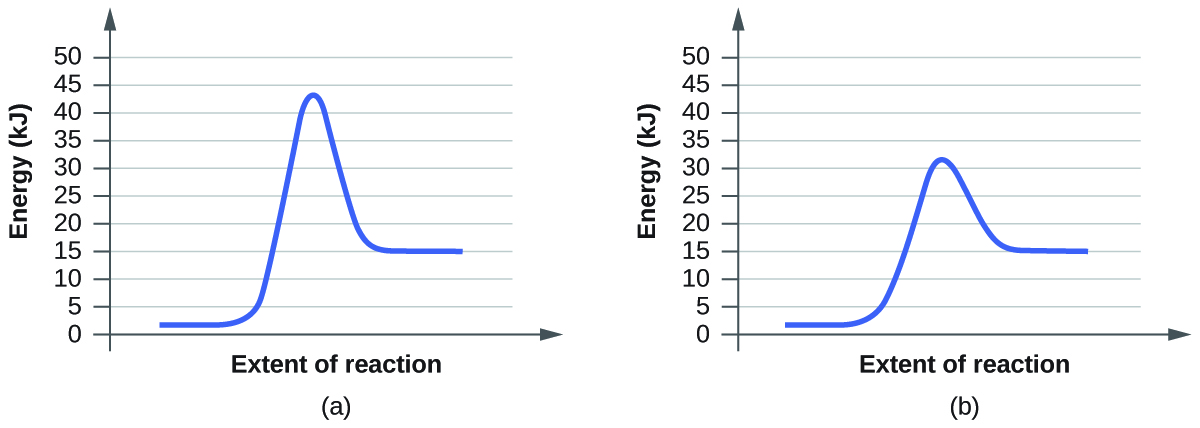
Diagram (b) is a catalyzed reaction with an activation energy of about 70 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants.
Use the multistep reaction shown to the right to answer the following: ... E a = +28kJ/mol. Label the axes, activation energy, ∆H, site of the activated complex, reactants and products. ... Draw a potential energy diagram for the the reaction. ...
energy diagram in Fig. 1.2, which compares the non-catalytic and the catalytic reac-tion. For the non-catalytic reaction, the figure is simply the familiar way to visualize the Arrhenius equation: the reaction proceeds when A and B collide with sufficient energy to overcome the activation barrier in Fig. 1.2. The change in Gibbs free
Self-test question #1 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction that is exothermic overall, and consists of a fast but endothermic first step, and a slow but exothermic second step. Indicate DGrxn, as well as DG1* and DG2* for the first and second activation energies, respectively.
Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram. Label the following multi-step reaction energy dia. Label the following multi-step reaction diagram.
Feb 13, 2017 — Label The Following Multi Step Reaction Energy Diagram ... At the peak of the activation energy hump the reactants are in the transition state ...
