42 molecular orbital diagram for n2
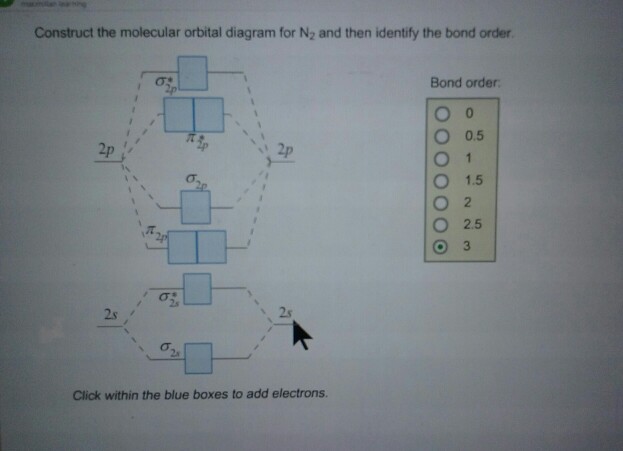
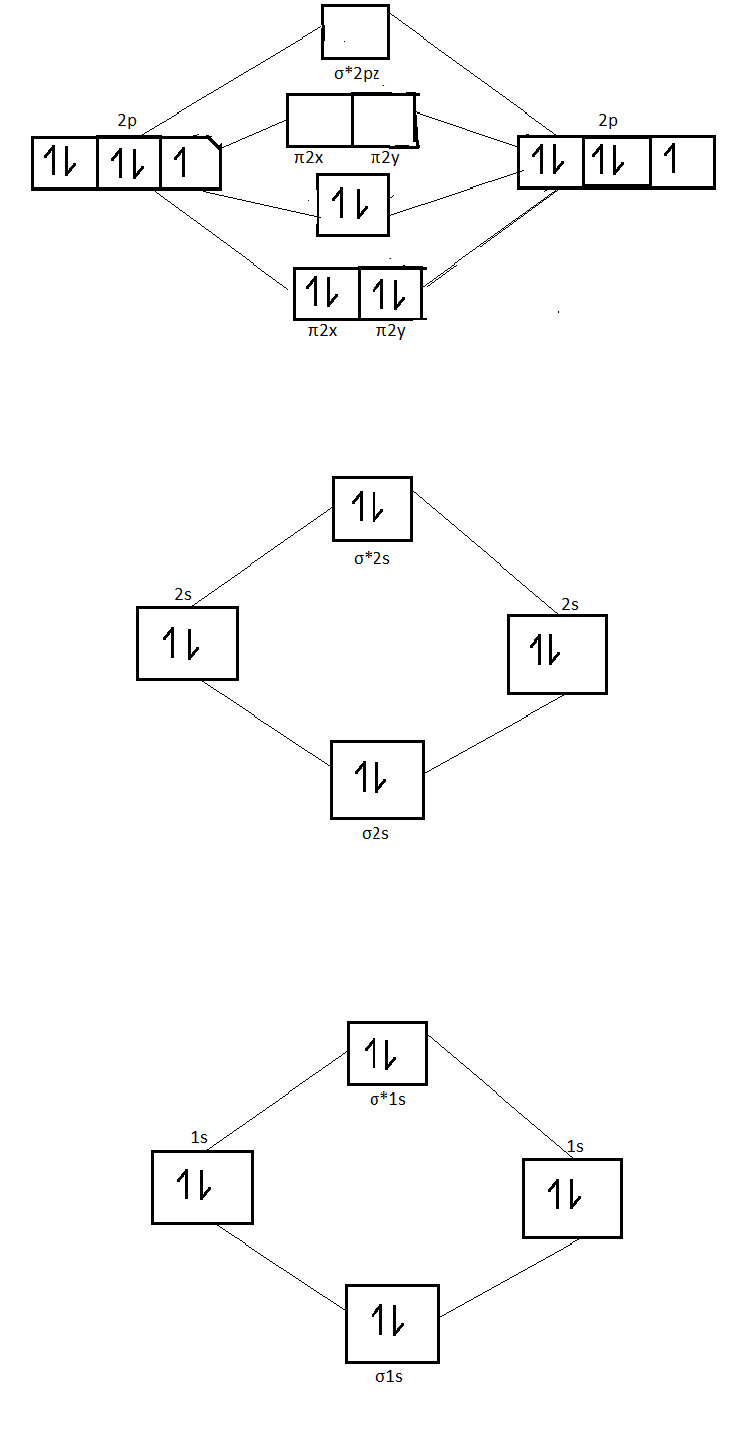
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for N2. Label all of the atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals and put the correct number of electrons in. You do not need to draw the shapes of any of the orbitals. a) MO diagram b) Based on your MO diagram, is N2 diamagnetic or paramagnetic? c) Calculate the bond order for N2. Question: 5. For