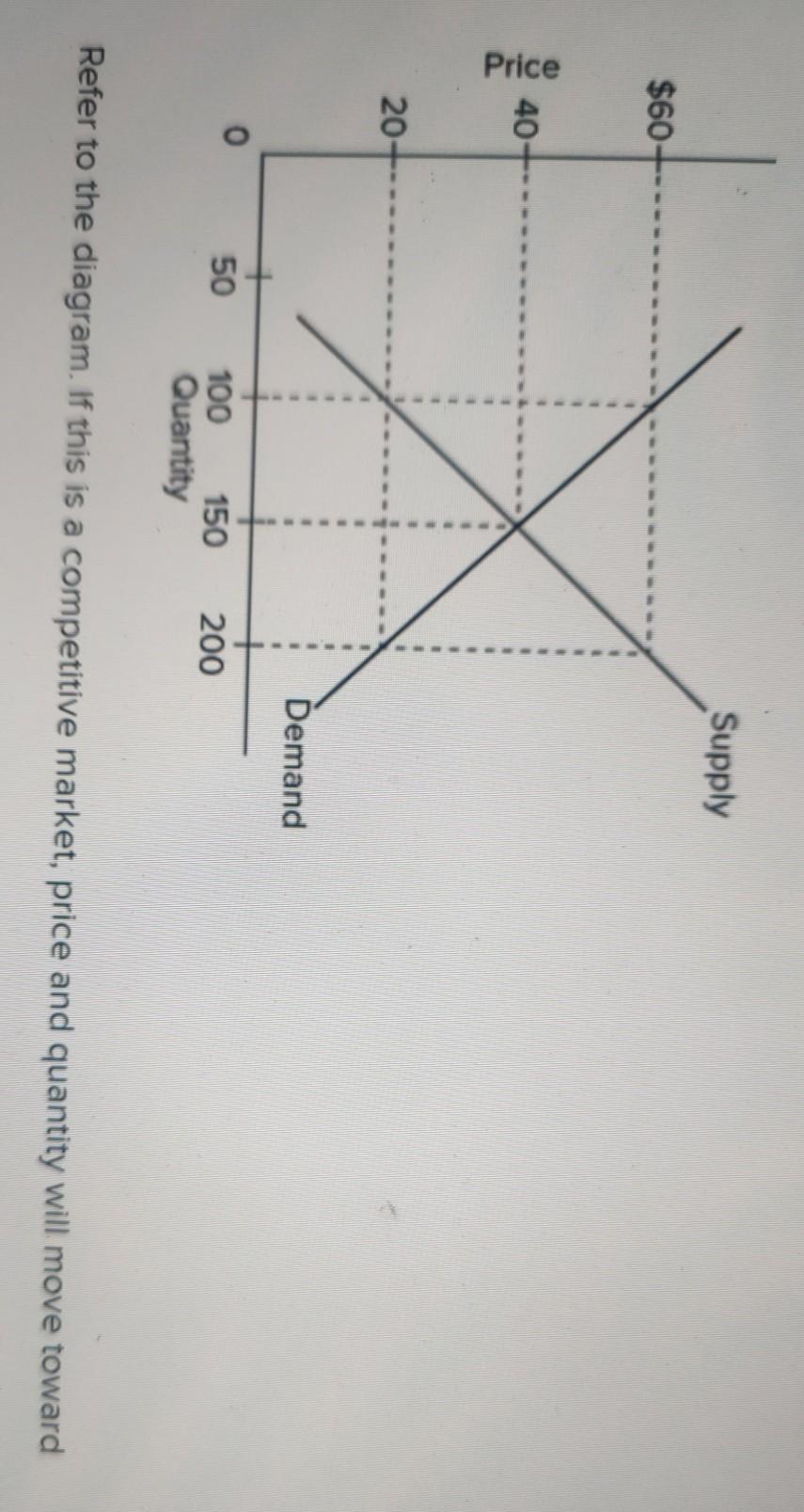
41 refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:
Asking because I have little understanding of the concept of relativity in these types of situations. This point was brought up by a classmate in a class forum. There are some people that I really like... but I'm terrified of being hurt therefore they don't know about it and I'm alone.