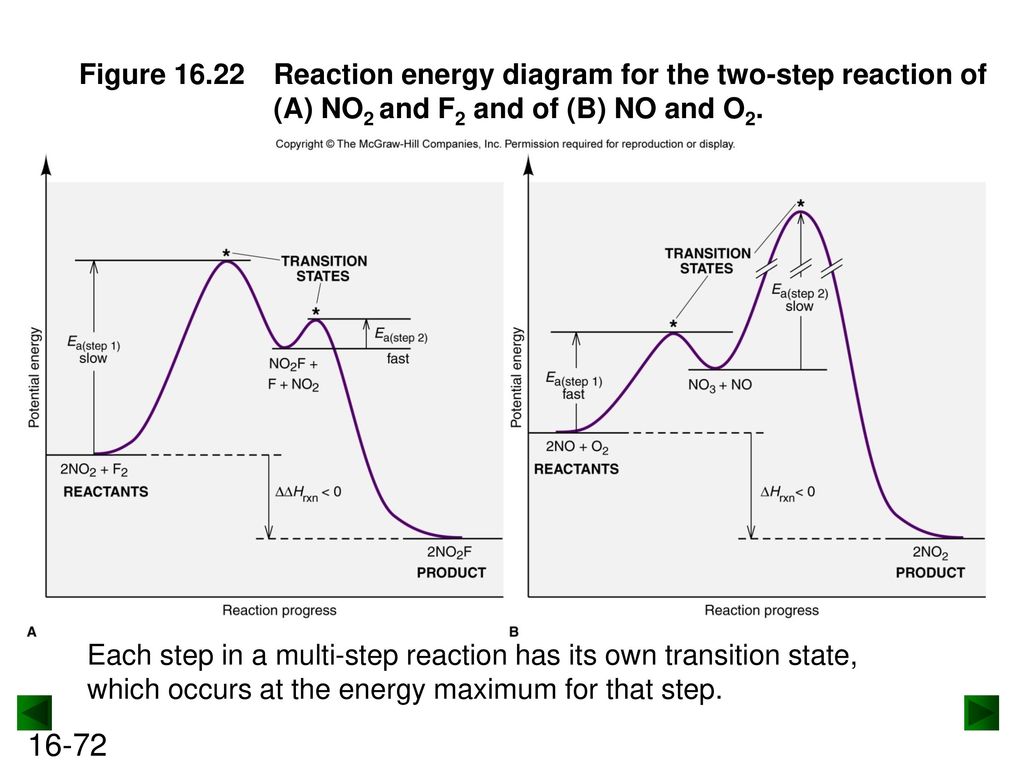
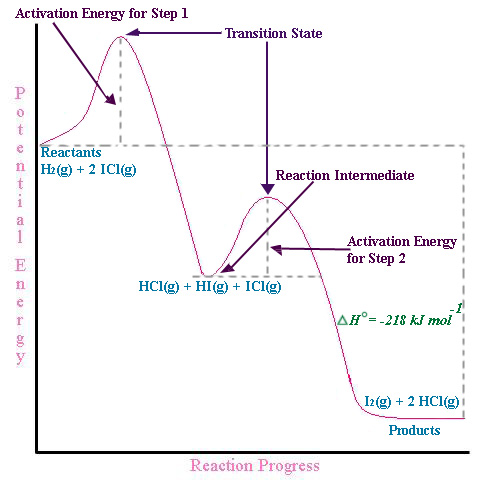
The mechanism of this reaction is believed to involve the following two elementary steps: 1) 2 NO 2 → NO 3 + NO 2) NO 3 → NO + O 2 Note that the intermediate species NO 3 has only a transient existence and does not appear in the net equation. A useful reaction mechanism
Draw the potential energy diagram for the following multi-step reaction . Properly label the diagram. Solution: Rate of Reaction is Determined by Slowest Step In a series of reactions that make up a multi-step reaction, each individual reaction step has its own reaction rate that is determined by the factors that have been discussed in this ...
Question: Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram AHn> 0 Reaction Intermediate Ealstep 2) Products Ea (step 1) Reactants Reaction progress This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (3 ratings)
Positive when the relationship is reversed. Problem Details. Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram. delta Hrxn > 0, Ea(step 2), ...1 answer · Top answer: [readmore]Notes:- The reactant is the flat level at the left side of the diagram and product the flat level at the right.- The transition state is the ...
Use the gray foam piece and the orange foam pieces (C 1 and C 2 ) to simulate an anabolic process. The orange pieces should not be assembled prior to the anabolism action. 13. Sketch and label the enzymeand substrateprior to enzyme action in the space below. 14. Place the small pointed orange piece (C 2 ) into the enzyme.
reaction. Use fishhook arrows! • Draw and completely label a reaction-energy diagram. • Deter min e th ra te-d ter ing sp of a ulti- ep re act ion-energy d gram. • Differentiate between transition states and intermediates. • Differentiate between kinetic and thermodynamic control. • Use the Hammond postulate to predict whether a
Fill in and label each diagram on the following page to illustrate the relative position of each atom's parts. Make sure to label the following parts: nucleus, proton, neutron, electron cloud region. Atomic Structure continued. Sample Released Test Items. Organizing Topic — Investigating Energy. Standards of Learning
Complete the unbalanced equation to generate one equivalent of glucose. Gluconeogenesis is the conversion of pyruvate to glucose. This metabolic pathway needs several cofactors to complete the conversion. Predict the positions of the glucose molecule that would become labeled from 1-14C1-14C pyruvate (the label in the carboxyl group of pyruvate).