the first part of the problem, we’re being asked to complete the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for an excited state of the N2 molecule. The given electron configuration for the excited state N2 is: (σ1s2) (σ*1s2) (σ2s2) (σ*2s2) (π2p4) (σ2p1) (π*2p1) From this, we can fill-up the molecular orbital diagram for the excited state N2:
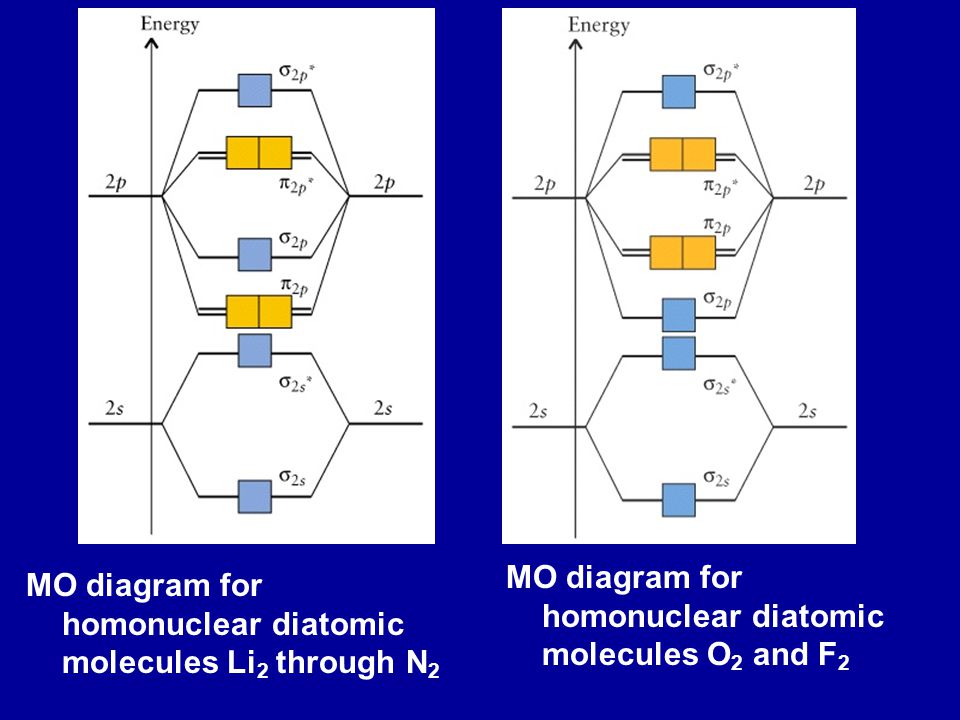
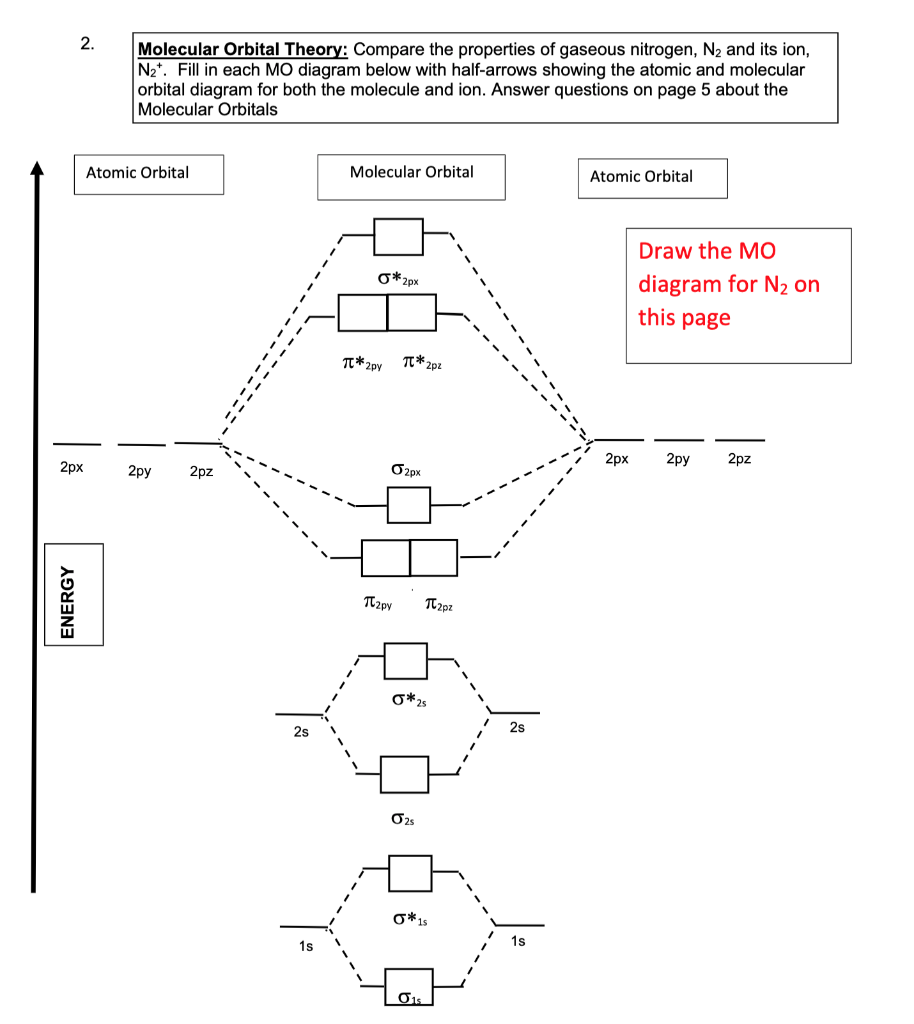
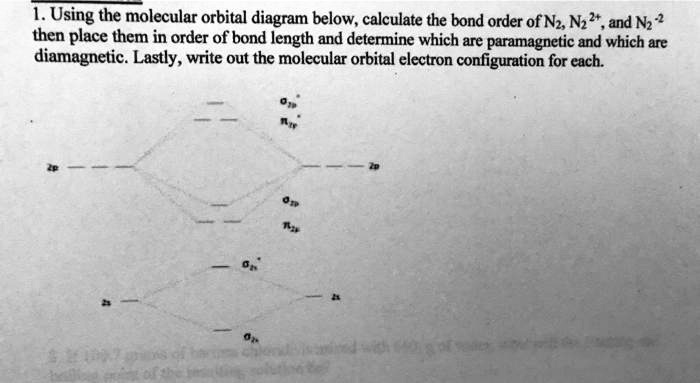