Assume the current price and quantity in a market is equal to $9 and 8 units respectively. Studies show that at the current price and quantity, price elasticity of demand is equal to …
Refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:
Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. ... R-2 F03090. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. equilibrium. B. a shortage of 50 units. C. a surplus of 50 units. D. a surplus of 100 units. E. a shortage of 100 units. 8. However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. Imagine, for example, that the price of a gallon of gasoline was above the equilibrium price—that is, instead of $1.40 per gallon, the price is $1.80 per gallon. Price and quantity will move towards their equilibrium points in a competitive market. Here, demand and supply are equal at P=40 and Q=150. Thus, equilibrium price is $40 and equilibrium quantity is 150 units. Therefore, price and quantity will move towards $40 and 150 respectively. Ans.39- (A)
Refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:. Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward. $40 and 150, respectively. The equilibrium price and quantity in a market usually produce allocative efficiency because. marginal benefit and marginal cost are equal at that point. ... In a competitive market, every consumer willing to pay the market ... [Source](https://youtu.be/DTolzXCcsuM?t=261) I'm not trying to attack one side or the other, I'm genuinely curious about this moment as I assumed there were verifiable facts about what transpired that led up to all of this. Step 1. Draw a demand and supply model to illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began. The demand curve D 0 and the supply curve S 0 show that the original equilibrium price is $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity is 250,000 fish. (This price per pound is what commercial buyers pay at the fishing docks; what … The price at which these two curves cross is called the equilibrium price, and the quantity is called the equilibrium quantity. Here the equilibrium price is $2.00 per cone, and the equilibrium quantity is 7 ice-cream cones. Breaking down Market Equilibrium. The actions of buyers and sellers naturally move markets toward the equilibrium of ...
Refer to Exhibit 2-5. As more fax machines are produced, the opportunity cost of producing them ... In the simple circular economic flow diagram, if goods produced by business firms flow counterclockwise, then the services of labor flow ... If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will gravitate toward. a. $6 and 10 units ... However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. Imagine, for example, that the price of a gallon of gasoline was above the equilibrium price—that is, instead of $1.40 per gallon, the price is $1.80 per gallon. In a free market, the market price and quantity in the above figure will adjust to equilibrium values of $2 per gallon and 30 million gallons. Consider the market for a good X. Suppose that P0=$3, P1=$12, PB=$10, PA=$4, and equilibrium price P*=$6. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: C. $40 and 150 respectively. 2. An economist for a bicycle company predicts that, other things equal, a rise in consumer incomes will increase the demand for bicycles.
Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100, respectively. B. $60 and 200, respectively. C. $40 and 150, respectively. D. $20 and 150, respectively. In a perfectly competitive market, each firm produces at a quantity where price is set equal to marginal cost, both in the short run and in the long run. This outcome is why perfect competition displays allocative efficiency: the social benefits of additional production, as measured by the marginal benefit, which is the same as the price, equal ... Page 4 of 12 2. (10 marks) Consider a perfectly competitive, constant cost industry with "n" identical firms. The industry demand and supply curves are defined by the following expressions: P = 70 - 0.04Q P = 10 + 0.02Q. Further suppose that the marginal cost equation for each firm is MC = 10 + 2q. a) What are the competitive equilibrium price and quantity in this market? Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership and control of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, a price system determined by supply and demand, private property, property rights recognition, voluntary exchange, and wage labor. In a capitalist …
Refer to the diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is. ... Next Post Next Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward.
See title. For obvious reasons I will not link to said site, but you've probably seen the bots posting comments here and there.
Answered: Refer to the above diagram. If this is… | bartleby. We've got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. Start exploring! Business Economics Q&;A Library Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: Refer to the above diagram.
Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A) ... If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A) $60 and 100 respectively. C) ... capacity of a competitive market to equate the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied. D) ...