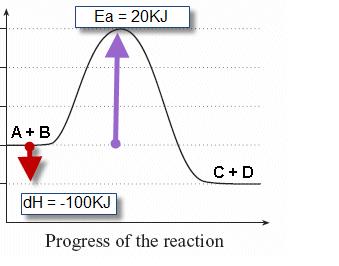
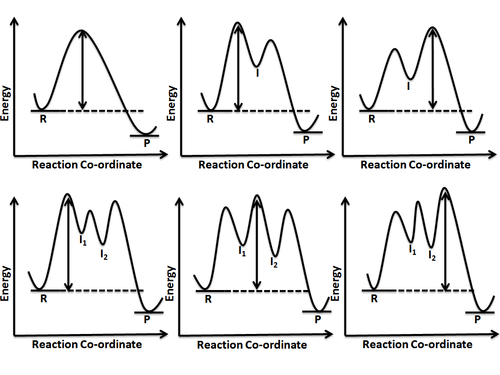
How to draw multi-steps energy profile diagrams: reactant, product, ∆h, activation energy, slow step
Answer to Solved Label the following multi-step reaction energy.
2. Draw a potential energy (E p ) diagram for a reaction in which ∆H = 80 kJ/mol and E a = +28kJ/mol. Label the axes, activation energy, ∆H, site of the activated complex, reactants and products. 3. Using the potential energy diagrams for an endothermic and
Foods that plants produce. glucose. gas produced by photosynthesis. O2. Drag the labels onto the equation to identify the inputs and outputs of cellular respiration. INPUTS---. 1 glucose (fuel) +6 O2 (gas we inhale) OUTPUTS---. 6CO2 (gas we exhale) + 6 H2O (water) + ATP (energy packets that cells use to do work.
h) Draw a potential energy diagram to illustrate this reaction mechanism, assuming that the overall reaction is endothermic. Label reaction intermediates with "RI," and activated complexes with "AC." Labelled potential energy diagram for an unknown multi-step endothermic reaction: 54. Missing question's answer!!** 55.
Because a reaction cannot proceed faster than its slowest step, this step will limit the rate at which the overall reaction occurs. The slowest step is therefore called the rate-limiting step (or rate-determining step) of the reaction Figure 2. Figure 2. A cattle chute is a nonchemical example of a rate-determining step.