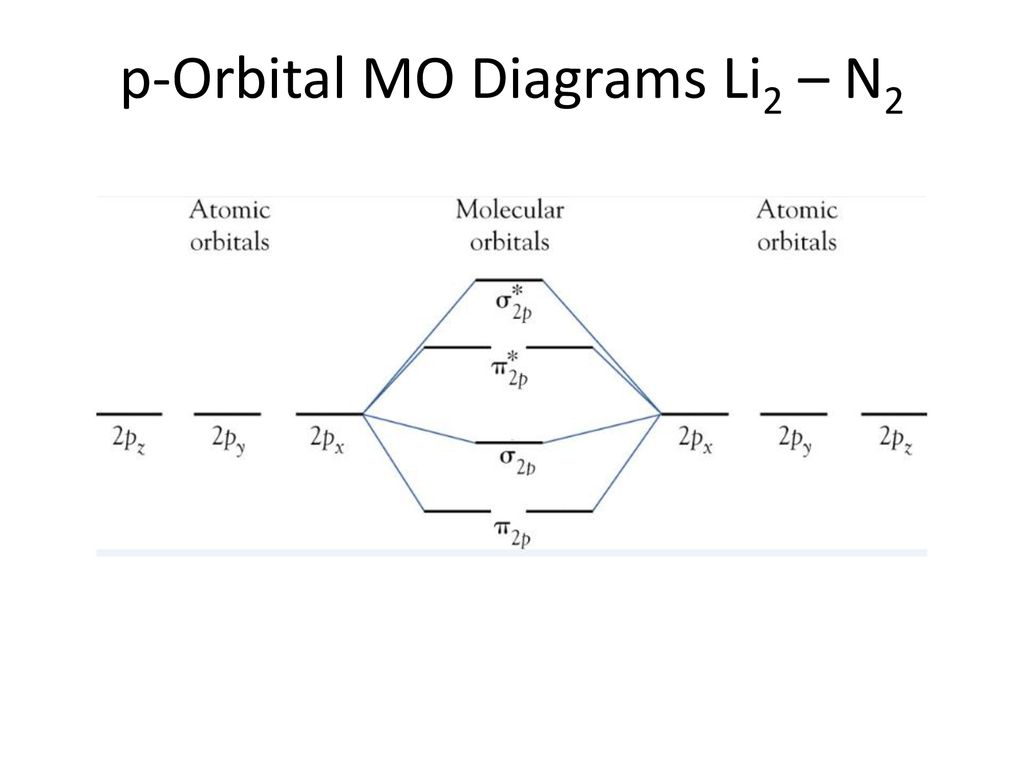
Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^- $-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction moving from $\ce{Li2}$ to $\ce{F2}$. The $\mathrm{s}$-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction is the bonding interaction between the $\mathrm{2s}$ orbital of one atom and the $\mathrm{2p_{z}}$ orbital of another atom which (among other things) increases the energy of the $\mathrm ...
Molecular orbital diagram for n2