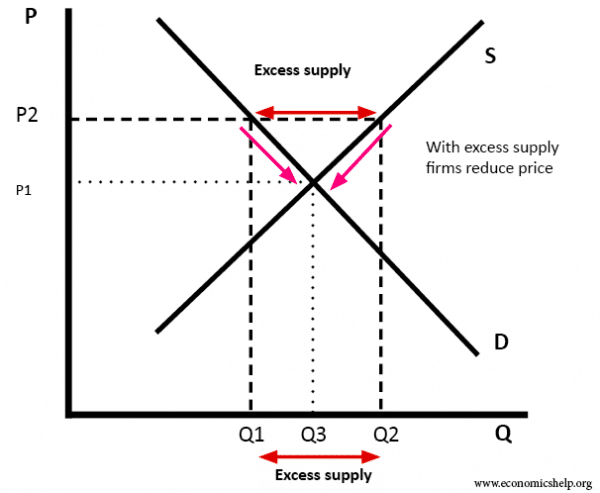
Surpluses. Figure 3.8 “A Surplus in the Market for Coffee” shows the same demand and supply curves we have just examined, but this time the initial price is $8 per pound of coffee. Because we no longer have a balance between quantity demanded and quantity supplied, this price is not the equilibrium price.
Previous Post Previous Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward. Next Post Next Why is regulation necessary to achieve "universal service"? Search for: Search. Recent Posts.
quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied. Question 3 1 / 1 pts Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: $60 and 100 respectively. $60 and 200 respectively. Correct! $40 and 150 respectively. $20 and 150 respectively.
The song I think she should sing is “My Life Would Suck Without You” by Kelly Clarkson.
Step 1. Draw a demand and supply model to illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began. The demand curve D 0 and the supply curve S 0 show that the original equilibrium price is $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity is 250,000 fish. (This price per pound is what commercial buyers pay at the fishing docks.
1. Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward. $40 and 150, respectively. 2. Because of unseasonably cold weather, the supply of oranges has substantially decreased. This statement indicates the. amount of oranges that will be available at various prices has declined. 3.
Transcribed image text: QUESTION 4 Supply $60 Price 40 20 Demand O 50 200 100 150 Quantity Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market price and quantity will move toward $60 and 100, respectively. $40 and 150, respectively, $60 and 200, respectively $20 and 150, respectively,
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100 respectively. B. $60 and 200 respectively. C. $40 and 150 respectively. D. $20 and 150 respectively.
In a competitive goods market, individual buyers cannot bargain for a lower price than others are willing to pay. Therefore they are price-takers. In the labour market the firms set the wage to minimize the cost of getting the worker to work and would not benefit by offering the lowest wage at which the worker (the seller) would accept the job.
some firms leaving an industry. In the above market, economists would call a government-set maximum price of $40 a: price ceiling. A demand curve: indicates the quantity demanded at each price in a series of prices. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $60 in this market will result in: a surplus of 100 units.
C) capacity of a competitive market to equalize quantity demanded and quantity supplied. D) ability of the market system to generate an equitable distribution of income. 21) 22) Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A) $20 and 150, respectively. B) $60 and 200, respectively. C) $60 and 100 ...
Market equilibrium can be shown using supply and demand diagrams. In the diagram below, the equilibrium price is P1. The equilibrium quantity is Q1. If price is below the equilibrium. In the above diagram, price (P2) is below the equilibrium. At this price, demand would be greater than the supply. Therefore there is a shortage of (Q2 – Q1) If ...
Business. Economics. Economics questions and answers. Supply $60 20 Demand 50 100 150 200 Quantity Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: O $60 and 100, respectively. O $60 and 200, respectively. O $40 and 150, respectively. O $20 and 150, respectively.
If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: Selected Answer: Correct Answer: $40 and 150 respectively. Question 2 1 out of 1 points College students living off-campus frequently consume large amounts of ramen noodles and boxed macaroni and cheese.
However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. This happens either because there is more supply than what the market is demanding, or because there is more demand than the market is supplying. This balance is a natural function of a free-market ...
Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: (Pic35) $60 and 100, respectively. $60 and 200, respectively. $40 and 150, respectively. $20 and 150, respectively.
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market.It postulates that, holding all else equal, in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied …
If a perfectly competitive firm is a price taker, then A. pressure from competing firms will force acceptance of the prevailing market price. B. it must be a relatively small player compared to its competitors in the overall market. C. it can increase or decrease its output without affecting overall quantity supplied in the market.
No, but if there is no interference, they tend to move toward equilibrium. Suppose that Mimi plays golf 5 times per month when the price is $40 and 4 times per month when the price is $50. ... The term _____ refers to a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market that must take the prevailing market price for its product. ... If the firm ...
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: $40 and 150 respectively. Where supply and demand meet. An effective price floor will Result in a product surplus The demand for most products varies directly with changes in consumer incomes. Such products are known as Normal goods
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: Definition. $40 and 150 respectively. Term. ... Assume that in a competitive market price is initially above the equilibrium level. We can predict that price will: Definition.
Putting the supply and demand curves from the previous sections together. These two curves will intersect at Price = $6, and Quantity = 20. In this market, the equilibrium price is $6 per unit, and equilibrium quantity is 20 units. At this price level, market is in equilibrium. Quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded ( Qs = Qd).
Price and quantity will move towards their equilibrium points in a competitive market. Here, demand and supply are equal at P=40 and Q=150. Thus, equilibrium price is $40 and equilibrium quantity is 150 units. Therefore, price and quantity will move towards $40 and 150 respectively. Ans.39- (A)