406 M-1 min-1 and the rate constant for the reverse reaction is 244 M-1 min-1. The activation energy for the forward reaction is 26.2 kJ mol-1 and that for the reverse reaction is 42.4 kJ mol-1. (a) (5 points) On the axes below, draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction, showing the
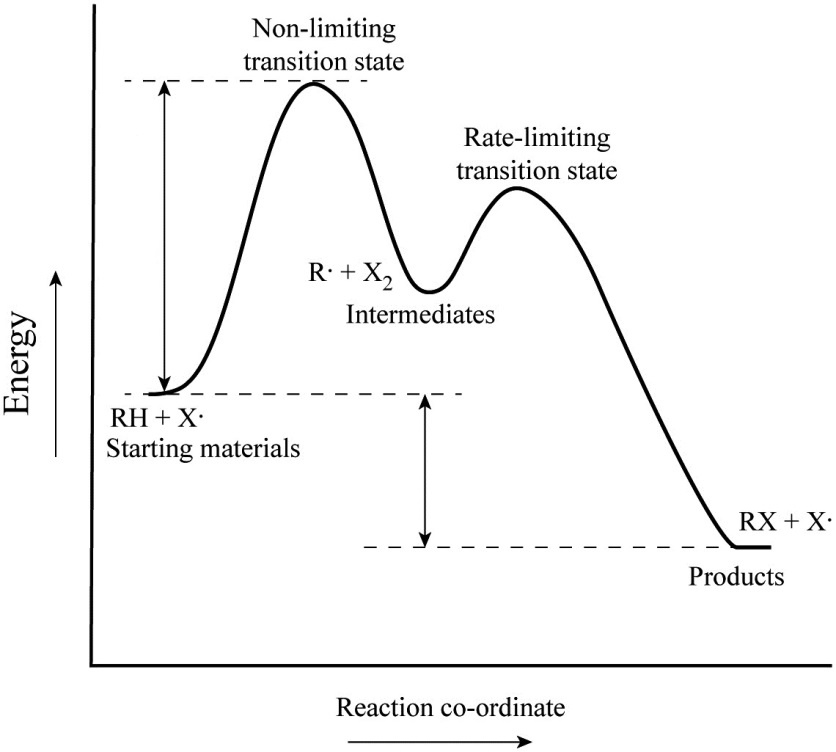
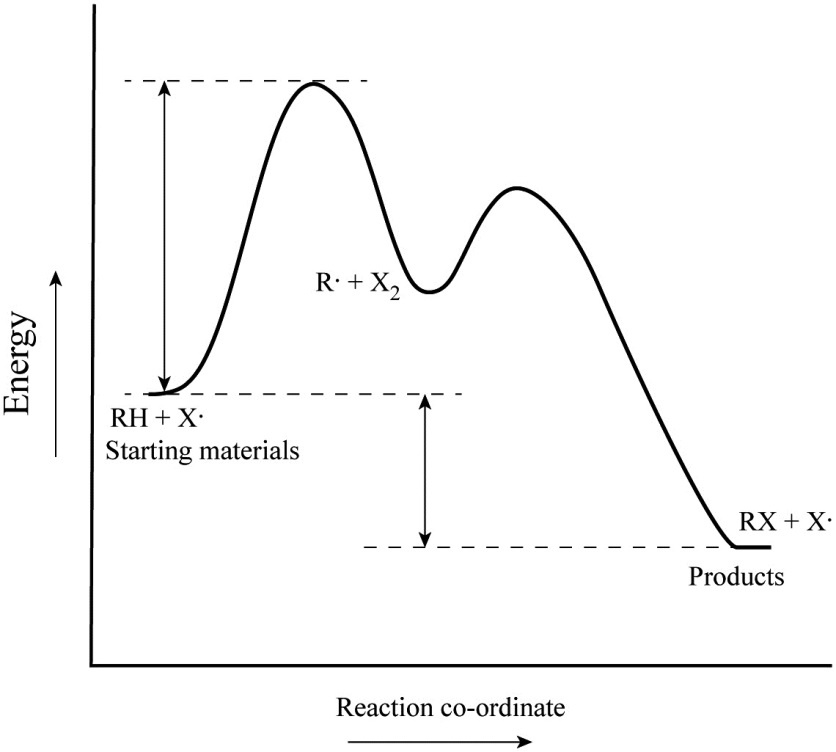
Step 1 has the higher transition energy state, thus it is the rate-determining step. In many reactions more than one step is involved in the formation of products. Step Two Exothermic because energy is released in forming B-C bond delta H is negative Products are lower than the starting materials
Diagrams like this are described as energy profiles.In the diagram above, you can clearly see that you need an input of energy to get the reaction going. Once the activation energy barrier has been passed, you can also see that you get even more energy released, and so the reaction is overall exothermic.
Sketch out an activation energy diagram for a multistep mechanism involving a rate-determining step, and relate this to the activation energy of the overall reaction. Write the rate law expression for a two-step mechanism in which the rate constants have significantly different magnitudes.
Among the characteristics shared by these reactions, three in particular set them apart.: 1. They are relatively unaffected by solvent changes, the presence of radical initiators or scavenging reagents, or (with some exceptions) by electrophilic or nucleophilic catalysts. 2.