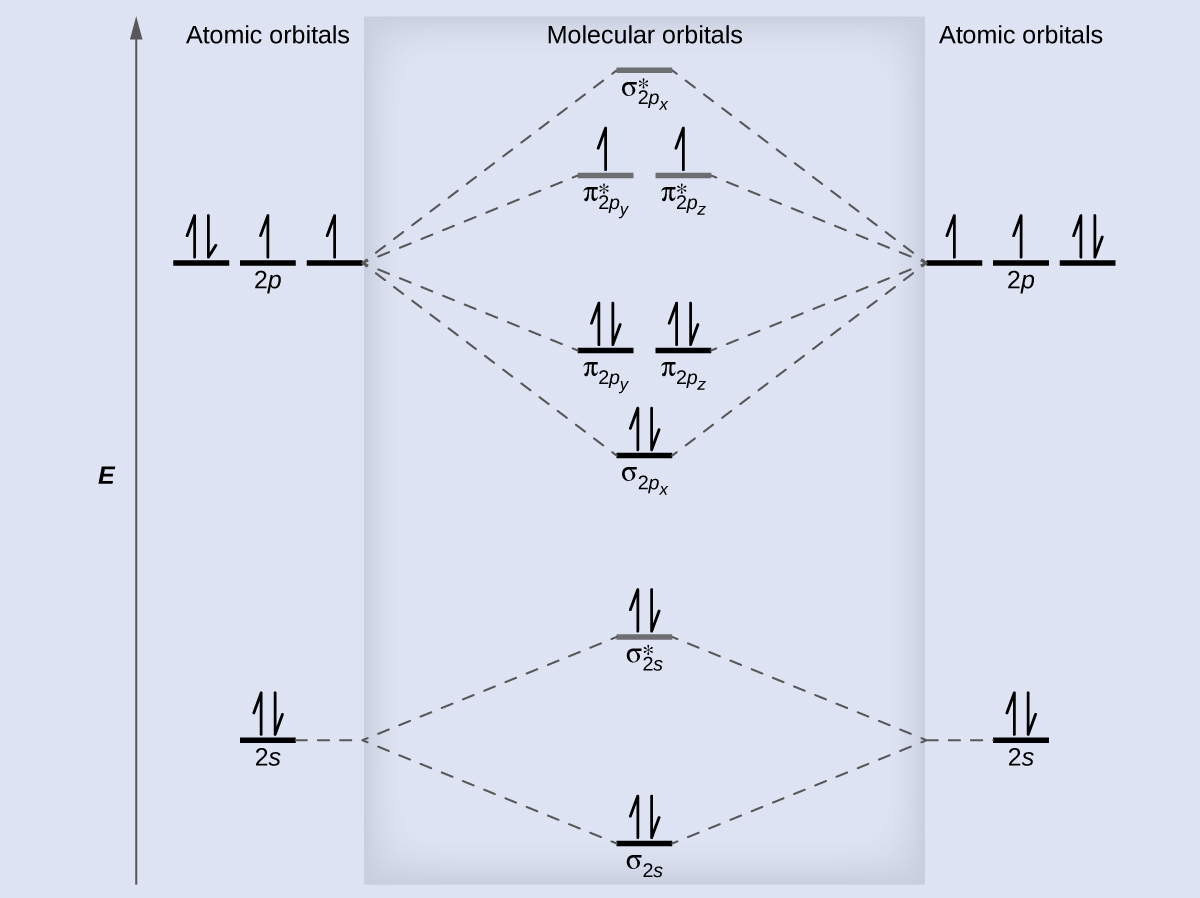
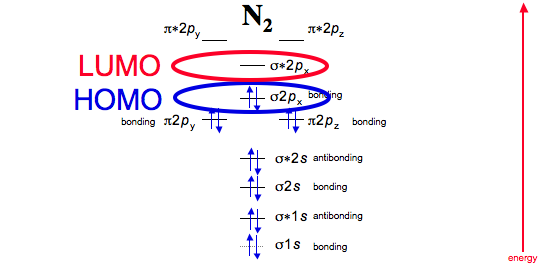
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds ... Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Molecular orbital energy level diagram of N2 molecule • Bond order = (8 2)/2 = 3 (N ≡ N) • Absence of unpaired electrons showed that N2 molecule is diamagnetic. MOED of 'O2' : Electronic configuration of Oxygen (Z = 8) is 1s2 2s2 2p4 .
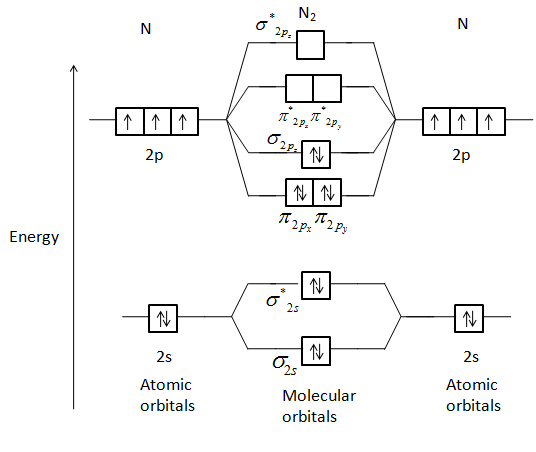