However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. Imagine, for example, that the price of a gallon of gasoline was above the equilibrium price—that is, instead of $1.40 per gallon, the price is $1.80 per gallon.
Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. ... R-2 F03090. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. equilibrium. B. a shortage of 50 units. C. a surplus of 50 units. D. a surplus of 100 units. E. a shortage of 100 units. 8.









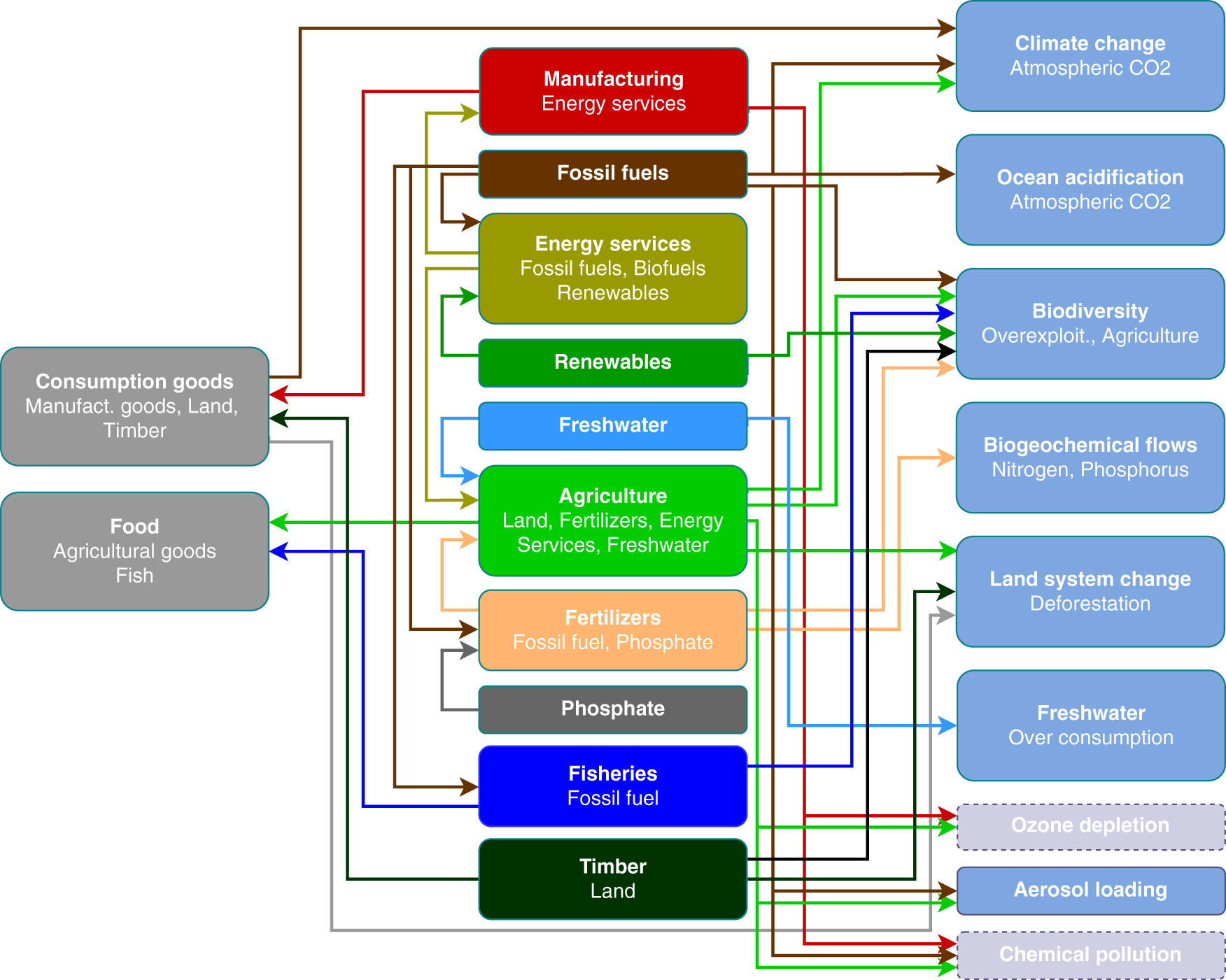


![PDF] Principles of Health Economics for Developing Countries ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/3a671b484d262a68f2475c3c123283c513e007e8/161-Figure6.6-1.png)
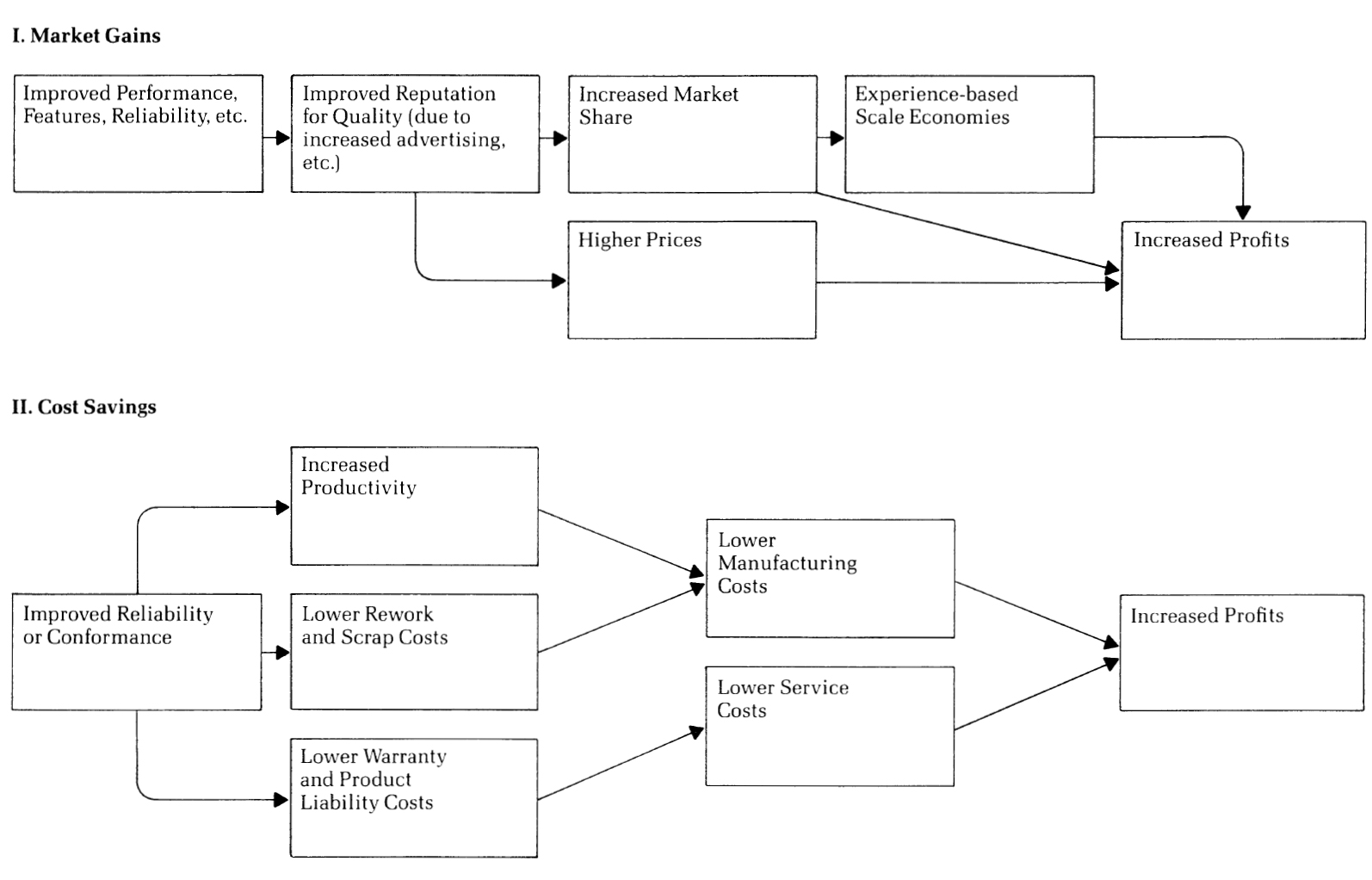






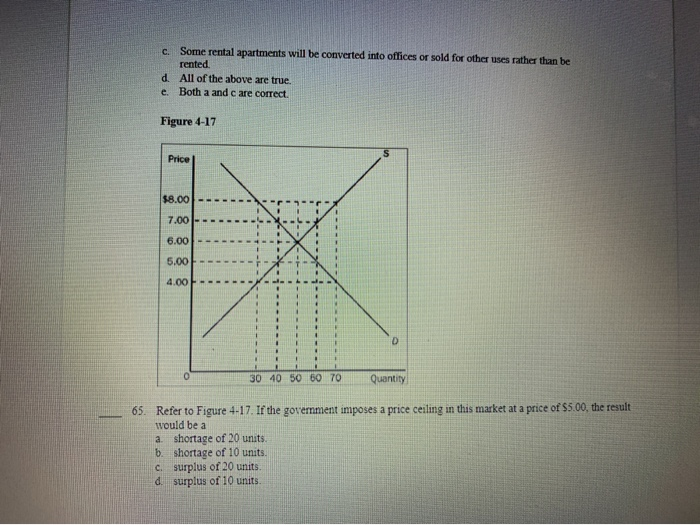

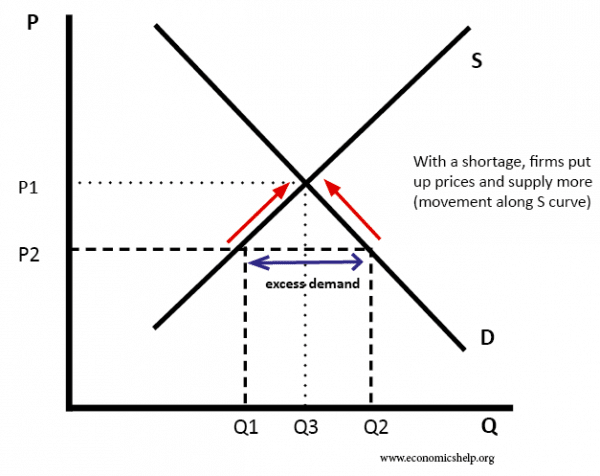


/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)

0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:"
Post a Comment