Dec 11, 2019 — Get the detailed answer: Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.1 answer · Top answer: At the first stage of the multi-step reaction process, you have the reactants first. At this time, no further reactions is happening. The increase ...
2. Label the large wooden block with an A (adenosine). 3. Label each of the other three with a P (phosphate group). 4. Use three rubber bands to represent the chemical bonds holding the phosphates to the adenosine molecule. The first rubber band goes around the adenosine block and one phosphate group.










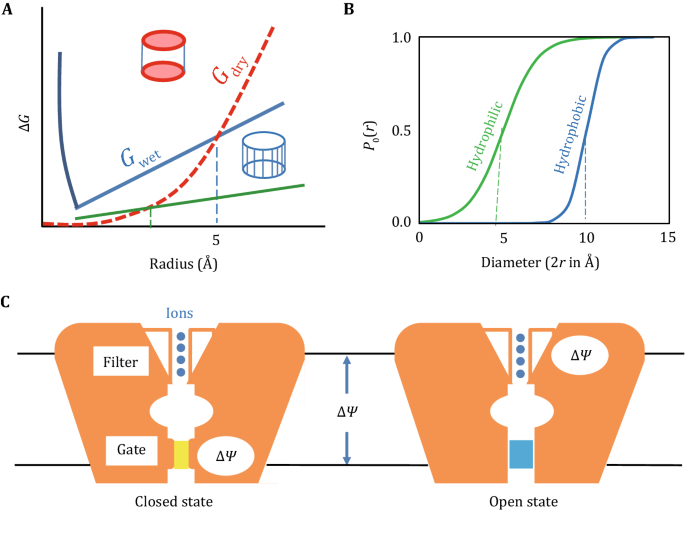
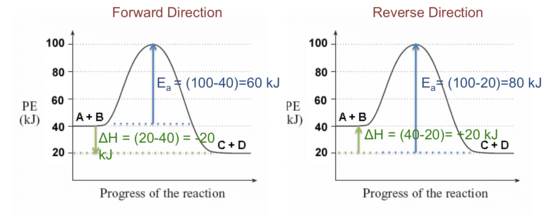



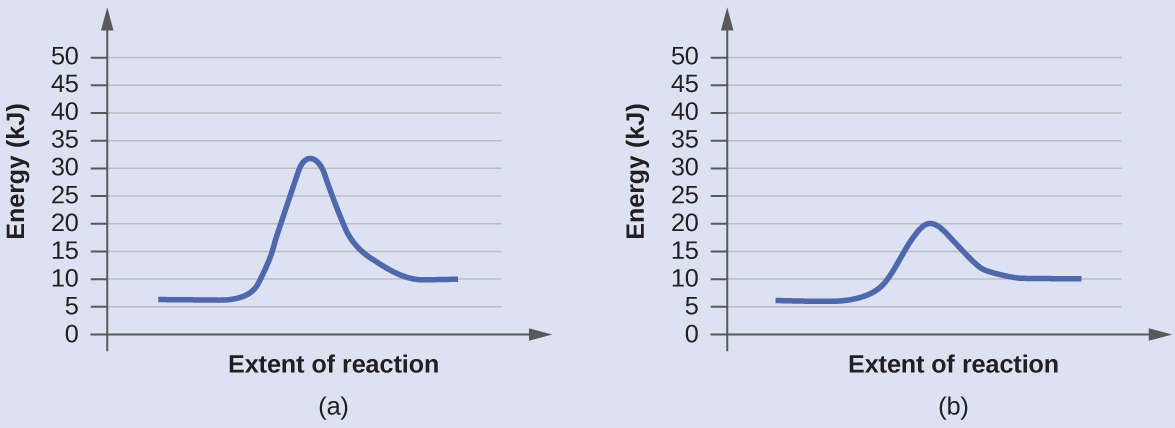




0 Response to "44 label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram."
Post a Comment