Molecular orbital diagram for n2. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular… There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start... Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of N2 using its diagram. one atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a N2 molecule will have 14 electrons so first ...
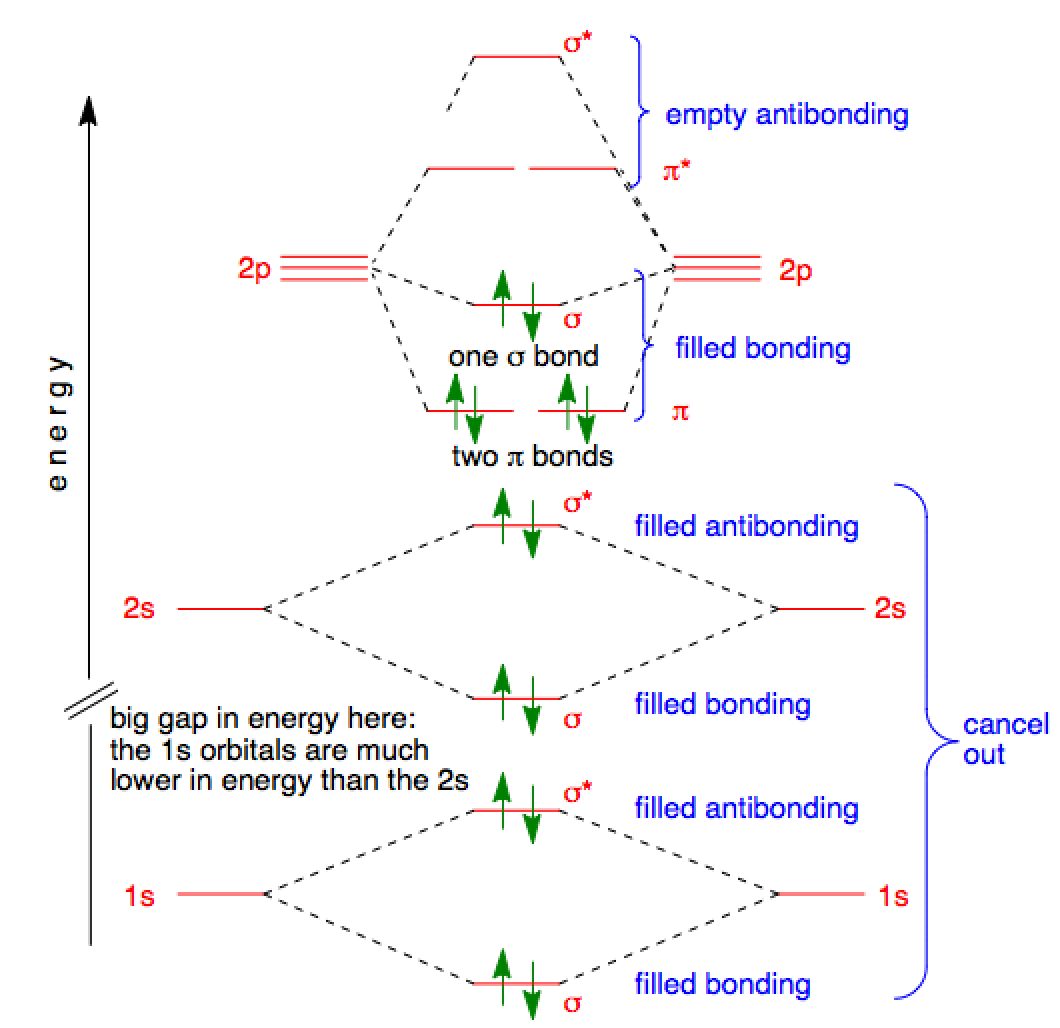
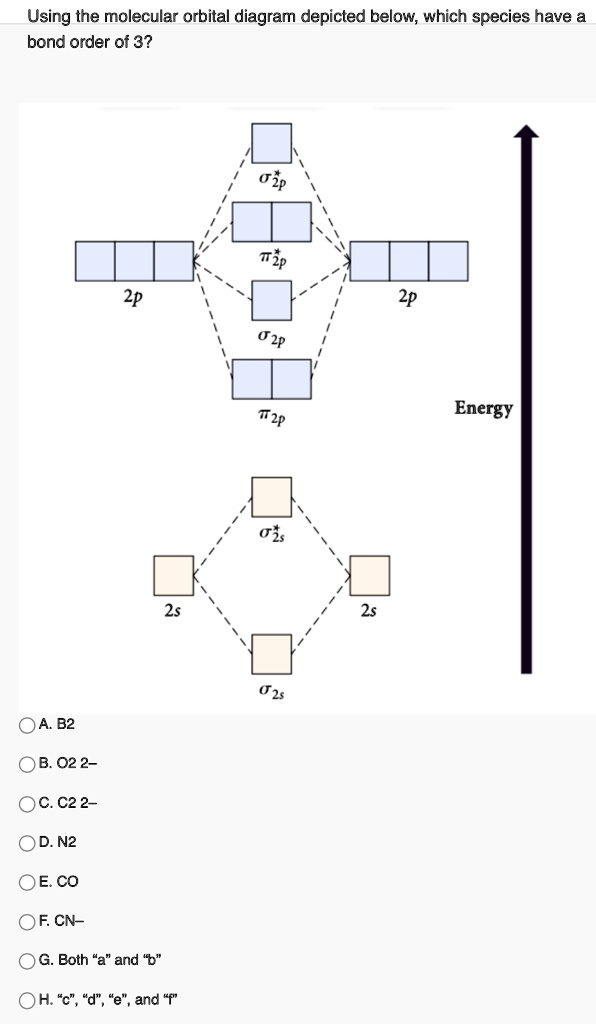
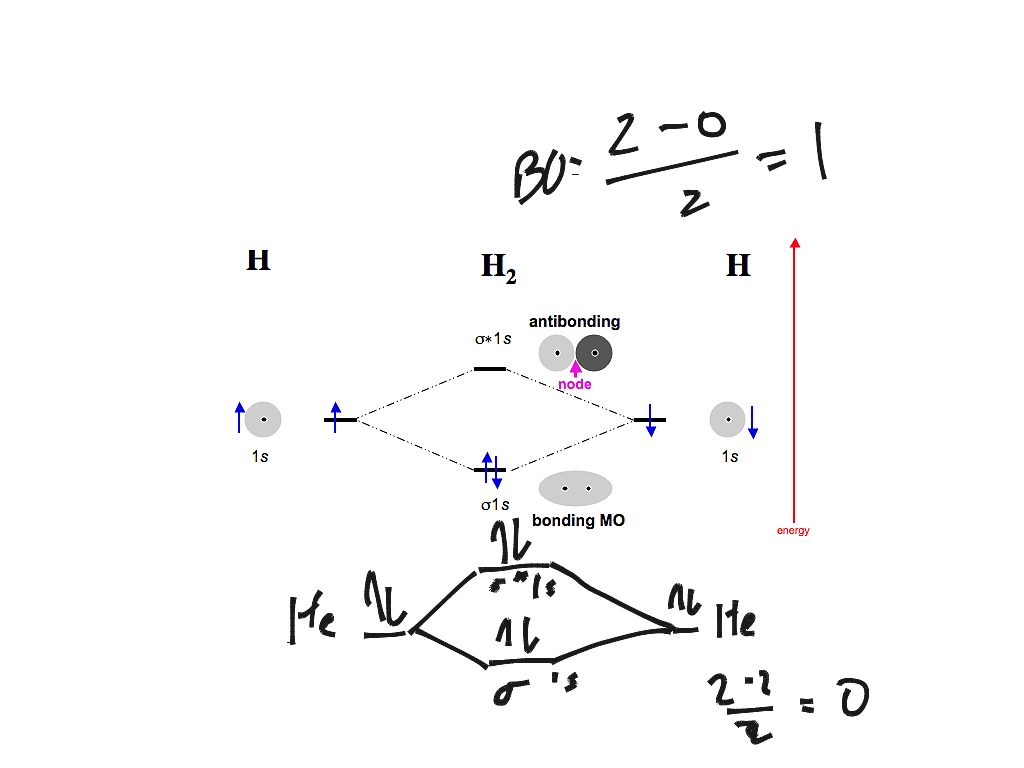
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine On a very general basis, electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but they move under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule. Molecular orbital theory is a method for describing the electronic structure of the molecule. Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ . Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and calculate the bond order. Answer: The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. The Bond Order Formula can be defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons in bonding orbitals and antibonding orbitals. Bond order formula is given as below In the molecular orbital diagram for the molecular ion, N 2 + , the number of electrons in the σ 2 p molecular orbital is: Hard. View solution. >. What is Molecular Orbital Theory. With the help of energy levels homonuclear diatomic orbitals, arrange the following species in increasing order of stability O 2 2 − , O 2 −, O 2 , O 2 +.
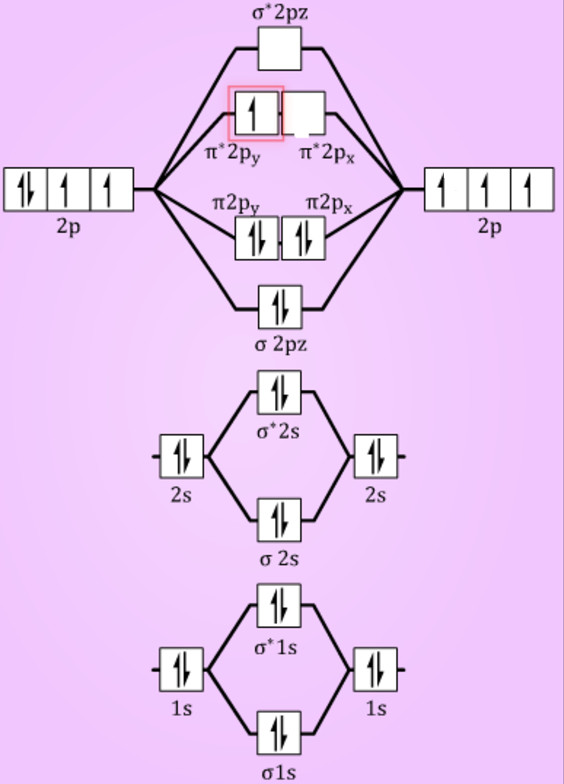
Interactive video lesson plan for: MO Diagram for N2+ (Molecular Orbital) Activity overview: There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc). With the help of molecular orbital theory, draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for `N_(2)^(+)` ion molecule. Also calculate its bond order and predictits magnetic behaviour. आण्विक ऊर्जा स्तर के आधार पर Molecular Orbitals for N2. Jmol models of calculated wavefunctions. To view a model, click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown Mouse Control of Models. Left mouse drag to rotate; Shift Left drag up or down to resize; Shift Right drag or Shift Left drag horizontally to z-rotate; Right click for menu Notes Usage Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for N2. Now we add the 10 electrons, 5 from each nitrogen atom. Note that the bottom sigma symmetry orbital is strongly bonding, the top one is strongly antibonding, and the 2 in the middle are only weakly bonding and antibonding, respectively.
For more detailed knowledge you can refer to the polarity of N2. Molecular Orbital Diagram of N2 Molecular orbitals exist in molecules where each molecule has its electron configuration in terms of a sigma bond and pi bond. According to molecular orbital theory, it tells about magnetic nature, stability order, and the number of bonds in a molecule.
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
the diagram above is the molecular.n2 molecular orbital energy level diagram picture, is usually depicted by a diatomic molecules chapter learn consider the molecular orbital electron configuration notation to a molecular orbitals diagrams web the molecular orbital energy level structures can construct the molecular orbital energy level the …
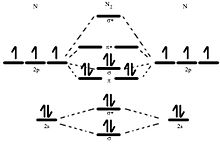
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
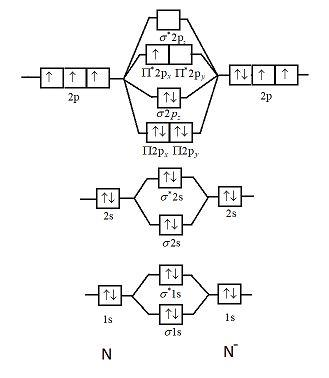
This picture shows the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 − . Orbitals represented by ∗ are antibonding orbitals and the orbitals without ∗ are bonding orbitals. Bond order can be calculated by the formula: Bond order = bonding electrons - antibonding electrons 2
I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For N X 2 the orbitals in increasing energy are: σ 1 s < σ 1 s ∗ < σ 2 s < σ 2 s ∗ < π 2 p x, π 2 p y < σ 2 p z < π 2 p x ∗, π 2 p y ∗ < σ 2 p z ∗ because it has 14 electrons.
The molecular orbital energy level diagram of N2 is given in Fig.. Is N2 2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? That means N2 is diamagnetic, with no unpaired electrons. Why C2 molecule has only PI bond? Their double bonds are made of two π bonds because four electrons need to be accommodated in each bond. In bond formation only valence electrons or ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) N2 Molecular Orbital Diagram.
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric. Explain What is the relationship between bond order and the dissociation energy of a molecule? ...
The total number of electrons present in the N 2 molecule is 14. N 2+ ion is formed by the loss of one electron from the N 2 molecule. This lost electron will be lost from σ (2p z) orbital. Hence, the electronic configuration of N 2+ ion will be N 2+ = KK [σ (2s)] 2 [σ* (2s)] 2 [π (2p x )] 2 [π (2p y )] 2 [σ (2p z )] 1 Here, N b =7, N a =2 so that
Molecular orbital energy level diagram of N2 molecule • Bond order = (8 2)/2 = 3 (N ≡ N) • Absence of unpaired electrons showed that N2 molecule is diamagnetic. MOED of 'O2' : Electronic configuration of Oxygen (Z = 8) is 1s2 2s2 2p4 .
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds ...





















0 Response to "42 molecular orbital diagram for n2"
Post a Comment